解决思路:轮廓检测+模板匹配
首先对数字模板进行处理
# 读取模板
img = cv2.imread('num.png')
show('img', img)

# 灰度图
ref = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
show('ref', ref)

# 二值化处理
ref = cv2.threshold(ref, 10, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)[1]
show('ref', ref)

# 计算轮廓
# cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL只计算外轮廓,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE只保留终点坐标
refCnts, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(ref.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cv2.drawContours(img, refCnts, -1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
show('img', img)
print(np.array(refCnts).shape)

def sort_contours(refCnts):
boundingBoxes = [cv2.boundingRect(c) for c in refCnts]
(refCnts, boundingBoxes) = zip(*sorted(zip(refCnts, boundingBoxes), key=lambda b: b[1][0], reverse=False))
return refCnts
# 对轮廓进行排序
refCnts = sort_contours(refCnts)
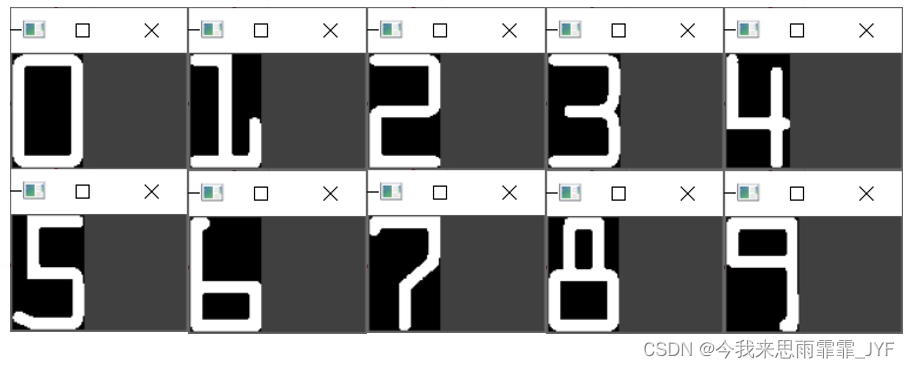
digits = {}
# 遍历每一个轮廓
for (i, c) in enumerate(refCnts):
# 计算外接矩阵且resize成合适的大小
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
roi = ref[y:y+h, x:x+w]
show('roi', roi)
roi = cv2.resize(roi, (57, 88))
# 每个数字对应一个模板
digits[i] = roi
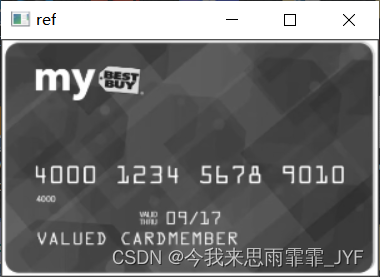
然后对输入图像进行处理
# 读取输入图像
img = cv2.imread('card.png')
show('img', img)
img = cv2.resize(img, (300, int((300 * img.shape[0])/img.shape[1])))
show('img', img)
# 灰度图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
show('gray', gray)


# 初始化卷积核
rectKernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (9, 3))
sqKernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (5, 5))
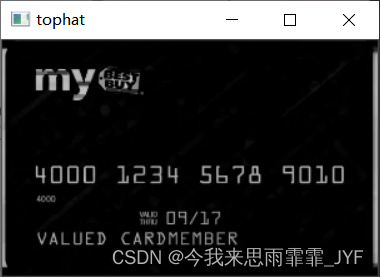
# 礼帽操作,突出更明亮的区域
tophat = cv2.morphologyEx(gray, cv2.MORPH_TOPHAT, rectKernel)
show('tophat', tophat)
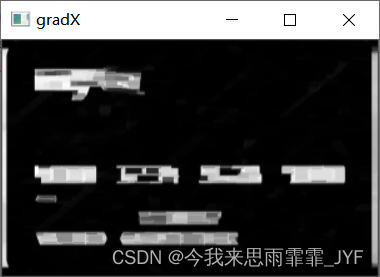
# Sobel算子
gradX = cv2.Sobel(tophat, ddepth=cv2.CV_32F, dx=1, dy=0, ksize=-1)
gradX = np.absolute(gradX)
(minVal, maxVal) = (np.min(gradX), np.max(gradX))
gradX = (255 * ((gradX - minVal) / (maxVal - minVal)))
gradX = gradX.astype("uint8")
show('gradX', gradX)

