(1~20)
1.Asuna and the Mosquitoes
(贪心)



具体的实现方法:
考虑最大值初始的奇偶性:
最大值最初为奇数,则我们让一个偶数将所有奇数操作至 0 或 1。钦定 1 个奇数,通过这个 奇数 与所有偶数作操作,直至它们变成 0 或 1,记此时的最大值(奇数)为 S1。
最大值最初为偶数,同理。我们让一个奇数先把所有偶数干掉,再让这个偶数去把这个奇数干掉,记此时的最大值为 S2。
显然,只有 S1 和 S2 是可能最大的。
故若干次操作后,送的塔的最大美观度为 max(S1,S2)。
由于奇数加奇数等于偶数,所以无论怎么消耗,最终剩下的奇数的数量一定不变,最终剩下的奇数:一堆没用的1,和一个最大值(奇数),偶数全被消耗殆尽了,直接输出就好了,时间复杂度O(1)。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
ll t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll n;cin>>n;
ll a[n+1];
ll sum1=0;ll sum2=0;
ll sum0=0;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
(a[i]&1)?sum1++:sum2++;
sum0+=a[i];
}
//全是奇数或者全是偶数不可操作取最大值
if(sum1==n||sum2==n){
cout<<*max_element(a+1,a+1+n)<<'\n';
}else{
ll jishu_1=sum1-1;
//ll gongxian=sum0-jishu_1-max(a[i]);
//max(a[i])=gongxian+max(a[i]);
ll ans=sum0-jishu_1;
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
}
return 0;
}2.Lady Bug

必须是:
假如:一个字符串的1是奇数位,则另一个字符串的0必须是偶数位,这样才能顺利交换,反之亦然。

(WA)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
ll t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll n;cin>>n;
string a,b;cin>>a>>b;
//a全为0或者全为1
if(a.find("0")==string::npos)cout<<"YES"<<'\n';
else if(a.find("1")==string::npos)cout<<"YES"<<'\n';
else{
a=" "+a;
b=" "+b;
ll ji_1=0;
ll ou_0=0;
ll ou_1=0;
ll ji_0=0;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(i&1){
if(a[i]=='1')ji_1++;
if(b[i]=='0')ji_0++;
}else{
if(a[i]=='1')ou_1++;
if(b[i]=='0')ou_0++;
}
}
if(ji_1<=ou_0&&ou_1<=ji_0){
cout<<"YES"<<'\n';
}else cout<<"NO"<<'\n';
}
}
return 0;
}3.Interesting Ratio
(线性筛,数论)


#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll N=1e7;
vector<bool> vis(N,1);
void isPrimes(){
vis[0]=0;
vis[1]=0;
for(ll i=2;i<=N;i++){
if(vis[i]){
for(ll j=i*i;j<=N;j+=i){
vis[j]=0;
}
}
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
isPrimes();
set<ll> s;
for(ll i=2;i<=N;i++){
if(vis[i]==1){
s.insert(i);
}
}
ll t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll n;cin>>n;
ll ans=0;
for(auto it:s){
if(it>n)break;
ans+=(n/it);
}
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
}4.Place of the Olympiad
(二分)


#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll N=1e9+5;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
ll t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll n,m,k;cin>>n>>m>>k;
ll minn=LONG_MAX;
if(n*m<k)minn=0;//连全放长度为一的凳子都满足不了
else if(k==1)minn=1;
ll l=1,r=N;
ll mid=0;
while(l<=r){
mid=(l+r)/2;
if((m/(mid+1)*mid+(m%(mid+1)))*n>=k)r=mid-1;
else l=mid+1;
}
minn=l;
cout<<minn<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}5.C. Combination Lock
(构造,同余)

这个规律已经屡见不鲜了,但是如果直接根据输入输出写代码,得到的代码不一定是对的,我们还是要知道这个题目的本质。



#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int a[200005];
bool cmp(int x,int y){
return x>y;
}
signed main(){
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--){
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n%2==0){
cout<<"-1\n";
}
else{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i+=2){
cout<<i<<" ";
}
for(int i=2;i<=n;i+=2){
cout<<i<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
}
}
return 0;
}


6.Serval and Final MEX
(构造)

