前言
记录一下自己学习的过程,内容主要来自于B站的一位up主,在此非常感谢他无私的奉献精神。看到他的视频请一键三连!
- up主的B站链接:https://space.bilibili.com/18161609/channel/series
- up主的csdn链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37541097?type=blog
- up主的github链接:https://github.com/WZMIAOMIAO/deep-learning-for-image-processing
1 VGG详解
VGG在2014年由牛津大学著名研究组VGG (Visual Geometry Group) 提出,斩获该年ImageNet竞赛中 Localization Task (定位任务) 第一名 和 Classification Task (分类任务) 第二名。
网络中的亮点
- 通过堆叠多个3×3的卷积核来替代大尺度卷积核,即二者拥有相同的感受野。(减少所需参数)
论文中提高,可以通过堆叠两个3×3的卷积核替代5×5的卷积核,堆叠三个3×3的卷积核替代7×7的卷积核。
1.1 感受野
1.1.1 定义
在卷积神经网络中,决定某一层输出结果中一个元素所对应的输入层的区域大小,被称作感受野(receptive field)。通俗的解释是,输出feature map上的一个单元对应输入层上的区域大小。
如下图所示,输出的特征矩阵一个单元在第二层的感受野是2×2,在第三层的感受野是5×5。
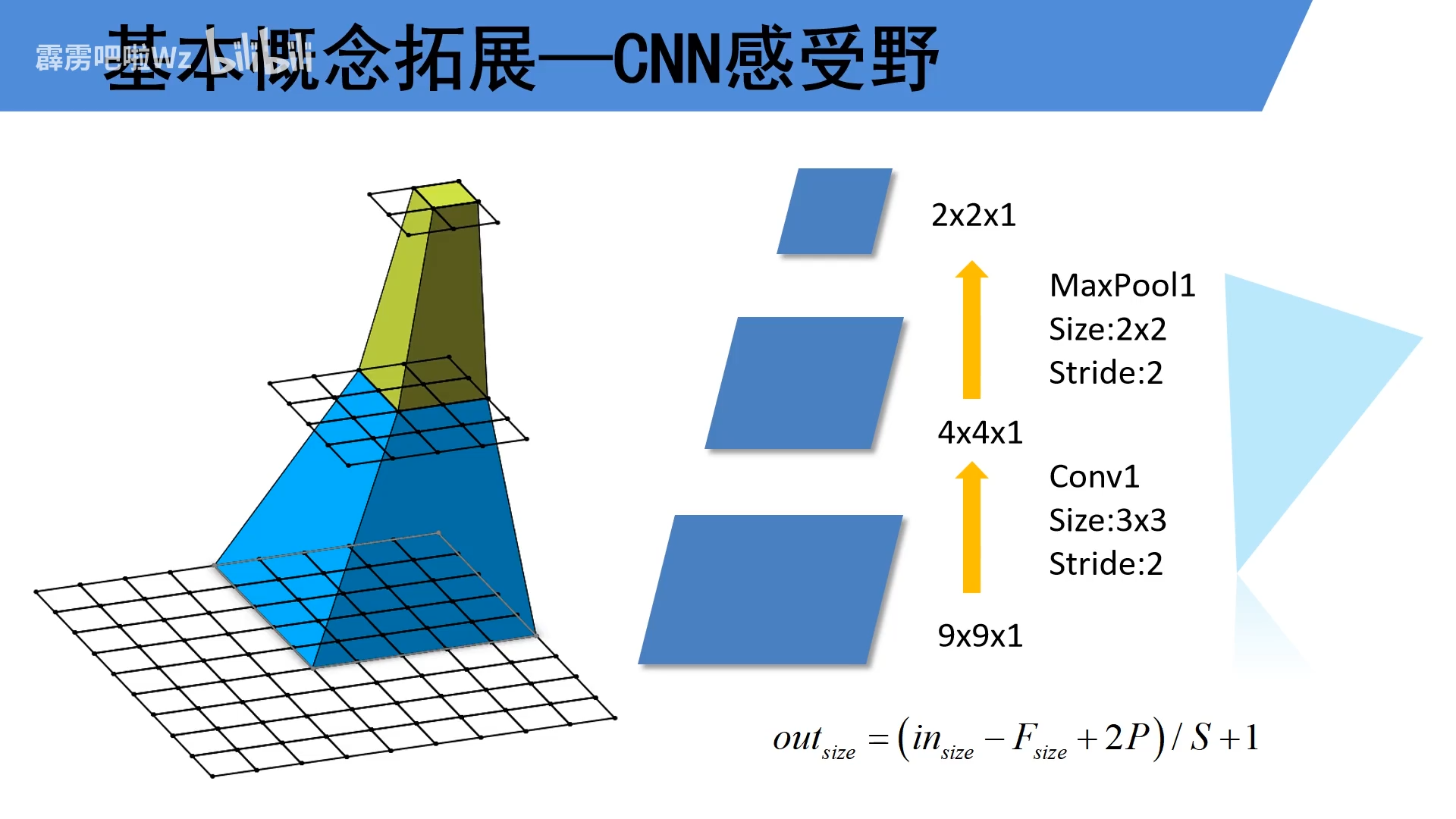
1.1.2 计算方法
重点:(当时听到这里懵,后面后知后觉才直到感受野是如何计算的)在感受野计算公式
F
(
i
)
=
(
F
(
i
+
1
)
−
1
)
×
S
t
r
i
d
e
+
K
s
i
z
e
F(i)=(F(i+1)-1)\times Stride+Ksize
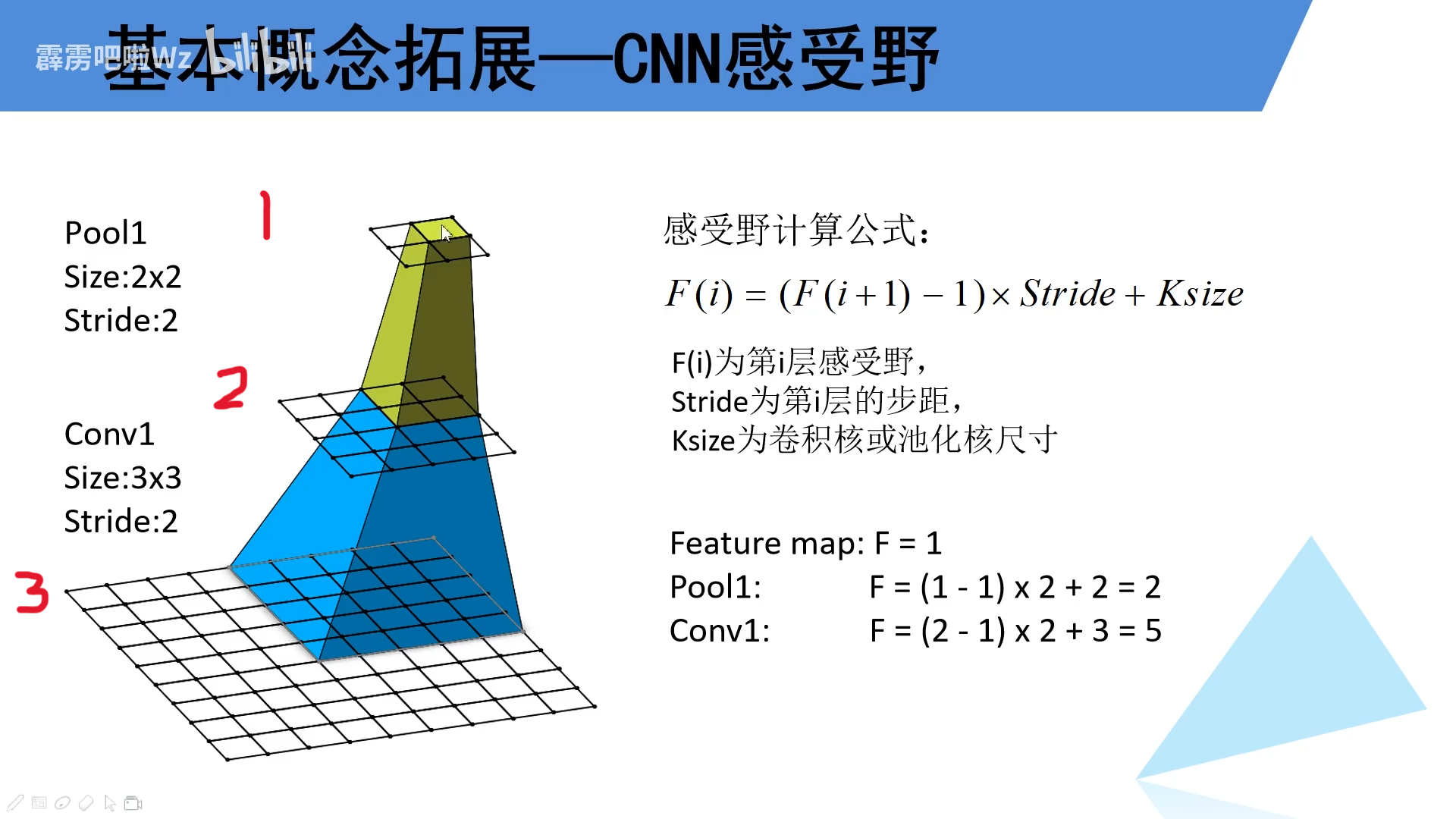
F(i)=(F(i+1)−1)×Stride+Ksize中,F(i)为当前第i层的感受野,F(i+1)为第i层前面一层的感受野。stride为第i层步距,Ksize为当前第i层卷积核或池化核大小。
如下面一个例子。第1层的感受野为1,那第二层的感受野就等于
(
第
1
层感受野
−
1
)
×
2
+
2
(第1层感受野-1)\times2+2
(第1层感受野−1)×2+2,即
2
×
2
2\times2
2×2,同样的第3层的感受野大小计算就是=
(
第
2
层的感受野
−
1
)
×
2
+
3
(第2层的感受野-1)\times2+3
(第2层的感受野−1)×2+3,即
5
×
5
5\times5
5×5。
前面我们说过,在VGG网络中作者使用到
3
个
3
×
3
的卷积核
(
s
t
r
i
d
e
=
1
)
\mathbf{3个3 \times 3的卷积核(stride=1)}
3个3×3的卷积核(stride=1)替代
1
个
7
×
7
的卷积核
\mathbf{1个7\times7的卷积核}
1个7×7的卷积核。同样的我们可以通过下式计算一下。
对于feature_map中的一个单元来讲,对三个卷积层对应的感受野如下:
- Conv1: ( 1 − 1 ) × 1 + 3 = 3 (1-1)\times1+3=3 (1−1)×1+3=3
- Conv2: ( 3 − 1 ) × 1 + 3 = 5 (3-1)\times1+3=5 (3−1)×1+3=5
- Conv3:
(
5
−
1
)
×
1
+
3
=
7
(5-1)\times1+3=7
(5−1)×1+3=7
假如我们使用一个 7 × 7 7\times7 7×7的卷积核(stride=1),则对应的感受野大小为 ( 1 − 1 ) × 1 + 7 = 7 (1-1)\times1+7=7 (1−1)×1+7=7,我们可以看出使用3个3×3卷积核与使用1个7×7的卷积核对应的感受野大小相同。但是它们的参数量可不一样(下述计算没有考虑偏置bias)。 - 使用1个7×7计算量: 7 × 7 × C × C = 49 C 2 7\times7\times C\times C=49C^2 7×7×C×C=49C2
