案例需求:
RFM模型的复习
在客户分类中,RFM模型是一个经典的分类模型,模型利用通用交易环节中最核心的三个维度——最近消费(Recency)、消费频率(Frequency)、消费金额(Monetary)细分客户群体,从而分析不同群体的客户价值。在某些商业形态中,客户与企业产生连接的核心指标会因产品特性而改变。如互联网产品中,以上三项指标可以相应地变为下图中的三项:最近一次登录、登录频率、在线时长。
商用航空行业LRFCM模型的推广:
我们说RFM模型由R(最近消费时间间隔)、F(消费频次)和M(消费总额)三个指标构成,通过该模型识别出高价值客户。但该模型并不完全适合所有行业,如航空行业,直接使用M指标并不能反映客户的真实价值,因为“长途低等舱”可能没有“短途高等舱”价值高。考虑到商用航空行业与一般商业形态的不同,决定在RFM模型的基础上,增加2个指标用于客户分群与价值分析,得到航空行业的LRFMC模型:
L:客户关系长度。客户加入会员的日期至观测窗口结束日期的间隔。(反映可能的活跃时长)
R:最近一次乘机时间。最近一次乘机日期至观测窗口结束日期的间隔。(反映当前的活跃状态)
F:乘机频率。客户在观测窗口期内乘坐飞机的次数。(反映客户的忠诚度)
M:飞行总里程。客户在观测窗口期内的飞行总里程。(反映客户对乘机的依赖性)
C:平均折扣率。客户在观测窗口期内的平均折扣率。(舱位等级对应的折扣系数,侧面反映客户价值高低)

-------------------------------------本次练习基于数据源提取上述五个指标分析航空客户商业价值。
数据源:数据源
数据指标说明:

 Hive操作:
Hive操作:
构建数据库表:
reate database air_data_base;
use air_data_base;
create table air_data_table(
member_no string,
ffp_date string,
first_flight_date string,
gender string,
ffp_tier int,
work_city string,
work_province string,
work_country string,
age int,
load_time string,
flight_count int,
bp_sum bigint,
ep_sum_yr_1 int,
ep_sum_yr_2 bigint,
sum_yr_1 bigint,
sum_yr_2 bigint,
seg_km_sum bigint,
weighted_seg_km double,
last_flight_date string,
avg_flight_count double,
avg_bp_sum double,
begin_to_first int,
last_to_end int,
avg_interval float,
max_interval int,
add_points_sum_yr_1 bigint,
add_points_sum_yr_2 bigint,
exchange_count int,
avg_discount float,
p1y_flight_count int,
l1y_flight_count int,
