概括
KAN网络结构思路来自Kolmogorov-Arnold表示定理。MLP 在节点(“神经元”)上具有固定的激活函数,而 KAN 在边(“权重”)上具有可学习的激活函数。在数据拟合和 PDE 求解中,较小的 KAN 可以比较大的 MLP 获得更好的准确性。
相对MLP,KAN也具备更好的可解释性,适合作为数学和物理研究中的辅助模型,帮助发现和寻找更基础的数值规律。
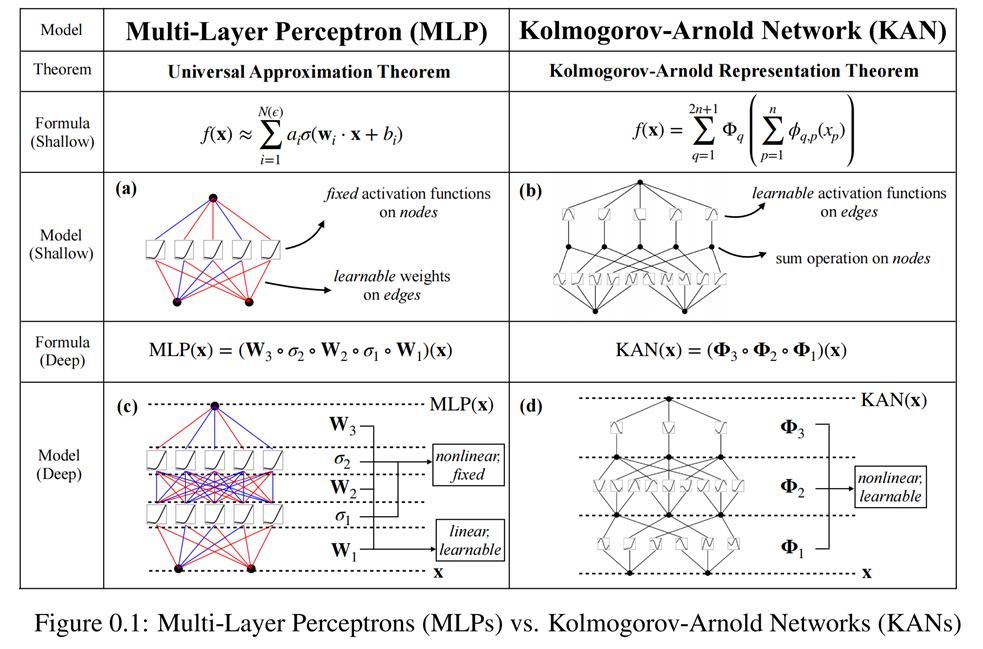

与MLP对比
与传统的MLP 相比,KAN 有4个主要特点:
1)激活函数位于“边”而不是节点(Node)上;
2)激活函数是可学习的而不是固定的;
3)可以使用非线性核函数来替代MLP“边”(Edge)上的线性函数;
4)可以设定细粒度的结点(Knot)来提高逼近精度。
动机
多层感知器 (MLP)
优点:表征能力强且已由通用逼近定理证明。
缺点:参数量大,且通常不具备可解释性。
—>
KAN = MLP + Spline

KAN定理
Kolmogorov-Arnold表示定理 Vladimir Arnold与 Andrey Kolmogorov提出
如果f是多元连续函数,则f可以写成有限数量的单变量连续函数的两层嵌套叠加。其数学表达式就是

