VL25:输入序列连续的序列检测
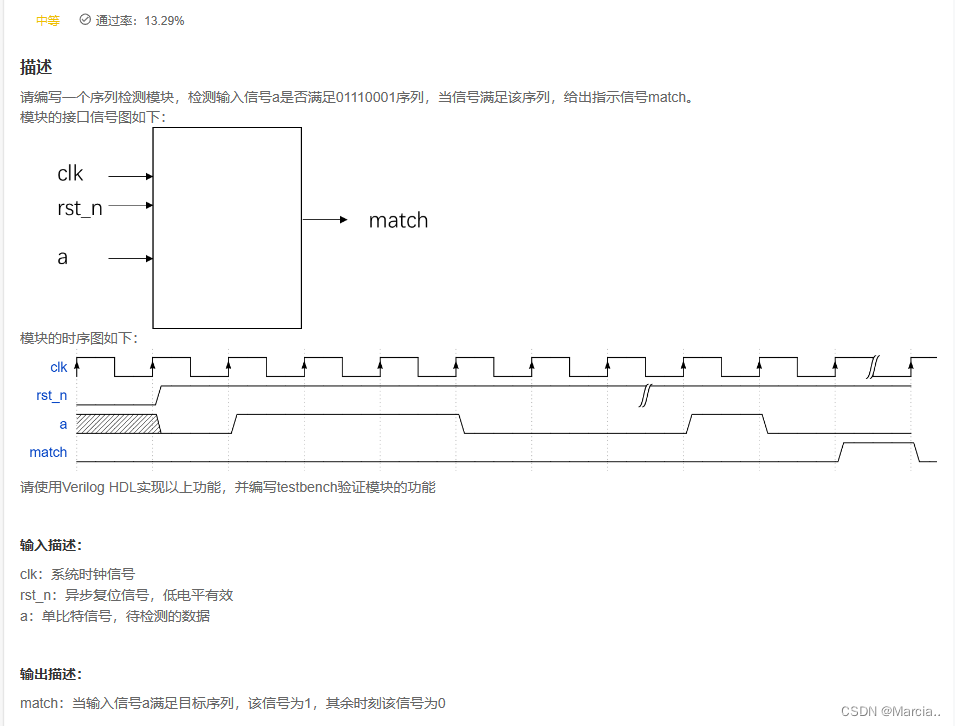
题解:对于序列检测题目,常规的解法有两种:状态机法和序列缓存对比法。
状态机法:
在初始状态中,先判断第一位是否符合,若符合则进入下一个状态,判断第二位是否符合;若第一位不符合则保持在初始状态,直到第一位匹配。如前两位匹配,则判断第三位是否符合,若第一位匹配,最新输入的数值和目标序列的第二位不匹配,则根据最新一位是否匹配第一位,进入第一位匹配状态或者初始状态。依次类推。
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module sequence_detect(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input a,
output reg match
);
parameter IDLE = 9'b0_0000_0001,
S1 = 9'b0_0000_0010,
S2 = 9'b0_0000_0100,
S3 = 9'b0_0000_1000,
S4 = 9'b0_0001_0000,
S5 = 9'b0_0010_0000,
S6 = 9'b0_0100_0000,
S7 = 9'b0_1000_0000,
S8 = 9'b1_0000_0000;
reg [8:0]state,next_state;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
state <= IDLE;
else
state <= next_state;
end
always@(*)
begin
if(!rst_n)
next_state <= IDLE;
else
case(state)
IDLE:next_state <= (~a)?S1:IDLE;//0
S1:next_state <= a?S2:IDLE;//1
S2:next_state <= a?S3:IDLE;//1
S3:next_state <= a?S4:IDLE;//1
S4:next_state <= (~a)?S5:IDLE;//0
S5:next_state <= (~a)?S6:IDLE;//0
S6:next_state <= (~a)?S7:IDLE;//0
S7:next_state <= a?S8:IDLE;//1
S8:next_state <= IDLE;
default:next_state <= IDLE;
endcase
end
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
match <= 1'b0;
else if(state==S8)
match <= 1'b1;
else
match <= 1'b0;
end
endmodule
序列缓存对比法:
将八个时刻的数据缓存,作为一个数组,每个时刻的输入位于数组的末尾,数组其它元素左移,把最早输入的数据移出。然后将数组和目标序列对比,如果数组和目标序列相等,则说明出现目标序列。
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module sequence_detect(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input a,
output reg match
);
reg [7:0]reg_a;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
reg_a <= 8'b0;
else
reg_a <= {reg_a[6:0],a};
end
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
match <= 1'b0;
else if(reg_a == 8'b0111_0001)
match <= 1'b1;
else
match <= 1'b0;
end
endmodule
说明:有的同学可能会用寄存器a_d1到a_d7用于暂存输入a的历史值,从而形成一个8位移位寄存器。这段代码在风格上可能不如使用一个单独的8位寄存器compact。
testbench
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module testbench();
reg clk,rst_n;
reg a;
wire match;
initial begin
$dumpfile("out.vcd");
$dumpvars(0,testbench);
// Initialize Inputs
clk = 0;
rst_n = 0; // Apply reset
a = 0; // Initialize 'a' to prevent X-state
// Release reset after sufficient time
#1 rst_n = 1;
// Apply Test Vector
#2 a = 0;
#2 a = 0;
#2 a = 1;
#2 a = 1;
#2 a = 1;
#2 a = 0;
#2 a = 0;
#2 a = 0;
#2 a = 1;
// Wait for response
#10;// Extra time for the match condition to be detected
// Finish the simulation
$finish;
end
always #1 clk=~clk;
sequence_detect dut(
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.a(a),
.match(match)
);
endmodule
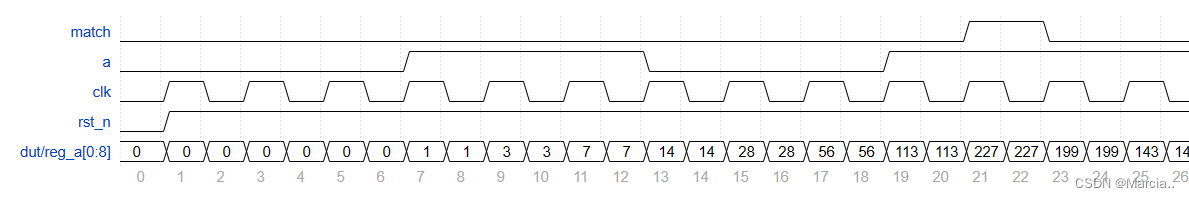







 本文介绍了两种在Verilog中实现的序列检测方法:状态机法通过状态转移判断输入序列,而序列缓存对比法则利用寄存器数组检测目标序列。通过示例代码详细展示了这两种技术的实现过程。
本文介绍了两种在Verilog中实现的序列检测方法:状态机法通过状态转移判断输入序列,而序列缓存对比法则利用寄存器数组检测目标序列。通过示例代码详细展示了这两种技术的实现过程。














 2028
2028

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








