MDP小例子
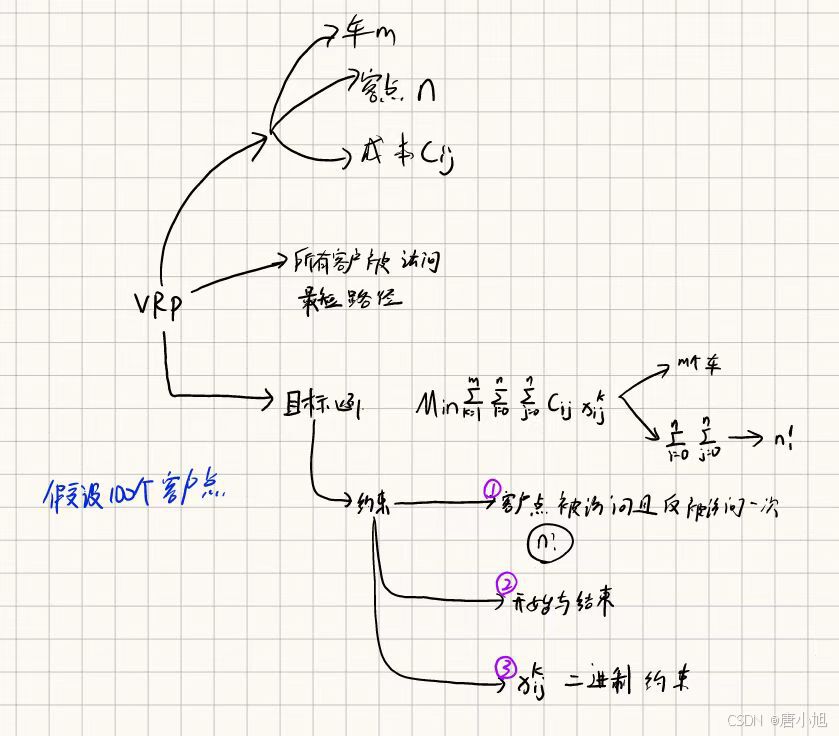
一、车辆路径问题(Vehicle Routing Problem,VRP)
二、VRP问题如何用MDP解决,用理论实现
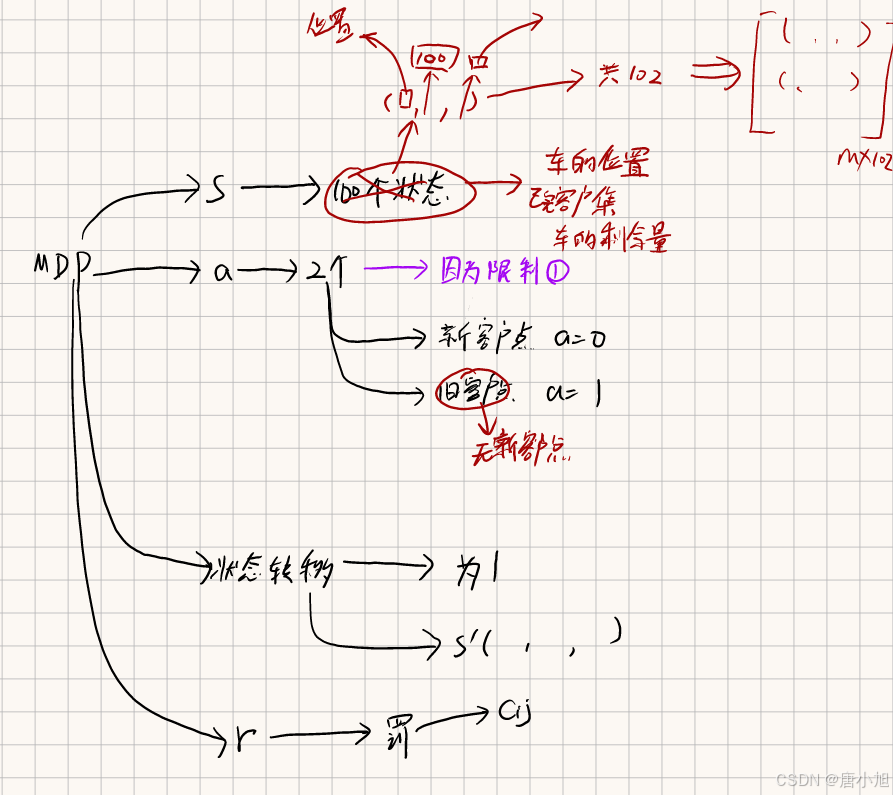
要用马尔可夫决策过程(MDP)来解决车辆路径问题(Vehicle Routing Problem,VRP),我们需要将 VRP 问题映射为 MDP 的各个要素:状态空间、动作空间、转移概率、奖励函数 和 策略。通过这种形式化,我们可以应用强化学习算法来求解最优的车辆路径。
1. MDP 建模的五个要素
1.1 状态空间 S S S
状态空间表示系统当前的所有可能的情况。对于 VRP 问题,状态可以包括以下内容:
- 当前车辆的位置:例如,配送中心或某个客户的位置。
- 车辆剩余的容量:表示车辆还可以承载的货物量。
- 已经访问过的客户集合:记录哪些客户已经被访问。
- 当前未访问客户的需求情况:记录每个未访问客户的需求。
状态空间可以表示为: s = ( 当前位置 , 剩余容量 , 已访问客户 ) s = (\text{当前位置}, \text{剩余容量}, \text{已访问客户}) s=(当前位置,剩余容量,已访问客户)
1.2 动作空间 A A A
动作空间表示在每个状态下可采取的行动。在 VRP 中,动作 a a a 可以表示车辆选择访问的下一个客户或返回配送中心。
动作空间的可能动作包括:
- 选择下一个客户进行配送(如果客户未被访问且需求量小于剩余容量)。
- 选择回到配送中心(终止条件或需要补充物资)。
动作空间可以表示为: a = { 下一个客户位置 } a = \{ \text{下一个客户位置} \} a={下一个客户位置}
1.3 转移概率 P ( s ′ ∣ s , a ) P(s'|s, a) P(s′∣s,a)
转移概率表示在状态 s s s 下采取动作 a a a 后,转移到下一个状态 s ′ s' s′ 的概率。在 VRP 中,通常假设状态的转移是确定性的,即车辆选择一个客户进行配送后,状态 s s s 会确定性地转移到 s ′ s' s′,因此转移概率可以定义为:
P ( s ′ ∣ s , a ) = { 1 , 如果车辆确定性地转移到状态 s ′ 0 , 其他状态 P(s'|s, a) = \begin{cases} 1, & \text{如果车辆确定性地转移到状态 } s' \\ 0, & \text{其他状态} \end{cases} P(s′∣s,a)={1,0,如果车辆确定性地转移到状态 s′其他状态
状态转移包括:
- 当前位置更新:车辆当前位置从当前位置变为所选择的下一个客户的位置。
- 剩余容量更新:从当前容量中减去被访问客户的需求。
- 访问的客户集合更新:更新已访问客户集合,加入当前访问的客户。
1.4 奖励函数 R ( s , a ) R(s, a) R(s,a)
奖励函数定义在状态 s s s 下采取动作 a a a 所获得的即时奖励。在 VRP 中,目标通常是最小化总路径长度或时间,因此可以设计一个负奖励函数,每次车辆行驶距离或消耗的时间都被视为负奖励。
例如:
- 负距离:每次行驶距离作为负奖励,距离越大,负奖励越大。
- 服务完所有客户后的额外奖励:当所有客户都被访问完,可以给予一个大额的正奖励,鼓励智能体更快完成任务。
奖励函数可以表示为: R ( s , a ) = − 行驶的距离 ( s , a ) R(s, a) = - \text{行驶的距离}(s, a) R(s,a)=−行驶的距离(s,a)
1.5 折扣因子 γ \gamma γ
折扣因子 γ ∈ [ 0 , 1 ] \gamma \in [0, 1] γ∈[0,1] 用于平衡即时奖励与未来奖励的重要性。在 VRP 中,折扣因子接近 1 时,车辆不仅考虑当前的路径,还要权衡未来的路径长度,因此我们可以选择 γ \gamma γ 接近 1,比如 0.99。
2. MDP 求解 VRP 的目标
在 MDP 中,目标是找到一个最优策略 $ \pi(s) $,该策略能够在每个状态下选择最优动作 a a a,使得智能体(即车辆)获得的总奖励最大化(在 VRP 中,等同于最小化行驶路径长度)。这个过程通常通过求解贝尔曼最优方程来完成。
贝尔曼最优方程可以表示为:
V ∗ ( s ) = max a [ R ( s , a ) + γ ∑ s ′ P ( s ′ ∣ s , a ) V ∗ ( s ′ ) ] V^*(s) = \max_{a} \left[ R(s, a) + \gamma \sum_{s'} P(s' | s, a) V^*(s') \right] V∗(s)=amax[R(s,a)+γs′∑P(s′∣s,a)V∗(s′)]
其中:
- V ∗ ( s ) V^*(s) V∗(s) 是状态 s s s 下的最优值函数,表示从状态 s s s 出发,执行最优策略能够获得的期望累计奖励。
- R ( s , a ) R(s, a) R(s,a) 是在状态 s s s 下采取动作 a a a 获得的即时奖励。
- γ \gamma γ 是折扣因子。
- P ( s ′ ∣ s , a ) P(s' | s, a) P(s′∣s,a) 是转移概率,表示在状态 s s s 下采取动作 a a a 转移到状态 s ′ s' s′ 的概率。
通过求解这个方程,我们可以找到每个状态下的最优值 V ∗ ( s ) V^*(s) V∗(s),进而找到最优策略。
3. 使用动态规划方法求解 MDP
在车辆路径问题中,我们可以使用动态规划方法求解最优策略。常用的算法包括:
3.1 值迭代算法(Value Iteration)
值迭代算法通过迭代更新值函数 V ( s ) V(s) V(s) 来找到最优策略。对于每个状态 s s s,我们通过最大化 Q ( s , a ) Q(s, a) Q(s,a) 来更新值函数:
V ( s ) ← max a [ R ( s , a ) + γ ∑ s ′ P ( s ′ ∣ s , a ) V ( s ′ ) ] V(s) \leftarrow \max_{a} \left[ R(s, a) + \gamma \sum_{s'} P(s'|s, a) V(s') \right] V(s)←amax[R(s,a)+γs′∑P(s′∣s,a)V(s′)]
值迭代的步骤:
- 初始化每个状态的值函数 V ( s ) = 0 V(s) = 0 V(s)=0。
- 对每个状态
s
s
s:
- 计算每个可能的动作 a a a 的 Q ( s , a ) Q(s, a) Q(s,a),然后选择最大值更新 V ( s ) V(s) V(s)。
- 直到值函数收敛。
3.2 策略迭代算法(Policy Iteration)
策略迭代算法通过交替执行策略评估和策略改进来找到最优策略。
- 策略评估:给定一个策略,计算该策略的状态值函数。
- 策略改进:根据当前的值函数更新策略,使得每个状态选择的动作能够最大化回报。
三、样例分析
样例1:
1. 构建Gymnasium环境
我们使用 gymnasium 来构建一个自定义的 VRP 环境。该环境将实现 MDP 模型,包括状态、动作、奖励函数 和 转移规则。
import gymnasium as gym
from gymnasium import spaces
import numpy as np
class VRPEnv(gym.Env):
"""
自定义的车辆路径问题(VRP)环境,用于MDP求解。
"""
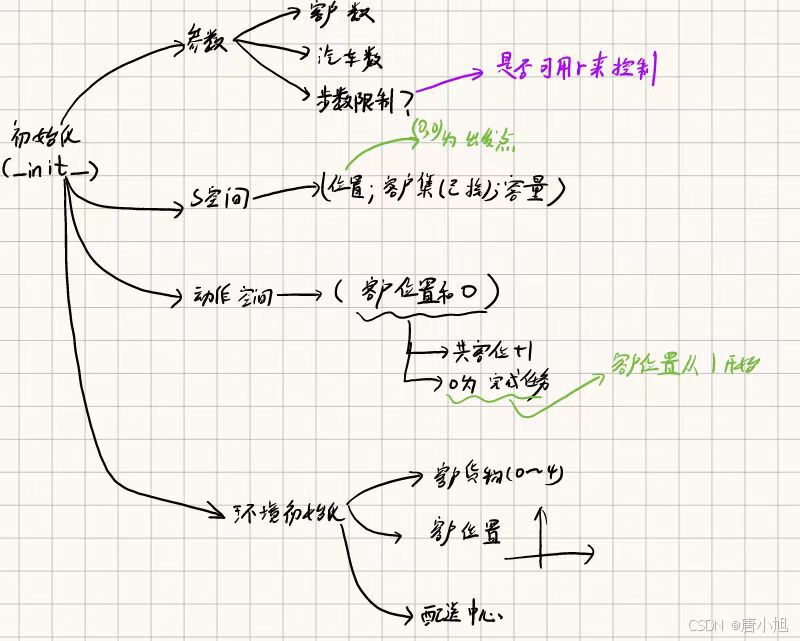
def __init__(self, num_customers=5, vehicle_capacity=10, max_steps=100):
super(VRPEnv, self).__init__()
# 参数
self.num_customers = num_customers # 客户数量
self.vehicle_capacity = vehicle_capacity # 车辆最大容量
self.max_steps = max_steps # 最大步数限制
self.current_step = 0
# 定义状态空间: 当前车辆的位置和剩余容量,访问过的客户
self.observation_space = spaces.Dict({
"vehicle_position": spaces.Discrete(num_customers + 1), # 位置: 0表示配送中心,1到num_customers表示客户
"vehicle_capacity": spaces.Discrete(vehicle_capacity + 1), # 剩余容量
"visited_customers": spaces.MultiBinary(num_customers), # 访问过的客户集合
})
# 定义动作空间: 车辆可以选择访问下一个客户
self.action_space = spaces.Discrete(num_customers + 1) # 动作空间为0到num_customers的整数,表示访问哪一个客户
# 初始化客户需求和位置
self.customer_demands = np.random.randint(1, 5, size=num_customers) # 随机生成每个客户的需求量
self.customer_positions = np.random.rand(num_customers, 2) * 10 # 在二维空间内生成客户位置
self.depot_position = np.array([0, 0]) # 配送中心位置固定在 (0, 0)
# 初始化环境状态
self.state = None
def reset(self, seed=None, options=None):
super().reset(seed=seed)
self.state = {
"vehicle_position": 0, # 车辆初始位置为配送中心
"vehicle_capacity": self.vehicle_capacity, # 初始化车辆满载
"visited_customers": np.zeros(self.num_customers, dtype=np.int32) # 没有访问任何客户
}
self.current_step = 0
return self.state, {}
def step(self, action):
assert self.action_space.contains(action), f"非法动作: {action}"
# 获取当前状态
vehicle_position = self.state["vehicle_position"]
vehicle_capacity = self.state["vehicle_capacity"]
visited_customers = self.state["visited_customers"]
# 计算距离并奖励(负的行驶距离)
if action == 0:
# 返回配送中心
reward = -np.linalg.norm(self.customer_positions[vehicle_position] - self.depot_position)
done = all(visited_customers) or self.current_step >= self.max_steps
else:
# 访问客户
if visited_customers[action - 1] == 1: # 客户已被访问,奖励为0(无效动作)
reward = -10 # 惩罚
done = False
else:
# 计算到客户的距离
reward = -np.linalg.norm(self.customer_positions[vehicle_position] - self.customer_positions[action - 1])
