设置
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
何时使用顺序模型
顺序模型适用于简单的层堆栈,其中每一层正好具有一个输入张量和一个输出张量。
从原理上讲,以下顺序模型:
# Define Sequential model with 3 layers
model = keras.Sequential(
[
layers.Dense(2, activation="relu", name="layer1"),
layers.Dense(3, activation="relu", name="layer2"),
layers.Dense(4, name="layer3"),
]
)
# Call model on a test input
x = tf.ones((3, 3))
y = model(x)
等效于以下功能:
# Create 3 layers
layer1 = layers.Dense(2, activation="relu", name="layer1")
layer2 = layers.Dense(3, activation="relu", name="layer2")
layer3 = layers.Dense(4, name="layer3")
# Call layers on a test input
x = tf.ones((3, 3))
y = layer3(layer2(layer1(x)))
顺序模型不适用于以下情况:
- 您的模型有多个输入或多个输出
- 您的任何一层都有多个输入或多个输出
- 您需要进行图层共享
- 您需要非线性拓扑(例如,残余连接,多分支模型)
创建一个顺序模型
您可以通过将图层列表传递给Sequential构造函数来创建Sequential模型:
model = keras.Sequential(
[
layers.Dense(2, activation="relu"),
layers.Dense(3, activation="relu"),
layers.Dense(4),
]
)
可通过layers属性访问其图层:
model.layers
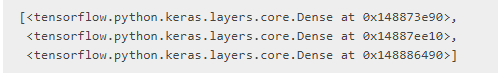
您还可以通过add()方法增量创建一个顺序模型:
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Dense(2, activation="relu"))
model.add(layers.Dense(3, activation="relu"))
model.add(layers.Dense(4))
请注意,还有一个相应的pop()方法可以删除图层:顺序模型的行为非常类似于图层列表。
model.pop()
print(len(model.layers)) # 2
还要注意,就像Keras中的任何层或模型一样,Sequential构造函数也接受name参数。 这对于用语义上有意义的名称注释TensorBoard图很有用。
model = keras.Sequential(name="my_sequential")
model.add(layers.Dense(2, activation="relu", name="layer1"))
model.add(layers.Dense(3, activation="relu", name="layer2"))
model.add(layers.Dense(4, name="layer3"))
预先指定输入形状
通常,Keras中的所有图层都需要知道其输入的形状,以便能够创建其权重。 因此,当您创建这样的图层时,最初没有权重:
layer = layers.Dense(3)
layer.weights # Empty
由于权重的形状取决于输入的形状,因此会在首次调用输入时创建其权重:
# Call layer on a test input
x = tf.ones((1, 4))
y = layer(x)
layer.weights # Now it has weights, of shape (4, 3) and (3,)
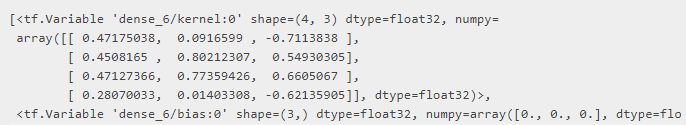
当然,这也适用于顺序模型。 当实例化没有输入形状的顺序模型时,它不是“构建”的:它没有权重(调用model.weights会导致错误,仅说明这一点)。 权重是在模型首次看到一些输入数据时创建的:
model = keras.Sequential(
[
layers.Dense(2, activation="relu"),
layers.Dense(3, activation="relu"),
layers.Dense(4),
]
) # No weights at this stage!
# At this point, you can't do this:
# model.weights
# You also can't do this:
# model.summary()
# Call the model on a test input
x = tf.ones((1, 4))
y = model(x)
print("Number of weights after calling the model:", len(model.weights)) # 6
一旦“构建”了模型,就可以调用其summary()方法以显示其内容:
model.summary()

但是,当逐步构建顺序模型时,能够显示到目前为止的模型摘要(包括当前输出形状)非常有用。 在这种情况下,应该通过将Input对象传递给模型来启动模型,以便从一开始就知道其输入形状:
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add(keras.Input(shape=(4,)))
model.add(layers.Dense(2, activation="relu"))
model.summary()

请注意,Input对象不显示为model.layers的一部分,因为它不是图层:
model.layers
一个简单的替代方法是只将input_shape参数传递给您的第一层:
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Dense(2, activation="relu", input_shape=(4,)))
model.summary()