WA代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
ll t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll n;cin>>n;
vector<ll> a(n,0);
set<ll> s;
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++)cin>>a[i],s.insert(a[i]);
if(find(a.begin(),a.end(),0)==a.end()){
cout<<1<<'\n'<<1<<" "<<n<<'\n';
}else{
if(s.size()==1){
cout<<3<<'\n';
cout<<1<<" "<<n/2<<'\n';
cout<<n/2+1<<" "<<n<<'\n';
}//样例三
else{
cout<<2<<'\n';
cout<<1<<" "<<n/2<<'\n';
cout<<n/2+1<<" "<<n<<'\n';
}
}
}
return 0;
} 
WA
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
int T, n;
ll a[5005];
// 检查 0-based 区间 [l..r] 是否包含 0
inline bool zero(int l, int r) {
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return true;
}
return false;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
int mid = n / 2;
// 左半段 [0..mid-1],右半段 [mid..n-1]
bool leftHas0 = zero(0, mid - 1);
bool rightHas0 = zero(mid, n - 1);
if (rightHas0 && leftHas0) {
// 两半都有 0 → 三步
cout << 3 << '\n';
// 1) 合并右半 [mid..n-1]
cout << mid+1 << ' ' << n << '\n';
// 2) 合并左半 [0..mid-1]
cout << 1 << ' ' << mid << '\n';
// 3) 合并头两位 [0..1]
cout << 1 << ' ' << 2 << '\n';
}
else if (!leftHas0&&rightHas0) {
// 只有右半有 0 → 两步
cout << 2 << '\n';
// 合并右半 [mid..n-1]
cout << mid+1 << ' ' << n << '\n';
// 合并剩下 [0..mid-1]
cout << 1 << ' ' << mid << '\n';
}
else if (leftHas0&&!rightHas0) {
// 只有左半有 0 → 两步
cout << 2 << '\n';
// 合并左半 [0..mid-1]
cout << 1 << ' ' << mid << '\n';
// 合并剩下 [mid..n-1]
cout << mid+1 << ' ' << n << '\n';
}
else {
// 都没有 0 → 一步
cout << 1 << '\n';
// 合并整段 [0..n-1]
cout << 1 << ' ' << n << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
AC
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
int T, n;
ll a[5005];
// 判断 0-based 区间 [l..r] 中是否含 0
inline bool zero(int l, int r) {
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) return true;
}
return false;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
// 前 n-2 元素:0-based [0..n-3]
// 后 2 元素:0-based [n-2..n-1]
bool headHas0 = zero(0, n-3);
bool tailHas0 = zero(n-2, n-1);
if (tailHas0 && headHas0) {
// 两段都有 0 → 三步
// [n-2..n-1], [0..n-3], [0..1]
cout << 3 << "\n";
cout << (n-2)+1 << " " << (n-1)+1 << "\n";
cout << 1 << " " << (n-3)+1 << "\n";
cout << 1 << " " << 2 << "\n";
}
else if (tailHas0) {
// 只有后两位有 0 → 两步
// [n-2..n-1], [0..n-2]
cout << 2 << "\n";
cout << (n-2)+1 << " " << (n-1)+1 << "\n";
cout << 1 << " " << (n-2)+1 << "\n";
}
else if (headHas0) {
// 只有前 n-2 位有 0 → 两步
// [0..n-3], [0..2]
cout << 2 << "\n";
cout << 1 << " " << (n-3)+1 << "\n";
cout << 1 << " " << 3 << "\n";
}
else {
// 都没有 0 → 一步
// [0..n-1]
cout << 1 << "\n";
cout << 1 << " " << n << "\n";
}
}
return 0;
}
细节点:
如果要先从后开始合并,如果是等于三的情况,后半段合并之后还剩一个数,所以从一开始合并的话,右端点是要加一的。从前开始合并同理。
7.Disappearing Permutation(WA)
(dfs)


AC
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=100005;
int t,n,p[N],d[N],ans;
bool f[N];
void dfs(int i){
if(!f[i]){//剪枝
f[i]=1;
ans++;
dfs(p[i]);
}
}
void solve(){
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)f[i]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>p[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>d[i];
dfs(d[i]);
cout<<ans<<' ';
}
cout<<'\n';
ans=0;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>t;
while(t--)solve();
return 0;
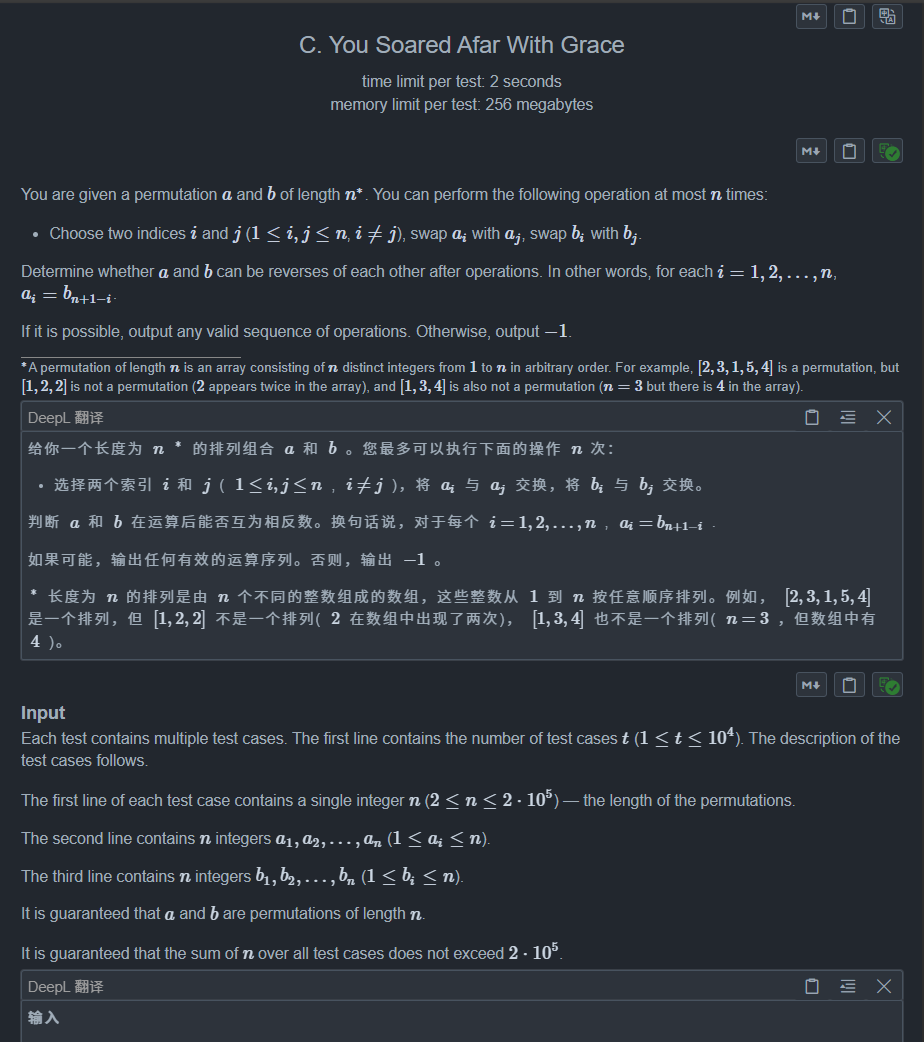
}8.You Soared Afar With Grace
(模拟)