# 检查车辆容量是否足够
demand = self.customer_demands[action - 1]
if demand <= vehicle_capacity:
# 更新车辆位置,更新已访问客户列表,减少剩余容量
vehicle_capacity -= demand
visited_customers[action - 1] = 1 # 标记为已访问
else:
reward = -100 # 容量不足的惩罚
done = False
# 更新状态
self.state = {
"vehicle_position": action,
"vehicle_capacity": vehicle_capacity,
"visited_customers": visited_customers
}
self.current_step += 1
return self.state, reward, done, False, {}
def render(self):
print(f"车辆位置: {self.state['vehicle_position']}, 剩余容量: {self.state['vehicle_capacity']}")
print(f"已访问客户: {self.state['visited_customers']}")
def close(self):
pass
样例分析__init__
def __init__(self, num_customers=5, vehicle_capacity=10, max_steps=100):
super(VRPEnv, self).__init__()
# 参数
self.num_customers = num_customers # 客户数量
self.vehicle_capacity = vehicle_capacity # 车辆最大容量
self.max_steps = max_steps # 最大步数限制
self.current_step = 0
# 定义状态空间: 当前车辆的位置和剩余容量,访问过的客户
self.observation_space = spaces.Dict({
"vehicle_position": spaces.Discrete(num_customers + 1), # 位置: 0表示配送中心,1到num_customers表示客户
"vehicle_capacity": spaces.Discrete(vehicle_capacity + 1), # 剩余容量
"visited_customers": spaces.MultiBinary(num_customers), # 访问过的客户集合
})
# 定义动作空间: 车辆可以选择访问下一个客户
self.action_space = spaces.Discrete(num_customers + 1) # 动作空间为0到num_customers的整数,表示访问哪一个客户
# 初始化客户需求和位置
self.customer_demands = np.random.randint(1, 5, size=num_customers) # 随机生成每个客户的需求量
self.customer_positions = np.random.rand(num_customers, 2) * 10 # 在二维空间内生成客户位置
self.depot_position = np.array([0, 0]) # 配送中心位置固定在 (0, 0)
# 初始化环境状态
self.state = None
def reset(self, seed=None, options=None):
super().reset(seed=seed)
self.state = {
"vehicle_position": 0, # 车辆初始位置为配送中心
"vehicle_capacity": self.vehicle_capacity, # 初始化车辆满载
"visited_customers": np.zeros(self.num_customers, dtype=np.int32) # 没有访问任何客户
}
self.current_step = 0
return self.state, {}
变量及解释__init__
-
num_customers:- 描述:客户数量,默认为5。代表需要访问的客户的数量。
-
vehicle_capacity:- 描述:车辆的最大容量,默认为10。表示车辆在配送时可以携带的最大物品数量。
-
max_steps:- 描述:最大步数限制,默认为100。代表在一个回合中车辆可以执行的最大动作数量,用于防止无限循环。
-
current_step:- 描述:当前的步数,初始化为0。记录车辆在环境中的当前步数。
-
observation_space:- 描述:定义了状态空间,使用
spaces.Dict()进行构建,包括:"vehicle_position":车辆的位置,0表示配送中心,1到num_customers表示客户位置。"vehicle_capacity":车辆的剩余容量,表示车辆当前还能装载的货物数量。"visited_customers":一个二进制数组,记录车辆是否已经访问过某个客户,1表示访问过,0表示未访问。
- 描述:定义了状态空间,使用
-
action_space:- 描述:定义了动作空间,使用
spaces.Discrete(num_customers + 1)构建。代表车辆的动作,0表示返回配送中心,1到num_customers表示访问对应客户。
- 描述:定义了动作空间,使用
-
customer_demands:- 描述:随机生成的客户需求量,表示每个客户需要的货物数量。使用
np.random.randint(1, 5, size=num_customers)生成,需求量在1到4之间。
- 描述:随机生成的客户需求量,表示每个客户需要的货物数量。使用
-
customer_positions:- 描述:随机生成的客户位置,表示每个客户的坐标。使用