使用这样的预定义输入形状构建的模型始终具有权重(甚至在查看任何数据之前),并且始终具有定义的输出形状。
通常,建议的最佳做法是始终事先指定顺序模型的输入形状(如果您知道它是什么)。
常见的调试工作流程:add()+ summary()
在构建新的顺序体系结构时,使用add()和频繁打印模型摘要来逐步堆叠图层很有用。 例如,这使您可以监视Conv2D和MaxPooling2D图层堆栈如何对图像特征图进行下采样:
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add(keras.Input(shape=(250, 250, 3))) # 250x250 RGB images
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, 5, strides=2, activation="relu"))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation="relu"))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D(3))
# Can you guess what the current output shape is at this point? Probably not.
# Let's just print it:
model.summary()
# The answer was: (40, 40, 32), so we can keep downsampling...
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation="relu"))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation="relu"))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D(3))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation="relu"))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation="relu"))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D(2))
# And now?
model.summary()
# Now that we have 4x4 feature maps, time to apply global max pooling.
model.add(layers.GlobalMaxPooling2D())
# Finally, we add a classification layer.
model.add(layers.Dense(10))

拥有模型后该怎么办
一旦模型架构准备就绪,您将需要:
- 训练模型,评估模型并进行推理。 请参阅我们的内置循环培训和评估指南
- 将模型保存到磁盘并还原。 请参阅我们的序列化和保存指南
- 通过利用多个GPU来加速模型训练。 请参阅我们的多GPU和分布式培训指南
使用顺序模型进行特征提取
一旦建立了顺序模型,它的行为就类似于功能API模型。 这意味着每个图层都具有输入和输出属性。 这些属性可用于执行整洁的事情,例如快速创建一个模型,以提取顺序模型中所有中间层的输出:
initial_model = keras.Sequential(
[
keras.Input(shape=(250, 250, 3)),
layers.Conv2D(32, 5, strides=2, activation="relu"),
layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation="relu"),
layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation="relu"),
]
)
feature_extractor = keras.Model(
inputs=initial_model.inputs,
outputs=[layer.output for layer in initial_model.layers],
)
# Call feature extractor on test input.
x = tf.ones((1, 250, 250, 3))
features = feature_extractor(x)
这是一个类似的示例,仅从一层中提取要素:
initial_model = keras.Sequential(
[
keras.Input(shape=(250, 250, 3)),
layers.Conv2D(32, 5, strides=2, activation="relu"),
layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation="relu", name="my_intermediate_layer"),
layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation="relu"),
]
)
feature_extractor = keras.Model(
inputs=initial_model.inputs,
outputs=initial_model.get_layer(name="my_intermediate_layer").output,
)
# Call feature extractor on test input.
x = tf.ones((1, 250, 250, 3))
features = feature_extractor(x)
使用顺序模型迁移学习
迁移学习包括冻结模型中的底层并仅训练顶层。 如果您不熟悉它,请务必阅读我们的迁移学习指南。
这是涉及顺序模型的两个常见的迁移学习蓝图。
首先,假设您有一个顺序模型,并且要冻结除最后一层之外的所有层。 在这种情况下,您只需遍历model.layers并在除最后一层之外的每一层上设置layer.trainable = False。 像这样:
model = keras.Sequential([
keras.Input(shape=(784))
layers.Dense(32, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(32, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(32, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(10),
])
# Presumably you would want to first load pre-trained weights.
model.load_weights(...)
# Freeze all layers except the last one.
for layer in model.layers[:-1]:
layer.trainable = False
# Recompile and train (this will only update the weights of the last layer).
model.compile(...)
model.fit(...)
另一个常见的蓝图是使用顺序模型来堆叠预先训练的模型和一些新初始化的分类层。 像这样:
# Load a convolutional base with pre-trained weights
base_model = keras.applications.Xception(
weights='imagenet',
include_top=False,
pooling='avg')
# Freeze the base model
base_model.trainable = False
# Use a Sequential model to add a trainable classifier on top
model = keras.Sequential([
base_model,
layers.Dense(1000),
])
# Compile & train
model.compile(...)
model.fit(...)
如果您进行迁移学习,您可能会经常使用这两种模式。
这就是您需要了解的顺序模型的全部内容!
要了解有关在Keras中构建模型的更多信息,请参见:






















 4068
4068











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








