标准差分进化算法
基本原理
差分进化算法(DE)起源于遗传算法(EA),也是一种基于种群进化的算法。通过对种群采取三种进化操作进行反复迭代使得算法的解趋于全局最优解。在所有的进化算法中,每种算法的个体都有其特有的新个体产生方式,差分进化算法利用差分这种变异操作来产生新的个体,借此来产生一个变异种群;在通过交叉操作,对变异种群和原始种群进行交叉,从而得来交叉种群;对原始种群和交叉种群,利用贪婪的选择操作方式来进行下一代种群的选取 。标准差分进化算法核心操作主要包括三部分:变异操作、交叉操作以及选择操作。DE算法根据具体操作的设置方式不同可以分为很多种,本文介绍的是其中的标准差分算法。
进化操作
变异操作
变异操作指新个体的产生由规模为NP的种群内多个单独个体的线性运算得到。DE算法的变异机制有很多种,最常用的方式如下所示,其中X表示当前原始种群,V表示变异种群,i表示种群中的第 i 个个体,g表示第 g 代种群。r1, r2, r3 为三个互不相等的个体,F是变异算子。F变异算子决定种群个体差分步长的大小。F较小会影响种群个体间的差异性 使得算法结果陷入局部最优;F越大会增强算法的全局搜索能力,有利于最优解的搜索,但会影响算法的收敛速度 。
交叉操作
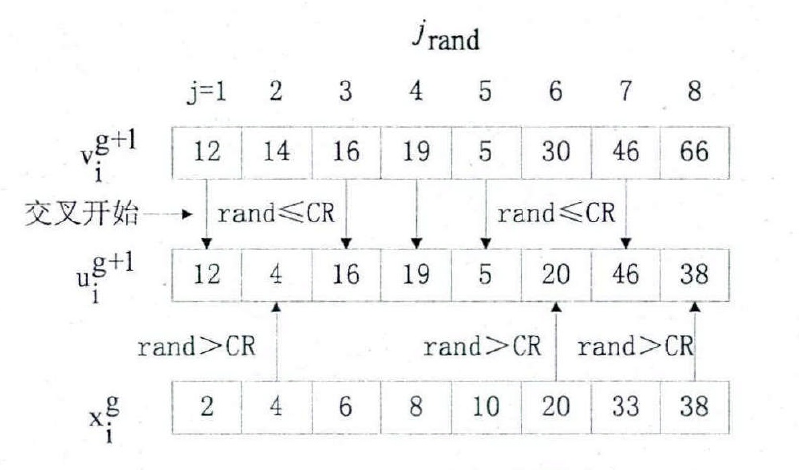
交叉操作是指利用当前种群中个体的部分分量与变异个体的对应分量按照某种规则进行交换生成交叉种群。常用的交换准则有:二项交叉与指数交叉,其中二项交叉指的是针对每个分量产生一个0到1的随机小数,若该随机数小于交叉算子CR则进行交换。交叉算子系数越大,交叉个体从变异个体获得的信息越大,全局搜索能力越强,收敛慢;反之,交叉算子越小,其局域搜索能力就越强,易早熟。交叉公式如下,其中U表示交叉种群,j表示个体的第j个分量,r为一个随机数,CR为交叉算子, i = j 这个约束表示至少有一个分量被交换 。
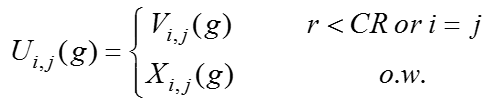
选择操作
选择操作在标准的DE算法中是指用当前种群个体与交叉个体各自的适应函数值相比,选择好的个体为下一代种群个体。具体操作方式如下,其中 f(expression)为适应值函数,就是将种群的个体(本质是一个向量)映射为一个实数。
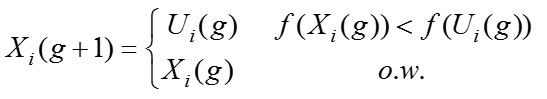
算法流程
标准DE算法迭代过程如下:
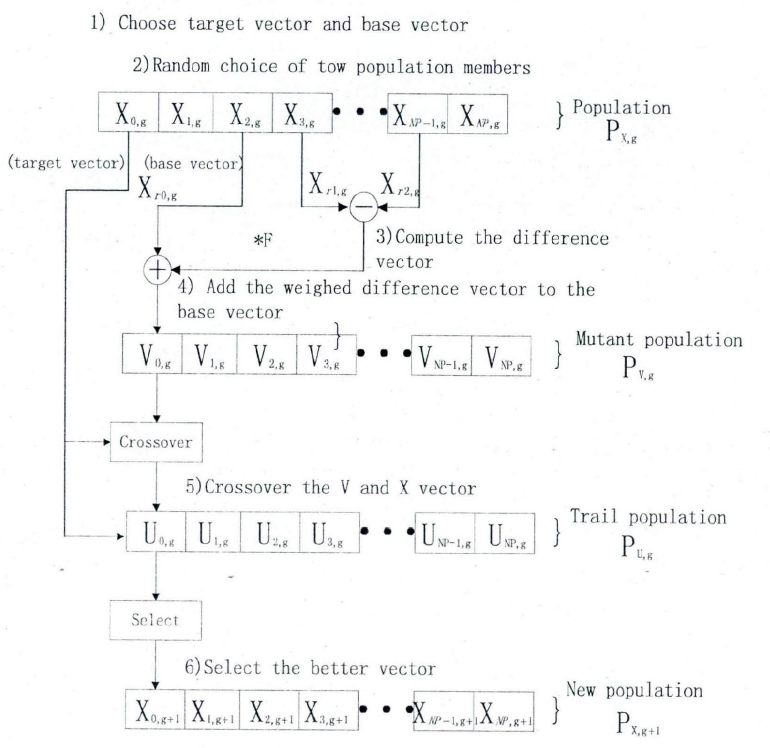
标准DE算法流程图如下:
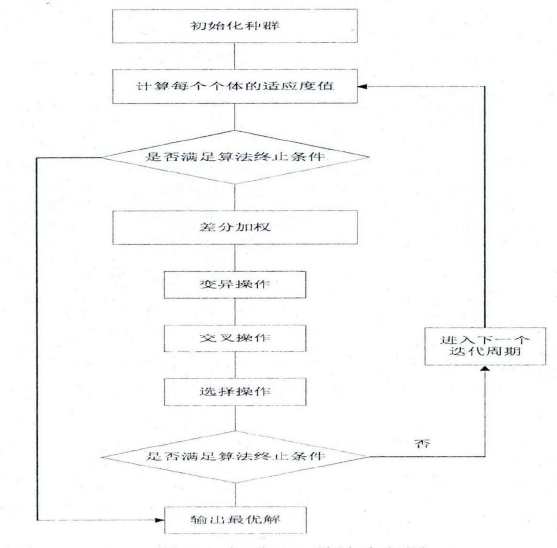
标准DE算法伪代码如下:

C++ 实现
//DE.h 头文件
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
# pragma region Default Setting
using namespace std;
//parameter
const int D(30);//维数
const int NP(100);//种群规模
const double F(0.5);//控制参数F
const double CR(0.5);//控制参数CR
const int N(1000);//迭代次数
//产生a和b间的随机整数
int RandomInt(int a, int b)
{
int Res = 0;
if (a<b)
{
Res = rand() % (b - a) + a;
}
else if (a >= b)
{
Res = rand() % (a - b) + b;
}
return Res;
}
//产生a和b间的随机实数
double RandomDouble(int a, int b)
{
double Res = 0;
if (a < b)
{
Res = a + (b - a) * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0);
}
else if (a > b)
{
