文章目录
前言
本文为7月18日数据科学库学习笔记,分为九个章节:
- numpy 数组创建:np.array、np.arange;
- 数据类型的操作:dtype、.astype、.round;
- 数组的形状:.shape、.reshape、.flatten() ;
- 数组的计算:广播机制、数组和数的计算、数组和数组的计算;
- 不同维度的数组计算:列数相同的数组、行数相同的数组;
- 数组的轴;
- numpy 读取本地数据:转置、索引和切片、数值修改、nan&inf;
- numpy 中数据的拼接&行列交换;
- 其他方法;
- numpy 生成随机数。
一、numpy 数组创建
1、 np.array
a = np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
b = np.array(range(1, 6))
a
b
>>> array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
>>> array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
2、np.arange
用法:arange([start, ] stop[, step,], dtype=)
二、数据类型的操作
1、dtype 指定创建的数组的数据类型
a = np.array([1,0,1,0], dtype='bool')
a
>>> array([ True, False, True, False])
2、.astype() 修改数组的数据类型
a.astype(int)
>>> array([1, 0, 1, 0])
3、.round 修改浮点型的小数位数
用法:np.round(b, 2)
三、数组的形状
1、.shape 查看数组的形状
a = np.array([[3,4,5,6,7,8], [4,5,6,7,8,9]])
a.shape
>>> (2, 6)
2、.reshape 修改数组的形状
返回新的数组,原数组不变
a.reshape(3, 4)
>>> array([[3, 4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8, 9]])
a.shape
>>> (2, 6)
3、.flatten() 转化为1维度数据
a.flatten()
>>> array([3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
四、数组的计算
广播机制:若两个数组从末尾开始算起的维度的轴长度相符或其中一方长度为1,则认为她们是广播兼容的。
1、数组和数的计算
(1)、加法
a = np.array([[3,4,5,6,7,8], [4,5,6,7,8,9]])
a+1
>>> array([[ 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
(2)、乘法
a*3
>>> array([[ 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24],
[12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27]])
2、数组和数组的计算
(1)、加法
a = np.array([[3,4,5,6,7,8], [4,5,6,7,8,9]])
b = np.array([[21,22,23,24,25,26], [27,28,29,30,31,32]])
a+b
>>> array([[24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34],