np.random.rand(num_customers, 2) * 10生成二维平面上的随机位置。
- 描述:随机生成的客户位置,表示每个客户的坐标。使用
-
depot_position:- 描述:配送中心的固定位置,默认为
[0, 0]。
- 描述:配送中心的固定位置,默认为
-
state:- 描述:当前的环境状态,使用字典存储。包括:
"vehicle_position":当前车辆的位置。"vehicle_capacity":车辆的剩余容量。"visited_customers":记录访问过的客户,初始化为全零的数组。
- 描述:当前的环境状态,使用字典存储。包括:
-
seed:- 描述:用于环境重置时的随机种子。默认是
None,可以设置为特定的值来保证环境的可重复性。
- 描述:用于环境重置时的随机种子。默认是
-
options:- 描述:用于传递额外的选项参数。默认是
None。
- 描述:用于传递额外的选项参数。默认是
样例分析step

def step(self, action):
assert self.action_space.contains(action), f"非法动作: {action}"
# 获取当前状态
vehicle_position = self.state["vehicle_position"]
vehicle_capacity = self.state["vehicle_capacity"]
visited_customers = self.state["visited_customers"]
# 计算距离并奖励(负的行驶距离)
if action == 0:
# 返回配送中心
reward = -np.linalg.norm(self.customer_positions[vehicle_position] - self.depot_position)
done = all(visited_customers) or self.current_step >= self.max_steps
else:
# 访问客户
if visited_customers[action - 1] == 1: # 客户已被访问,奖励为0(无效动作)
reward = -10 # 惩罚
done = False
else:
# 计算到客户的距离
reward = -np.linalg.norm(self.customer_positions[vehicle_position] - self.customer_positions[action - 1])
# 检查车辆容量是否足够
demand = self.customer_demands[action - 1]
if demand <= vehicle_capacity:
# 更新车辆位置,更新已访问客户列表,减少剩余容量
vehicle_capacity -= demand
visited_customers[action - 1] = 1 # 标记为已访问
else:
reward = -100 # 容量不足的惩罚
done = False
# 更新状态
self.state = {
"vehicle_position": action,
"vehicle_capacity": vehicle_capacity,
"visited_customers": visited_customers
}
self.current_step += 1
return self.state, reward, done, False, {}
s参数列表及解释step
-
action- 描述:表示车辆执行的动作,范围是
0到num_customers的整数值。0:表示返回配送中心。1到num_customers:表示访问相应的客户。
- 描述:表示车辆执行的动作,范围是
-
vehicle_position- 描述:当前车辆所在的位置,在状态字典
self.state["vehicle_position"]中存储。 - 取值:
0表示配送中心,1到num_customers表示对应客户的位置。
- 描述:当前车辆所在的位置,在状态字典
-
vehicle_capacity- 描述:当前车辆的剩余容量,表示车辆还能携带的货物数量,在状态字典
self.state["vehicle_capacity"]中存储。 - 取值:从
0到vehicle_capacity的整数,表示车辆的剩余运输能力。
- 描述:当前车辆的剩余容量,表示车辆还能携带的货物数量,在状态字典
-
visited_customers- 描述:二进制数组,记录哪些客户已经被访问。
1表示该客户已被访问,0表示未访问。 - 存储在状态字典
self.state["visited_customers"]中。
- 描述:二进制数组,记录哪些客户已经被访问。
-
customer_positions- 描述:每个客户的位置,是一个二维坐标数组,存储在
self.customer_positions中。 - 取值:由
np.random.rand(num_customers, 2) * 10生成,表示每个客户在二维平面中的随机坐标。
- 描述:每个客户的位置,是一个二维坐标数组,存储在
-
depot_position- 描述:配送中心的位置,固定为
[0, 0],存储在self.depot_position中。 - 取值:固定为
(0, 0)。
- 描述:配送中心的位置,固定为
-
customer_demands- 描述:每个客户的需求量,是一个整数数组,存储在
self.customer_demands中。 - 取值:使用
np.random.randint(1, 5, size=num_customers)生成,表示每个客户需要的货物量(范围从1到4)。
- 描述:每个客户的需求量,是一个整数数组,存储在
-
current_step- 描述:当前的步数,表示车辆在当前回合中已经执行的步数。
- 取值:从0开始,每执行一步
self.current_step增加1。
-
