睿智的目标检测39——TF2搭建YoloV4-Tiny目标检测平台(tensorflow2)
学习前言
Tiny系列一直没去关注,做一下试试看。

什么是YOLOV4-Tiny
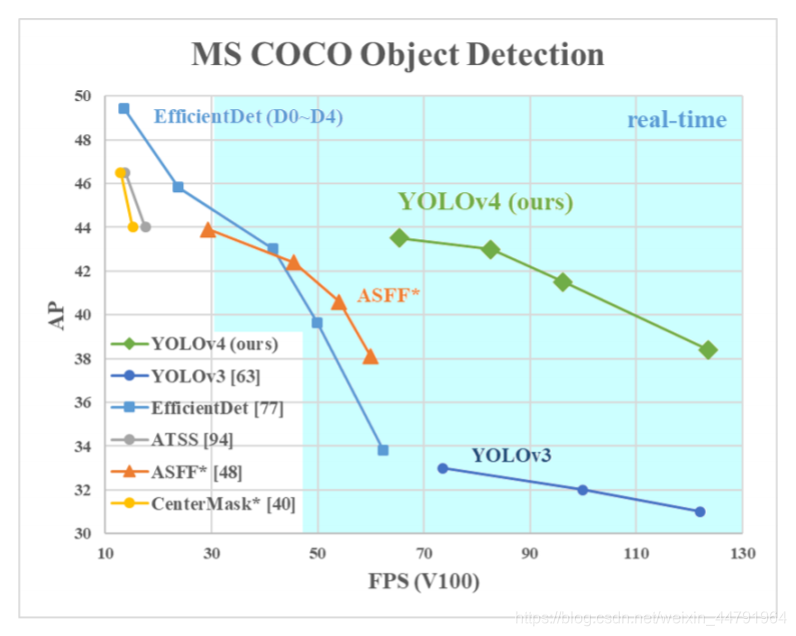
YOLOV4是YOLOV3的改进版,在YOLOV3的基础上结合了非常多的小Tricks。
尽管没有目标检测上革命性的改变,但是YOLOV4依然很好的结合了速度与精度。
根据上图也可以看出来,YOLOV4在YOLOV3的基础上,在FPS不下降的情况下,mAP达到了44,提高非常明显。
YOLOV4整体上的检测思路和YOLOV3相比相差并不大,都是使用三个特征层进行分类与回归预测。
YoloV4-Tiny是YoloV4的简化版,少了一些结构,但是速度大大增加了,YoloV4共有约6000万参数,YoloV4-Tiny则只有600万参数。
YoloV4-Tiny仅使用了两个特征层进行分类与回归预测。
代码下载
https://github.com/bubbliiiing/yolov4-tiny-tf2
喜欢的可以给个star噢!
YoloV4-Tiny结构解析
1、主干特征提取网络Backbone
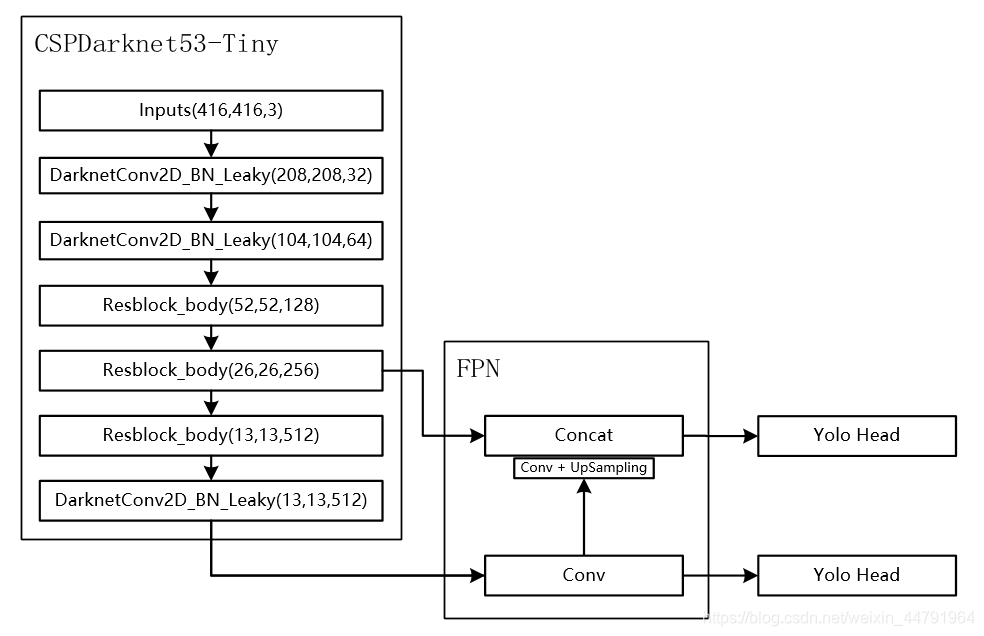
当输入是416x416时,特征结构如下:
当输入是608x608时,特征结构如下:
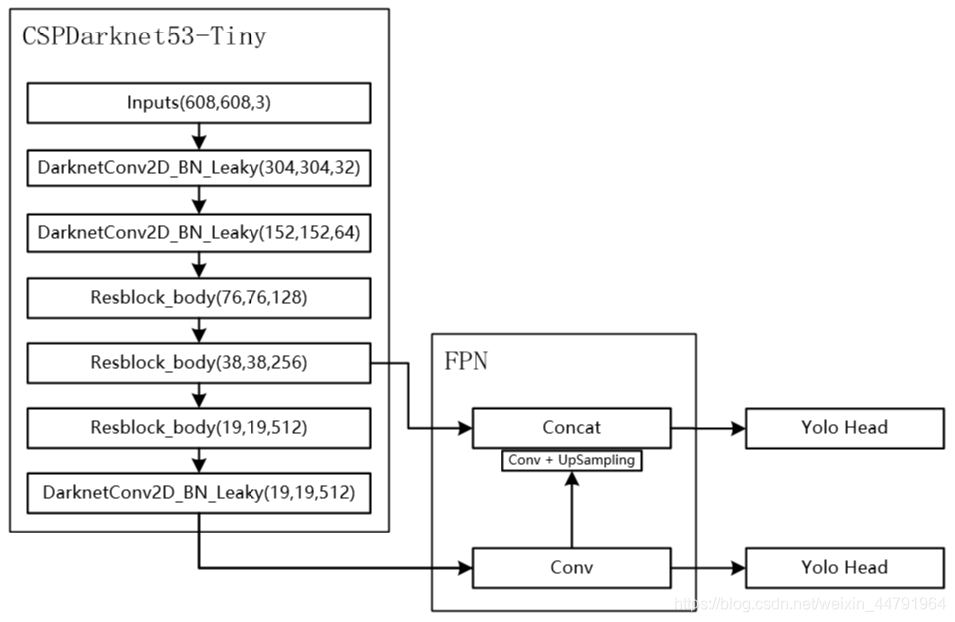
(上述框图有一点错误,第二个Resblock_body不引出有效特征层,第三个Resblock_body才引出,图中是为了和矩阵shape对应上才从第二个Resblock_body引出)
而在YoloV4-Tiny中,其使用了CSPdarknet53_tiny作为主干特征提取网络。
和CSPdarknet53相比,为了更快速,将激活函数重新修改为LeakyReLU。
CSPdarknet53_tiny具有两个特点:
1、使用了CSPnet结构。
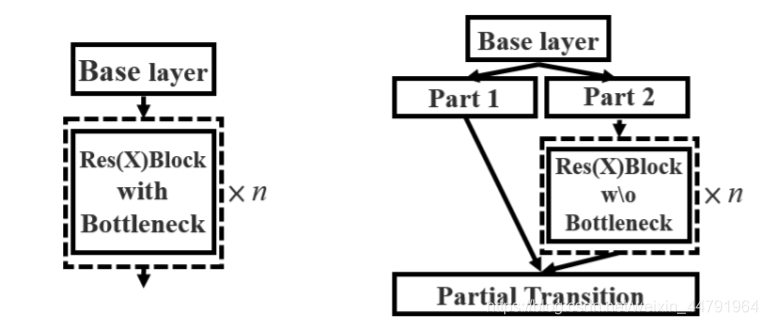
CSPnet结构并不算复杂,就是将原来的残差块的堆叠进行了一个拆分,拆成左右两部分:
主干部分继续进行原来的残差块的堆叠;
另一部分则像一个残差边一样,经过少量处理直接连接到最后。
因此可以认为CSP中存在一个大的残差边。
2、进行通道的分割
在CSPnet的主干部分,CSPdarknet53_tiny会对一次3x3卷积后的特征层进行通道的划分,分成两部分,取第二部分。
在tensorflow中使用tf.split进行划分。
#---------------------------------------------------#
# CSPdarknet的结构块
# 存在一个大残差边
# 这个大残差边绕过了很多的残差结构
#---------------------------------------------------#
def resblock_body(x, num_filters):
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (3,3))(x)
route = x
x = Lambda(route_group,arguments={'groups':2, 'group_id':1})(x)
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(int(num_filters/2), (3,3))(x)
route_1 = x
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(int(num_filters/2), (3,3))(x)
x = Concatenate()([x, route_1])
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (1,1))(x)
feat = x
x = Concatenate()([route, x])
x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=[2,2],)(x)
# 最后对通道数进行整合
return x, feat
利用主干特征提取网络,我们可以获得两个shape的有效特征层,即CSPdarknet53_tiny最后两个shape的有效特征层,传入加强特征提取网络当中进行FPN的构建。
全部实现代码为:
from functools import wraps
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.initializers import RandomNormal
from tensorflow.keras.layers import (BatchNormalization, Concatenate,
Conv2D, Lambda, LeakyReLU,
MaxPooling2D, ZeroPadding2D)
from tensorflow.keras.regularizers import l2
from utils.utils import compose
def route_group(input_layer, groups, group_id):
# 对通道数进行均等分割,我们取第二部分
convs = tf.split(input_layer, num_or_size_splits=groups, axis=-1)
return convs[group_id]
#------------------------------------------------------#
# 单次卷积DarknetConv2D
# 如果步长为2则自己设定padding方式。
#------------------------------------------------------#
@wraps(Conv2D)
def DarknetConv2D(*args, **kwargs):
darknet_conv_kwargs = {'kernel_initializer' : RandomNormal(stddev=0.02), 'kernel_regularizer': l2(5e-4)}
darknet_conv_kwargs['padding'] = 'valid' if kwargs.get('strides')==(2,2) else 'same'
darknet_conv_kwargs.update(kwargs)
return Conv2D(*args, **darknet_conv_kwargs)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 卷积块
# DarknetConv2D + BatchNormalization + LeakyReLU
#---------------------------------------------------#
def DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(*args, **kwargs):
no_bias_kwargs = {'use_bias': False}
no_bias_kwargs.update(kwargs)
return compose(
DarknetConv2D(*args, **no_bias_kwargs),
BatchNormalization(),
LeakyReLU(alpha=0.1))
'''
input
|
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky
-----------------------
| |
route_group route
| |
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky |
| |
------------------- |
| | |
route_1 DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky |
| | |
-------------Concatenate |
| |
----DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky |
| | |
feat Concatenate-----------------
|
MaxPooling2D
'''
#---------------------------------------------------#
# CSPdarknet_tiny的结构块
# 存在一个大残差边
# 这个大残差边绕过了很多的残差结构
#---------------------------------------------------#
def resblock_body(x, num_filters):
# 利用一个3x3卷积进行特征整合
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (3,3))(x)
# 引出一个大的残差边route
route = x
# 对特征层的通道进行分割,取第二部分作为主干部分。
x = Lambda(route_group,arguments={'groups':2, 'group_id':1})(x)
# 对主干部分进行3x3卷积
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(int(num_filters/2), (3,3))(x)
# 引出一个小的残差边route_1
route_1 = x
# 对第主干部分进行3x3卷积
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(int(num_filters/2), (3,3))(x)
# 主干部分与残差部分进行相接
x = Concatenate()([x, route_1])
# 对相接后的结果进行1x1卷积
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (1,1))(x)
feat = x
x = Concatenate()([route, x])
# 利用最大池化进行高和宽的压缩
x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=[2,2],)(x)
return x, feat
#---------------------------------------------------#
# CSPdarknet_tiny的主体部分
#---------------------------------------------------#
def darknet_body(x):
# 首先利用两次步长为2x2的3x3卷积进行高和宽的压缩
# 416,416,3 -> 208,208,32 -> 104,104,64
x = ZeroPadding2D(((1,0),(1,0)))(x)
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(32, (3,3), strides=(2,2))(x)
x = ZeroPadding2D(((1,0),(1,0)))(x)
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(64, (3,3), strides=(2,2))(x)
# 104,104,64 -> 52,52,128
x, _ = resblock_body(x,num_filters = 64)
# 52,52,128 -> 26,26,256
x, _ = resblock_body(x,num_filters = 128)
# 26,26,256 -> x为13,13,512
# -> feat1为26,26,256
x, feat1 = resblock_body(x,num_filters = 256)
# 13,13,512 -> 13,13,512
x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(512, (3,3))(x)
feat2 = x
return feat1, feat2
2、特征金字塔
当输入是416x416时,特征结构如下:

当输入是608x608时,特征结构如下:

YoloV4-Tiny中使用了FPN的结构,主要是对第一步获得的两个有效特征层进行特征融合。
FPN会将最后一个shape的有效特征层卷积后进行上采样,然后与上一个shape的有效特征层进行堆叠并卷积。
实现代码如下:
#--------------------------------------------------#
# 单次卷积
#--------------------------------------------------#
@wraps(Conv2D)
def DarknetConv2D(*args, **kwargs):
darknet_conv_kwargs = {'kernel_regularizer': l2(5e-4)}
darknet_conv_kwargs = {}
darknet_conv_kwargs['padding'] = 'valid' if kwargs.get('strides')==(2,2) else 'same'
darknet_conv_kwargs.update(kwargs)
return Conv2D(*args, **darknet_conv_kwargs)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 卷积块
# DarknetConv2D + BatchNormalization + LeakyReLU
#---------------------------------------------------#
def DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(*args, **kwargs):
no_bias_kwargs = {'use_bias': False}
no_bias_kwargs.update(kwargs)
return compose(
DarknetConv2D(*args, **no_bias_kwargs),
BatchNormalization(),
LeakyReLU(alpha=0.1))
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 特征层->最后的输出
#---------------------------------------------------#
def yolo_body(inputs, num_anchors, num_classes):
# 生成darknet53的主干模型
feat1,feat2 = darknet_body(inputs)
# 第一个特征层
# y1=(batch_size,13,13,3,85)
P5 = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(256, (1,1))(feat2)
P5_output = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(512, (3,3))(P5)
P5_output = DarknetConv2D(num_anchors*(num_classes+5), (1,1))(P5_output)
P5_upsample = compose(DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(128, (1,1)), UpSampling2D(2))(P5)
P4 = Concatenate()([feat1, P5_upsample])
P4_output = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(256, (3,3))(P4)
P4_output = DarknetConv2D(num_anchors*(num_classes+5), (1,1))(P4_output)
return Model(inputs, [P5_output, P4_output])
3、YoloHead利用获得到的特征进行预测
当输入是416x416时,特征结构如下:

当输入是608x608时,特征结构如下:

1、在特征利用部分,YoloV4-Tiny提取多特征层进行目标检测,一共提取两个特征层,两个特征层的shape分别为(26,26,128)、(13,13,512)。
2、输出层的shape分别为(13,13,75),(26,26,75),最后一个维度为75是因为该图是基于voc数据集的,它的类为20种,YoloV4-Tiny只有针对每一个特征层存在3个先验框,所以最后维度为3x25;
如果使用的是coco训练集,类则为80种,最后的维度应该为255 = 3x85,两个特征层的shape为(13,13,255),(26,26,255)
实现代码如下:
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 特征层->最后的输出
#---------------------------------------------------#
def yolo_body(inputs, num_anchors, num_classes):
# 生成darknet53的主干模型
feat1,feat2 = darknet_body(inputs)
# 第一个特征层
# y1=(batch_size,13,13,3,85)
P5 = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(256, (1,1))(feat2)
P5_output = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(512, (3,3))(P5)
P5_output = DarknetConv2D(num_anchors*(num_classes+5), (1,1))(P5_output)
P5_upsample = compose(DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(128, (1,1)), UpSampling2D(2))(P5)
P4 = Concatenate()([feat1, P5_upsample])
P4_output = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(256, (3,3))(P4)
P4_output = DarknetConv2D(num_anchors*(num_classes+5), (1,1))(P4_output)
return Model(inputs, [P5_output, P4_output])
4、预测结果的解码
由第三步我们可以获得两个特征层的预测结果,shape分别为(N,13,13,255),(N,26,26,255)的数据,对应每个图分为13x13、26x26的网格上3个预测框的位置。
但是这个预测结果并不对应着最终的预测框在图片上的位置,还需要解码才可以完成。
此处要讲一下yolo的预测原理,yolo的特征层分别将整幅图分为13x13、26x26的网格,每个网络点负责一个区域的检测。
我们知道特征层的预测结果对应着三个预测框的位置,我们先将其reshape一下,其结果为(N,13,13,3,85),(N,26,26,3,85)。
最后一个维度中的85包含了4+1+80,分别代表x_offset、y_offset、h和w、置信度、分类结果。
yolo的解码过程就是将每个网格点加上它对应的x_offset和y_offset,加完后的结果就是预测框的中心,然后再利用 先验框和h、w结合 计算出预测框的长和宽。这样就能得到整个预测框的位置了。

当然得到最终的预测结构后还要进行得分排序与非极大抑制筛选
这一部分基本上是所有目标检测通用的部分。不过该项目的处理方式与其它项目不同。其对于每一个类进行判别。
1、取出每一类得分大于self.obj_threshold的框和得分。
2、利用框的位置和得分进行非极大抑制。
实现代码如下,当调用yolo_eval时,就会对每个特征层进行解码:
import tensorflow as tf
from keras import backend as K
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 对box进行调整,使其符合真实图片的样子
#---------------------------------------------------#
def yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image):
#-----------------------------------------------------------------#
# 把y轴放前面是因为方便预测框和图像的宽高进行相乘
#-----------------------------------------------------------------#
box_yx = box_xy[..., ::-1]
box_hw = box_wh[..., ::-1]
input_shape = K.cast(input_shape, K.dtype(box_yx))
image_shape = K.cast(image_shape, K.dtype(box_yx))
if letterbox_image:
#-----------------------------------------------------------------#
# 这里求出来的offset是图像有效区域相对于图像左上角的偏移情况
# new_shape指的是宽高缩放情况
#-----------------------------------------------------------------#
new_shape = K.round(image_shape * K.min(input_shape/image_shape))
offset = (input_shape - new_shape)/2./input_shape
scale = input_shape/new_shape
box_yx = (box_yx - offset) * scale
box_hw *= scale
box_mins = box_yx - (box_hw / 2.)
box_maxes = box_yx + (box_hw / 2.)
boxes = K.concatenate([box_mins[..., 0:1], box_mins[..., 1:2], box_maxes[..., 0:1], box_maxes[..., 1:2]])
boxes *= K.concatenate([image_shape, image_shape])
return boxes
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测值的每个特征层调成真实值
#---------------------------------------------------#
def get_anchors_and_decode(feats, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, calc_loss=False):
num_anchors = len(anchors)
#------------------------------------------#
# grid_shape指的是特征层的高和宽
#------------------------------------------#
grid_shape = K.shape(feats)[1:3]
#--------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 获得各个特征点的坐标信息。生成的shape为(13, 13, num_anchors, 2)
#--------------------------------------------------------------------#
grid_x = K.tile(K.reshape(K.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[1]), [1, -1, 1, 1]), [grid_shape[0], 1, num_anchors, 1])
grid_y = K.tile(K.reshape(K.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[0]), [-1, 1, 1, 1]), [1, grid_shape[1], num_anchors, 1])
grid = K.cast(K.concatenate([grid_x, grid_y]), K.dtype(feats))
#---------------------------------------------------------------#
# 将先验框进行拓展,生成的shape为(13, 13, num_anchors, 2)
#---------------------------------------------------------------#
anchors_tensor = K.reshape(K.constant(anchors), [1, 1, num_anchors, 2])
anchors_tensor = K.tile(anchors_tensor, [grid_shape[0], grid_shape[1], 1, 1])
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测结果调整成(batch_size,13,13,3,85)
# 85可拆分成4 + 1 + 80
# 4代表的是中心宽高的调整参数
# 1代表的是框的置信度
# 80代表的是种类的置信度
#---------------------------------------------------#
feats = K.reshape(feats, [-1, grid_shape[0], grid_shape[1], num_anchors, num_classes + 5])
#------------------------------------------#
# 对先验框进行解码,并进行归一化
#------------------------------------------#
box_xy = (K.sigmoid(feats[..., :2]) + grid) / K.cast(grid_shape[::-1], K.dtype(feats))
box_wh = K.exp(feats[..., 2:4]) * anchors_tensor / K.cast(input_shape[::-1], K.dtype(feats))
#------------------------------------------#
# 获得预测框的置信度
#------------------------------------------#
box_confidence = K.sigmoid(feats[..., 4:5])
box_class_probs = K.sigmoid(feats[..., 5:])
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 在计算loss的时候返回grid, feats, box_xy, box_wh
# 在预测的时候返回box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
if calc_loss == True:
return grid, feats, box_xy, box_wh
return box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 图片预测
#---------------------------------------------------#
def DecodeBox(outputs,
anchors,
num_classes,
image_shape,
input_shape,
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 13x13的特征层对应的anchor是[81,82],[135,169],[344,319]
# 26x26的特征层对应的anchor是[10,14],[23,27],[37,58]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
anchor_mask = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],
max_boxes = 100,
confidence = 0.5,
nms_iou = 0.3,
letterbox_image = True):
box_xy = []
box_wh = []
box_confidence = []
box_class_probs = []
for i in range(len(outputs)):
sub_box_xy, sub_box_wh, sub_box_confidence, sub_box_class_probs = \
get_anchors_and_decode(outputs[i], anchors[anchor_mask[i]], num_classes, input_shape)
box_xy.append(K.reshape(sub_box_xy, [-1, 2]))
box_wh.append(K.reshape(sub_box_wh, [-1, 2]))
box_confidence.append(K.reshape(sub_box_confidence, [-1, 1]))
box_class_probs.append(K.reshape(sub_box_class_probs, [-1, num_classes]))
box_xy = K.concatenate(box_xy, axis = 0)
box_wh = K.concatenate(box_wh, axis = 0)
box_confidence = K.concatenate(box_confidence, axis = 0)
box_class_probs = K.concatenate(box_class_probs, axis = 0)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 在图像传入网络预测前会进行letterbox_image给图像周围添加灰条,因此生成的box_xy, box_wh是相对于有灰条的图像的
# 我们需要对其进行修改,去除灰条的部分。 将box_xy、和box_wh调节成y_min,y_max,xmin,xmax
# 如果没有使用letterbox_image也需要将归一化后的box_xy, box_wh调整成相对于原图大小的
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
boxes = yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image)
box_scores = box_confidence * box_class_probs
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 判断得分是否大于score_threshold
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
mask = box_scores >= confidence
max_boxes_tensor = K.constant(max_boxes, dtype='int32')
boxes_out = []
scores_out = []
classes_out = []
for c in range(num_classes):
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 取出所有box_scores >= score_threshold的框,和成绩
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
class_boxes = tf.boolean_mask(boxes, mask[:, c])
class_box_scores = tf.boolean_mask(box_scores[:, c], mask[:, c])
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 非极大抑制
# 保留一定区域内得分最大的框
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
nms_index = tf.image.non_max_suppression(class_boxes, class_box_scores, max_boxes_tensor, iou_threshold=nms_iou)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 获取非极大抑制后的结果
# 下列三个分别是:框的位置,得分与种类
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
class_boxes = K.gather(class_boxes, nms_index)
class_box_scores = K.gather(class_box_scores, nms_index)
classes = K.ones_like(class_box_scores, 'int32') * c
boxes_out.append(class_boxes)
scores_out.append(class_box_scores)
classes_out.append(classes)
boxes_out = K.concatenate(boxes_out, axis=0)
scores_out = K.concatenate(scores_out, axis=0)
classes_out = K.concatenate(classes_out, axis=0)
return boxes_out, scores_out, classes_out
5、在原图上进行绘制
通过第四步,我们可以获得预测框在原图上的位置,而且这些预测框都是经过筛选的。这些筛选后的框可以直接绘制在图片上,就可以获得结果了。
YoloV4-Tiny的训练
1、YOLOV4的改进训练技巧
a)、Mosaic数据增强
Yolov4的mosaic数据增强参考了CutMix数据增强方式,理论上具有一定的相似性!
CutMix数据增强方式利用两张图片进行拼接。