Res = b + (a - b) * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0);
}
else
{
Res = (double)a;
}
return Res;
}
# pragma endregion
# pragma region 连续个体类
class Vector
{
public:
double Element[D];//个体元素值
double FitnessValue;//个体目标函数值
Vector();
~Vector();
double Evaluate();//个体评价函数
};
Vector::Vector()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < D; i++)
{
Element[i] = RandomDouble(UPBOUND, LOWBOUND);//个体元素初始化
}
}
Vector::~Vector()
{
}
double Vector::Evaluate()
{
FitnessValue = 0;
//==============适应值函数=================
for (size_t i = 0; i < D; i++)
{
FitnessValue += pow(Element[i], 2);//Function 1
//FitnessValue += pow(Element[i], 2) - 10 * cos(2 *3.14*Element[i]) + 10;//Function 2
}
//================================================
return FitnessValue;
}
# pragma endregion
# pragma region DE 算法类
class DE
{
public:
DE();
~DE();
void Initial(Vector* Init);//评价初始种群
void Mutation(Vector* Init, Vector* Muta);//变异操作
void Cross(Vector* Init, Vector* Muta, Vector* Cross);//交叉操作
void Select(Vector* Init, Vector* Cross);//选择操作
int BestVector();//挑出当前种群最优个体
void WriteLine(int Index);//输出中间结果
void DE_Run();//DE算法程序
public:
int BestVect;//当前种群中的最优个体
double BestValue;//当前最优个体的适应值
Vector PopInit[NP];//当前种群
Vector PopMuta[NP];//变异种群
Vector PopCross[NP];//交叉种群
int randA;//随机数
int randB;//随机数
int randC;//随机数
double resultInit[NP];//父代种群适应值
double resultCross[NP];//子代种群适应值
clock_t clockBegin, clockEnd;//记录计算时间
int Step = 100;//输出间隔
};
DE::DE()
{
}
DE::~DE()
{
}
void DE::Initial(Vector* Init)
{
for (int i = 0; i < NP; i++)
{
resultInit[i] = Init[i].Evaluate();
}
}
void DE::Mutation(Vector* Init, Vector* Muta)
{
for (int i = 0; i < NP; i++)
{
//先产生合适的随机数
do
{
randA = RandomInt(0, NP);
randB = RandomInt(0, NP);
randC = RandomInt(0, NP);
