该系列仅在原课程基础上部分知识点添加个人学习笔记,或相关推导补充等。如有错误,还请批评指教。在学习了 Andrew Ng 课程的基础上,为了更方便的查阅复习,将其整理成文字。因本人一直在学习英语,所以该系列以英文为主,同时也建议读者以英文为主,中文辅助,以便后期进阶时,为学习相关领域的学术论文做铺垫。- ZJ
转载请注明作者和出处:ZJ 微信公众号-「SelfImprovementLab」
知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/c_147249273
CSDN:http://blog.csdn.net/JUNJUN_ZHAO/article/details/78959295
Part 1:Python Basics with Numpy (optional assignment)
1 - Building basic functions with numpy
Numpy is the main package for scientific computing in Python.(Numpy 是在 python 中 用作科学计算主要的 库\包) It is maintained by a large community (www.numpy.org). In this exercise you will learn several key numpy functions such as np.exp, np.log, and np.reshape.(主要的函数 指数 log 对数 还有矩阵的 reshape) You will need to know how to use these functions for future assignments.
1.1 - sigmoid function, np.exp()
Exercise: Build a function that returns the sigmoid of a real number x. Use math.exp(x) for the exponential function.
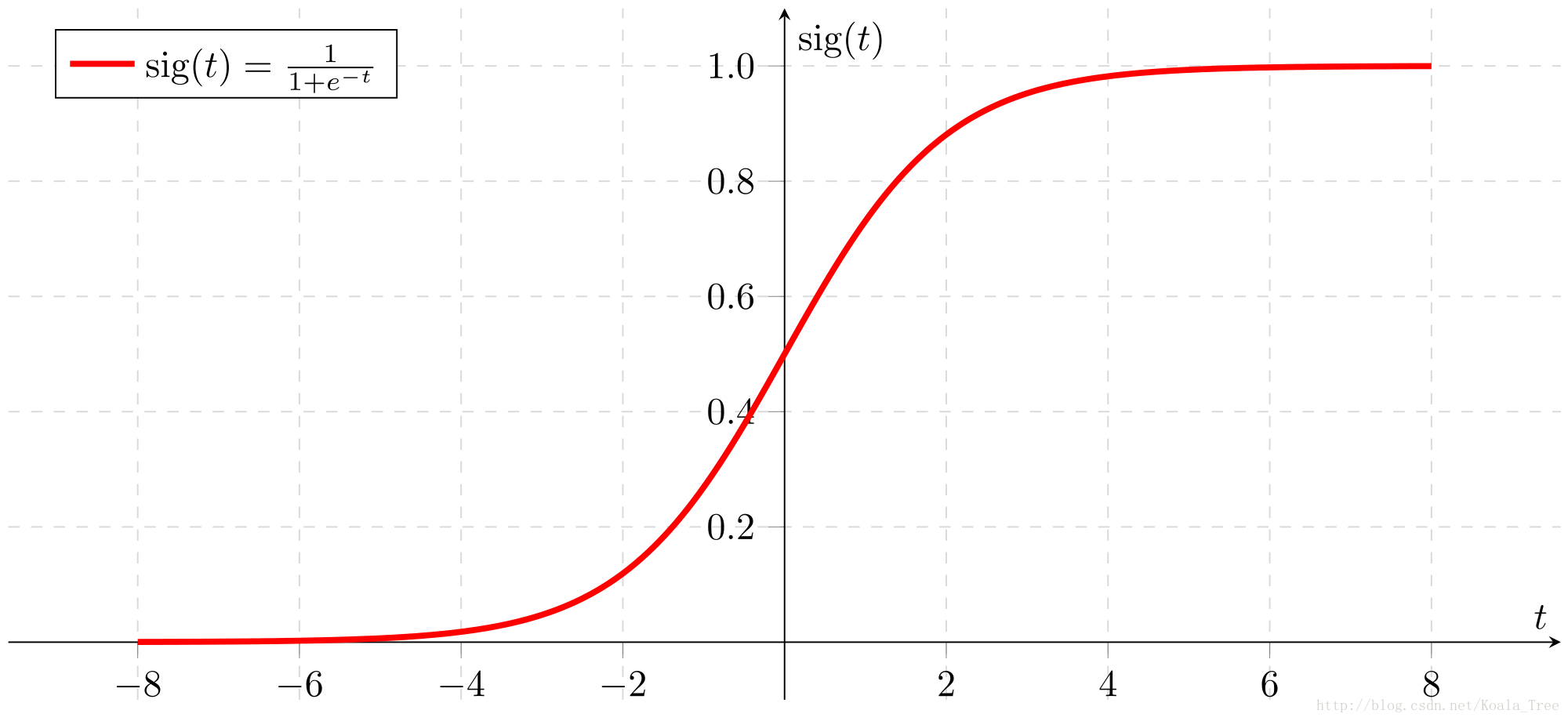
Reminder:
sigmoid(x)=11+e−x
s
i
g
m
o
i
d
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
is sometimes also known as the logistic function. It is a non-linear function used not only in Machine Learning (Logistic Regression), but also in Deep Learning.