- 使用3个3×3计算量:
3
×
3
×
3
×
C
×
C
=
27
C
2
3\times3\times3\times C\times C=27C^2
3×3×3×C×C=27C2
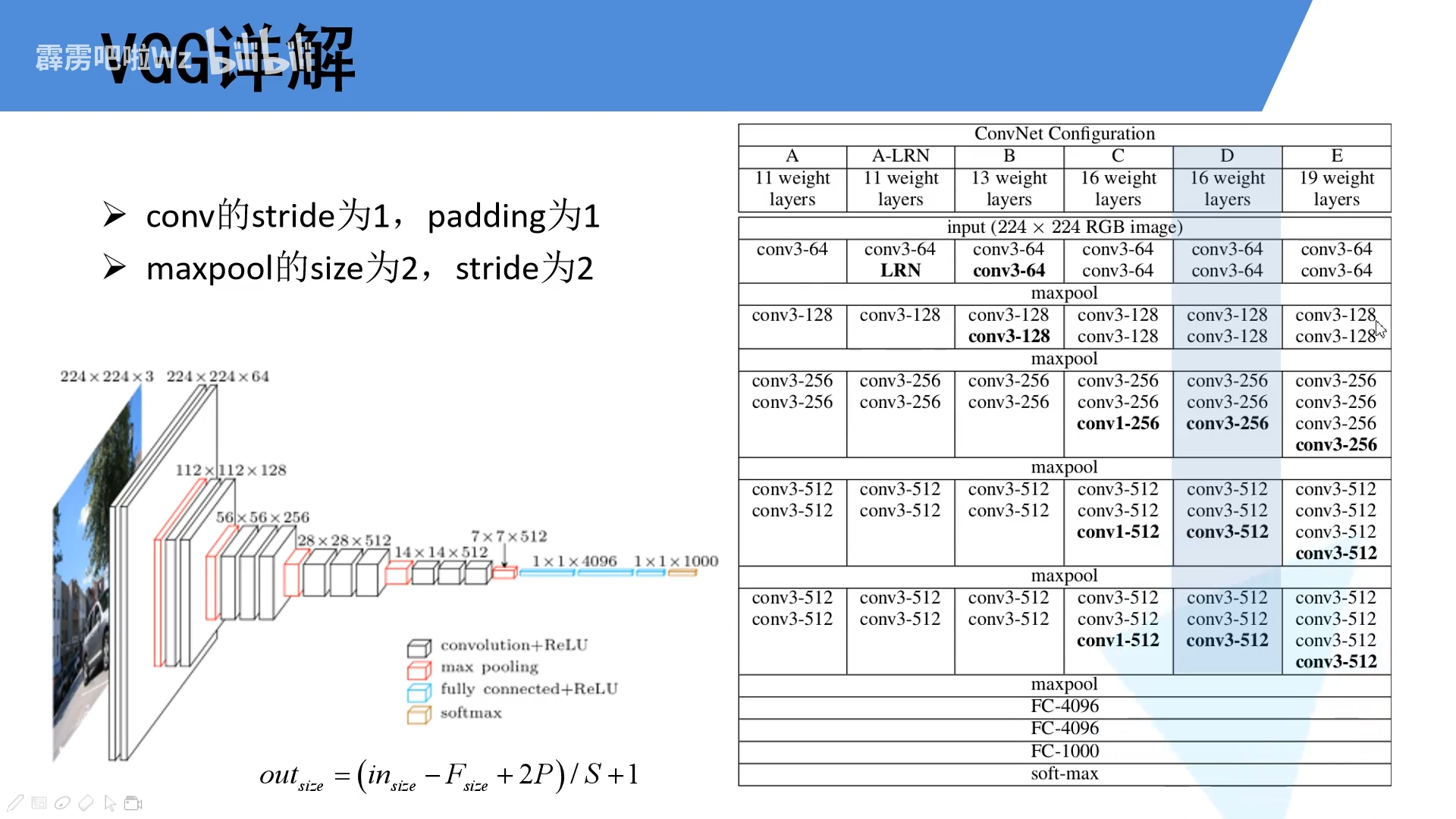
1.2 VGG16网络
VGG网络有很多版本,我们经常使用的就是VGG16网络,VGG16网络配置如下图所示。
- 卷积层 所有卷积层的kenerl_size为3×3,stride=1,padding=1。即经过卷积操作后特征图的大小不变,只改变通道数。
o u t = ( w − 3 + 2 × 1 ) / 1 + 1 = w out =(w-3+2\times1)/1+1=w out=(w−3+2×1)/1+1=w - 池化层 所有池化层的kenerl_size为2×2,stride=2。即经过池化操作后特征图的通道数不改变,其大小变成原来的一半。
o u t = ( w − 2 ) / 2 + 1 = w / 2 out=(w-2)/2+1=w/2 out=(w−2)/2+1=w/2
2 model.py
2.1 问题
1 args
args是可变参数,并且args接收的是一个元组tuple类型。
input:
def add(*args):
print(type(args))
sum = 0
for i in args:
sum = sum + i
return sum
print(add(1,2))
output:
<class 'tuple'>
3
2 kwargs
kwargs是非关键字参数,并且kwargs接收的是一个字典dict类型。
input:
def person(name, age, **kwargs):
print(type(kwargs))
print('name:', name, 'age:', age, 'other:', kwargs)
output:
<class 'dict'>
name: A age: 13 other: {}
person('A', 13)
input:
def person(name, age, **kwargs):
print(type(kwargs))
print('name:', name, 'age:', age, 'other:', kwargs)
person('A', 13, city='Beijing')
output:
<class 'dict'>
name: A age: 13 other: {'city': 'Beijing'}
3 item()和items()的区别
- item()
item()的作用就是取出单个元素张量的元素值。
input:
import torch
a = torch.tensor([1])
print(a.item())
output:
1
- items()
items()的作用就是把字典里的键值对组成元组提取出来,然后把这些键值对组成的元组放在列表中返回。
input:
a = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
print(a.items())
output:
dict_items([('a', 1), ('b', 2), ('c', 3)])
2.2 代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class VGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features, num_classes=1000, init_weights=False):
super(VGG, self).__init__()
self.features = features
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(7 * 7 * 512, 4096),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes)