但是mosaic利用了四张图片,根据论文所说其拥有一个巨大的优点是丰富检测物体的背景!且在BN计算的时候一下子会计算四张图片的数据!
就像下图这样:

实现思路如下:
1、每次读取四张图片。




2、分别对四张图片进行翻转、缩放、色域变化等,并且按照四个方向位置摆好。




3、进行图片的组合和框的组合

def merge_bboxes(self, bboxes, cutx, cuty):
merge_bbox = []
for i in range(len(bboxes)):
for box in bboxes[i]:
tmp_box = []
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]
if i == 0:
if y1 > cuty or x1 > cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y2 = cuty
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x2 = cutx
if i == 1:
if y2 < cuty or x1 > cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y1 = cuty
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x2 = cutx
if i == 2:
if y2 < cuty or x2 < cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y1 = cuty
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x1 = cutx
if i == 3:
if y1 > cuty or x2 < cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y2 = cuty
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x1 = cutx
tmp_box.append(x1)
tmp_box.append(y1)
tmp_box.append(x2)
tmp_box.append(y2)
tmp_box.append(box[-1])
merge_bbox.append(tmp_box)
return merge_bbox
def get_random_data_with_Mosaic(self, annotation_line, input_shape, max_boxes=100, hue=.1, sat=1.5, val=1.5):
h, w = input_shape
min_offset_x = self.rand(0.25, 0.75)
min_offset_y = self.rand(0.25, 0.75)
nws = [ int(w * self.rand(0.4, 1)), int(w * self.rand(0.4, 1)), int(w * self.rand(0.4, 1)), int(w * self.rand(0.4, 1))]
nhs = [ int(h * self.rand(0.4, 1)), int(h * self.rand(0.4, 1)), int(h * self.rand(0.4, 1)), int(h * self.rand(0.4, 1))]
place_x = [int(w*min_offset_x) - nws[0], int(w*min_offset_x) - nws[1], int(w*min_offset_x), int(w*min_offset_x)]
place_y = [int(h*min_offset_y) - nhs[0], int(h*min_offset_y), int(h*min_offset_y), int(h*min_offset_y) - nhs[3]]
image_datas = []
box_datas = []
index = 0
for line in annotation_line:
# 每一行进行分割
line_content = line.split()
# 打开图片
image = Image.open(line_content[0])
image = cvtColor(image)
# 图片的大小
iw, ih = image.size
# 保存框的位置
box = np.array([np.array(list(map(int,box.split(',')))) for box in line_content[1:]])
# 是否翻转图片
flip = self.rand()<.5
if flip and len(box)>0:
image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
box[:, [0,2]] = iw - box[:, [2,0]]
nw = nws[index]
nh = nhs[index]
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
# 将图片进行放置,分别对应四张分割图片的位置
dx = place_x[index]
dy = place_y[index]
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
image_data = np.array(new_image)
index = index + 1
box_data = []
# 对box进行重新处理
if len(box)>0:
np.random.shuffle(box)
box[:, [0,2]] = box[:, [0,2]]*nw/iw + dx
box[:, [1,3]] = box[:, [1,3]]*nh/ih + dy
box[:, 0:2][box[:, 0:2]<0] = 0
box[:, 2][box[:, 2]>w] = w
box[:, 3][box[:, 3]>h] = h
box_w = box[:, 2] - box[:, 0]
box_h = box[:, 3] - box[:, 1]
box = box[np.logical_and(box_w>1, box_h>1)]
box_data = np.zeros((len(box),5))
box_data[:len(box)] = box
image_datas.append(image_data)
box_datas.append(box_data)
# 将图片分割,放在一起
cutx = int(w * min_offset_x)
cuty = int(h * min_offset_y)
new_image = np.zeros([h, w, 3])
new_image[:cuty, :cutx, :] = image_datas[0][:cuty, :cutx, :]
new_image[cuty:, :cutx, :] = image_datas[1][cuty:, :cutx, :]
new_image[cuty:, cutx:, :] = image_datas[2][cuty:, cutx:, :]
new_image[:cuty, cutx:, :] = image_datas[3][:cuty, cutx:, :]
# 进行色域变换
hue = self.rand(-hue, hue)
sat = self.rand(1, sat) if self.rand()<.5 else 1/self.rand(1, sat)
val = self.rand(1, val) if self.rand()<.5 else 1/self.rand(1, val)
x = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(new_image/255,np.float32), cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
x[..., 0] += hue*360
x[..., 0][x[..., 0]>1] -= 1
x[..., 0][x[..., 0]<0] += 1
x[..., 1] *= sat
x[..., 2] *= val
x[x[:, :, 0]>360, 0] = 360
x[:, :, 1:][x[:, :, 1:]>1] = 1
x[x<0] = 0
new_image = cv2.cvtColor(x, cv2.COLOR_HSV2RGB)*255
# 对框进行进一步的处理
new_boxes = self.merge_bboxes(box_datas, cutx, cuty)
# 将box进行调整
box_data = np.zeros((max_boxes, 5))
if len(new_boxes)>0:
if len(new_boxes)>max_boxes: new_boxes = new_boxes[:max_boxes]
box_data[:len(new_boxes)] = new_boxes
return new_image, box_data
b)、Label Smoothing平滑
标签平滑的思想很简单,具体公式如下:
new_onehot_labels = onehot_labels * (1 - label_smoothing) + label_smoothing / num_classes
当label_smoothing的值为0.01得时候,公式变成如下所示:
new_onehot_labels = y * (1 - 0.01) + 0.01 / num_classes
其实Label Smoothing平滑就是将标签进行一个平滑,原始的标签是0、1,在平滑后变成0.005(如果是二分类)、0.995,也就是说对分类准确做了一点惩罚,让模型不可以分类的太准确,太准确容易过拟合。
实现代码如下:
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 平滑标签
#---------------------------------------------------#
def _smooth_labels(y_true, label_smoothing):
num_classes = K.shape(y_true)[-1],
label_smoothing = K.constant(label_smoothing, dtype=K.floatx())
return y_true * (1.0 - label_smoothing) + label_smoothing / num_classes
c)、CIOU
IoU是比值的概念,对目标物体的scale是不敏感的。然而常用的BBox的回归损失优化和IoU优化不是完全等价的,寻常的IoU无法直接优化没有重叠的部分。
于是有人提出直接使用IOU作为回归优化loss,CIOU是其中非常优秀的一种想法。
CIOU将目标与anchor之间的距离,重叠率、尺度以及惩罚项都考虑进去,使得目标框回归变得更加稳定,不会像IoU和GIoU一样出现训练过程中发散等问题。而惩罚因子把预测框长宽比拟合目标框的长宽比考虑进去。
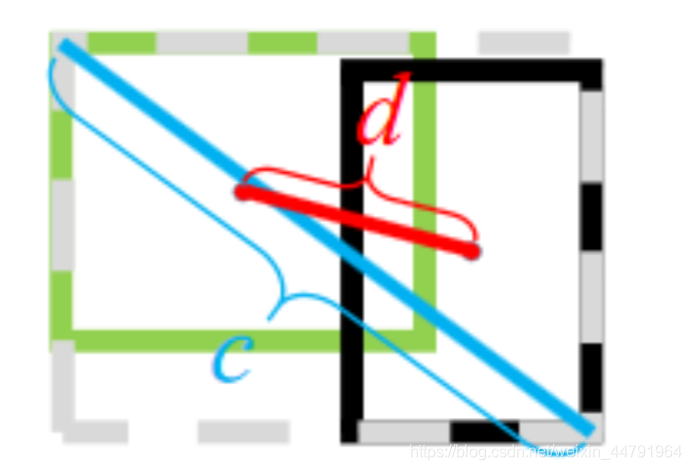
CIOU公式如下
C
I
O
U
=
I
O
U
−
ρ
2
(
b
,
b
g
t
)
c
2
−
α
v
CIOU = IOU - \frac{\rho^2(b,b^{gt})}{c^2} - \alpha v
CIOU=IOU−c2ρ2(b,bgt)−αv
其中,
ρ
2
(
b
,
b
g
t
)
\rho^2(b,b^{gt})
ρ2(b,bgt)分别代表了预测框和真实框的中心点的欧式距离。 c代表的是能够同时包含预测框和真实框的最小闭包区域的对角线距离。
而
α
\alpha
α和
v
v
v的公式如下
α
=
v
1
−
I
O
U
+
v
\alpha = \frac{v}{1-IOU+v}
α=1−IOU+vv
v
=
4
π
2
(
a
r
c
t
a
n
w
g
t
h
g
t
−
a
r
c
t
a
n
w
h
)
2
v = \frac{4}{\pi ^2}(arctan\frac{w^{gt}}{h^{gt}}-arctan\frac{w}{h})^2
v=π24(arctanhgtwgt−arctanhw)2
把1-CIOU就可以得到相应的LOSS了。
L
O
S
S
C
I
O
U
=
1
−
I
O
U
+
ρ
2
(
b
,
b
g
t
)
c
2
+
α
v
LOSS_{CIOU} = 1 - IOU + \frac{\rho^2(b,b^{gt})}{c^2} + \alpha v
LOSSCIOU=1−IOU+c2ρ2(b,bgt)+αv
def box_ciou(b1, b2):
"""
输入为:
----------
b1: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
b2: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
返回为:
-------
ciou: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 1)
"""
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 求出预测框左上角右下角
# b1_mins (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 2)
# b1_maxes (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 2)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
b1_xy = b1[..., :2]
b1_wh = b1[..., 2:4]
b1_wh_half = b1_wh/2.
b1_mins = b1_xy - b1_wh_half
b1_maxes = b1_xy + b1_wh_half
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 求出真实框左上角右下角
# b2_mins (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 2)
# b2_maxes (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 2)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
b2_xy = b2[..., :2]
