In mathematics, a concave function is the negative of a convex function. A concave function is also synonymously called concave downwards, concave down, convex upwards, convex cap or upper convex.
Definition[edit]
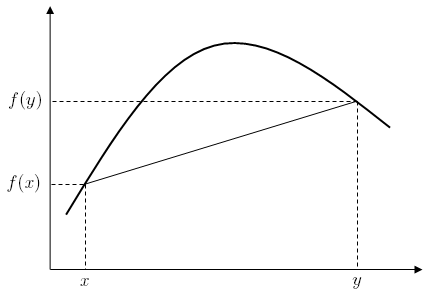
A real-valued function f on an interval (or, more generally, a convex set in vector space) is said to be concave if, for any x and y in the interval and for anyα in [0,1],[1]
A function is called strictly concave if
for any α in (0,1) and x ≠ y.
For a function f:R→R, this definition merely states that for every z between x and y, the point (z, f(z) ) on the graph of f is above the straight line joining the points (x, f(x) ) and (y, f(y) ).
A function f is quasiconcave if the upper contour sets of the function  are convex sets.[2]:496
are convex sets.[2]:496
Properties[edit]
1. A function f is concave over a convex set if and only if the function −f is a convex function over the set.
2. A differentiable function f is concave on an interval if its derivative function f ′ is monotonically decreasing on that interval: a concave function has a decreasing slope. ("Decreasing" here means non-increasing, rather than strictly decreasing, and thus allows zero slopes.)
3. Points where concavity changes (between concave and convex) are inflection points.
4. The sum of two concave functions is itself concave and so is the pointwise minimum of two concave functions, i.e. the set of concave functions on a given domain form a semifield.
5. Near a local maximum in the interior of the domain of a function, the function must be concave; as a partial converse, if the derivative of a strictly concave function is zero at some point, then that point is a local maximum.
6. If f is twice-differentiable, then f is concave if and only if f ′′ is non-positive (or, if the acceleration is non-positive). If its second derivative isnegative then it is strictly concave, but the opposite is not true, as shown by f(x) = −x4.
7. Any local maximum of a concave function is also a global maximum. A strictly concave function will have at most one global maximum.
8. If f is concave and differentiable, then it is bounded above by its first-order Taylor approximation:[2]:489
9. A continuous function on C is concave if and only if for any x and y in C
10. If a function f is concave, and f(0) ≥ 0, then f is subadditive. Proof:
- since f is concave, let y = 0,


Examples[edit]
- The functions
 and
and  are concave on their domains, as their second derivatives
are concave on their domains, as their second derivatives  and
and  are always negative.
are always negative. - The logarithm function
 is concave on its domain
is concave on its domain  , as its derivative
, as its derivative  is a strictly decreasing function.
is a strictly decreasing function. - Any affine function
 is both concave and convex, but not strictly-concave nor strictly-convex.
is both concave and convex, but not strictly-concave nor strictly-convex. - The sine function is concave on the interval
![[0, \pi]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/math/e/1/8/e1868564b62b4e2f1c063321df289469.png) .
. - The function
 , where
, where  is the determinant of a nonnegative-definite matrix B, is concave.[3]
is the determinant of a nonnegative-definite matrix B, is concave.[3] - Practical example: rays bending in computation of radiowave attenuation in the atmosphere.
See also[edit]
- Concave polygon
- Convex function
- Jensen's inequality
- Logarithmically concave function
- Quasiconcave function
References[edit]
- Jump up^ LENHART, S.; WORKMAN, J. T, Optimal Control Applied to biological models, Chapman & Hall/ CRC, Mathematical and Computational Biology Series, 2007.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Varian, Hal (1992). Microeconomic Analysis (Third ed.). New York: Norton. ISBN 0393957357.
- Jump up^ Thomas M. Cover and J. A. Thomas (1988). "Determinant inequalities via information theory". SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications 9 (3): 384–392.doi:10.1137/0609033.
Further References[edit]
- Crouzeix, J.-P. (2008). "Quasi-concavity". In Durlauf, Steven N.; Blume, Lawrence E. The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics (Second ed.). Palgrave Macmillan. doi:10.1057/9780230226203.1375.
- Rao, Singiresu S. (2009). Engineering Optimization: Theory and Practice. John Wiley and Sons. p. 779. ISBN 0-470-18352-7.










![f(y) \leq f(x) + f'(x)[y-x].](https://upload.wikimedia.org/math/5/7/1/5714bd090bbe381e3d0087e23bc0cc94.png)















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








