1 概述 Summary
对于流场中守恒的物理量,均可采用输运方程进行描述其随时间变化和在空间的分布规律。输运方程的通用形式为:
For conserved physical quantities in a flow field, their temporal evolution and spatial distribution can all be described using transport equations. The general form of a transport equation is:

输运方程描述了流动过程中的物理量守恒,其包括瞬态、对流、扩散、源四个部分。
通常满足守恒的都是广延量(质量,动量等),而基于广延量守恒的输运方程,其方程实际求解的是对应的强度量(密度,浓度等)的物理场
The transport equation describes the conservation of physical quantities in fluid flow, and includes four components: transient, convection, diffusion and source.
Typically, the conserved quantities are extensive properties like mass, momentum, etc. But the transport equations derived from conservation laws are solved for the corresponding intensive quantities like density, concentration, etc, that represent the physical field of that property.
2 适用范围 Application socpe
输运方程应用的前提条件为流体满足连续介质假设。
流体力学的三个基本方程(连续性方程、动量方程、能量方程)均为输运方程针对不同物理量的表述形式,纳维-斯托克斯方程(N-S方程)为动量方程针对牛顿流体的特定表述。
输运方程也适用于固体热传导等非流动现象。
The prerequisite for applying transport equations is that the fluid satisfies the continuum hypothesis.
The three fundamental equations in fluid dynamics (continuity equation, momentum equation, energy equation) are all formulations of the transport equation for different physical quantities. The Navier-Stokes equations (N-S equations) are a specific formulation of the momentum equation for Newtonian fluids.
Transport equations are also applicable to non-flow phenomena such as heat conduction in solids.
3 推导过程 Derivation
本文中,采用弱形式的积分推导,更有助于理解输运方程中各个项的物理含义。
In this article, a weak integral formulation is adopted to better understand the physical meaning of each term in the transport equation.
做出以下定义:
V:空间任意固定区域(不随时间改变),即控制体
S:V 的外表面,即控制面,既可是流场真实边界(如固体表面),也可是流场内部虚拟边界
Φ:流场的物理量,其分布随时间和空间变化,即以物理场的形式存在
Make the following definitions:
V: An arbitrary fixed region in space (does not change with time), i.e. the control volume
S: The outer surface of V, i.e. the control surface, which can be either a real boundary of the flow field (such as a solid surface) or an internal virtual boundary within the flow field
Φ: A physical quantity of the flow field, whose distribution varies with time and space, i.e. exists in the form of a physical field
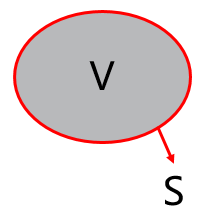
对于 Φ,其随时间的变化影响因素包括:
1 通过表面 S 和周围环境的作用通量(例如流量)
2 内部源项引发的改变(例如热源)
For Φ, the factors influencing its change over time include:
1 The flux (e.g. flow rate) across the surface S due to interaction with the surrounding environment
2 Changes induced by internal source terms (e.g. heat source)
对于区域 V,Φ 的变化率为 Φ 在 V 的体积分对时间导数:
For the region V, the rate of change of Φ is the volume integral of the time derivative of Φ over V:

将 S 上和 Φ 相关的通量命名为 J,则穿过表面 S 的总通量为:
Denoting the flux associated with Φ across the surface S as J, the total flux through the surface S is:

法向量为外法向,此项表征了离开区域 V 的 Φ 通量。
The unit normal vector points outward, representing the flux of Φ leaving the region V.
在区域 V 内,源项的作用为:
Inside the region V, the effect of the source term is:

对于区域 V,Φ 变化率和源项、表面通量之间满足关系:
For the region V, the rate of change of Φ, source term and surface flux satisfy:

通量密度 J 包括对流和扩散两个部分,两者由于物理机理不同,因此可线性叠加:
The flux density J consists of convection and diffusion, which can be linearly superimposed due to different physical mechanisms:

对流通量由流体宏观速度引发,其表达式为:
Convective flux is induced by the macroscopic fluid velocity, with an expression of:

扩散通量由 Φ 的梯度引发,其表达式为:
Diffusive flux is induced by the gradient of Φ, with an expression of:

其中,D 为介质的固有属性,根据物理量 Φ 的不同,有扩散率、热传导率、电传导率、粘度等多种属性。负号表示扩散方向是逆梯度的(从大向小扩散)。
Where D is an intrinsic property of the medium. Based on the physical quantity Φ, D can represent diffusivity, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, viscosity, etc. The negative sign indicates diffusion is opposite the gradient (from high to low).
综上可知:
In summary:

根据高斯公式:
According to Gauss's theorem:
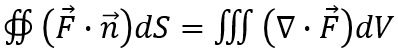
可将通量改写为体积分形式:
The flux can be rewritten in volume integral form:

对于瞬态项,有:
For the transient term:

因此可得:
Therefore:

由于积分区域 V 为任意形状,因此等式成立的充要条件为:
Since the integration region V is arbitrary, the necessary and sufficient condition for the equation to hold is:

此为输运方程的通用表达形式。
This is the general expression for the transport equation.
4 后记 Postscript
为什么使用积分形式推导:
1 物理含义清晰,推导过程始终围绕“守恒”这个物理本质展开
2 积分形式适用于不连续的流场,例如存在点质量源等情况
3 积分形式在推导过程中不受空间维度和坐标系选择影响
Why use integral formulation for derivation:
1 Clear physical meaning, the derivation always revolves around the physical essence of "conservation".
2 Integral form applies to discontinuous flow fields, such as point mass sources.
3 Integral form is unaffected by spatial dimensions or coordinate system choice during derivation.
几个重要概念:
Some key concepts:
1 体积分表示对函数在三维空间求积分,约等于将三维空间分成若干小块后进行求和
1 Volume integral represents integration of a function over three-dimensional space, approximately equivalent to summing over many small chunks filling the space.
2 通量表示了向量穿过曲面的强度。数学定义中,曲面可封闭也可不封闭
2 Flux represents the intensity of a vector across a surface. In mathematical definition, the surface can be closed or open.
3 梯度表示了函数在空间定点上最快的上升率及其方向。梯度运算针对标量,运算结果为向量。在三维空间,梯度运算为:
3 Gradient represents the fastest spatial rate of increase of a function and its direction at a point. Gradient operates on scalars and returns vectors. In three-dimensional space:

4 散度表示了当体积收缩到一个点时,其通量的极限状态。散度运算针对向量,运算结果为标量。在三维空间,散度运算为:
4 Divergence represents the limiting state of flux when a volume shrinks to a point. Divergence operates on vectors and returns scalars. In three-dimensional space:


























 4196
4196

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