#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve() {
ll n;
cin >> n;
// 1-based 数组 a, b,以及 bpos 用于记录 b 中每个值的位置
vector<ll> a(n+1, 0), b(n+1, 0), bpos(n+1, 0);
// 读入排列 a
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
// flag 检测 b 是否已经是 a 的反序
// 同时填充 bpos[value] = index
ll flag = 0;
for (ll j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
cin >> b[j];
// 如果 b[j] != a[n+1-j] 则说明还没达到反序
flag |= (b[j] != a[n - j + 1]);
bpos[b[j]] = j;
}
// 如果已经反序,无需操作
if (flag == 0) {
cout << 0 << '\n';
return;
}
// 存储交换操作
vector<pair<ll,ll>> ops;
// mid 用于记录“固定点”下标(a[i] == b[i])
ll mid = 0;
// 可行性检查:
// 1) 对每个 i,检查 a[i] 在 b 中的位置是否恰好是 n+1-i
// 2) 检查固定点 a[i] == b[i] 只允许奇数长度中心出现一次
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// 映射一致性:a[i] 出现在 bpos[a[i]],应当等于对称下标 n+1-i
if (bpos[a[i]] != n + 1 - i) {
cout << -1 << '\n';
return;
}
// 固定点检查
if (a[i] == b[i]) {
// 偶数长度不允许固定点,或已出现过一个固定点也不行
if (n % 2 == 0 || mid != 0) {
cout << -1 << '\n';
return;
}
mid = i;
}
}
// 辅助 Lambda:同时在 a, b, bpos 上执行一次对调,并记录操作
auto change = [&](int x, int y) {
if (x == y) return;
ops.emplace_back(x, y);
swap(a[x], a[y]);
swap(b[x], b[y]);
// bpos 里存的是 b 的值对应的下标,需要同步更新
swap(bpos[b[x]], bpos[b[y]]);
};
// 如果存在固定点,将它交换到中间位置 (n+1)/2
if (mid) {
change(mid, (n + 1) / 2);
}
// 对于 i = 1..n/2,将 a[i] 在 b 中的当前位置调到对称位 n+1-i
for (ll i = 1; i <= n/2; i++) {
int curPos = bpos[a[i]]; // a[i] 现在在 b 中的位置
int target = n - i + 1; // 它应当去的位置
change(curPos, target);
}
// 输出操作序列
cout << ops.size() << '\n';
for (auto [l, r] : ops) {
cout << l << " " << r << '\n';
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr);
ll t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
9. Breach of Faith
(构造)

AC
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define unsyncio() cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false)
int main() {
unsyncio();
int tt;
cin >> tt;
while (tt--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<long long> a(n * 2);
for (auto &i : a) cin >> i;
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
long long s1 = 0, s0 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n * 2-1; i += 2) {
s1 += a[i];
s0 += a[i + 1];
}
s1 += a[n * 2 - 1];
s0 -= a[n * 2 - 1];
a.push_back(s1 - s0);
swap(a[n * 2], a[n * 2 - 1]);
for (auto i : a) cout << i << ' ';
cout << '\n';
}
}