max_steps- 描述:最大允许的步数限制,表示车辆在环境中能执行的最大动作数,超过此步数回合结束。
- 取值:由初始化时设置(默认值为100)。
-
reward
- 描述:当前步数的奖励值,基于车辆的移动距离和其他条件(如客户是否被访问、容量是否足够)计算。
- 取值:负的行驶距离(成本),以及特定的惩罚值(如重复访问客户的惩罚
-10,容量不足的惩罚-100)。
done
- 描述:布尔值,表示回合是否结束。回合结束的条件是所有客户都已访问,或者达到最大步数限制。
- 取值:
True表示回合结束,False表示回合继续。
info
- 描述:额外信息,当前返回值为空字典
{},可以用于扩展,如返回其他调试信息。
def render(self):
print(f"车辆位置: {self.state['vehicle_position']}, 剩余容量: {self.state['vehicle_capacity']}")
print(f"已访问客户: {self.state['visited_customers']}")
def close(self):
pass
2. 强化学习算法解决 VRP
我们可以使用 Q-learning 等强化学习算法来在这个环境中找到最优策略。以下是使用 Q-learning 解决的示例代码:
import numpy as np
# 初始化Q表 (车辆位置 × 客户访问状态)
num_customers = 5
Q = np.zeros((num_customers + 1, 2 ** num_customers, num_customers + 1))
# Q-learning 参数
alpha = 0.1
gamma = 0.9
epsilon = 0.1
num_episodes = 1000
env = VRPEnv(num_customers=num_customers, vehicle_capacity=10, max_steps=100)
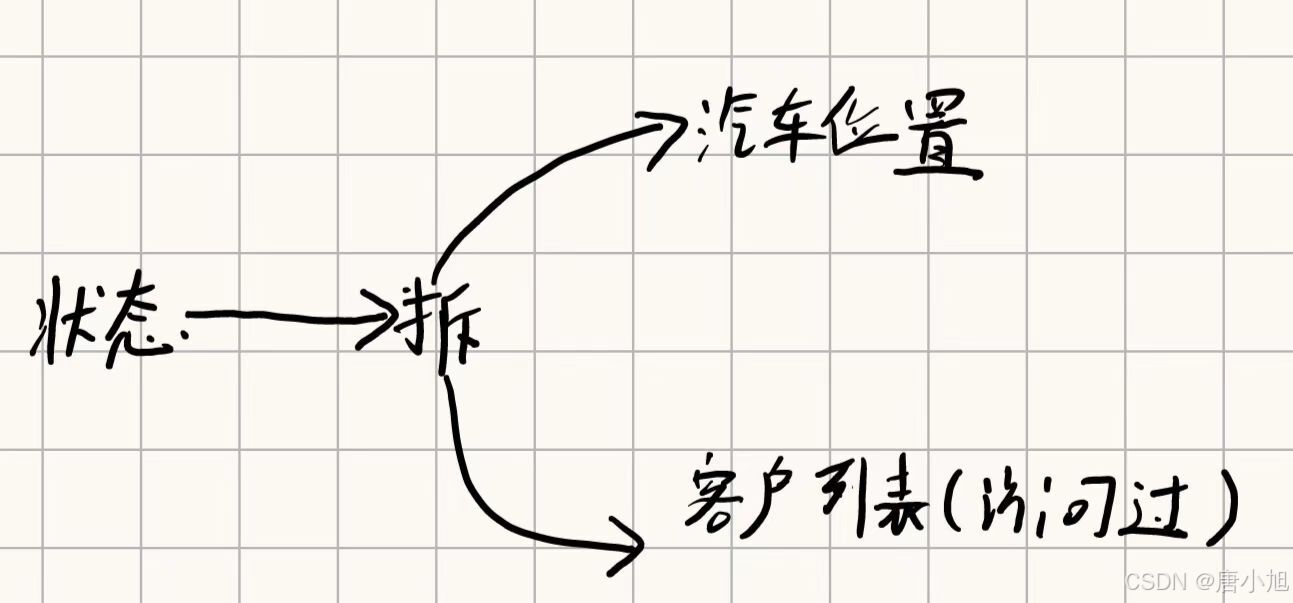
def state_to_index(state):
"""将状态转换为Q表的索引"""
vehicle_pos = state['vehicle_position']
visited_customers = int("".join(map(str, state['visited_customers'])), 2)
return vehicle_pos, visited_customers
# Q-learning 训练过程
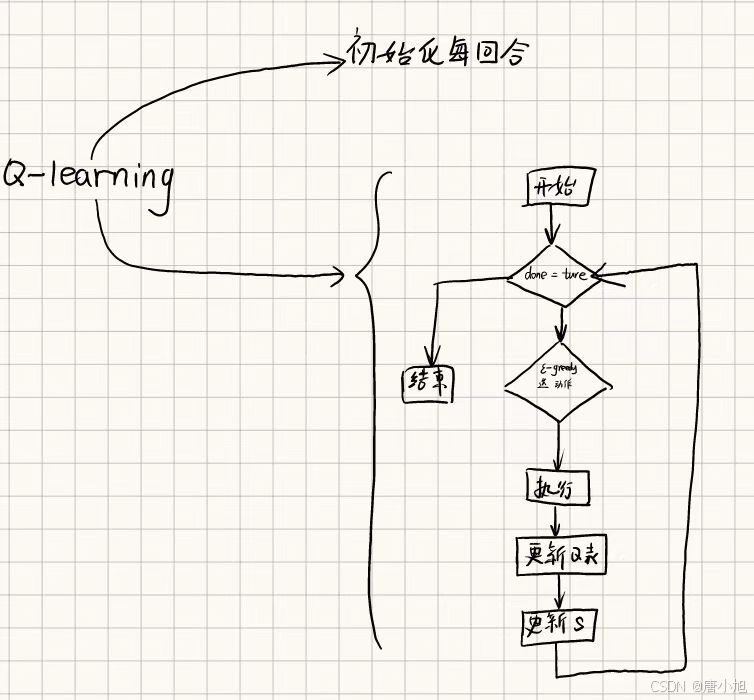
for episode in range(num_episodes):
state, _ = env.reset()
done = False
while not done:
vehicle_pos, visited_customers = state_to_index(state)
# epsilon-greedy选择动作
if np.random.rand() < epsilon:
action = env.action_space.sample() # 随机选择动作
else:
action = np.argmax(Q[vehicle_pos, visited_customers]) # 选择Q值最大的动作
# 执行动作
next_state, reward, done, _, _ = env.step(action)
next_vehicle_pos, next_visited_customers = state_to_index(next_state)
# 更新Q表
Q[vehicle_pos, visited_customers, action] += alpha * (
reward + gamma * np.max(Q[next_vehicle_pos, next_visited_customers]) - Q[vehicle_pos, visited_customers, action]
)
# 更新状态
state = next_state
print("训练完成")
样例分析state_to_index
def state_to_index(state):
"""将状态转换为Q表的索引"""
vehicle_pos = state['vehicle_position']
visited_customers = int("".join(map(str, state['visited_customers'])), 2)
return vehicle_pos, visited_customers
state_to_index 函数中的变量及解释
-
state- 描述:表示当前环境的状态,是一个字典,包含车辆的位置、车辆剩余容量以及已访问的客户。
- 结构:
state = {"vehicle_position": ..., "visited_customers": ...}。 - 取值:
vehicle_position是车辆的位置,visited_customers是一个二进制数组,记录哪些客户已被访问。
-
vehicle_pos- 描述:车辆当前位置,提取自状态字典
state['vehicle_position']。 - 取值:
0表示配送中心,1到num_customers表示对应客户的位置。
- 描述:车辆当前位置,提取自状态字典
-
visited_customers- 描述:表示已访问客户的二进制值,将客户访问状态数组转换为整数。通过
map(str, state['visited_customers'])将客户访问状态列表转换为字符串形式,并通过"".join(...)拼接成完整的二进制字符串,最后用int(..., 2)将该二进制字符串转换为整数。 - 取值:一个整数,表示车辆已经访问过的客户,使用二进制编码。
- 描述:表示已访问客户的二进制值,将客户访问状态数组转换为整数。通过
-
map(str, state['visited_customers'])- 描述:将