b2_wh = b2[..., 2:4]
b2_wh_half = b2_wh/2.
b2_mins = b2_xy - b2_wh_half
b2_maxes = b2_xy + b2_wh_half
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 求真实框和预测框所有的iou
# iou (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
intersect_mins = K.maximum(b1_mins, b2_mins)
intersect_maxes = K.minimum(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
intersect_wh = K.maximum(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, 0.)
intersect_area = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1]
b1_area = b1_wh[..., 0] * b1_wh[..., 1]
b2_area = b2_wh[..., 0] * b2_wh[..., 1]
union_area = b1_area + b2_area - intersect_area
iou = intersect_area / K.maximum(union_area, K.epsilon())
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算中心的差距
# center_distance (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
center_distance = K.sum(K.square(b1_xy - b2_xy), axis=-1)
enclose_mins = K.minimum(b1_mins, b2_mins)
enclose_maxes = K.maximum(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
enclose_wh = K.maximum(enclose_maxes - enclose_mins, 0.0)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算对角线距离
# enclose_diagonal (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
enclose_diagonal = K.sum(K.square(enclose_wh), axis=-1)
ciou = iou - 1.0 * (center_distance) / K.maximum(enclose_diagonal ,K.epsilon())
v = 4 * K.square(tf.math.atan2(b1_wh[..., 0], K.maximum(b1_wh[..., 1], K.epsilon())) - tf.math.atan2(b2_wh[..., 0], K.maximum(b2_wh[..., 1],K.epsilon()))) / (math.pi * math.pi)
alpha = v / K.maximum((1.0 - iou + v), K.epsilon())
ciou = ciou - alpha * v
ciou = K.expand_dims(ciou, -1)
return ciou
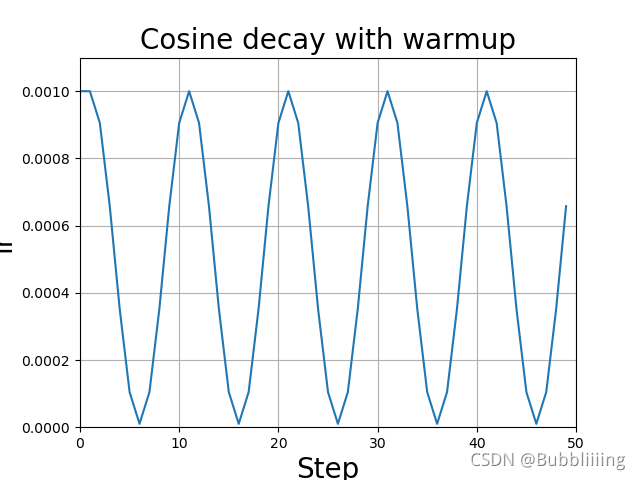
d)、学习率余弦退火衰减
余弦退火衰减法,学习率会先上升再下降,这是退火优化法的思想。(关于什么是退火算法可以百度。)
上升的时候使用线性上升,下降的时候模拟cos函数下降。执行多次。
效果如图所示:
实现方式如下,利用Callback实现,与普通的ReduceLROnPlateau调用方式类似:
class WarmUpCosineDecayScheduler(keras.callbacks.Callback):
def __init__(self, T_max, eta_min=0, verbose=0):
super(WarmUpCosineDecayScheduler, self).__init__()
self.T_max = T_max
self.eta_min = eta_min
self.verbose = verbose
self.init_lr = 0
self.last_epoch = 0
def on_train_begin(self, batch, logs=None):
self.init_lr = K.get_value(self.model.optimizer.lr)
def on_epoch_end(self, batch, logs=None):
learning_rate = self.eta_min + (self.init_lr - self.eta_min) * (1 + math.cos(math.pi * self.last_epoch / self.T_max)) / 2
self.last_epoch += 1
K.set_value(self.model.optimizer.lr, learning_rate)
if self.verbose > 0:
print('Setting learning rate to %s.' % (learning_rate))
2、loss组成
a)、计算loss所需参数
在计算loss的时候,实际上是y_pre和y_true之间的对比:
y_pre就是一幅图像经过网络之后的输出,内部含有两个特征层的内容;其需要解码才能够在图上作画
y_true就是一个真实图像中,它的每个真实框对应的(13,13)、(26,26)网格上的偏移位置、长宽与种类。其仍需要编码才能与y_pred的结构一致
实际上y_pre和y_true内容的shape都是
(batch_size,13,13,3,85)
(batch_size,26,26,3,85)
b)、y_pre是什么
网络最后输出的内容就是两个特征层每个网格点对应的预测框及其种类,即两个特征层分别对应着图片被分为不同size的网格后,每个网格点上三个先验框对应的位置、置信度及其种类。
对于输出的y1、y2、y3而言,[…, : 2]指的是相对于每个网格点的偏移量,[…, 2: 4]指的是宽和高,[…, 4: 5]指的是该框的置信度,[…, 5: ]指的是每个种类的预测概率。
现在的y_pre还是没有解码的,解码了之后才是真实图像上的情况。
c)、y_true是什么。
y_true就是一个真实图像中,它的每个真实框对应的(13,13)、(26,26)网格上的偏移位置、长宽与种类。其仍需要编码才能与y_pred的结构一致
在yolo4中,其使用了一个专门的函数用于处理读取进来的图片的框的真实情况。
def preprocess_true_boxes(true_boxes, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
其输入为:
true_boxes:shape为(m, T, 5)代表m张图T个框的x_min、y_min、x_max、y_max、class_id。
input_shape:输入的形状,此处为608、608
anchors:代表9个先验框的大小
num_classes:种类的数量。
其实对真实框的处理是将真实框转化成图片中相对网格的xyhw,步骤如下:
1、取框的真实值,获取其框的中心及其宽高,除去input_shape变成比例的模式。
2、建立全为0的y_true,y_true是一个列表,包含两个特征层,shape分别为(batch_size,13,13,3,85)、(batch_size,26,26,3,85)
3、对每一张图片处理,将每一张图片中的真实框的wh和先验框的wh对比,计算IOU值,选取其中IOU最高的一个,得到其所属特征层及其网格点的位置,在对应的y_true中将内容进行保存。
for t, n in enumerate(best_anchor):
for l in range(num_layers):
if n in anchor_mask[l]:
# 计算该目标在第l个特征层所处网格的位置
i = np.floor(true_boxes[b,t,0]*grid_shapes[l][1]).astype('int32')
j = np.floor(true_boxes[b,t,1]*grid_shapes[l][0]).astype('int32')
# 找到best_anchor索引的索引
k = anchor_mask[l].index(n)
c = true_boxes[b,t, 4].astype('int32')
# 保存到y_true中
y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 0:4] = true_boxes[b,t, 0:4]
y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 4] = 1
y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 5+c] = 1
对于最后输出的y_true而言,只有每个图里每个框最对应的位置有数据,其它的地方都为0。
preprocess_true_boxes全部的代码如下:
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 读入xml文件,并输出y_true
#---------------------------------------------------#
def preprocess_true_boxes(self, true_boxes, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
assert (true_boxes[..., 4]<num_classes).all(), 'class id must be less than num_classes'
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 获得框的坐标和图片的大小
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
true_boxes = np.array(true_boxes, dtype='float32')
input_shape = np.array(input_shape, dtype='int32')
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 一共有三个特征层数
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
num_layers = len(self.anchors_mask)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# m为图片数量,grid_shapes为网格的shape
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
m = true_boxes.shape[0]
grid_shapes = [input_shape // {0:32, 1:16, 2:8}[l] for l in range(num_layers)]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# y_true的格式为(m,13,13,3,85)(m,26,26,3,85)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
y_true = [np.zeros((m, grid_shapes[l][0], grid_shapes[l][1], len(self.anchors_mask[l]), 5 + num_classes),
dtype='float32') for l in range(num_layers)]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 通过计算获得真实框的中心和宽高
# 中心点(m,n,2) 宽高(m,n,2)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
boxes_xy = (true_boxes[..., 0:2] + true_boxes[..., 2:4]) // 2
boxes_wh = true_boxes[..., 2:4] - true_boxes[..., 0:2]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 将真实框归一化到小数形式
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
true_boxes[..., 0:2] = boxes_xy / input_shape[::-1]
true_boxes[..., 2:4] = boxes_wh / input_shape[::-1]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# [9,2] -> [1,9,2]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
anchors = np.expand_dims(anchors, 0)
anchor_maxes = anchors / 2.
anchor_mins = -anchor_maxes
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 长宽要大于0才有效
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
valid_mask = boxes_wh[..., 0]>0
for b in range(m):
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 对每一张图进行处理