p1y_bp_sum bigint,
1y_bp_sum bigint,
ep_sum bigint,
add_point_sum bigint,
eli_add_point_sum bigint,
l1y_eli_add_points bigint,
points_sum bigint,
l1y_points_sum float,
ration_l1y_flight_count float,
ration_p1y_flight_count float,
ration_p1y_bps float,
ration_l1y_bps float,
point_notflight int
)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',';将数据源上传到Linux本地文件夹中,再从本地上传到hive数据库中:
load data local inpath '/home/hadoop/air_data.csv' overwrite into table air_data_table;
select * from air_data_table limit 20;统计观测窗口的票价收入(SUM_YR_1)、观测窗口的总飞行公里数(SEG_KM_SUM)、
平均折扣率(AVG_DISCOUNT)三个字段的空值记录,并将结果保存到名为sum_seg_avg_null的表中:
create table sum_seg_avg_null as select * from
(select count(*) as sum_yr_1_null_count from air_data_table where sum_yr_1 is null) sum_yr_1,
(select count(*) as seg_km_sum_null from air_data_table where seg_km_sum is null) seg_km_sum,
(select count(*) as avg_discount_null from air_data_table where avg_discount is null) avg_discount;
统计观测窗口的SUM_YR_1(票价收入)、SEG_KM_SUM(总飞行公里数)、AVG_DISCOUNT(平均折扣率)三列的最小值sum_seg_avg_min表中:
create table sum_seg_avg_min as select
min(sum_yr_1) as sum_yr_1,
min(seg_km_sum) as seg_km_sum,
min(avg_discount) as avg_discount
from air_data_table;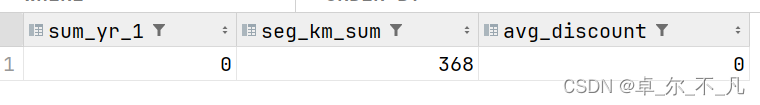
数据清洗:
过滤掉票价为空的记录、平均折扣率为0.0的记录、票价为0、平均折扣率不为0、总飞行公里数大于0的记录。
create table sas_not_0 as
select * from air_data_table
where sum_yr_1 is not null and
avg_discount <> 0 and
seg_km_sum > 0;提取有用数据项:
create table flfasl as select ffp_date,load_time,flight_count,avg_discount,seg_km_sum,last_to_end from sas_not_0;
select * from flfasl limit 10; 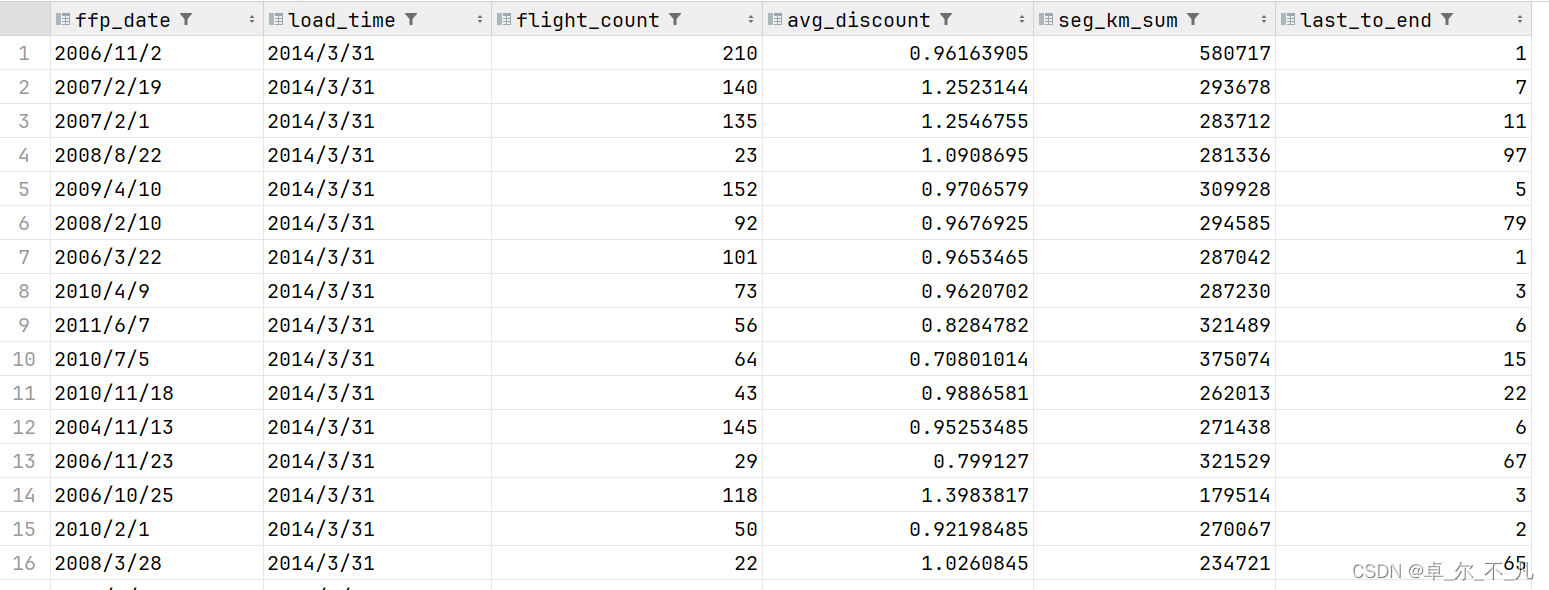
--L的构造:会员入会时间距离观测窗口结束的月数 = 观测窗口的结束时间 - 入会时间 [单位:月] --R的构造:客户最近一次乘坐公司飞机距观测窗口结束的月数 = 最后一次乘机时间至观测窗口末端时长[单位:月] -F的构造:客户再观测窗口内乘坐公司飞机的次数 = 观测窗口的飞行次数[单位:次] --M的构造:客户再观测时间内在公司累计的飞行里程 = 观测窗口总飞行公里数[单位:公里] --C的构造:客户在观测时间内乘坐舱位所对应的折扣系数的平均值 = 平均折扣率 [单位:无]
create table lrfmc as
select
round((unix_timestamp(load_time,'yyyy/MM/dd')-unix_timestamp(ffp_date,'yyyy/MM/dd'))/(30*24*60*60),2) as l,
round(last_to_end/30,2) as r,
flight_count as f,
seg_km_sum as m,
round(avg_discount,2) as c
from flfasl;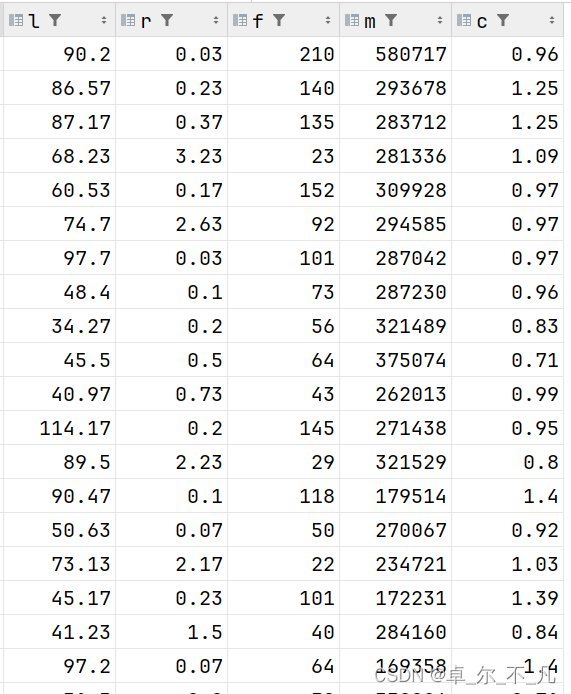
数据标准化:
create table standard_lrfmc as
select (lrfmc.l-minlrfmc.l)/(maxlrfmc.l-minlrfmc.l) as l,
(lrfmc.r-minlrfmc.r)/(maxlrfmc.r-minlrfmc.r) as r,
(lrfmc.f-minlrfmc.f)/(maxlrfmc.f-minlrfmc.f) as f,
(lrfmc.m-minlrfmc.m)/(maxlrfmc.m-minlrfmc.m) as m,
(lrfmc.c-minlrfmc.c)/(maxlrfmc.c-minlrfmc.c) as c
from lrfmc,
(select max(l) as l,max(r) as r,max(f) as f,max(m) as m,max(c) as c from lrfmc) as maxlrfmc,
(select min(l) as l,min(r) as r,min(f) as f,min(m) as m,min(c) as c from lrfmc) as minlrfmc;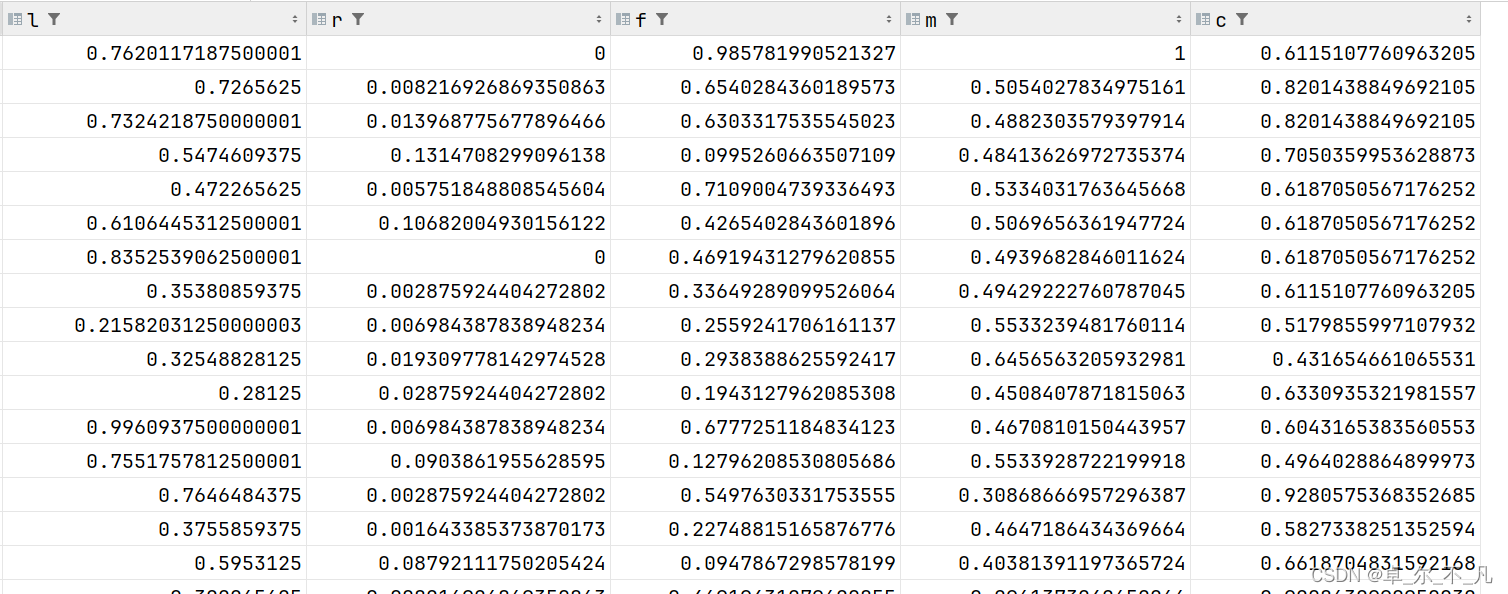
数据挖掘:(客户分类)未完待续……
参考资料:
26个数据分析案例——第二站:基于Hive的民航客户价值分析























 2234
2234











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