[31, 33, 35, 37, 39, 41]])
(2)、乘法
a = np.array([[3,4,5,6,7,8], [4,5,6,7,8,9]])
b = np.array([[21,22,23,24,25,26], [27,28,29,30,31,32]])
a*b
>>> array([[ 63, 88, 115, 144, 175, 208],
[108, 140, 174, 210, 248, 288]])
3、不同维度的数组计算
1、列数相同的数组
a = np.array([[3,4,5,6,7,8], [4,5,6,7,8,9]]) # 2行6列
c = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6]) # 1行6列
a-c
>>> array([[2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3]])
2、行数相同的数组
a = np.array([[3,4,5,6,7,8], [4,5,6,7,8,9]]) # 2行6列
c = np.array([[1],
[2]]) # 2行1列
a+c
array([[ 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]])
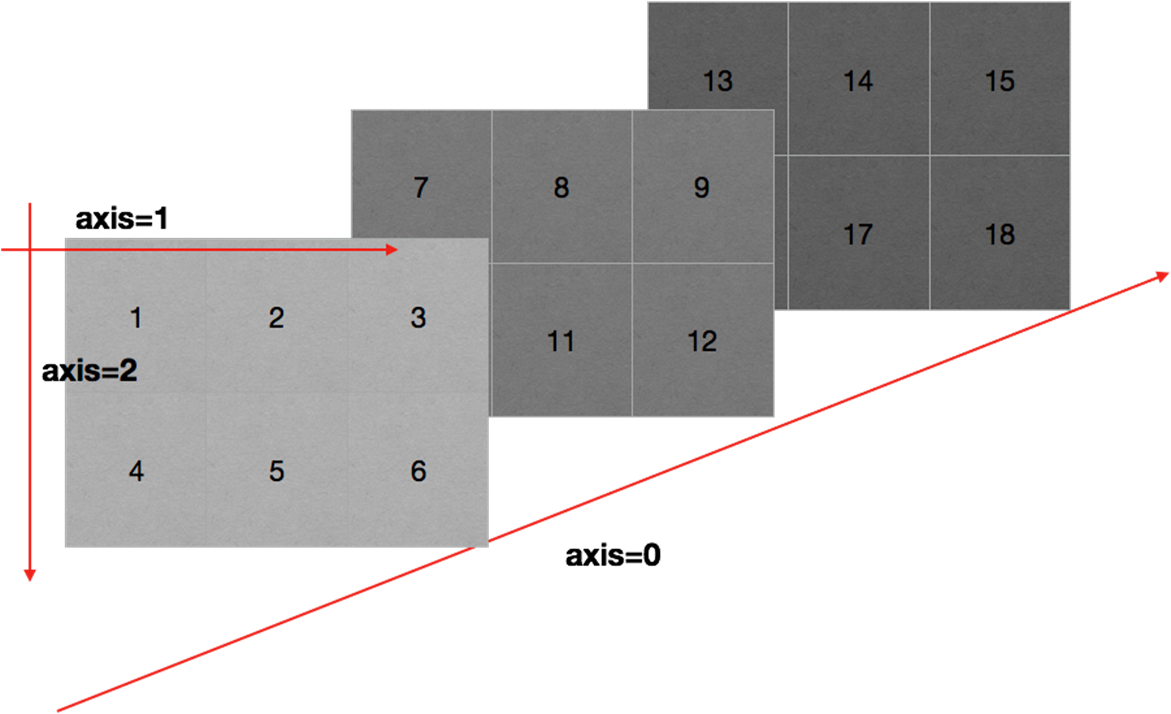
五、数组的轴
- 二维数组的轴:

- 三维数组的轴:
六、numpy 读取本地数据
np.loadtxt(fname, dtype=, delimiter=, skiprows=, usecols=, unpack=)
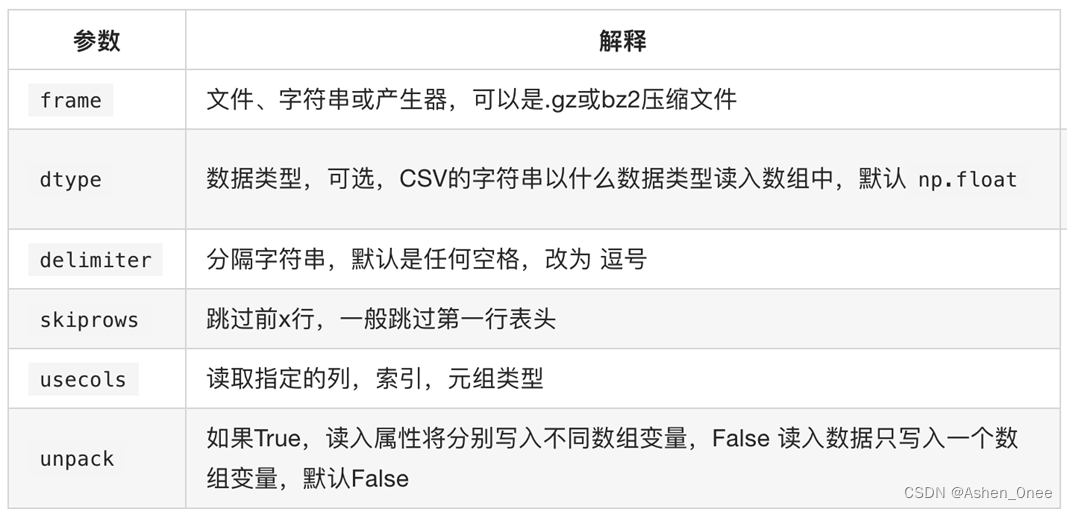
- 示例:有英国和美国各自 youtube 1000多个视频的点击、喜欢、不喜欢、评论数量,对其进行操作:
# numpy 读取文件
#coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
us_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/US_video_data_numbers.csv"
uk_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/GB_video_data_numbers.csv"
t1 = np.loadtxt(us_file_path, delimiter=',', dtype='int', unpack=True) # unpack: 转置
t2 = np.loadtxt(us_file_path, delimiter=',', dtype='int')
1、numpy 中的转置
(1)、t.transpose()
t
>>> array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17]])
t.transpose()
>>> array([[ 0, 6, 12],
[ 1, 7, 13],
[ 2, 8, 14],
[ 3, 9, 15],
[ 4, 10, 16],
[ 5, 11, 17]])
(2)、t.swapaxes()
t
>>> array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17]])
t.swapaxes(1,0)
>>> array([[ 0, 6, 12],
[ 1, 7, 13],
[ 2, 8, 14],
[ 3, 9, 15],