To refer to a function belonging to a specific package you could call it using package_name.function(). Run the code below to see an example with math.exp().
# GRADED FUNCTION: basic_sigmoid
import math
def basic_sigmoid(x):
"""
Compute sigmoid of x.
Arguments:
x -- A scalar
Return:
s -- sigmoid(x)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
# math.exp(x) 相当于 e 的 x 次方
s = 1.0 / (1 + 1/ math.exp(x))
### END CODE HERE ###
return sbasic_sigmoid(3)0.9525741268224334
Actually, we rarely use the “math” library in deep learning because the inputs of the functions are real numbers. In deep learning we mostly use matrices and vectors. This is why numpy is more useful.
不常用 math 这个库,因为因为它的输入参数为实数,而实际上,在 deep learning 中,我们常用到的训练数据
都是 矩阵 或向量的形式,所以 numpy 这个库,非常的有用
### One reason why we use "numpy" instead of "math" in Deep Learning ###
x = [1, 2, 3]
basic_sigmoid(x) # you will see this give an error when you run it, because x is a vector.参数类型错误---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-3-c400bf07df70> in <module>()
1 ### One reason why we use "numpy" instead of "math" in Deep Learning ###
2 x = [1, 2, 3]
----> 3 basic_sigmoid(x) # you will see this give an error when you run it, because x is a vector.参数类型错误
<ipython-input-1-92da315cf1e3> in basic_sigmoid(x)
16 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
17 # math.exp(x) 相当于 e 的 x 次方
---> 18 s = 1.0 / (1 + 1/ math.exp(x))
19 ### END CODE HERE ###
20
TypeError: must be real number, not list
In fact, if x=(x1,x2,...,xn) x = ( x 1 , x 2 , . . . , x n ) is a row vector then np.exp(x) n p . e x p ( x ) will apply the exponential(指数) function to every element of x.每个元素的指数 The output will thus be: np.exp(x)=(ex1,ex2,...,exn) n p . e x p ( x ) = ( e x 1 , e x 2 , . . . , e x n )
import numpy as np
# example of np.exp
a = np.array([1,2,3])
print(np.exp(a))# result is (exp(1), exp(2), exp(3))[ 2.71828183 7.3890561 20.08553692]
Furthermore 此外, if x is a vector, then a Python operation such as s=x+3 s = x + 3 or s=1x s = 1 x will output s s as a vector of the same size as . S 作为一个向量,其大小和 X 是一样的。
# example of vector operation
x = np.array([1,2,3])
print(x+3)[4 5 6]
Exercise: Implement the sigmoid function using numpy. 使用 numpy 实现 sigmoid 函数
Instructions: x could now be either a real number, a vector, or a matrix.可以是 实数、向量、矩阵 The data structures we use in numpy to represent these shapes (vectors, matrices…) are called numpy arrays. You don’t need to know more for now.