state['visited_customers']数组中的每个元素(0或1)转换为字符串。 - 取值:列表中的每个元素被转换为字符串 “0” 或 “1”。
- 描述:将
-
"".join(map(str, state['visited_customers']))- 描述:将客户访问状态的字符串形式拼接成一个二进制字符串,例如,
[1, 0, 1]会转换为"101"。
- 描述:将客户访问状态的字符串形式拼接成一个二进制字符串,例如,
-
int("".join(map(str, state['visited_customers'])), 2)- 描述:将拼接好的二进制字符串转换为整数,指定基数为2。这个整数表示客户访问的组合状态,方便在Q表中查找。
-
返回值
- 描述:
return vehicle_pos, visited_customers表示函数返回的是一个包含车辆当前位置和已访问客户组合状态(整数形式)的元组。
- 描述:
样例分析Q-learning 训练过程
# Q-learning 训练过程
for episode in range(num_episodes):
state, _ = env.reset()
done = False
while not done:
vehicle_pos, visited_customers = state_to_index(state)
# epsilon-greedy选择动作
if np.random.rand() < epsilon:
action = env.action_space.sample() # 随机选择动作
else:
action = np.argmax(Q[vehicle_pos, visited_customers]) # 选择Q值最大的动作
# 执行动作
next_state, reward, done, _, _ = env.step(action)
next_vehicle_pos, next_visited_customers = state_to_index(next_state)
# 更新Q表
Q[vehicle_pos, visited_customers, action] += alpha * (
reward + gamma * np.max(Q[next_vehicle_pos, next_visited_customers]) - Q[vehicle_pos, visited_customers, action]
)
# 更新状态
state = next_state
print("训练完成")
代码中的变量及其解释
-
num_episodes- 描述:总的训练回合数,即智能体在环境中进行多少次完整的探索。
-
state- 描述:当前环境的状态,通常为字典格式,包括车辆位置、剩余容量和访问过的客户信息。由
env.reset()或env.step()返回。
- 描述:当前环境的状态,通常为字典格式,包括车辆位置、剩余容量和访问过的客户信息。由
-
done- 描述:布尔值,表示当前回合是否结束。回合结束条件可能是达到最大步数或满足任务条件。
- 取值:
True或False。
-
vehicle_pos- 描述:车辆当前位置的索引,由
state_to_index(state)函数返回。 - 取值:从
0(配送中心)到num_customers(客户位置)的整数。
- 描述:车辆当前位置的索引,由
-
visited_customers- 描述:已访问客户的二进制编码。将访问记录转换为整数形式,用于在Q表中查找和更新。
- 取值:二进制编码的整数,表示客户访问状态的组合。
-
epsilon- 描述:探索率,决定智能体选择随机动作还是选择当前Q值最大的动作。用于epsilon-greedy策略。
- 取值:
0到1之间的浮点数,epsilon越大,探索概率越高。
-
action- 描述:智能体在当前状态下执行的动作。动作选择基于epsilon-greedy策略,要么随机选择,要么选择最大Q值的动作。
- 取值:整数,范围是
0(返回配送中心)到num_customers(访问对应客户)。
-
Q- 描述:Q值表,用于存储每个状态-动作对的Q值。更新Q表是Q-learning算法的核心过程。
- 结构:三维数组
Q[state_index, visited_customers_index, action],表示在某个状态和访问过的客户组合下采取某个动作的价值。
-
alpha- 描述:学习率,控制Q值更新的幅度。决定新学到的信息与旧信息的权重。
- 取值:
0到1之间的浮点数,alpha越大,更新幅度越大。
-
gamma
- 描述:折扣因子,控制未来奖励对当前Q值的影响。用于平衡短期和长期奖励。
- 取值:
0到1之间的浮点数,gamma越接近1,智能体越重视长期回报。
next_state
- 描述:智能体在执行动作后,环境返回的下一个状态。由
env.step(action)返回。 - 结构:与
state类似,是字典或其他复杂结构。
reward
- 描述:当前动作的即时奖励。由环境根据动作的效果返回,用于Q值更新。
- 取值:浮点数或整数,可以是正值(奖励)或负值(惩罚)。
next_vehicle_pos
- 描述:车辆在下一状态中的位置索引,由
state_to_index(next_state)函数返回。 - 取值:
0到num_customers的整数,表示下一状态中的车辆位置。
next_visited_customers
- 描述:下一个状态中已访问客户的二进制编码,由
state_to_index(next_state)函数返回。 - 取值:二进制编码的整数,表示下一状态中的客户访问情况。
np.argmax()
- 描述:选择当前状态下Q值最大的动作。用于epsilon-greedy策略中的利用部分。
- 返回值:动作的索引(整数)。
np.random.rand()
- 描述:生成一个随机浮点数,用于决定当前回合是否进行探索(随机选择动作)。