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
wh = boxes_wh[b, valid_mask[b]]
if len(wh) == 0: continue
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# [n,2] -> [n,1,2]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
wh = np.expand_dims(wh, -2)
box_maxes = wh / 2.
box_mins = - box_maxes
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算所有真实框和先验框的交并比
# intersect_area [n,9]
# box_area [n,1]
# anchor_area [1,9]
# iou [n,9]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
intersect_mins = np.maximum(box_mins, anchor_mins)
intersect_maxes = np.minimum(box_maxes, anchor_maxes)
intersect_wh = np.maximum(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, 0.)
intersect_area = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1]
box_area = wh[..., 0] * wh[..., 1]
anchor_area = anchors[..., 0] * anchors[..., 1]
iou = intersect_area / (box_area + anchor_area - intersect_area)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 维度是[n,] 感谢 消尽不死鸟 的提醒
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
best_anchor = np.argmax(iou, axis=-1)
for t, n in enumerate(best_anchor):
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 找到每个真实框所属的特征层
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
for l in range(num_layers):
if n in self.anchors_mask[l]:
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# floor用于向下取整,找到真实框所属的特征层对应的x、y轴坐标
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
i = np.floor(true_boxes[b,t,0] * grid_shapes[l][1]).astype('int32')
j = np.floor(true_boxes[b,t,1] * grid_shapes[l][0]).astype('int32')
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# k指的的当前这个特征点的第k个先验框
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
k = self.anchors_mask[l].index(n)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# c指的是当前这个真实框的种类
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
c = true_boxes[b, t, 4].astype('int32')
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# y_true的shape为(m,13,13,3,85)(m,26,26,3,85)
# 最后的85可以拆分成4+1+80,4代表的是框的中心与宽高、
# 1代表的是置信度、80代表的是种类
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 0:4] = true_boxes[b, t, 0:4]
y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 4] = 1
y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 5+c] = 1
return y_true
d)、loss的计算过程
在得到了y_pre和y_true后怎么对比呢?不是简单的减一下!
loss值需要对两个特征层进行处理,这里以最小的特征层为例。
1、利用y_true取出该特征层中真实存在目标的点的位置(m,13,13,3,1)及其对应的种类(m,13,13,3,80)。
2、将yolo_outputs的预测值输出进行处理,得到reshape后的预测值y_pre,shape为(m,13,13,3,85)。还有解码后的xy,wh。
3、对于每一幅图,计算其中所有真实框与预测框的IOU,如果某些预测框和真实框的重合程度大于0.5,则忽略。
4、计算ciou作为回归的loss,这里只计算正样本的回归loss。
5、计算置信度的loss,其有两部分构成,第一部分是实际上存在目标的,预测结果中置信度的值与1对比;第二部分是实际上不存在目标的,预测结果中置信度的值与0对比。
6、计算预测种类的loss,其计算的是实际上存在目标的,预测类与真实类的差距。
其实际上计算的总的loss是三个loss的和,这三个loss分别是:
- 实际存在的框,CIOU LOSS。
- 实际存在的框,预测结果中置信度的值与1对比;实际不存在的框,预测结果中置信度的值与0对比,该部分要去除被忽略的不包含目标的框。
- 实际存在的框,种类预测结果与实际结果的对比。
其实际代码如下,使用yolo_loss就可以获得loss值:
import math
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
from utils.utils_bbox import get_anchors_and_decode
def box_ciou(b1, b2):
"""
输入为:
----------
b1: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
b2: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
返回为:
-------
ciou: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 1)
"""
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 求出预测框左上角右下角
# b1_mins (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 2)
# b1_maxes (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 2)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
b1_xy = b1[..., :2]
b1_wh = b1[..., 2:4]
b1_wh_half = b1_wh/2.
b1_mins = b1_xy - b1_wh_half
b1_maxes = b1_xy + b1_wh_half
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 求出真实框左上角右下角
# b2_mins (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 2)
# b2_maxes (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 2)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
b2_xy = b2[..., :2]
b2_wh = b2[..., 2:4]
b2_wh_half = b2_wh/2.
b2_mins = b2_xy - b2_wh_half
b2_maxes = b2_xy + b2_wh_half
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 求真实框和预测框所有的iou
# iou (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
intersect_mins = K.maximum(b1_mins, b2_mins)
intersect_maxes = K.minimum(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
intersect_wh = K.maximum(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, 0.)
intersect_area = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1]
b1_area = b1_wh[..., 0] * b1_wh[..., 1]
b2_area = b2_wh[..., 0] * b2_wh[..., 1]
union_area = b1_area + b2_area - intersect_area
iou = intersect_area / K.maximum(union_area, K.epsilon())
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算中心的差距
# center_distance (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
center_distance = K.sum(K.square(b1_xy - b2_xy), axis=-1)
enclose_mins = K.minimum(b1_mins, b2_mins)
enclose_maxes = K.maximum(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
enclose_wh = K.maximum(enclose_maxes - enclose_mins, 0.0)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算对角线距离
# enclose_diagonal (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
enclose_diagonal = K.sum(K.square(enclose_wh), axis=-1)
ciou = iou - 1.0 * (center_distance) / K.maximum(enclose_diagonal ,K.epsilon())
v = 4 * K.square(tf.math.atan2(b1_wh[..., 0], K.maximum(b1_wh[..., 1], K.epsilon())) - tf.math.atan2(b2_wh[..., 0], K.maximum(b2_wh[..., 1],K.epsilon()))) / (math.pi * math.pi)
alpha = v / K.maximum((1.0 - iou + v), K.epsilon())
ciou = ciou - alpha * v
ciou = K.expand_dims(ciou, -1)
return ciou
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 平滑标签
#---------------------------------------------------#
def _smooth_labels(y_true, label_smoothing):
num_classes = tf.cast(K.shape(y_true)[-1], dtype=K.floatx())
label_smoothing = K.constant(label_smoothing, dtype=K.floatx())
return y_true * (1.0 - label_smoothing) + label_smoothing / num_classes
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 用于计算每个预测框与真实框的iou
#---------------------------------------------------#
def box_iou(b1, b2):
#---------------------------------------------------#
# num_anchor,1,4
# 计算左上角的坐标和右下角的坐标
#---------------------------------------------------#
b1 = K.expand_dims(b1, -2)
b1_xy = b1[..., :2]
b1_wh = b1[..., 2:4]
b1_wh_half = b1_wh/2.
b1_mins = b1_xy - b1_wh_half
b1_maxes = b1_xy + b1_wh_half
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 1,n,4
# 计算左上角和右下角的坐标
#---------------------------------------------------#