如果还看不懂,就把数组倒置一下看。

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
ll t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll n;cin>>n;
vector<ll> b(2*n,0);
for(ll i=0;i<2*n;i++)cin>>b[i];
sort(b.rbegin(),b.rend());
//for(ll i=0;i<2*n;i++)cout<<b[i]<<'\n';
ll s1=0;
ll s2=0;
for(ll i=0;i+1<2*n;i+=2){
s1+=b[i];
s2+=b[i+1];
}
ll a1=s1-s2;
//cout<<s1<<" "<<s2;
cout<<a1<<" ";
for(ll i=0;i<2*n;i++)cout<<b[i]<<" ";
cout<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}


10.Two Colors
(二分,组合数学)

正解:

想用双指针,一直没调对。。。放一个WA双指针代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve(){
ll n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<ll> color(m, 0);
for (ll i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> color[i];
}
sort(color.begin(), color.end());
if (m == 1) {
cout << 1 << '\n';
return;
}
ll ans = 0;
ll i = 0, j = 1; // 初始化i和j,确保i < j
while (i < m - 1) {
// 确保 i < j 并且尝试找到符合条件的 j
while (j < m && color[i] + color[j] < n) {
j++;
}
// 计算每一对的有效组合数
while (j < m) {
ll t=0;
if(color[j]>=n)t=color[j];//(8,16)8种,(8,17)也应该是8种而不是9种
t=color[j]-(color[j]-n+1);
ll cur=0;
if(color[j]<n){
cur=cur = min(color[i], color[j]) - (n - max(color[i], color[j])) + 1;
}else{
cur = min(color[i], color[j]) - (n - max(color[i], t)) + 1;
}
//cout<<color[i]<<" "<<color[j]<<" "<<cur<<'\n';
ans += cur;
j++;
}
i++;
j = i + 1; // 更新 j 保证 j 始终大于 i
}
cout << ans * 2 << '\n'; // 乘以2是因为左右两边颜色可以交换
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
ll t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
11.Array Recoloring
(贪心)

不要读错题目了。刚开始还以为。。。就直接排序+前缀和输出了。。。
题目不难,只有一个细节点需要注意一下,就是要读懂第二个操作到底怎么染色的,注释掉的是错误代码。



AC code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll n,k;
void solve(){
cin>>n>>k;
vector<ll> color(n+1,0);
vector<ll> a(n+1,0);
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>color[i],a[i]=color[i];
ll ans=0;
if(k!=1){
sort(color.begin(),color.end());
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)color[i]+=color[i-1];
ans=color[n]-color[n-k-1];
}else{
int maxx = 0;
for (int i = 2 ; i <= n - 1 ; i++)
{
maxx = max((ll)maxx, a[i]);
}
ans=max(maxx + max(a[1], a[n]), a[1] + a[n]);
//sort(a.begin(),a.end());
//ans=a[n]+a[n-1];
}
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
ll t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}12.Counting Points
(暴力枚举)

正解:
由于 m≤2×1e5 所以,在所有的圆没有交点的情况下,并且均外切的情况下,x所能覆盖的最大区间长度也就是2m,4*1e5,所以直接暴力。


AC code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> pii;
ll n,m;
void solve(){
cin>>n>>m;
vector<pii> p(n,{0,0});
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++)cin>>p[i].first;
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++)cin>>p[i].second;
sort(p.begin(),p.end(),[&](const pii &x,const pii &y){
if(x.first==y.first)return x.second<y.second;
else return x.first<y.first;
});
ll ans=0;
//y<= sqrt( (r*r)-(x-xi)*(x-xi) );
map<ll,ll> mp;
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
auto[x,r]=p[i];
for(ll j=x-r;j<=x+r;j++){
mp[j]=max((ll)mp[j],(ll)sqrt(r*r-(x-j)*(x-j)));
}
}
for(pii mm: mp)ans+=mm.second*2+1;
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
ll t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}WA
本来想让时间复杂度变成O(1),直接输出,还是以失败告终(不想转牛角尖了,留个小尾巴,来日方长)。

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> pii;
ll n,m;
string relation(ll x1,ll r1,ll x2,ll r2){
if(x2-x1+r2<r1)return "neihan";
else if(x2-x1+r2==r1)return "neiqie";
else if((x2-x1)==(r1+r2))return "waiqie";
else if((x2-x1)<(r1+r2))return "xiangjiao";
else return "buxiangjiao";
}
ll jisuan(ll r){
ll x=(r-1)*(r-1)+1;
return x*x+4;
}
void solve(){
cin>>n>>m;
vector<pii> p(n,{0,0});
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++)cin>>p[i].first;
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++)cin>>p[i].second;
sort(p.begin(),p.end(),[&](const pii &x,const pii &y){
if(x.first==y.first)return x.second<y.second;
else return x.first<y.first;
});
ll ans=0;
//y<= sqrt( (r*r)-(x-xi)*(x-xi) );
for(ll i=0;i<n-1;i++){
auto[x1,r1]=p[i];
auto[x2,r2]=p[i+1];
string t=relation(x1,r1,x2,r2);
if(t=="neihan"||t=="waiqie"){
ans+=jisuan(r1)+jisuan(r2)-1;
}else if(t=="neihan"){
ans+=jisuan(max(r1,r2));
}else if(t=="buxiangjiao"){
ans+=jisuan(r1)+jisuan(r2);
}else{
ans+=jisuan(r1)+jisuan(r2)-( );
}
}
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
ll t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}13.Do You Love Your Hero and His Two-Hit Multi-Target Attacks?
(贪心,暴力枚举)


