🚀🚀🚀本文改进:CBAM注意力,引入到YOLOv8,多种实现方式
🚀🚀🚀CBAM在不同检测领域中应用广泛
🚀🚀🚀YOLOv8改进专栏:http://t.csdnimg.cn/hGhVK
学姐带你学习YOLOv8,从入门到创新,轻轻松松搞定科研;

1.CBAM注意力介绍

论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1807.06521.pdf
摘要:我们提出了卷积块注意力模块(CBAM),这是一种用于前馈卷积神经网络的简单而有效的注意力模块。 给定中间特征图,我们的模块沿着两个独立的维度(通道和空间)顺序推断注意力图,然后将注意力图乘以输入特征图以进行自适应特征细化。 由于 CBAM 是一个轻量级通用模块,因此它可以无缝集成到任何 CNN 架构中,且开销可以忽略不计,并且可以与基础 CNN 一起进行端到端训练。 我们通过在 ImageNet-1K、MS COCO 检测和 VOC 2007 检测数据集上进行大量实验来验证我们的 CBAM。我们的实验显示各种模型在分类和检测性能方面的持续改进,证明了 CBAM 的广泛适用性。 代码和模型将公开。
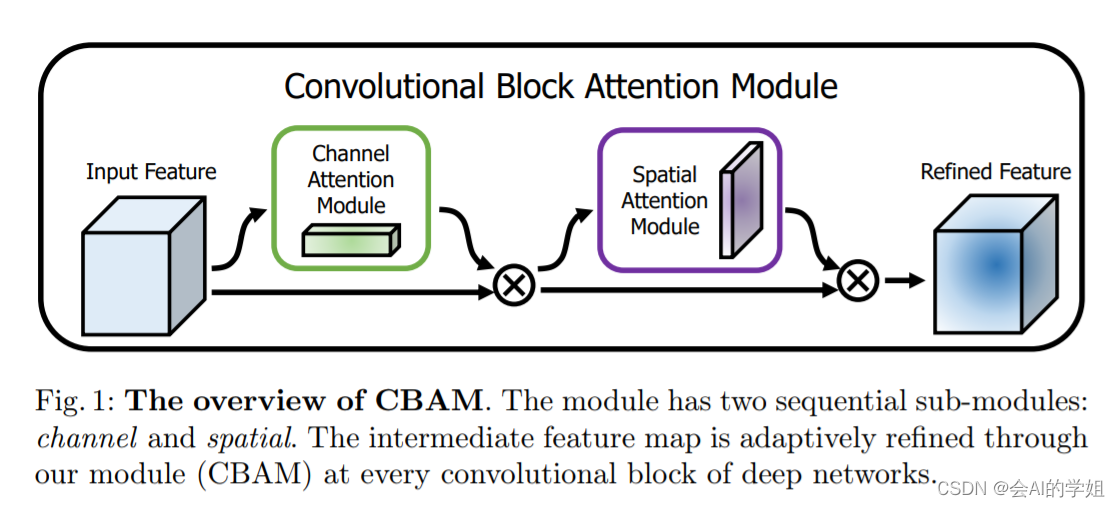
上图可以看到,CBAM包含CAM(Channel Attention Module)和SAM(Spartial Attention Module)两个子模块,分别进行通道和空间上的Attention。这样不只能够节约参数和计算力,并且保证了其能够做为即插即用的模块集成到现有的网络架构中去。