b2 = K.expand_dims(b2, 0)
b2_xy = b2[..., :2]
b2_wh = b2[..., 2:4]
b2_wh_half = b2_wh/2.
b2_mins = b2_xy - b2_wh_half
b2_maxes = b2_xy + b2_wh_half
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 计算重合面积
#---------------------------------------------------#
intersect_mins = K.maximum(b1_mins, b2_mins)
intersect_maxes = K.minimum(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
intersect_wh = K.maximum(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, 0.)
intersect_area = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1]
b1_area = b1_wh[..., 0] * b1_wh[..., 1]
b2_area = b2_wh[..., 0] * b2_wh[..., 1]
iou = intersect_area / (b1_area + b2_area - intersect_area)
return iou
#---------------------------------------------------#
# loss值计算
#---------------------------------------------------#
def yolo_loss(args, input_shape, anchors, anchors_mask, num_classes, ignore_thresh=.7, label_smoothing=0.1, print_loss=False):
num_layers = len(anchors_mask)
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测结果和实际ground truth分开,args是[*model_body.output, *y_true]
# y_true是一个列表,包含三个特征层,shape分别为:
# (m,13,13,3,85)
# (m,26,26,3,85)
# yolo_outputs是一个列表,包含三个特征层,shape分别为:
# (m,13,13,3,85)
# (m,26,26,3,85)
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
y_true = args[num_layers:]
yolo_outputs = args[:num_layers]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 得到input_shpae为416,416
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
input_shape = K.cast(input_shape, K.dtype(y_true[0]))
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 取出每一张图片
# m的值就是batch_size
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
m = K.shape(yolo_outputs[0])[0]
loss = 0
num_pos = 0
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# y_true是一个列表,包含三个特征层,shape分别为(m,13,13,3,85),(m,26,26,3,85)。
# yolo_outputs是一个列表,包含三个特征层,shape分别为(m,13,13,3,85),(m,26,26,3,85)。
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
for l in range(num_layers):
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 以第一个特征层(m,13,13,3,85)为例子
# 取出该特征层中存在目标的点的位置。(m,13,13,3,1)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
object_mask = y_true[l][..., 4:5]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 取出其对应的种类(m,13,13,3,80)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
true_class_probs = y_true[l][..., 5:]
if label_smoothing:
true_class_probs = _smooth_labels(true_class_probs, label_smoothing)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 将yolo_outputs的特征层输出进行处理、获得四个返回值
# 其中:
# grid (13,13,1,2) 网格坐标
# raw_pred (m,13,13,3,85) 尚未处理的预测结果
# pred_xy (m,13,13,3,2) 解码后的中心坐标
# pred_wh (m,13,13,3,2) 解码后的宽高坐标
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
grid, raw_pred, pred_xy, pred_wh = get_anchors_and_decode(yolo_outputs[l],
anchors[anchors_mask[l]], num_classes, input_shape, calc_loss=True)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# pred_box是解码后的预测的box的位置
# (m,13,13,3,4)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
pred_box = K.concatenate([pred_xy, pred_wh])
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 找到负样本群组,第一步是创建一个数组,[]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
ignore_mask = tf.TensorArray(K.dtype(y_true[0]), size=1, dynamic_size=True)
object_mask_bool = K.cast(object_mask, 'bool')
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 对每一张图片计算ignore_mask
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
def loop_body(b, ignore_mask):
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 取出n个真实框:n,4
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
true_box = tf.boolean_mask(y_true[l][b,...,0:4], object_mask_bool[b,...,0])
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算预测框与真实框的iou
# pred_box 13,13,3,4 预测框的坐标
# true_box n,4 真实框的坐标
# iou 13,13,3,n 预测框和真实框的iou
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
iou = box_iou(pred_box[b], true_box)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# best_iou 13,13,3 每个特征点与真实框的最大重合程度
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
best_iou = K.max(iou, axis=-1)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 判断预测框和真实框的最大iou小于ignore_thresh
# 则认为该预测框没有与之对应的真实框
# 该操作的目的是:
# 忽略预测结果与真实框非常对应特征点,因为这些框已经比较准了
# 不适合当作负样本,所以忽略掉。
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
ignore_mask = ignore_mask.write(b, K.cast(best_iou<ignore_thresh, K.dtype(true_box)))
return b+1, ignore_mask
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 在这个地方进行一个循环、循环是对每一张图片进行的
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
_, ignore_mask = tf.while_loop(lambda b,*args: b<m, loop_body, [0, ignore_mask])
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# ignore_mask用于提取出作为负样本的特征点
# (m,13,13,3)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
ignore_mask = ignore_mask.stack()
# (m,13,13,3,1)
ignore_mask = K.expand_dims(ignore_mask, -1)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 真实框越大,比重越小,小框的比重更大。
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
box_loss_scale = 2 - y_true[l][...,2:3]*y_true[l][...,3:4]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算Ciou loss
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
raw_true_box = y_true[l][...,0:4]
ciou = box_ciou(pred_box, raw_true_box)
ciou_loss = object_mask * box_loss_scale * (1 - ciou)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 如果该位置本来有框,那么计算1与置信度的交叉熵
# 如果该位置本来没有框,那么计算0与置信度的交叉熵
# 在这其中会忽略一部分样本,这些被忽略的样本满足条件best_iou<ignore_thresh
# 该操作的目的是:
# 忽略预测结果与真实框非常对应特征点,因为这些框已经比较准了
# 不适合当作负样本,所以忽略掉。
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
confidence_loss = object_mask * K.binary_crossentropy(object_mask, raw_pred[...,4:5], from_logits=True)+ \
(1-object_mask) * K.binary_crossentropy(object_mask, raw_pred[...,4:5], from_logits=True) * ignore_mask
class_loss = object_mask * K.binary_crossentropy(true_class_probs, raw_pred[...,5:], from_logits=True)
location_loss = K.sum(ciou_loss)
confidence_loss = K.sum(confidence_loss)
class_loss = K.sum(class_loss)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算正样本数量
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
num_pos += tf.maximum(K.sum(K.cast(object_mask, tf.float32)), 1)
loss += location_loss + confidence_loss + class_loss
# if print_loss:
# loss = tf.Print(loss, [loss, location_loss, confidence_loss, class_loss, K.sum(ignore_mask)], message='loss: ')
loss = loss / num_pos
return loss
训练自己的YoloV4模型
首先前往Github下载对应的仓库,下载完后利用解压软件解压,之后用编程软件打开文件夹。
注意打开的根目录必须正确,否则相对目录不正确的情况下,代码将无法运行。
一定要注意打开后的根目录是文件存放的目录。