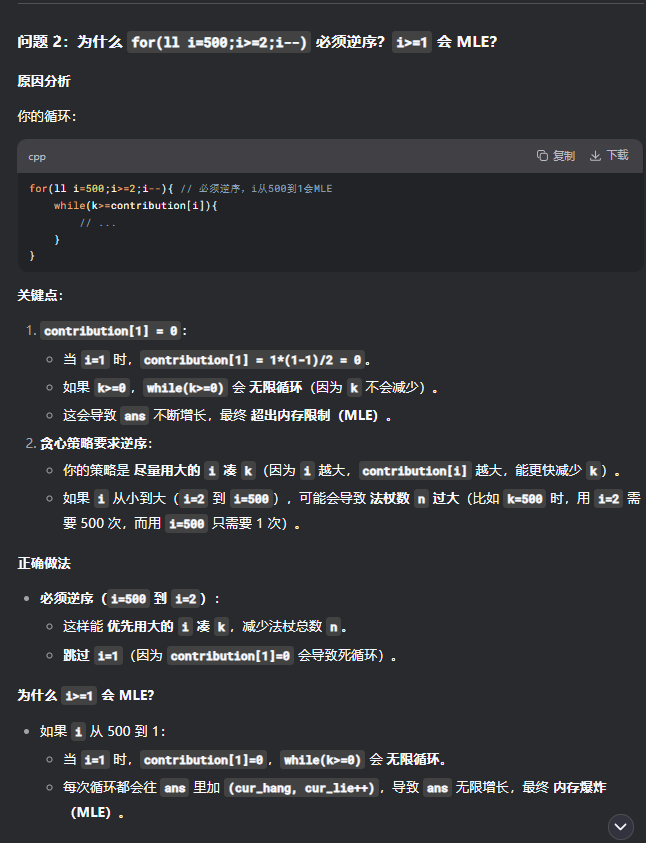
要读懂题目说的什么,放不超过500根法杖,要满足恰好有k对,注意是k对,不是k个,比如我放置了x根法杖,这x根法杖,任意两两之间如果满足条件都可以给出贡献点1,两两之间能构成也好不能构成也好,只要保证不超过500根棍子,并且总贡献点恰好为k即可。
AC code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> pii;
ll contribution[505];
void init(){
for(ll i=1;i<505;i++){
contribution[i]=i*(i-1)/2;
}
}
void solve(){
ll k;cin>>k;
/*特判的不对
if(k==0){
cout<<1<<" "<<2<<'\n'<<3<<" "<<4<<'\n';
return;
}
*/
if(k==0){
cout << "500\n";
for(int i=0;i<500;i++) cout<<i<<" "<<i+1000<<"\n"; // 500个点,全部不同行不同列
return;
}
ll cur_hang=-500;
ll cur_lie=0;
//cur_hang,cur_lie最好都从-1e9开始,防止溢出,当然这样也行
vector<pii> ans;
for(ll i=500;i>=2;i--){//必须逆序,i从500到1,会MLE
while(k>=contribution[i]){
for(ll j=1;j<=i;j++){
ans.push_back({cur_hang,cur_lie++});
}
k-=contribution[i];
cur_hang++;
}
}
cout<<ans.size()<<'\n';
for(auto[x,y]:ans){
cout<<x<<" "<<y<<'\n';
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
ll t;cin>>t;
init();
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
14. For Wizards, the Exam Is Easy, but I Couldn't Handle It
(暴力枚举,贪心)

好水的一道题,就是把一个数向后移动到某个位置,使得逆序对数量最大地减小。逆序对,不就是后面的数比前面小,所以在区间 (l,r] 中,我们要尽量让小于 al 的尽量多,大于 al 的尽量少。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
int main() {
int t; std::cin >> t;
for(; t; --t) {
// 输入
int n; std::cin >> n;
std::vector<int> arr(n+3, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
std::cin >> arr[i];
// 统计答案
int ans = 0, l = 1, r = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { // 固定 l
int cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0;
for(int j = i; j <= n; ++j) {
// 用cnt分别统计比 a[l] 大的和比 a[l] 小的
if(arr[j] > arr[i]) ++cnt2;
if(arr[j] < arr[i]) ++cnt1;
if(ans < cnt1 - cnt2) // 更新答案
ans = cnt1 - cnt2, l = i, r = j;
}
}
std::cout << l << ' ' << r << '\n'; // 输出
}
}15.Limited Repainting
(二分,贪心)