[ 4, 10, 16],
[ 5, 11, 17]])
(3)、t.T
t
>>> array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17]])
t.T
>>> array([[ 0, 6, 12],
[ 1, 7, 13],
[ 2, 8, 14],
[ 3, 9, 15],
[ 4, 10, 16],
[ 5, 11, 17]])
2、numpy 索引和切片
(1)、取一行
a
>>> array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])
a[1]
>>> array([4, 5, 6, 7])
(2)、取多行
a[1:3]
>>> array([[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])
(3)、取一列
a[:, 2]
>>> array([ 2, 6, 10])
(3)、取多列
a[:, 2:4]
array([[ 2, 3],
[ 6, 7],
[10, 11]])
(4)、取不连续多行
a[[0,2]]
>>> array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])
(4)、取不连续多列
a[:, [1,3]]
>>> array([[ 1, 3],
[ 5, 7],
[ 9, 11]])
(5)、取元素
# 取一个元素
a[1,2]
>>> 6
# 取第1行第1列和第2行第2列的元素
a[[0,1],[0,1]]
>>> array([0, 5])
3、numpy 数值修改
t
>>> array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17]])
# 把 t 中小于10的数字替换成3
t[t<10]=3
t
>>> array([[ 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3],
[ 3, 3, 3, 3, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17]])
# 把 t 中小于10的数字替换成0,大于10的替换成10
np.where(t<10, 0, 10)
>>> array([[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 10, 10],
[10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10]])
# .clip: 小于10的替换为10,大于18的替换为18
t.clip(10, 18)
>>> array([[10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10],
[10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17]])
4、nan&inf
(1)、两个 nan 不相等
np.nan == np.nan
>>> False
(2)、np.count_nonzero() 判断数组中 nan 的个数
t
>>> array([[ 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3],
[ 3, 3, 3, 3, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17]])
np.count_nonzero(t!=t)
>>> 0