- 取值:
0到1之间的浮点数。
env.reset()
- 描述:重置环境,返回初始状态,通常用于每个回合的开始。
env.step(action)
- 描述:执行指定动作,更新环境,返回新的状态、奖励、是否回合结束以及其他信息。
四、伪代码实现

Gymnasium_env.py
这里是引用
进行MDP的初始化
import gymnasium as gym
from gymnasium import spaces
import numpy as np
class VRPEnv(gym.Env):
"""
自定义的车辆路径问题(VRP)环境,用于MDP求解。
"""
def __init__(self, num_customers=5, vehicle_capacity=10, max_steps=100):
super(VRPEnv, self).__init__()
# 参数
self.num_customers = num_customers # 客户数量
self.vehicle_capacity = vehicle_capacity # 车辆最大容量
self.max_steps = max_steps # 最大步数限制
self.current_step = 0
# 定义状态空间: 当前车辆的位置和剩余容量,访问过的客户
self.observation_space = spaces.Dict({
"vehicle_position": spaces.Discrete(num_customers + 1), # 位置: 0表示配送中心,1到num_customers表示客户
"vehicle_capacity": spaces.Discrete(vehicle_capacity + 1), # 剩余容量
"visited_customers": spaces.MultiBinary(num_customers), # 访问过的客户集合
})
# 定义动作空间: 车辆可以选择访问下一个客户
self.action_space = spaces.Discrete(num_customers + 1) # 动作空间为0到num_customers的整数,表示访问哪一个客户
# 初始化客户需求和位置
self.customer_demands = np.random.randint(1, 5, size=num_customers) # 随机生成每个客户的需求量
self.customer_positions = np.random.rand(num_customers, 2) * 10 # 在二维空间内生成客户位置
self.depot_position = np.array([0, 0]) # 配送中心位置固定在 (0, 0)
# 将配送中心的位置插入到第一个位置
self.customer_positions = np.vstack([self.depot_position, self.customer_positions])
# #方法二-错
# 将配送中心的位置添加到 self.customer_positions 的第一个位置
# self.customer_positions = np.vstack([self.depot_position, self.customer_positions])
# 现在 customer_positions 的索引范围为 [0, num_customers],
# 其中 0 是配送中心,1 到 num_customers 是客户的位置
# customer_positions_with_index = [(i, pos) for i, pos in enumerate(self.customer_positions)]
# #方法一-错
# # 将配送中心信息也纳入到这个结构中,作为第一个位置
# self.customer_positions_with_index.insert(0, {'index': 'Depot', 'position': self.depot_position})
# # 为每个客户生成序号和位置,使用列表生成式
# self.customer_positions_with_index = [
# {'index': i, 'position': pos}
# for i, pos in enumerate(self.customer_positions)
# ]
# 初始化环境状态
self.state = None
def reset(self, seed=None, options=None):
super().reset(seed=seed)
self.state = {
"vehicle_position": 0, # 车辆初始位置为配送中心
"vehicle_capacity": self.vehicle_capacity, # 初始化车辆满载
"visited_customers": np.zeros(self.num_customers, dtype=np.int32) # 没有访问任何客户
}
self.current_step = 0
return self.state, {}
def step(self, action):
assert self.action_space.contains(action), f"非法动作: {action}"
# 获取当前状态
vehicle_position = self.state["vehicle_position"]
vehicle_capacity = self.state["vehicle_capacity"]
visited_customers = self.state["visited_customers"]
# 动作范围应在 [0, num_customers]
if action < 0 or action > self.num_customers:
raise ValueError(f"Action {action} is out of bounds!")