} while (i == randA || i == randB || i == randC || randA == randB || randA == randC
|| randB == randC);
for (int j = 0; j < D; j++)
{
//变异策略
Muta[i].Element[j] = Init[randC].Element[j] + F * (Init[randA].Element[j] - Init[randB].Element[j]);
}
}
}
void DE::Cross(Vector* Init, Vector* Muta, Vector* Cross)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < NP; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < D; j++)
{
if (RandomDouble(0,1)<CR)
{
Cross[i].Element[j] = Muta[i].Element[j];
}
else
{
Cross[i].Element[j] = Init[i].Element[j];
}
}
}
}
void DE::Select(Vector* Init, Vector* Cross)
{
for (int i = 0; i < NP; i++)
{
resultCross[i] = Cross[i].Evaluate();
if ((resultInit[i] - resultCross[i])>1E-8)
{
resultInit[i] = resultCross[i];
for (int j = 0; j < D; j++)
{
Init[i].Element[j] = Cross[i].Element[j];
}
}
}
}
int DE::BestVector()
{
BestVect = 0;
BestValue = resultInit[0];
for (size_t i = 0; i < NP; i++)
{
if (BestValue > resultInit[i])
{
BestVect = i;
BestValue = resultInit[i];
}
}
return BestVect;
}
void DE::WriteLine(int Index)
{
if (Index%Step == 0)
{
cout << Index << " " << scientific << setprecision(2) << resultInit[BestVect] << endl;
}
}
void DE::DE_Run()
{
clockBegin = clock();//计时开始
Initial(PopInit);//评价初始种群
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
Mutation(PopInit, PopMuta);//变异
Cross(PopInit, PopMuta, PopCross);//交叉
Select(PopInit, PopCross);//选择
BestVector();//最好个体
WriteLine(i);//输出
}
clockEnd = clock();//计时结束
cout << " 算法耗时(ms):" << difftime(clockEnd, clockBegin) << endl;//输出最终结果
}# include "DE.h"
void main()
{
srand((int)time(NULL));
//=====标准DE=====
DE Test;
Test.DE_Run();
system("pause");
}






















 1301
1301

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