(3)、np.isnan(a) 判断元素是否为 nan
t
>>> array([ 1., 2., nan])
np.isnan(t[2])
>>> True
(4)、nan 和任何值计算都为 nan
5、nan 和常用统计方法
- 求和:t.sum(axis=None);
- 均值:t.mean(a,axis=None);
- 中值:np.median(t,axis=None);
- 最大值:t.max(axis=None);
- 最小值:t.min(axis=None);
- 极值:np.ptp(t,axis=None);
- 标准差:t.std(axis=None)。
6、填充 nan
在一组数据中单纯的把nan替换为0不合适。比如,全部替换为0后,替换之前的平均值如果大于0,替换之后的均值肯定会变小。所以,更合适的方式是把缺失的数值替换为均值(中值)或者是直接删除有缺失值的一行:
import numpy as np
def fill_ndarray(t1):
for i in range(t1.shape[1]):
temp_col = t1[:, i] # 当前列
nan_num = np.count_nonzero(temp_col != temp_col) # 统计 nan 个数
if nan_num != 0: # 不为0,说明这一列有 nan
temp_not_nan_col = temp_col[temp_col == temp_col] # 当前一列不为 nan 的 array
temp_col[np.isnan(temp_col)] = temp_not_nan_col.mean() # 选中当前 nan 的位置,赋值均值
return t1
if __name__ == '__main__':
t1 = np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4).astype('float')
t1[1, 2:] = np.nan
print(t1)
print('#'*20)
t1 = fill_ndarray(t1)
print(t1)
7、实操
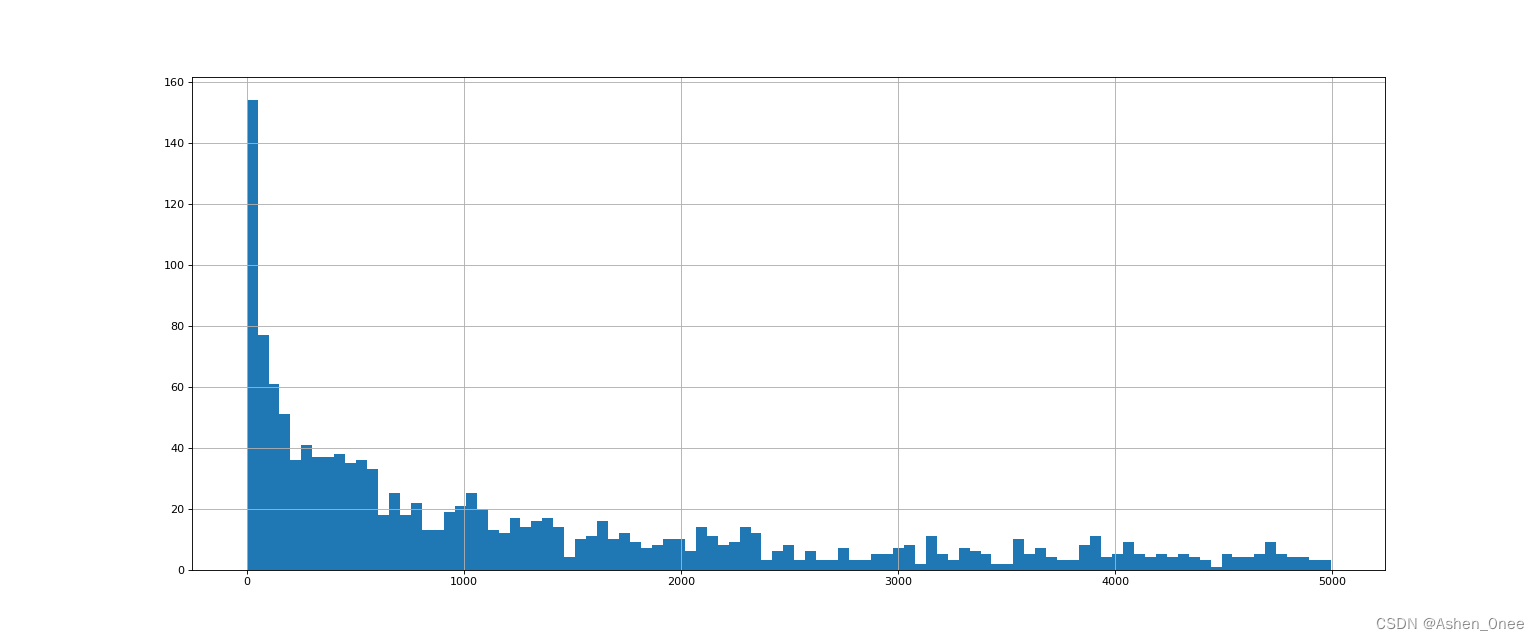
(1)、绘制美国 youtube 视频评论数量的直方图
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
us_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/US_video_data_numbers.csv"
uk_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/GB_video_data_numbers.csv"
#t1 = np.loadtxt(us_file_path, delimiter=',', dtype='int', unpack=True) # unpack: 转置
t_us = np.loadtxt(us_file_path, delimiter=',', dtype='int')
# 取评论的数据
t_us_comments = t_us[:, -1]
# 选择比 5000 小的数据
t_us_comments = t_us_comments[t_us_comments < 5000]
print(t_us_comments.max(), t_us_comments.min())
d = 50
bin_nums = (t_us_comments.max() - t_us_comments.min()) // d
# 绘制直方图
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80)