#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve() {
ll n, k;cin >> n >> k;
string s;cin >> s;
vector<ll> a(n + 1);
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> a[i];
// 目标串里没有 'B',不用操作
if (s.find('B') == string::npos) {
cout << 0 << '\n';
return;
}
ll l = 0, r = 1e9; // 搜索 [l, r] 内最小可行惩罚值
while (l <= r) {
ll mid = (l + r) / 2; // 本轮假设的最大允许惩罚
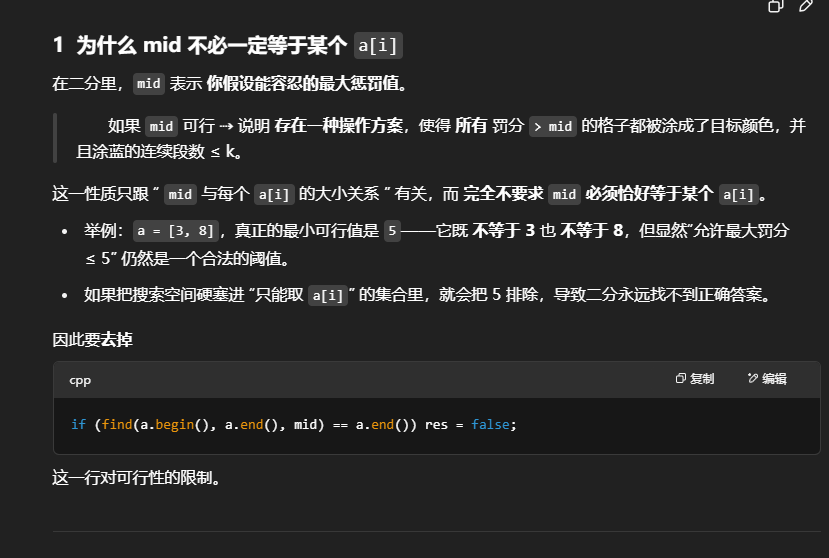
/*
if(find(a.begin(),a.end(),mid)==a.end()) res=false;
这句不可取,不该拒绝那些 “不在数组里” 的 mid 值,
*/
// ---- check(mid) 开始 ----
bool res = true;
ll cnt = 0; // 统计需要涂蓝的连续段数
char lst = 'R'; // 每次 check 都要重新置成 'R'
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (a[i] > mid) {
if (s[i - 1] == 'B' && lst != 'B') cnt++;
//如果s[i-1]=='B'&&lst=='B'则说明两个属于同一个蓝色段区间
lst = s[i - 1];
}
}
if (cnt > k) res = false;
// ---- check(mid) 结束 ----
if (res) r = mid-1; // mid 可以做到,再压缩右边界
else l = mid + 1; // mid 做不到,提高下界
}
cout << l << '\n'; // l == r,即最小可行惩罚阈值
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T; cin >> T;
while (T--) solve();
return 0;
}
16.Beautiful Sequence(WA)
(构造,模拟)