一、数据集的准备
本文使用VOC格式进行训练,训练前需要自己制作好数据集,如果没有自己的数据集,可以通过Github连接下载VOC12+07的数据集尝试下。
训练前将标签文件放在VOCdevkit文件夹下的VOC2007文件夹下的Annotation中。
训练前将图片文件放在VOCdevkit文件夹下的VOC2007文件夹下的JPEGImages中。

此时数据集的摆放已经结束。
二、数据集的处理
在完成数据集的摆放之后,我们需要对数据集进行下一步的处理,目的是获得训练用的2007_train.txt以及2007_val.txt,需要用到根目录下的voc_annotation.py。
voc_annotation.py里面有一些参数需要设置。
分别是annotation_mode、classes_path、trainval_percent、train_percent、VOCdevkit_path,第一次训练可以仅修改classes_path
'''
annotation_mode用于指定该文件运行时计算的内容
annotation_mode为0代表整个标签处理过程,包括获得VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets里面的txt以及训练用的2007_train.txt、2007_val.txt
annotation_mode为1代表获得VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets里面的txt
annotation_mode为2代表获得训练用的2007_train.txt、2007_val.txt
'''
annotation_mode = 0
'''
必须要修改,用于生成2007_train.txt、2007_val.txt的目标信息
与训练和预测所用的classes_path一致即可
如果生成的2007_train.txt里面没有目标信息
那么就是因为classes没有设定正确
仅在annotation_mode为0和2的时候有效
'''
classes_path = 'model_data/voc_classes.txt'
'''
trainval_percent用于指定(训练集+验证集)与测试集的比例,默认情况下 (训练集+验证集):测试集 = 9:1
train_percent用于指定(训练集+验证集)中训练集与验证集的比例,默认情况下 训练集:验证集 = 9:1
仅在annotation_mode为0和1的时候有效
'''
trainval_percent = 0.9
train_percent = 0.9
'''
指向VOC数据集所在的文件夹
默认指向根目录下的VOC数据集
'''
VOCdevkit_path = 'VOCdevkit'
classes_path用于指向检测类别所对应的txt,以voc数据集为例,我们用的txt为:

训练自己的数据集时,可以自己建立一个cls_classes.txt,里面写自己所需要区分的类别。
三、开始网络训练
通过voc_annotation.py我们已经生成了2007_train.txt以及2007_val.txt,此时我们可以开始训练了。
训练的参数较多,大家可以在下载库后仔细看注释,其中最重要的部分依然是train.py里的classes_path。
classes_path用于指向检测类别所对应的txt,这个txt和voc_annotation.py里面的txt一样!训练自己的数据集必须要修改!

修改完classes_path后就可以运行train.py开始训练了,在训练多个epoch后,权值会生成在logs文件夹中。
其它参数的作用如下:
#--------------------------------------------------------#
# 训练前一定要修改classes_path,使其对应自己的数据集
#--------------------------------------------------------#
classes_path = 'model_data/voc_classes.txt'
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# anchors_path代表先验框对应的txt文件,一般不修改。
# anchors_mask用于帮助代码找到对应的先验框,一般不修改。
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
anchors_path = 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt'
anchors_mask = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 权值文件请看README,百度网盘下载
# 训练自己的数据集时提示维度不匹配正常,预测的东西都不一样了自然维度不匹配
# 预训练权重对于99%的情况都必须要用,不用的话权值太过随机,特征提取效果不明显
# 网络训练的结果也不会好,数据的预训练权重对不同数据集是通用的,因为特征是通用的
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
model_path = 'model_data/yolo4_weight.h5'
#------------------------------------------------------#
# 输入的shape大小,一定要是32的倍数
#------------------------------------------------------#
input_shape = [416, 416]
#------------------------------------------------------#
# Yolov4的tricks应用
# mosaic 马赛克数据增强 True or False
# 实际测试时mosaic数据增强并不稳定,所以默认为False
# Cosine_scheduler 余弦退火学习率 True or False
# label_smoothing 标签平滑 0.01以下一般 如0.01、0.005
#------------------------------------------------------#
mosaic = False
Cosine_scheduler = False
label_smoothing = 0
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 训练分为两个阶段,分别是冻结阶段和解冻阶段
# 冻结阶段训练参数
# 此时模型的主干被冻结了,特征提取网络不发生改变
# 占用的显存较小,仅对网络进行微调
#----------------------------------------------------#
Init_Epoch = 0
Freeze_Epoch = 50
Freeze_batch_size = 4
Freeze_lr = 1e-3
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 解冻阶段训练参数
# 此时模型的主干不被冻结了,特征提取网络会发生改变
# 占用的显存较大,网络所有的参数都会发生改变
# batch不能为1
#----------------------------------------------------#
UnFreeze_Epoch = 100
Unfreeze_batch_size = 4
Unfreeze_lr = 1e-4
#------------------------------------------------------#
# 是否进行冻结训练,默认先冻结主干训练后解冻训练。
#------------------------------------------------------#
Freeze_Train = True
#------------------------------------------------------#
# 用于设置是否使用多线程读取数据,0代表关闭多线程
# 开启后会加快数据读取速度,但是会占用更多内存
# keras里开启多线程有些时候速度反而慢了许多
# 在IO为瓶颈的时候再开启多线程,即GPU运算速度远大于读取图片的速度。
#------------------------------------------------------#
num_workers = 0
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 获得图片路径和标签
#----------------------------------------------------#
train_annotation_path = '2007_train.txt'
val_annotation_path = '2007_val.txt'
四、训练结果预测
训练结果预测需要用到两个文件,分别是yolo.py和predict.py。
我们首先需要去yolo.py里面修改model_path以及classes_path,这两个参数必须要修改。
model_path指向训练好的权值文件,在logs文件夹里。
classes_path指向检测类别所对应的txt。

完成修改后就可以运行predict.py进行检测了。运行后输入图片路径即可检测。























 4032
4032











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