plt.hist(t_us_comments, bin_nums)
plt.grid()
plt.show()
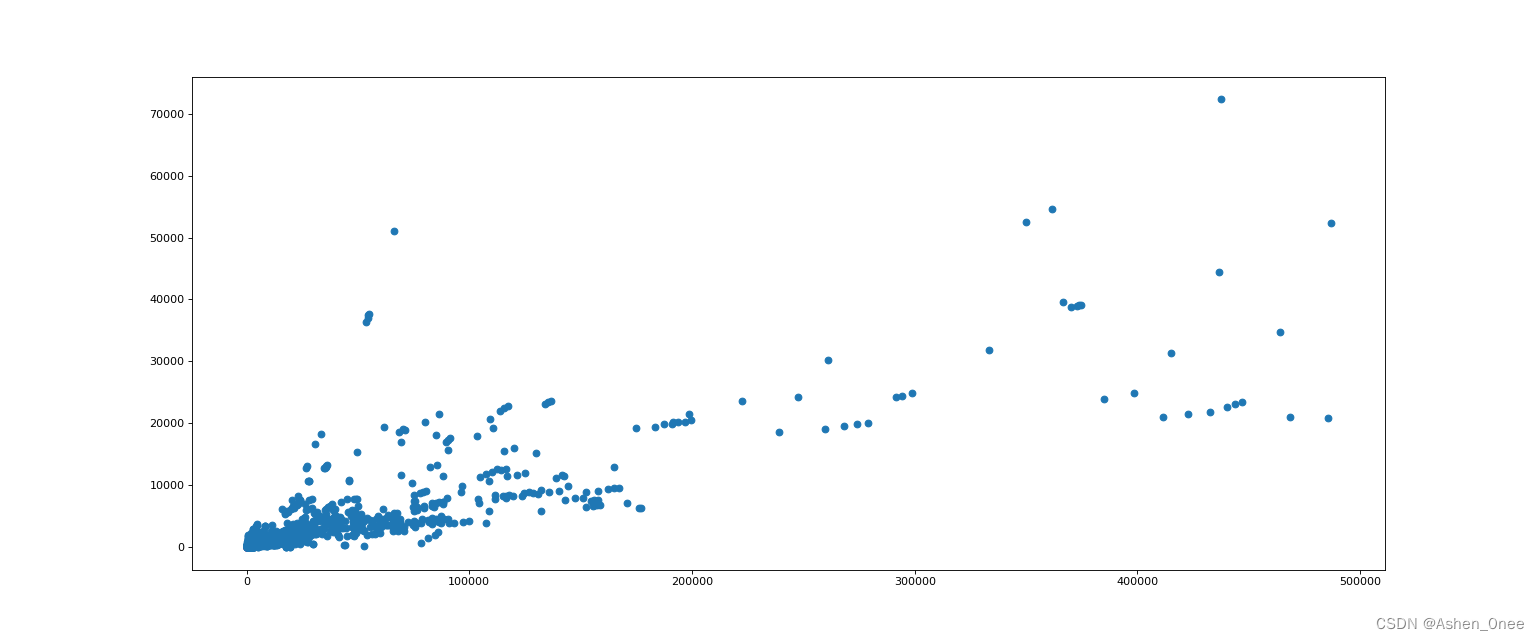
(2)、绘制英国 youtube 视频评论数和喜欢数的关系的散点图
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
us_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/US_video_data_numbers.csv"
uk_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/GB_video_data_numbers.csv"
#t1 = np.loadtxt(us_file_path, delimiter=',', dtype='int', unpack=True) # unpack: 转置
t_uk = np.loadtxt(uk_file_path, delimiter=',', dtype='int')
# 选择喜欢数比 500000 小的数据
t_uk = t_uk[t_uk[:, 1] < 500000]
t_uk_comments = t_uk[:, -1]
t_uk_like = t_uk[:, 1]
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80)
plt.scatter(t_uk_like, t_uk_comments)
plt.show()
七、数据的拼接&行列交换
- np.vstack((t1, t2)) 竖直拼接;
- np.hstack((t1, t2)) 水平拼接;
- t[[1, 2], :] = t[[2, 1], :] 行交换;
- t[0, [0, 2]] = t[:, [2, 0]] 列交换。
示例:将之前案例中两个国家的数据方法放在一起研究:
import numpy as np
us_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/US_video_data_numbers.csv"
uk_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/GB_video_data_numbers.csv"
# 加载国家数据
us_data = np.loadtxt(us_file_path, delimiter=',', dtype=int)
uk_data = np.loadtxt(uk_file_path, delimiter=',', dtype=int)
# 添加国家信息
# 构造全为 0 的数据
zeros_data = np.zeros((us_data.shape[0], 1)).astype(int)
ones_data = np.ones((uk_data.shape[0], 1)).astype(int)
# 分别添加一列全为 0, 1 的数据
us_data = np.hstack((us_data, zeros_data))
uk_data = np.hstack((uk_data, ones_data))
# 拼接两组数据
final_data = np.vstack((us_data, uk_data))
print(final_data)
>>> [[4394029 320053 5931 46245 0]
[7860119 185853 26679 0 0]
[5845909 576597 39774 170708 0]
...