大佬的题解简直精妙绝伦 !
#include<bits/extc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int mod = 998244353;
int n;
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
vector<int>a(n + 5);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
int cnt = 0,ans = 0,now = 0;
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--)
{//从后往前循环,模拟即可
if (a[i] == 3)
{
cnt++;
now++;
}
else if (a[i] == 1)
ans = (ans + now - cnt + mod) % mod;
else
now = (now << 1) % mod;
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}17. Devyatkino
(构造,模拟)
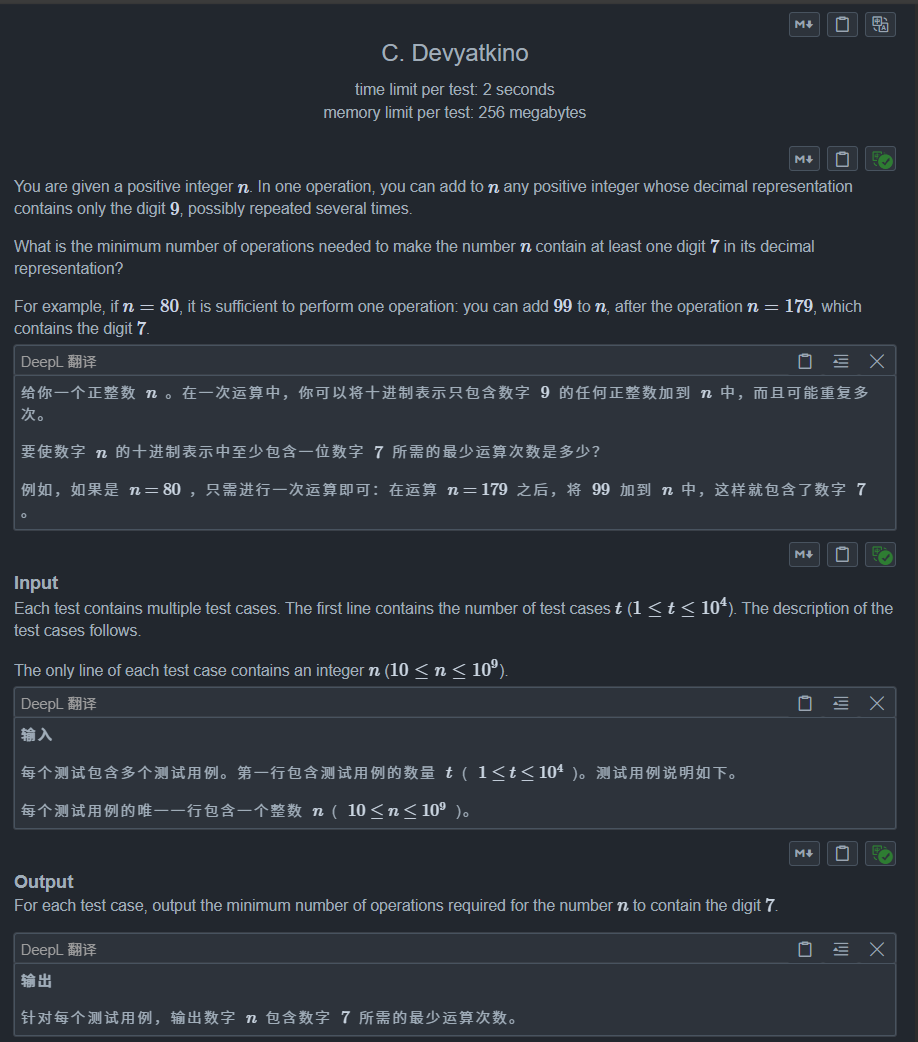
 本来想用bfs,结果样例10老是T。。。。大佬们的题解也是八仙过海各显神通。
本来想用bfs,结果样例10老是T。。。。大佬们的题解也是八仙过海各显神通。
bfs(TLE)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool containsSeven(long long num) {
// 判断数字 num 是否含有数字 7
while (num > 0) {
if (num % 10 == 7) {
return true;
}
num /= 10;
}
return false;
}
void solve() {
long long n;
cin >> n;
// 如果 n 已经包含数字 7,则不需要操作
if (containsSeven(n)) {
cout << 0 << endl;
return;
}
// BFS 初始化
queue<long long> q;
set<long long> visited;
q.push(n);
visited.insert(n);
int steps = 0;
// BFS 循环
while (!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
steps++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
long long current = q.front();
q.pop();
// 构造添加的数字(9, 99, 999, ...),直到足够大
long long add = 9;
while (add <= 1000000000) {
long long newNum = current + add;
if (containsSeven(newNum)) {
cout << steps << endl;
return;
}
if (visited.find(newNum) == visited.end()) {
visited.insert(newNum);
q.push(newNum);
}
// 生成下一个 9 99 999 等
add = add * 10 + 9;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
正解:



mdddddddddddddddd,,,,,,ll不是11,,,人在无语的时候真的会笑。。。

AC code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll jiu[] = {0, 9, 99, 999, 9999, 99999, 999999, 9999999, 99999999, 999999999};
void solve() {
ll n;
cin >> n;
// 检查n本身是否已经包含7
string s = to_string(n);
if (s.find('7') != string::npos) {
cout << 0 << '\n';
return;
}
// 枚举操作次数 i 从 0 到 9
for (ll i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
ll num = n + jiu[i]; // 只加一次 jiu[i]
string t = to_string(num);
if (t.find('7') != string::npos) {
cout << 1 << '\n';
return;
}
// 进一步的检查,是否可以通过多次加 9, 99, ... 来包含 7
for (ll j = 1; j <= 9; j++) {
num = n + jiu[j] * i;
string t = to_string(num);
if (t.find('7') != string::npos) {
cout << i << '\n';
return;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ll t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}

AC code
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int t,n;
int main(){
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>n;
for(int x=0;x<10;x++){
int res=7;
string s=to_string(n-x);
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
if(s[i]>='0'&&s[i]<='7') res=min(res,'7'-s[i]);
if(res<=x){
cout<<x<<endl;
break;
}
}
}
}18.Set of Strangers
(贪心,dfs)

