类的抽象
用abstract关键字修饰的方法和类在抽象方法中是没有方法体的,并且以分号结尾
抽象方法:使用abstract修饰符修饰的方法
抽象类:使用abstract修饰符修饰的类
- 抽象类不能创建对象也就是不能给抽象类创建类的实例(即不能用new创建对象)
- 子类继承抽象类时,必须对父类中的所有抽象方法进行重写,即子类继承父类时需要实现父类所有的抽象方法,否则也要将子类定义为抽象类
- final方法不能为抽象方法, (final的方法不能被重写)
- 私有方法不能被定义为抽象方法,(私有方法并不能被子类继承)
- 静态方法不能被定义为抽象方法,(抽象方法不能够被实例化,静态方法是可以通过类名调用,但这样调用抽象方法没有任何意义)
person类实例
定义一个抽象类,定义名字和年龄属性,一个打印属性的抽象方法。定义一个抽象类的实现类,定义学号和分数属性,并覆写父类的抽象方法。最后给实现类设置属性,打印属性信息。
思路要求:
定义一个Person的抽象类,定义名字(name)和年龄(age)属性,并创建属性的setter/getter方法,定义一个打印属性的抽象方法printInfo。定义一个Person类的子类Student,定义属性学号(stuNun)(score)和成绩属性,并创建属性的setter/getter方法,并实现打印属性的方法printInfo。
package person;
public abstract class Person {
public String name;//姓名
public int age;//年龄
public abstract void printInfo();//打印
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
package person;
public class Student extends Person {
private int stuNum;//学号
private double score;//成绩
@Override
public void printInfo() {//打印
System.out.println("学号="+getStuNum()+";姓名="+getName()+";年龄="+getAge()+";成绩="+getScore());
}
public Student(String name, int age, int stuNum, double score) {
super(name, age);
this.stuNum = stuNum;
this.score = score;
}
public int getStuNum() {
return stuNum;
}
public void setStuNum(int stuNum) {
this.stuNum = stuNum;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
}
package person;
public class TestPerson {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student("张三", 12, 2021001, 90.6);
student.printInfo();
}
}
运行结果:

抽象类机动⻋Motovercal实例
定义⼀个抽象类机动⻋Motovercal,⾥⾯有⻋牌号no,类型type,价格price属性,⾥⾯有⼀个show()⽅法是抽象⽅法,定义⼀个轿⻋Car类,他有特有的属性颜⾊color,有⼀个公共汽⻋Bus,他有特有属性座位数seatCount,实现如图功能:

提示: (1)定义⼀个抽象类Motovercal,⾥⾯有属性⻋牌号no,类型type,价格price,⾥⾯有抽象⽅法show()
(2)定义⼀个轿⻋Car类,继承Motovercal,他有特有的属性颜⾊color
(3)定义⼀个轿⻋Bus类,继承Motovercal,他有特有的属性座位数seatCount
(4)编写测试类MotovercalTest
package motovercal;
public abstract class Motovercal {
private String no;//车牌号
private String type;//类型
private double price;//价格
public abstract void show();
public Motovercal(String no, String type, double price) {
this.no = no;
this.type = type;
this.price = price;
}
public String getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(String no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
package motovercal;
public class Car extends Motovercal {
private String color;//颜色
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println("本车车牌号为:"+super.getNo()+",类型为:"+super.getType()+",价格为:"+super.getPrice()+",颜色为:"+this.getColor());
}
public Car(String no, String type, double price, String color) {
super(no, type, price);
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
}
package motovercal;
public class Bus extends Motovercal {
private int seatCount;//座位数
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println("本车车牌号为:"+super.getNo()+",类型为:"+super.getType()+",价格为:"+super.getPrice()+",拥有:"+this.getSeatCount()+"个座位");
}
public Bus(String no, String type, double price, int seatCount) {
super(no, type, price);
this.seatCount = seatCount;
}
public int getSeatCount() {
return seatCount;
}
public void setSeatCount(int seatCount) {
this.seatCount = seatCount;
}
}
package motovercal;
public class MotovercalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car = new Car("A00001", "jeep", 2000, "绿色");
car.show();
Bus bus = new Bus("B00002", "金龙", 25000, 20);
bus.show();
}
}
Pet实例
1.抽象类 Pet类:属性:姓名,健康值,亲密度; 行为:吃
2. Dog类:继承Pet类; 属性:品种; 行为:吃骨头
3. Penguin类:继承Pet类;属性:性别;行为:吃鱼
实现如图