# 计算距离并奖励(负的行驶距离)
if action == 0:
if vehicle_position == 0:
#效果不好
# reward = -100 # 已经在配送中心,无需移动
reward =0
else:
reward = -np.linalg.norm(self.customer_positions[vehicle_position] - self.depot_position)
# 方法一:解决self.customer_positions 数组和vehicle_position的矛盾
# reward = -np.linalg.norm(self.customer_positions_with_index[vehicle_position - 1] - self.depot_position)
done = all(visited_customers) or self.current_step >= self.max_steps
# # 返回配送中心
# reward = -np.linalg.norm(self.customer_positions[vehicle_position] - self.depot_position)
# done = all(visited_customers) or self.current_step >= self.max_steps
# done用来判断主循环的结束与否
else:
# 访问客户
if visited_customers[action - 1] == 1: # 客户已被访问,奖励为0(无效动作)
reward = -10 # 惩罚
done = False
else:
# 计算到客户的距离
reward = -np.linalg.norm(self.customer_positions[vehicle_position] - self.customer_positions[action - 1])
# 方法一:解决self.customer_positions 数组和vehicle_position的矛盾
# reward = -np.linalg.norm(self.customer_positions_with_index[vehicle_position] - self.customer_positions_with_index[action - 1])
# 检查车辆容量是否足够
demand = self.customer_demands[action - 1]
if demand <= vehicle_capacity:
# 更新车辆位置,更新已访问客户列表,减少剩余容量
vehicle_capacity -= demand
visited_customers[action - 1] = 1 # 标记为已访问
else:
reward = -100 # 容量不足的惩罚
done = False
# 更新状态
self.state = {
"vehicle_position": action,
"vehicle_capacity": vehicle_capacity,
"visited_customers": visited_customers
}
self.current_step += 1
# return self.state, reward, done, False, {}
return self.state, reward, done, {}
def render(self):
print(f"车辆位置: {self.state['vehicle_position']}, 剩余容量: {self.state['vehicle_capacity']}")
print(f"已访问客户: {self.state['visited_customers']}")
def close(self):
pass
Q-learning
选取一个测略实现
import numpy as np
from Gymnasium_env import VRPEnv
# 初始化Q表 (车辆位置 × 客户访问状态)
num_customers = 5
Q = np.zeros((num_customers + 1, 2 ** num_customers, num_customers + 1))
# Q-learning 参数
alpha = 0.1
gamma = 0.9
epsilon = 0.1
num_episodes = 5000
env = VRPEnv(num_customers=num_customers, vehicle_capacity=10, max_steps=100)
def state_to_index(state):
"""将状态转换为Q表的索引"""
vehicle_pos = state['vehicle_position']
visited_customers = int("".join(map(str, state['visited_customers'])), 2)
return vehicle_pos, visited_customers
# Q-learning 训练过程
for episode in range(num_episodes):
state, _ = env.reset()
done = False
# epsilon 随时间逐渐减少
epsilon = max(epsilon * 0.99, 0.01)
while not done:
vehicle_pos, visited_customers = state_to_index(state)
# epsilon-greedy选择动作
if np.random.rand() < epsilon:
action = env.action_space.sample() # 随机选择动作
else:
# 在多个相同 Q 值动作中随机选择
action = np.random.choice(np.flatnonzero(Q[vehicle_pos, visited_customers] == Q[vehicle_pos, visited_customers].max()))
# 执行动作
next_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
next_vehicle_pos, next_visited_customers = state_to_index(next_state)
# 更新Q表
Q[vehicle_pos, visited_customers, action] += alpha * (
reward + gamma * np.max(Q[next_vehicle_pos, next_visited_customers]) - Q[vehicle_pos, visited_customers, action]
)
# 更新状态
state = next_state
print("训练完成")
s_test_01
观测结果
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from Gymnasium_env import VRPEnv
import numpy as np
def plot_route(route, env):
customer_positions = np.vstack([env.depot_position, env.customer_positions]) # 包含配送中心和客户位置
route_positions = customer_positions[route]
plt.plot(customer_positions[:, 0], customer_positions[:, 1], 'bo', label='Customers')
plt.plot(route_positions[:, 0], route_positions[:, 1], 'r--', label='Route')
plt.plot(customer_positions[0, 0], customer_positions[0, 1], 'gs', label='Depot', markersize=10) # 配送中心
plt.legend()
plt.title('Vehicle Routing Problem - Test Route')
plt.xlabel('X position')
plt.ylabel('Y position')
plt.show()
# 初始化环境
env = VRPEnv(num_customers=5, vehicle_capacity=10, max_steps=100)
# 假设你有车辆的路径
route = [0, 2, 3, 1, 4, 0] # 举例:从配送中心出发,访问客户2,3,1,4,再返回配送中心
# 绘制路径图
plot_route(route, env)

总结
由图可知,显然实验效果十分差。需要进行改进。























 809
809

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