)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
# nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
# nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def make_features(cfg: list):
layers = []
in_channels = 3
for v in cfg:
if v == 'M':
layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
else:
conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=v, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
layers += [conv2d, nn.ReLU(True)]
in_channels = v
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
# int:卷积核的个数 'M':maxpool操作
cfgs = {
'vgg11': [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg13': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg16': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg19': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
}
def vgg(model_name='vgg16', **kwargs):
assert model_name in cfgs, "Warning: model number {} not in cfgs dict!".format(model_name)
cfg = cfgs[model_name]
model = VGG(make_features(cfg), **kwargs)
return model
3 train.py
import json
import os
import sys
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch.optim as optim
from model import vgg
from tqdm import tqdm
def main():
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available else "cpu")
print("Using device{}".format(device))
# 一些预处理操作
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])}
# 这是我数据存放的路径
data_root = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "../../../../"))
image_path = os.path.join(data_root, 'data_set', 'data_spec')
assert os.path.exists(image_path), "Path {} does not exist".format(image_path)
# trainset
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, 'train'),
transform=data_transform['train'])
val_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, 'val'),
transform=data_transform['val'])
# trainset and val_dataset的数量
train_num = len(train_dataset)
val_num = len(val_dataset)
# 生成一个类别的json文件
data_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx
cla_dict = dict((val, key) for key, val in data_list.items())
json_str = json.dumps(cla_dict, indent=4)
with open('class_indices.json', 'w') as json_file:
json_file.write(json_str)
batch_size = 32
nw = min([os.cpu_count(), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, 8]) # number of workers
print('Using {} dataloader workers every process'.format(nw))
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True, num_workers=nw)
val_loader = DataLoader(dataset=val_dataset, batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False, num_workers=nw)
print('Using {} images for training, {} images for validation'.format(train_num, val_num))
model_name = "vgg16"
net = vgg(model_name=model_name, num_classes=5, init_weights=True)
net.to(device)
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
epochs = 30
best_acc = 0.0
save_path = './{}Net.pth'.format(model_name)
train_steps = len(train_loader)
for epoch in range(epochs):
# train
net.train()
running_loss = 0
train_bar = tqdm(train_loader, file=sys.stdout)
for step, data in enumerate(train_bar):
images, labels = data
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(images.to(device))
loss = loss_function(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# print statistics
running_loss += loss.item()
train_bar.desc = "train epoch[{}/{}] loss:{:.3f}".format(epoch + 1,
epochs,
loss)
net.eval()
acc = 0.0
with torch.no_grad():
val_bar = tqdm(val_loader, file=sys.stdout)
for val_data in val_bar:
val_images, val_labels = val_data
outputs = net(val_images.to(device))
predict_y = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1]
acc += torch.eq(predict_y, val_labels.to(device)).sum().item()
val_accurate = acc / val_num
print('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f val_accuracy: %.3f' %
(epoch + 1, running_loss / train_steps, val_accurate))
if val_accurate > best_acc:
best_acc = val_accurate
torch.save(net.state_dict(), save_path)
print('Finished Training')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
4 predict.py
import os
import json
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from model import vgg
def main():
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
# load image
img_path = "../tulip.jpg"
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
plt.imshow(img)
# [N, C, H, W]
img = data_transform(img)
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
# read class_indict
json_path = './class_indices.json'
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path)
with open(json_path, "r") as f:
class_indict = json.load(f)
# create model
model = vgg(model_name="vgg16", num_classes=5).to(device)
# load model weights
weights_path = "./vgg16Net.pth"
assert os.path.exists(weights_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(weights_path)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights_path, map_location=device))
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = torch.squeeze(model(img.to(device))).cpu()
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
print_res = "class: {} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(predict_cla)],
predict[predict_cla].numpy())
plt.title(print_res)
for i in range(len(predict)):
print("class: {:10} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(i)],
predict[i].numpy()))
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