[ 109222 4840 35 212 1]
[ 626223 22962 532 1559 1]
[ 99228 1699 23 135 1]]
八、其他方法
- 获取最大值最小值的位置:
- np.argmax(t,axis=0);
- np.argmin(t,axis=1)。
- 创建一个全0的数组: np.zeros((3,4));
- 创建一个全1的数组:np.ones((3,4));
- 创建一个对角线为1的正方形数组(方阵):np.eye(3)。
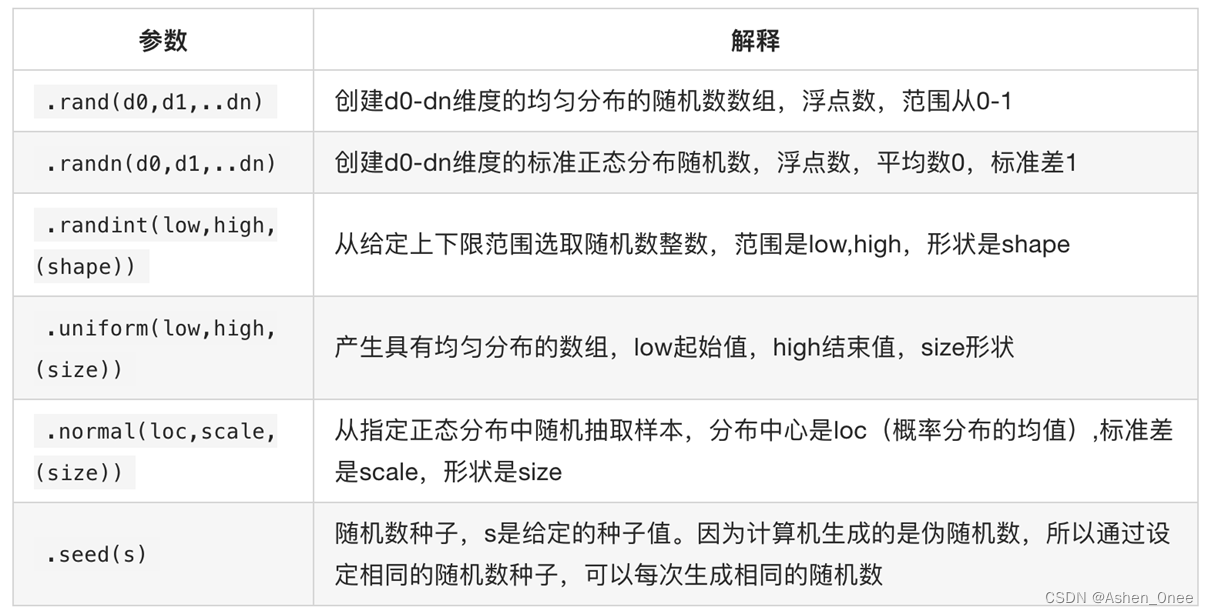
九、numpy 生成随机数




 本文详细介绍了NumPy库在数组创建、数据类型转换、数组形状操作、数组计算、数据处理等方面的应用,包括转置、索引、切片、数值修改等,并通过实例展示了如何使用NumPy读取和处理CSV数据,绘制直方图和散点图。此外,还涵盖了数据拼接、行列交换等数据操作技巧。
本文详细介绍了NumPy库在数组创建、数据类型转换、数组形状操作、数组计算、数据处理等方面的应用,包括转置、索引、切片、数值修改等,并通过实例展示了如何使用NumPy读取和处理CSV数据,绘制直方图和散点图。此外,还涵盖了数据拼接、行列交换等数据操作技巧。
















 1359
1359

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








