如果数据集没有很大,同时在训练集上又拟合得很好,但是在测试集的效果却不是很好,这时候就要使用正则化来使得其拟合能力不会那么强。
import numpy as np
import sklearn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sklearn.datasets
from reg_utils import load_2D_dataset,compute_cost,forward_propagation,predict,predict_dec,relu,sigmoid
from reg_utils import initialize_parameters,backward_propagation,update_parameters,plot_decision_boundary
import scipy.io
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"]=(7,4) #the figure size,which wight is 7,while height is 4
plt.rcParams["image.interpolation"]="nearest" #
plt.rcParams["image.cmap"]="gray"
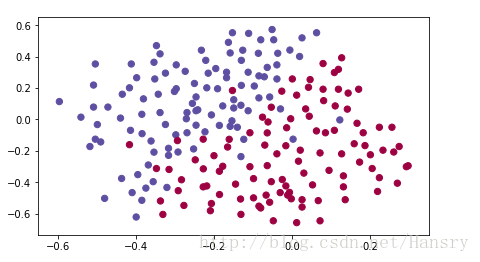
train_x,train_y,test_x,test_x,test_y=load_2D_dataset()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import h5py
import sklearn
import sklearn.datasets
import sklearn.linear_model
import scipy.io
####reg_utils.py##### 以下是reg_utils.py 文件的内容
def sigmoid(x):
s = 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
return s
def relu(x):
s = np.maximum(0,x)
return s
def load_planar_dataset(seed):
np.random.seed(seed)
m = 400 # number of examples
N = int(m/2) # number of points per class
D = 2 # dimensionality
X = np.zeros((m,D)) # data matrix where each row is a single example
Y = np.zeros((m,1), dtype='uint8') # labels vector (0 for red, 1 for blue)
a = 4 # maximum ray of the flower
for j in range(2):
ix = range(N*j,N*(j+1))
t = np.linspace(j*3.12,(j+1)*3.12,N) + np.random.randn(N)*0.2 # theta
r = a*np.sin(4*t) + np.random.randn(N)*0.2 # radius
X[ix] = np.c_[r*np.sin(t), r*np.cos(t)]
Y[ix] = j
X = X.T
Y = Y.T
return X, Y
def initialize_parameters(layer_dims):
"""
Arguments:
layer_dims -- python array (list) containing the dimensions of each layer in our network
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", ..., "WL", "bL":
W1 -- weight matrix of shape (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])
b1 -- bias vector of shape (layer_dims[l], 1)
Wl -- weight matrix of shape (layer_dims[l-1], layer_dims[l])
bl -- bias vector of shape (1, layer_dims[l])
Tips:
- For example: the layer_dims for the "Planar Data classification model" would have been [2,2,1].
This means W1's shape was (2,2), b1 was (1,2), W2 was (2,1) and b2 was (1,1). Now you have to generalize it!
- In the for loop, use parameters['W' + str(l)] to access Wl, where l is the iterative integer.
"""
np.random.seed(3)
parameters = {}
L = len(layer_dims) # number of layers in the network
for l in range(1, L):
parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]) / np.sqrt(layer_dims[l-1])
parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l], 1))
assert(parameters['W' + str(l)].shape == layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])
assert(parameters['W' + str(l)].shape == layer_dims[l], 1)
return parameters
def forward_propagation(X, parameters):
"""
Implements the forward propagation (and computes the loss) presented in Figure 2.
Arguments:
X -- input dataset, of shape (input size, number of examples)
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", "W2", "b2", "W3", "b3":
W1 -- weight matrix of shape ()
b1 -- bias vector of shape ()
W2 -- weight matrix of shape ()
b2 -- bias vector of shape ()
W3 -- weight matrix of shape ()
b3 -- bias vector of shape ()
Returns:
loss -- the loss function (vanilla logistic loss)
"""
# retrieve parameters
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
W3 = parameters["W3"]
b3 = parameters["b3"]
# LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID
Z1 = np.dot(W1, X) + b1
A1 = relu(Z1)
Z2 = np.dot(W2, A1) + b2
A2 = relu(Z2)
Z3 = np.dot(W3, A2) + b3
A3 = sigmoid(Z3)
cache = (Z1, A1, W1, b1, Z2, A2, W2, b2, Z3, A3, W3, b3)
return A3, cache
def backward_propagation(X, Y, cache):
"""
Implement the backward propagation presented in figure 2.
Arguments:
X -- input dataset, of shape (input size, number of examples)
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if cat, 1 if non-cat)
cache -- cache output from forward_propagation()
Returns:
gradients -- A dict








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章














 781
781











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








