1 数列绝对值
Prove that if
lim
{
a
n
}
→
a
\lim \{a_n\}\to a
lim{an}→a then
lim
{
∣
a
n
∣
}
→
∣
a
∣
\lim \{|a_n|\}\to|a|
lim{∣an∣}→∣a∣. Is the converse true?
Prove:
By definition, if
lim
n
→
∞
a
n
=
a
\lim_{n \rightarrow \infty} a_n=a
n→∞liman=a then for all
ε
>
0
\varepsilon>0
ε>0 there exists a
N
∈
N
N \in \mathbb{N}
N∈N such that
n
≥
N
n \geq N
n≥N implies
∣
a
n
−
a
∣
≤
ε
|a_n-a| \leq \varepsilon
∣an−a∣≤ε.
-We may also verify case-by-case that ∣ ∣ x ∣ − ∣ y ∣ ∣ ≤ ∣ x − y ∣ \big||x|-|y|\big| \leq |x-y| ∣∣∣x∣−∣y∣∣∣≤∣x−y∣ for all x , y ∈ R x,y \in \mathbb{R} x,y∈R. In particular, ∣ ∣ a n ∣ − ∣ a ∣ ∣ ≤ ∣ a n − a ∣ . ( 1 ) \big||a_n|-|a|\big| \leq |a_n-a|. \,\,\, (1) ∣∣∣an∣−∣a∣∣∣≤∣an−a∣.(1)
Combining these yields the proof.
评注:反之,不正确! 如
∣
(
−
1
)
n
∣
|(-1)^n|
∣(−1)n∣ 极限是
1
1
1,但是
(
−
1
)
n
(-1)^n
(−1)n 极限不存在,
但是如果
∣
a
n
∣
|a_n|
∣an∣ 极限是
0
0
0,能推出
a
n
a_n
an 极限为 0,原因在于证明过程的
(
1
)
(1)
(1)不等式变成了等号., 即
∣
∣
a
n
∣
−
∣
0
∣
∣
=
∣
a
n
−
0
∣
\big||a_n|-|0|\big| =|a_n-0|
∣∣∣an∣−∣0∣∣∣=∣an−0∣.
2与子列极限关系
Prove that if the subsequences
a
2
n
a_{2n}
a2n and
a
2
n
+
1
a_{2n+1}
a2n+1 of a sequence
a
n
a_n
an of real numbers both converge to the same limit
l
l
l, then
a
n
a_n
an converges to
l
l
l.
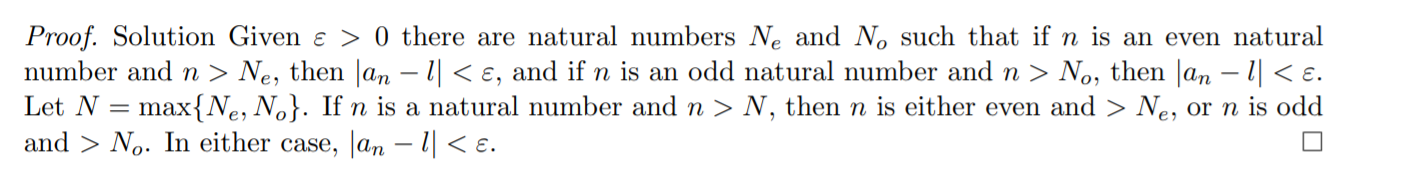























 528
528











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