import numpy as np # this means you can access numpy functions by writing np.function() instead of numpy.function()
def sigmoid1(x):
"""
Compute the sigmoid of x
Arguments:
x -- A scalar (标量) or numpy array of any size.或任意大小的数组
Return:
s -- sigmoid1(x)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
s = 1.0/(1+1/np.exp(x))
### END CODE HERE ###
return s
x = np.array([1,2,3])
print(sigmoid1(x))[ 0.73105858 0.88079708 0.95257413]
1.2 - Sigmoid gradient 梯度
Exercise: Implement the function sigmoid_grad() to compute the gradient of the sigmoid function with respect to its input x. 计算关于 x 的梯度,就是求导 。The formula 公式is:
sigmoid_derivative(x)=σ′(x)=σ(x)(1−σ(x))(2) (2) s i g m o i d _ d e r i v a t i v e ( x ) = σ ′ ( x ) = σ ( x ) ( 1 − σ ( x ) )
You often code this function in two steps:
1. Set s to be the sigmoid of x. You might find your sigmoid(x) function useful.
2. Compute
σ′(x)=s(1−s)
σ
′
(
x
)
=
s
(
1
−
s
)
# GRADED FUNCTION: sigmoid_derivative
def sigmoid_derivative(x):
"""
Compute the gradient (also called the slope or derivative) 梯度,也叫 斜率 或 导数 of the sigmoid function with respect to its input x.
You can store the output of the sigmoid function into variables and then use it to calculate the gradient.
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array
Return:
ds -- Your computed gradient.
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
s = 1.0 / (1 + 1 / np.exp(x))
ds = s * (1 - s)
### END CODE HERE ###
return ds
# when x equals to 0, it has the biggest derivatation , 0.25
print("sigmoid_derivative(0):",str(sigmoid_derivative(0)))
x = np.array([1,2,3])
print("sigmoid_derivative(x):",str(sigmoid_derivative(x)))sigmoid_derivative(0): 0.25
sigmoid_derivative(x): [ 0.19661193 0.10499359 0.04517666]
1.3 - Reshaping arrays
Two common numpy functions used in deep learning are np.shape and np.reshape().
- X.shape is used to get the shape (dimension) of a matrix/vector X.
- X.reshape(…) is used to reshape X into some other dimension.
For example, in computer science, an image is represented by a 3D array of shape (length,height,depth=3) . However, when you read an image as the input of an algorithm you convert it to a vector of shape (length∗height∗3,1). In other words, you “unroll”, or reshape, the 3D array into a 1D vector. 将 3 维 数组转化成 1 维 数组。

Exercise: Implement image2vector() that takes an input of shape (length, height, 3) and returns a vector of shape (length*height*3, 1). For example, if you would like to reshape an array v of shape (a, b, c) into a vector of shape (a*b,c) you would do:
图片转化为向量,将 shape 为(length, height, 3) 转化为 shape 为(length*height*3, 1)的向量。
v = v.reshape((v.shape[0]* v.shape[1], v.shape[2])) # v.shape[0] = a ; v.shape[1] = b ; v.shape[2] = c- Please don’t hardcode the dimensions of image as a constant.不要硬编码,不要将 image 的维度 作为常量 Instead look up the quantities you need with image.shape[0], etc.# GRADED FUNCTION: image2vector
def image2vector(image):
"""
Argument:
image -- a numpy array of shape (length, height, depth) image 是 shape 为 (length, height, depth)的数组 取值 shape[0] shape[1] shape[2]
Returns:
v -- a vector of shape (length*height*depth, 1) 返回 shape 为 (length * height * depth, 1) 的向量
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
# reshape 只是改变形状,但里面的元素不会进行计算, image.shape[0] = 几个数组, image.shape[1] =每个数组的行数 image.shape[2]=每个数组的列数
v = image.reshape(image.shape[0]*image.shape[1]*image.shape[2],1)
### END CODE HERE ###
return v
# This is a 3 by 3 by 2 array, 是一个 3 × (3 × 2 )的数组,理解为 3个 数组,每个数组里面是 3 行 2 列
# typically images will be (num_px_x, num_px_y,3) where 3 represents the RGB values.典型的 images
image = np.array([[[ 0.67826139, 0.29380381],
[ 0.90714982, 0.52835647],
[ 0.4215251 , 0.45017551]],
[[ 0.92814219, 0.96677647],
[ 0.85304703, 0.52351845],
[ 0.19981397, 0.27417313]],
[[ 0.60659855, 0.00533165],
[ 0.10820313, 0.49978937],
[ 0.34144279, 0.94630077]]])
# 相当于转化为 18 行 1 列的数组
print ("image2vector(image) = " + str(image2vector(image)))image2vector(image) = [[ 0.67826139]
[ 0.29380381]
[ 0.90714982]
[ 0.52835647]
[ 0.4215251 ]
[ 0.45017551]
[ 0.92814219]
[ 0.96677647]
[ 0.85304703]
[ 0.52351845]
[ 0.19981397]
[ 0.27417313]
[ 0.60659855]
[ 0.00533165]
[ 0.10820313]
[ 0.49978937]
[ 0.34144279]
[ 0.94630077]]
1.4 - Normalizing rows 规范行
Another common technique (常用技巧 )we use in Machine Learning and Deep Learning is to normalize our data.(规范化我们的数据) It often leads to a better performance because gradient descent converges faster after normalization.(在规范化之后,梯度下降 收敛的速度更快) Here, by normalization we mean changing x to x∥x∥ x ‖ x ‖ (dividing each row vector of x by its norm 范式).
