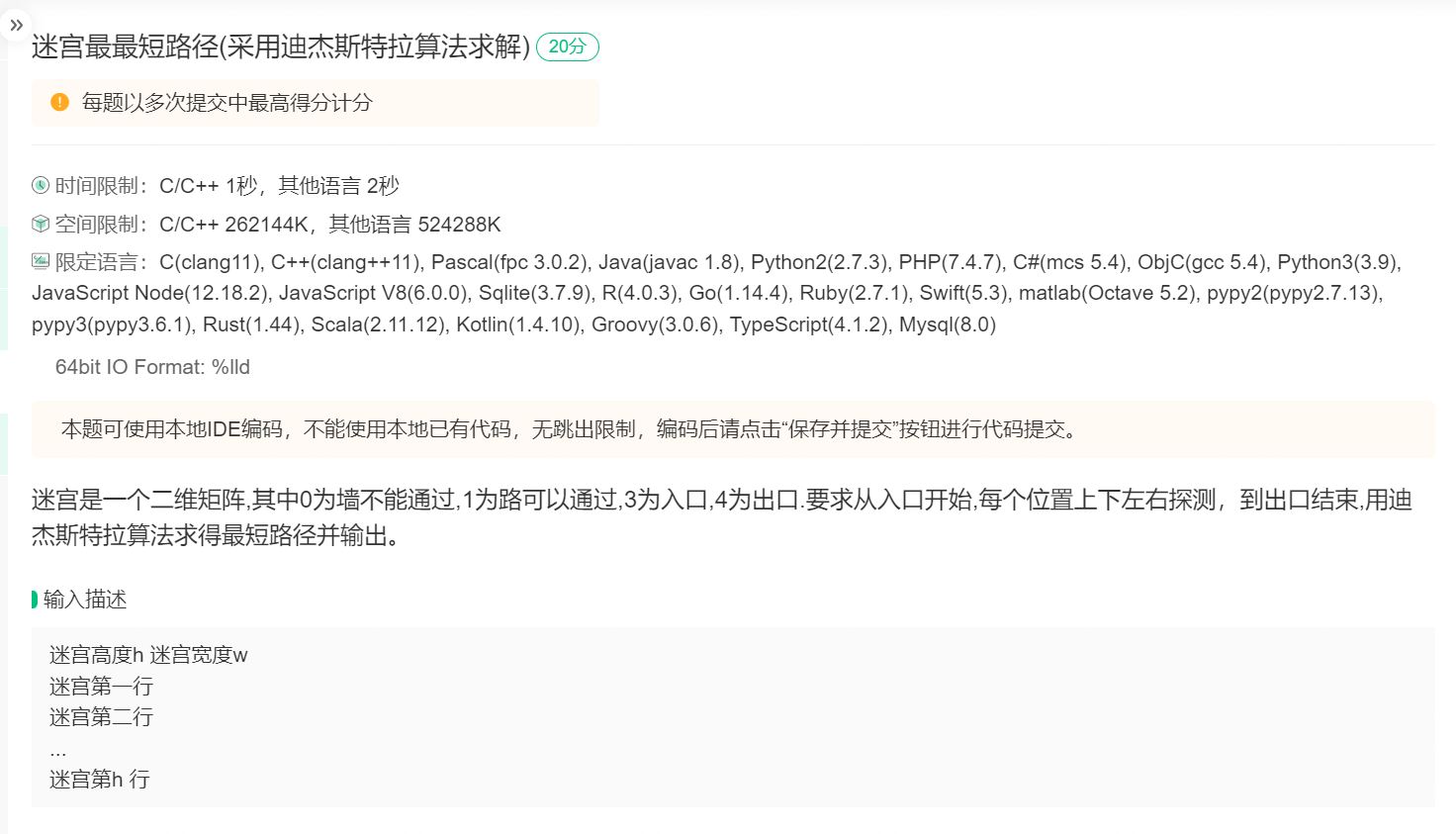
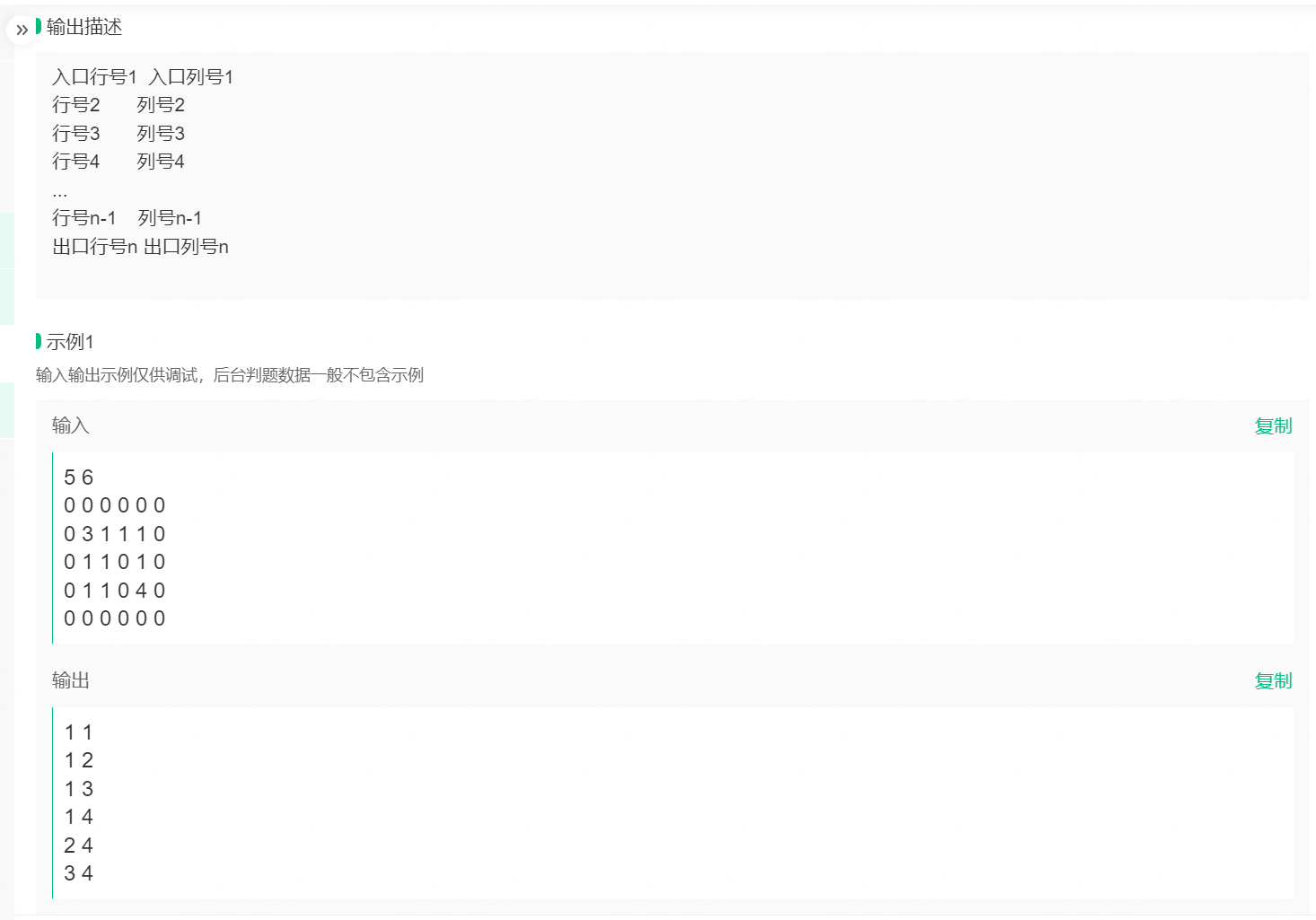
#include <iostream>
#include<queue>
#define max 0x7fffffff
using namespace std;
int x1,y1;
int x2,y2;
int L[4][2]={{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}};
class node{
public:
int x,y,key;
node * p;
node(int x=-1,int y=-1,int key=max, node*p=NULL){
this->x=x;
this->y=y;
this->key=key;
this->p=p;
}
};
int main()
{
int m,n;
cin>>m>>n;
int t[m][n];
node T[m][n];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
cin>>t[i][j];
T[i][j].x=i;
T[i][j].y=j;
T[i][j].p=NULL;
if(t[i][j]==3){
x1=i;y1=j;
}
else if(t[i][j]==4){
x2=i;y2=j;
}
}
}
queue<node> q;
T[x2][y2].key=0;
q.push(T[x2][y2]);
while(!q.empty()){
node loc=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int tempx,tempy;
tempx=loc.x+L[i][0];
tempy=loc.y+L[i][1];
if(tempx<0||tempx>=m||tempy<0||tempy>=n||t[tempx][tempy]==0||T[tempx][tempy].key<=loc.key+1){
continue;
}