一个格子上下左右颜色都不一样,则把这个格子变成最终颜色的操作次数是1,反之如果存在相同的颜色,则需要的操作次数为2(这个结论自行体会) ,至于哪个颜色被选定作为最终颜色,就是需要操作次数最多的那个颜色,因为我们要让操作次数最少,所以不管三七二十一,遍历整个地图,记录一下总数,最后减去所需要最大操作次数的颜色就好了,因为我们只需要除 需要最大操作次数的颜色 之外的颜色改变就行了。dfs模版题,nice。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll dx[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
ll dy[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ll t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
ll n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<ll>> mp(n + 1, vector<ll>(m + 1, 0));
// 读取表格
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (ll j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
cin >> mp[i][j];
}
}
// 记录每种颜色的操作次数
map<ll, ll> op;
// 遍历每个单元格,检查它与相邻单元格的颜色是否相同
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (ll j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
ll flag = 0;
for (ll k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
ll nx = i + dx[k];
ll ny = j + dy[k];
if (nx >= 1 && nx <= n && ny >= 1 && ny <= m) {
if (mp[i][j] == mp[nx][ny]) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
}
op[mp[i][j]] = max(op[mp[i][j]], 1 + flag); // 更新颜色的操作次数
}
}
// 计算最小操作次数
ll maxx = 0;
ll ans = 0;
for (auto it = op.begin(); it != op.end(); ++it) {
maxx = max(maxx, it->second); // 最大操作次数
ans += it->second; // 累加所有颜色的操作次数
}
// 输出结果:总操作次数 - 最大操作次数
cout << ans - maxx << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
19.Two Large Bags
(贪心,构造)

不难发现,我们可以把一个数放进第二个袋子里,所有跟它一样大的数就都能加一。
但我们不能太贪心,为了让方案合法,我们还要一个数保持不动,来达到两个袋子平衡的目的。
假设有 x 个一样大的数,那么就有 x−2 个数能晋级,而我们知道,x 和 x−2 的奇偶性相同,所以一定不亏。
我们可以开一个桶记录每个数字出现的次数,然后依次遍历 1 至 n,如果发现某个数字只出现了一次,我们发现会无法分配,于是直接输出 NO。否则如果某个数字出现了至少两次的话,给这个数字留下两个数就刚好可以分配了,多出来的数直接加一,交给比它大 1 的数来处理,以此类推。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve(){
ll n;cin>>n;
vector<ll> a(n);
unordered_map<ll,ll> mp;
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
mp[a[i]]++;
}
//for(auto[u,v]:mp)cout<<v<<'\n';
ll flag=0;
for(ll i=0;i<=n;i++){
if(mp[i]==1){//注意可不是mp[a[i]]==1
cout<<"NO"<<'\n';
return;
}else if(mp[i]>=2)mp[i+1]+=mp[i]-2;
}
cout<<"YES"<<'\n';
/*
我们并没有对a数组排序,a数组是乱序的,只有当所有元素排列整齐时,
所作的操作2才可能使两个袋内的元素尽可能的匹配上。因为,
如果我们要将 x 增加到 y,对面必然有数字 [x,y−1]。
一共n个元素,a[i]最多出现n次,所以放心大胆的让mp[i]取值范围由0到n
*/
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
ll t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}20.Skibidus and Sigma
(贪心,构造)

首先要读懂题目,神金,这句话一点都没用。。。。。 一个排列指的是一个包含 1 到 n 的所有整数且每个整数恰好出现一次的序列。。。。。。。

将给定的 n 个各含有 m 个元素的数组,让我们将这 n 个数组以任意顺序拼接起来,使得前缀和数组的元素之和最大。
自行推一下式子,可以发现前缀和数组的元素之和,原数组 a1 出现 n×m 次,a2 出现 n×m−1 次,a n×m 出现 1 次。
对于第 k 个长度为 m 的数组,如果它在最终的数组的位置左移 1,那么答案就会增加这个数组的元素和,如果右移 1,答案就会减少这个数组的元素和,那么,元素之和更大的放在更前面,将数组按元素和降序排序,最后统计一下即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+5;
int T,n,m,ans;
struct dis
{
int p,q;//p是数组元素之和,q是数组前缀和之和
}a[N];
bool cmp(dis x,dis y)
{
return x.p>y.p;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
ans=0;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int x=0,v=0;
a[i].p=a[i].q=0;
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) {cin>>x;a[i].p+=x;v+=a[i].p;}
a[i].q=v;
}
sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) ans+=a[i].q+a[i-1].p*m,a[i].p+=a[i-1].p;
cout<<ans<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}// 4 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
struct node{
ll p,q;
//当前数组的和
//前缀和的和
};
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
ll t;cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll n,m;cin>>n>>m;
vector<node> a(n,{0,0});
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
for(ll j=0;j<m;j++){
ll x;cin>>x;
a[i].p+=x;
a[i].q+=a[i].p;
}
}
sort(a.begin(),a.end(),[&](const node&x,const node&y){
return x.p>y.p;
});
ll ans=0;
ll cur=0;
for(ll i=0;i<a.size();i++){
//好好理解这两个公式
ans+=a[i].q+cur*m;
cur+=a[i].p;
}
cout<<ans<<'\n';
/*
根据样例不可以对每个数组内部排序
vector<ll> b;
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
sort(mp[i].begin(),mp[i].end());
for(ll j=0;j<m;j++){
b.push_back(mp[i][j]);
}
}
ll sum=0;
for(ll i=1;i<b.size();i++){
b[i]+=b[i-1];
sum+=b[i];
}
//cout<<sum<<'\n';
*/
}
return 0;
}






















 5267
5267

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