For example, if
x=[034 264 ] (3) x = [ 0 3 4 2 6 4 ] ( 3 )
then
|x|=np.linalg.norm(x,axis=1,keepdims=True)=[5 56−−√ ] (4) | x | = n p . l i n a l g . n o r m ( x , a x i s = 1 , k e e p d i m s = T r u e ) = [ 5 56 ] ( 4 ) // 5and56−−√:32+42=52,22+62+42=56−−√2 5 a n d 56 : 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 , 2 2 + 6 2 + 4 2 = 56 2
and
xnormalized=x|x|=[03545 256√656√456√ ] (5) x n o r m a l i z e d = x | x | = [ 0 3 5 4 5 2 56 6 56 4 56 ] ( 5 )
Note that you can divide matrices of different sizes and it works fine: this is called broadcasting and you’re going to learn about it in part 5.
请注意 你可以将 矩阵 划分成不同大小,并且还是有效有作用的:这个叫做广播 后面会讲。
Exercise: Implement normalizeRows() to normalize the rows of a matrix. After applying this function to an input matrix x, each row of x should be a vector of unit length (meaning length 1).
实现 normalizeRows() 方法,去规范化 matrix 的行。length 1 的向量。
# GRADED FUNCTION: normalizeRows
def normalizeRows(x):
"""
Implement a function that normalizes each row of the matrix x (to have unit length).为了得到 单位长度
Argument:
x -- A numpy matrix of shape (n, m)
Returns:
x -- The normalized (by row) numpy matrix. You are allowed to modify x.
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
# Compute x_norm as the norm 2 of x.2 范式 Use np.linalg.norm(..., ord = 2, axis = ..., keepdims = True)
x_norm = np.linalg.norm(x, axis=1,keepdims = True)#计算每一行的长度,得到一个列向量
print("x_norm.shape():",np.shape(x_norm),'x_norm:\n',x_norm)
# Divide x by its norm.
x = x / x_norm #利用numpy的广播,用矩阵与列向量相除。
### END CODE HERE ###
return x
x = np.array([
[0, 3, 4],
[1, 6, 4]])
print("normalizeRows(x) = \n" + str(normalizeRows(x)))
# 相当于 将所有数据都规范到 [0,1]x_norm.shape(): (2, 1) x_norm:
[[ 5. ]
[ 7.28010989]]
normalizeRows(x) =
[[ 0. 0.6 0.8 ]
[ 0.13736056 0.82416338 0.54944226]]
Note:
In normalizeRows(), you can try to print the shapes of x_norm and x, and then return the assessment 评估. You’ll find out that they have different shapes. 规范后的 x_norm 是 n 行 1 列,This is normal given that x_norm takes the norm of each row of x. So x_norm has the same number of rows but only 1 column. So how did it work when you divided x by x_norm? 当你 用 x 除以 x_norm 后,为什么是有效的? This is called broadcasting and we’ll talk about it now!来,我们说下广播。
1.5 - Broadcasting and the softmax function 广播和 softmax 函数
A very important concept to understand in numpy is “broadcasting”.(在 numpy 中非常重要的需要理解的一个概念是“广播”) It is very useful for performing mathematical operations between arrays of different shapes. (对于不同 shape 的 数组之间 ,去进行数学操作非常有用)For the full details on broadcasting, you can read the official broadcasting documentation.