T[tempx][tempy].key=loc.key+1;
T[tempx][tempy].p=&T[loc.x][loc.y];
q.push(T[tempx][tempy]);
}
}
node* k=&T[x1][y1];
while(k!=NULL){
cout<<k->x<<" "<<k->y<<endl;
k=k->p;
}
return 0;
}
理解了一下午终于有点眉目了,这个算法的本质就是一个迪杰斯特拉算法,搜索的过程中为每一个点保存路径。每个结点都是一个链表,搜索的时候就把当前的搜索路径存到链表上,还有就这也是一个广搜,广搜到的路径就是最短路径。因为上下左右循环寻找了多个temp,但是最后最快到达终点、最先满足条件的temp路径一定是最短的。一开始不懂为什么先传进队列的是出口,有两个解决办法:一种就是搜索的过程中为每一个点保存路径,一种就是搜完了以后再返回来搜第二遍
,这个代码用的是第一种。
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
int y;
int x;
node* next;
node(int d = 0, int yy = 0, int xx = 0, node* p = NULL) :data(d), y(yy), x(xx), next(p) {}
};
int h, w, ansy,ansx;
node** maze;
bool** searched;
//右左下上
//int bfsy[4] = { 0,0,1,-1 };
//int bfsx[4] = { -1,1,0,0 };
//上下左右
int bfsy[4] = { -1,1,0,0 };
int bfsx[4] = { 0,0,-1,1 };
void bfs(int x,int y) {
queue<node> bfsqueue;
bfsqueue.push(maze[y][x]);
for (;;) {
node temp = bfsqueue.front();
bfsqueue.pop();
searched[temp.y][temp.x] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
y = temp.y + bfsy[i];
x = temp.x + bfsx[i];
if (y < h && y >= 0 && x < w && x >= 0 && maze[y][x].data!=0 && !searched[y][x]) {
maze[y][x].next = &(maze[temp.y][temp.x]);
if (maze[y][x].data == 1) bfsqueue.push(maze[y][x]);
else { ansy = y; ansx = x; return; }
}
}
}
}
int main() {
// freopen("out.out", "w", stdout); //调试用
cin >> h >> w;
int startx = 0;
int starty = 0;
maze = new node * [h];
searched = new bool * [h];
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++)
{
maze[i] = new node[w];
searched[i] = new bool[w];
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++)
{
int d;
cin >> d;
if (d == 4) {
starty = i;
startx = j;
}
maze[i][j] = node(d, i, j);
searched[i][j] = false;
}
}
bfs(startx, starty);
node* p = &(maze[ansy][ansx]);
while (p != NULL) {
cout << p->y << " " << p->x << endl;
p = p->next;
}
}






















 6534
6534











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