# 闭操作
gradX = cv2.morphologyEx(gradX, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, rectKernel)
show('gradX', gradX)
# 自适应阈值处理
thresh = cv2.threshold(gradX, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
show('thresh', thresh)
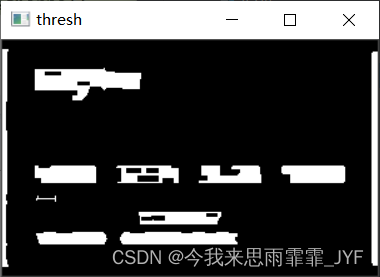
# 闭操作
thresh = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, sqKernel)
show('thresh', thresh)
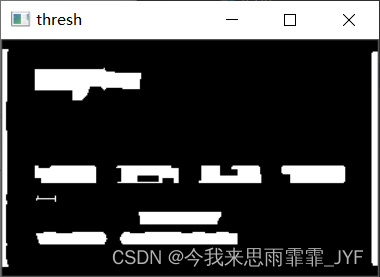
# 计算轮廓
threshCnts, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
locs = []
# 遍历轮廓
for (i, c) in enumerate(threshCnts):
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
ar = w / float(h)
if ar > 2.5 and ar < 4.0:
if (w > 40 and w < 55) and (h >10 and h < 20):
# roi = thresh[y:y + h, x:x + w]
# show('roi', roi)
locs.append((x, y, w, h))
# 将符合的轮廓从左到右排序
locs = sorted(locs, key=lambda x: x[0])
output = []
# 遍历每个轮廓中的数字
for (i, (gX, gY, gW, gH)) in enumerate(locs):
gOutput = []
group = gray[gY-5:gY+gH+5, gX-5:gX+gW+5]
# show('group', group)
# 对轮廓阈值处理
group = cv2.threshold(group, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
# show('group', group)
# 计算数字轮廓
digitCnts, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(group.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
digitCnts = sort_contours(digitCnts)
for c in digitCnts:
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
roi = group[y:y + h, x:x + w]
roi = cv2.resize(roi, (57, 88))
# show('roi', roi)
scores = []
for (digit, digitROI) in digits.items():
# 模板匹配
result = cv2.matchTemplate(roi, digitROI, cv2.TM_CCOEFF)
(_,score,_,_) = cv2.minMaxLoc(result)
scores.append(score)
gOutput.append(str(np.argmax(scores))) # np.argmax()返回最大的那个元素的索引
cv2.rectangle(img, (gX-5, gY-5), (gX+gW+5, gY+gH+5), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(img, "".join(gOutput), (gX, gY-15), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.65, (0, 0, 255), 2)
output.extend(gOutput)

完整代码及效果
import cv2 # opencv读取的格式是BGR
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 卡号识别
def show(name, img):
cv2.imshow(name, img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# 读取模板
img = cv2.imread('num.png')
# show('img', img)
# 灰度图
ref = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# show('ref', ref)
# 二值化处理
ref = cv2.threshold(ref, 10, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)[1]
# show('ref', ref)
# 计算轮廓
# cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL只计算外轮廓,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE只保留终点坐标
refCnts, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(ref.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cv2.drawContours(img, refCnts, -1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# show('img', img)
# print(np.array(refCnts).shape)
def sort_contours(refCnts):
boundingBoxes = [cv2.boundingRect(c) for c in refCnts]
(refCnts, boundingBoxes) = zip(*sorted(zip(refCnts, boundingBoxes), key=lambda b: b[1][0], reverse=False))
return refCnts
# 对轮廓进行排序
refCnts = sort_contours(refCnts)
digits = {}
# 遍历每一个轮廓
for (i, c) in enumerate(refCnts):
# 计算外接矩阵且resize成合适的大小
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
roi = ref[y:y+h, x:x+w]
# show('roi', roi)
roi = cv2.resize(roi, (57, 88))
# 每个数字对应一个模板
digits[i] = roi
# 初始化卷积核
rectKernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (9, 3))
sqKernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (5, 5))
# 读取输入图像
img = cv2.imread('card.png')
# show('img', img)
img = cv2.resize(img, (300, int((300 * img.shape[0])/img.shape[1])))
# show('img', img)
# 灰度图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# show('gray', gray)
# 礼帽操作,突出更明亮的区域
tophat = cv2.morphologyEx(gray, cv2.MORPH_TOPHAT, rectKernel)
# show('tophat', tophat)
# Sobel算子
gradX = cv2.Sobel(tophat, ddepth=cv2.CV_32F, dx=1, dy=0, ksize=-1)
gradX = np.absolute(gradX)
(minVal, maxVal) = (np.min(gradX), np.max(gradX))
gradX = (255 * ((gradX - minVal) / (maxVal - minVal)))
gradX = gradX.astype("uint8")
# show('gradX', gradX)
# 闭操作
gradX = cv2.morphologyEx(gradX, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, rectKernel)
# show('gradX', gradX)
# 自适应阈值处理
thresh = cv2.threshold(gradX, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
# show('thresh', thresh)
# 闭操作
thresh = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, sqKernel)
# show('thresh', thresh)
# 计算轮廓
threshCnts, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
locs = []
# 遍历轮廓
for (i, c) in enumerate(threshCnts):
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
ar = w / float(h)
if ar > 2.5 and ar < 4.0:
if (w > 40 and w < 55) and (h >10 and h < 20):
# roi = thresh[y:y + h, x:x + w]
# show('roi', roi)
locs.append((x, y, w, h))
# 将符合的轮廓从左到右排序
locs = sorted(locs, key=lambda x: x[0])
output = []
# 遍历每个轮廓中的数字
for (i, (gX, gY, gW, gH)) in enumerate(locs):
gOutput = []
group = gray[gY-5:gY+gH+5, gX-5:gX+gW+5]
# show('group', group)
# 对轮廓阈值处理
group = cv2.threshold(group, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
# show('group', group)
# 计算数字轮廓
digitCnts, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(group.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
digitCnts = sort_contours(digitCnts)
for c in digitCnts:
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
roi = group[y:y + h, x:x + w]
roi = cv2.resize(roi, (57, 88))
# show('roi', roi)
scores = []
for (digit, digitROI) in digits.items():
# 模板匹配
result = cv2.matchTemplate(roi, digitROI, cv2.TM_CCOEFF)
(_,score,_,_) = cv2.minMaxLoc(result)
scores.append(score)
gOutput.append(str(np.argmax(scores))) # np.argmax()返回最大的那个元素的索引
cv2.rectangle(img, (gX-5, gY-5), (gX+gW+5, gY+gH+5), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(img, "".join(gOutput), (gX, gY-15), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.65, (0, 0, 255), 2)
output.extend(gOutput)
# 打印结果
print("Card:{}".format("".join(output)))
show('img', img)























 4716
4716











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