Exercise: Implement a softmax function using numpy. (用 numpy 实现一个 softmax 函数)You can think of softmax as a normalizing function used when your algorithm needs to classify two or more classes. (你可以认为 softmax 是一个规范化函数,当你的算法需要 进行二分类或更多分类的时候)You will learn more about softmax in the second course of this specialization.
Instructions:

说明:首先对 x 进行指数处理,(i 所在行,j 所在列, x−>exij x − > e x i j ,然后 再除以 x 所在 当前行,每一个数据所有列,指数运算后的总和)
# GRADED FUNCTION: softmax
import numpy as np
def softmax(x):
"""Calculates the softmax for each row of the input x.
计算 input x 每一个行的 softmax
Your code should work for a row vector and also for matrices of shape (n, m).
代码需要对 一个 行向量,或者 shape 为 (n,m)维度,形状的,都有效。
Argument:
x -- A numpy matrix of shape (n,m)
Returns:
s -- A numpy matrix equal to the softmax of x, of shape (n,m)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code)
# Apply exp() element-wise to x. Use np.exp(...).先用 np.exp() 方法对每个x 进行指数化操作。
x_exp = np.exp(x) # (n,m)
# Create a vector x_sum that sums each row of x_exp. Use np.sum(..., axis = 1, keepdims = True).
# axis=1 代表以行为单位,每一行中所有数据的操作,keepdims的含义是是否保持维数 ,最后相当于 变为 维度为 (n,1) 的列向量
x_sum = np.sum(x_exp, axis = 1, keepdims = True) # (n,1)
# Compute softmax(x) by dividing x_exp by x_sum. It should automatically use numpy broadcasting.
# 计算 softmax 通过 用 x_exp 除以 x_sum,是自动使用 numpy 中广播的
s = x_exp / x_sum # (n,m) 广播的作用
### END CODE HERE ###
return s
x = np.array([
[9, 2, 5, 0, 0],
[7, 5, 0, 0 ,0]])
print("softmax(x) = \n" + str(softmax(x)))softmax(x) =
[[ 9.80897665e-01 8.94462891e-04 1.79657674e-02 1.21052389e-04
1.21052389e-04]
[ 8.78679856e-01 1.18916387e-01 8.01252314e-04 8.01252314e-04
8.01252314e-04]]
Note:
- If you print the shapes of x_exp, x_sum and s above and rerun the assessment cell, you will see that x_sum is of shape (2,1) while x_exp and s are of shape (2,5). x_exp/x_sum works due to python broadcasting.
如果你打印出来 x_exp and x_sum 的 shape, 会发现 x_sum 是 (2,1),x_exp 是 (2,5) n 的维度相同,x_exp/x_sum 有效,可以相除是因为 python 中的广播起作用,(其内部是自动在横向,或纵向数据的 copy ,可参见课程中有关广播那节 video)
What you need to remember:
- np.exp(x) works for any np.array x and applies the exponential function to every coordinate
np.exp(x) 对所有 array 都起作用, - the sigmoid function and its gradient 。记住 sigmoid 函数 和它的梯度 也叫斜率 导数 σ′(x)=s(1−s) σ ′ ( x ) = s ( 1 − s )
- image2vector is commonly used in deep learning .image 转化为向量在 deep learning 中用的很广泛。
- np.reshape is widely used. In the future, you’ll see that keeping your matrix/vector dimensions straight will go toward eliminating a lot of bugs. np.reshape 也十分常用,将来 你会发现 使用 reshape 会帮你避免很多 bug
- numpy has efficient built-in functions 。numpy 在函数中构建很有效
- broadcasting is extremely useful 。 广播极其的有用。
PS: 欢迎扫码关注公众号:「SelfImprovementLab」!专注「深度学习」,「机器学习」,「人工智能」。以及 「早起」,「阅读」,「运动」,「英语 」「其他」不定期建群 打卡互助活动。
























 7万+
7万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