package pet1;
public abstract class Pet {
private String name;//姓名
private double health;//健康值
private double love;//亲密度
public abstract void eat();
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getHealth() {
return health;
}
public void setHealth(double health) {
this.health = health;
}
public double getLove() {
return love;
}
public void setLove(double love) {
this.love = love;
}
}
package pet1;
public class Dog extends Pet {
private String strain;//品种
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("跑回来啃骨头!");
}
public String getStrain() {
return strain;
}
public void setStrain(String strain) {
this.strain = strain;
}
}
package pet1;
public class Penguin extends Pet {
private String sex;//性别
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("跑回来吃鱼!");
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
package pet1;
public class PetFactory {
public void getPet(Pet m) {
if(m instanceof Dog) {
Dog dog = (Dog)m;
((Dog) m).setStrain("拉布拉多犬");
m.setHealth(100);
m.setLove(20);
System.out.print("名叫:小花的小狗,");
System.out.print("是一只"+((Dog) m).getStrain());
System.out.print(",健康值为"+m.getHealth());
System.out.print(",亲密度为"+m.getLove());
m.eat();
}
else if(m instanceof Penguin) {
Penguin penguin = new Penguin();
((Penguin)m).setSex("美女");
m.setHealth(90);
m.setLove(80);
System.out.print("名叫:QQ的企鹅,");
System.out.print("是个"+((Penguin)m).getSex());
System.out.print(",健康值为"+m.getHealth());
System.out.print(",亲密度为"+m.getLove());
m.eat();
}
}
}
package pet1;
public class PetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
Penguin penguin = new Penguin();
PetFactory petFactory = new PetFactory();
petFactory.getPet(dog);
System.out.println();
petFactory.getPet(penguin);
}
}
类的接口
-
子类可以同时接收多个接口,而一个子类只能有一个父类
-
在接口中定义的变量,实际上是公共的静态变量,格式为:
public static final int p=3; -
接口中的方法是抽象的
-
接口中的方法只有在实现接口的类中,重写方法后才能被使用
-
当一个类实现多个接口时,需要重写所有接口中的所有方法
-
抽象类和接口的区别
接口是抽象类的特殊版本。接口里的方法都为抽象方法,而抽象类里方法可以为抽象方法或其他形式的方法
| 抽象类 | 接口 |
|---|---|
| 可存在非抽象方法 | 方法全部被修饰为公共的抽象方法 |
| 可以实现所有方法,也可以实现部分方法 | 必须全部实现 |
| 可以有私有的方法和私有的成员变量 | 方法被修饰为public abstract类型,变量被修饰为public static final类型 |
| 一个类只能继承一个抽象类,单继承 | 一个类可以实现一个接口或多个接口 |
Animal实例
⻢继承Animal,还能实现能⻜的能⼒,简称⻜⻢,运⾏结果如下:

(1)抽象类Animal,⾥⾯有name属性
(2)Flyable接⼝,表示⻜的能⼒,有⻜fly()的⽅法,返回void
(3)Horse类,继承抽象类Animal,并实现接⼝Flyable
package animal;
public abstract class Animal {
private String name;
public Animal(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
package animal;
public interface Flyable {
public abstract void flyAble();
}
package animal;
public class Horse extends Animal implements Flyable{
public Horse(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void flyAble() {
System.out.println("小马嘟嘟,是一只会飞的飞马");
}
}
package animal;
public class TestAnimal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Horse horse = new Horse("嘟嘟");
horse.flyAble();
}
}
Person实例
- ⽗类Person,属性:姓名name、性别sex,年龄age;抽象show⽅法()
- 能说的接⼝Sayable; 能听的接⼝Hearable;能吃的接⼝Eatable
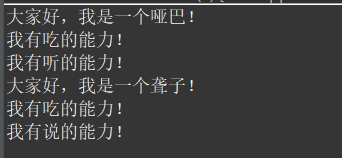
- 哑巴Dumb是不能说,聋⼦Deaf是不能听到,但他们都有姓名,年龄,性别,运⾏结果如下:
package person1;
public abstract class Person {
public String name;//姓名
public String sex;//性别
public int age;//年龄
public abstract void show();
}
package person1;
public interface Sayable {
public abstract void say();//能说
}
package person1;
public interface Hearable {
public abstract void hear();//能听
}
package person1;
public interface Eatable {
public abstract void eat();//能吃
}
package person1;
public class Dumb extends Person implements Hearable,Eatable{
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println("大家好,我是一个哑巴!");
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("我有吃的能力!");
}
@Override
public void hear() {
System.out.println("我有听的能力!");
}
}
package person1;
public class Deaf extends Person implements Sayable,Eatable{
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println("大家好,我是一个聋子!");
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("我有吃的能力!");
}
@Override
public void say() {
System.out.println("我有说的能力!");
}
}
package person1;
public class TestPerson {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dumb dumb = new Dumb();
dumb.show();
dumb.eat();
dumb.hear();
Deaf deaf = new Deaf();
deaf.show();
deaf.eat();
deaf.say();
}
}






















 2371
2371











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