这表明在实数域上,唯一真正的多元函数是求和,因为所有其他函数都可以使用单变量函数求和来表征。
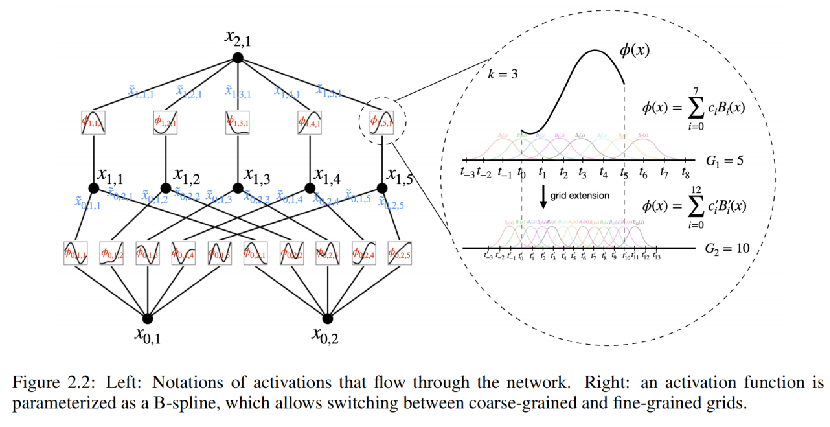
KAN的架构设计来自一个数学问题:对一个由输入输出对 {xi, yi} 组成的有监督学习任务,寻找函数f 使得所有数据点的 yi≈ f (xi)。其核心在于找到合适的外部函数和内部函数。
方法:使用B-spline(B样条,Basic Spline)来构建
对于B-spline,函数在其定义域内、在结点(Knot)都具有相同的连续性。其多项式表达可由Cox-de Boor 递推公式表达:
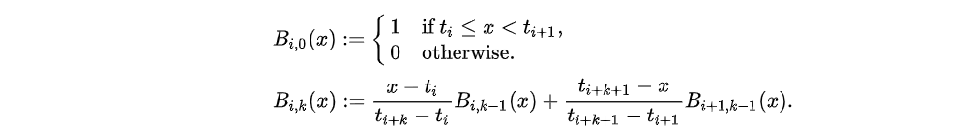
根据KA定理,理论上只要2个KAN层就可以充分表征实数域的各类有监督学习任务。
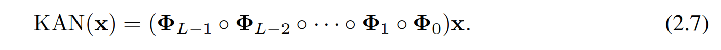
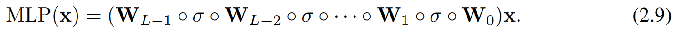
KAN资源分享:
Papers
- KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks : Inspired by the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem, we propose Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) as promising alternatives to Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs). While MLPs have fixed activation functions on nodes (“neurons”), KANs have learnable activation functions on edges (“weights”). KANs have no linear weights at all – every weight parameter is replaced by a univariate function parametrized as a spline. We show that this seemingly simple change makes KANs outperform MLPs in terms of accuracy and interpretability. For accuracy, much smaller KANs can achieve comparable or better accuracy than much larger MLPs in data fitting and PDE solving. Theoretically and empirically, KANs possess faster neural scaling laws than MLPs. For interpretability, KANs can be intuitively visualized and can easily interact with human users. Through two examples in mathematics and physics, KANs are shown to be useful collaborators helping scientists (re)discover mathematical and physical laws. In summary, KANs are promising alternatives for MLPs, opening opportunities for further improving today’s deep learning models which rely heavily on MLPs.
- Chebyshev Polynomial-Based Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks : The document discusses a novel neural network architecture called the Chebyshev Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (Chebyshev KAN) for approximating complex nonlinear functions. It combines the theoretical foundations of the Kolmogorov-Arnold Theorem with the powerful approximation capabilities of Chebyshev polynomials. The Chebyshev KAN layer approximates a target multivariate function by representing it as a weighted sum of Chebyshev polynomials, leveraging the Kolmogorov-Arnold Theorem’s guarantee of the existence of a superposition of univariate functions to represent any continuous multivariate function. The paper provides a detailed mathematical explanation of the implementation, training, and optimization of the Chebyshev KAN layer, as well as experimental results demonstrating its effectiveness in approximating complex fractal-like functions.
Library
- pykan : Offical implementation for Kolmogorov Arnold Networks
- efficient-kan : An efficient pure-PyTorch implementation of Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN).
- Convolutional-KANs : This project extends the idea of the innovative architecture of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN) to the Convolutional Layers, changing the classic linear transformation of the convolution to non linear activations in each pixel.






















 1543
1543

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