2.CBAM加入YOLOv8
2.1加入ultralytics/nn/attention/attention.py
###################### CBAM #### start ###############################
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
# Channel-attention module https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/tree/v3.0.0rc1/configs/rtmdet
def __init__(self, channels: int) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=True)
self.act = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
return x * self.act(self.fc(self.pool(x)))
class SpatialAttention(nn.Module):
# Spatial-attention module
def __init__(self, kernel_size=7):
super().__init__()
assert kernel_size in (3, 7), 'kernel size must be 3 or 7'
padding = 3 if kernel_size == 7 else 1
self.cv1 = nn.Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size, padding=padding, bias=False)
self.act = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
return x * self.act(self.cv1(torch.cat([torch.mean(x, 1, keepdim=True), torch.max(x, 1, keepdim=True)[0]], 1)))
class CBAM(nn.Module):
# Convolutional Block Attention Module
def __init__(self, c1, kernel_size=7): # ch_in, kernels
super().__init__()
self.channel_attention = ChannelAttention(c1)
self.spatial_attention = SpatialAttention(kernel_size)
def forward(self, x):
return self.spatial_attention(self.channel_attention(x))
###################### CBAM #### end ###############################2.2 修改tasks.py
首先CBAM进行注册
from ultralytics.nn.attention.attention import *函数def parse_model(d, ch, verbose=True): # model_dict, input_channels(3)进行修改
#####attention ####
elif m in (CBAM,SimAM,MHSA,ECAAttention,TripletAttention,BAM,CoTAttention,PolarizedSelfAttention):
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != nc:
c2 = make_divisible(min(c2, max_channels) * width, 8)
args = [c1, *args[1:]]
#####attention ####2.3 yaml实现
2.3.1 yolov8_CBAM.yaml
加入backbone SPPF后

# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
- [-1, 1, CBAM, [1024]] # 10
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 13
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 16 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 13], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 19 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 22 (P5/32-large)
- [[16, 19, 22], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
2.3.2 yolov8_CBAM2.yaml
neck里的连接Detect的3个C2f结合

# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, CBAM, [256]] # 16
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 19 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, CBAM, [512]] # 20
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 23 (P5/32-large)
- [-1, 1, CBAM, [1024]] # 24
- [[16, 20, 24], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
2.3.3 yolov8_CBAM3.yaml
放入neck的C2f后面
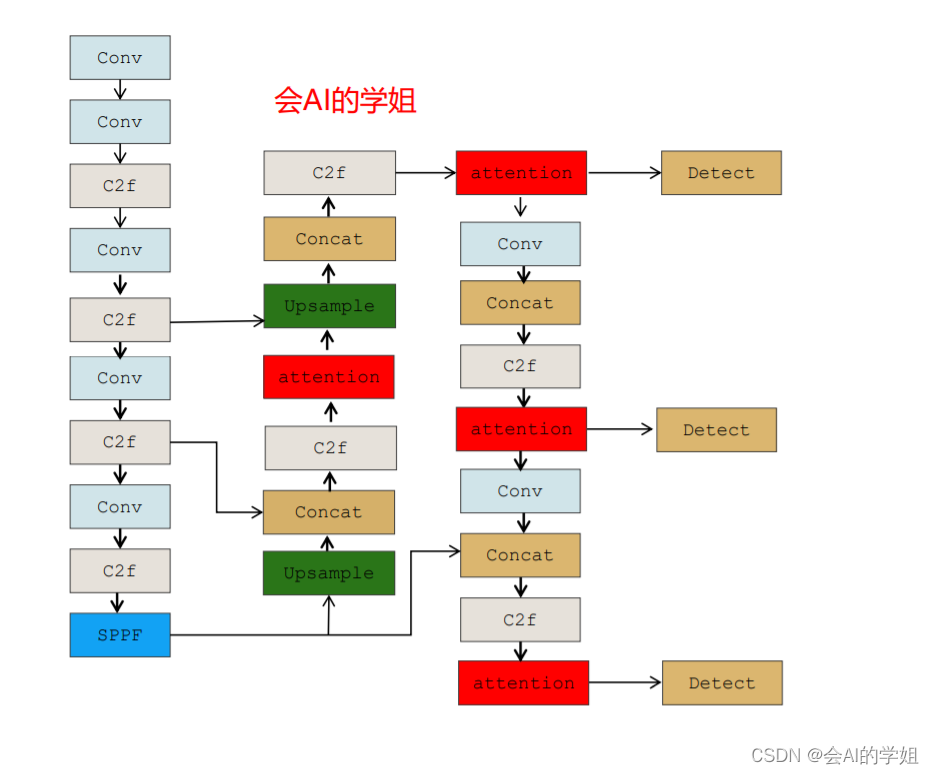
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, GPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 1 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, CBAM, [512]] # 13
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 16 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, CBAM, [256]] # 17 (P5/32-large)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 13], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 20 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, CBAM, [512]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 24 (P5/32-large)
- [-1, 1, CBAM, [1024]] # 25 (P5/32-large)
- [[17, 21, 25], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)

























 5438
5438

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










