在《Craig, John J - Introduction to Robotics_ Mechanics and Control-Pearson (2013)》一书中提到 “a four-bar linkage has only one degree of freedom” ,即“四连杆机构只有一个自由度”。本文将从零基础开始解释此句的原因。由于自学,恐有疏漏,还望赐教。
1.What is a Planar Four-Bar Linkage? 什么是四连杆机构?
- The simplest of all closed loop mechanisms 最简单的闭环结构
- Comprises four bar-shaped links: 3 moving links, 1 fixed link and 4 pin joints 包含4个连杆,其中有3个移动连杆,1个固定连杆和4个枢接
- The four bar chain has four turning pairs 包含4个转动副

2.Terminology 相关术语
- Crank:A link which can make complete revolution is known as crank. 曲柄:能作完全旋转的连杆称为曲柄。
- Rocker:Any link which does not revolve is called a rocker.
摇杆:任何不旋转的链接都称为摇杆。 - Frame:The fixed link is known as frame.
框架:固定链接称为框架。 - Coupler/connecting rod:The opposite link of frame is known as connecting rod.
耦合器/连杆:框架的相对连杆称为连杆。 - Crank-rocker mechanism:In a four bar linkage, if the shorter side link revolves and the other one rocks (i.e., oscillates), it is called a crank-rocker mechanism.
曲柄摇杆机构:在四杆连杆机构中,如果较短的侧连杆旋转而另一侧连杆摇摆(即摆动),则称为曲柄摇杆机构。如图2.1。 - Double-crank mechanism:In a four bar linkage, if both of the side links revolve, it is called a double-crank mechanism.
双曲柄机构:在四连杆机构中,如果两个侧连杆都旋转,则称为双曲柄机构。如图2.2。 - Double-rocker mechanism:In a four bar linkage, if both of the side links rock, it is called a double-rocker mechanism.
双摇杆机构:在四连杆机构中,如果两个侧连杆都摇动,则称为双摇杆机构。如图2.3。

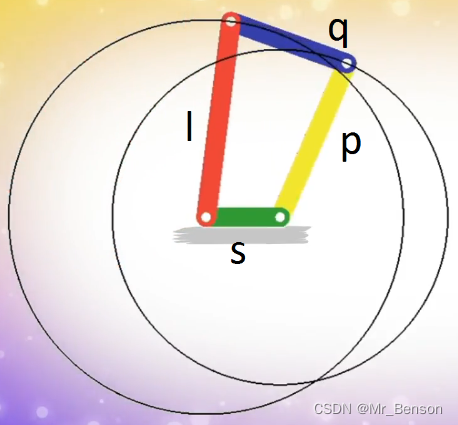

where s = length of the shortest link;l = length of the largest link;p and q = lengths of the other two links.
其中,s是最短链接的长度,l是最长链接的长度,p 和 q 是 其他两个链接的长度
3.Grashof’s Law 格拉霍夫定理
Grashof’s Law states that for a planar four-bar linkage system, the sum of the shortest and longest link lengths cannot be greater than the sum of the remaining two link lengths if there is to be a continuous relative rotation between two members.
Grashof 定律指出,对于平面四连杆系统,如果两个构件之间存在连续的相对旋转,则最短和最长连杆长度之和不能大于其余两个连杆长度之和。
在数学上表示该定理:假设 s 是最短链接的长度,l 是最长链接的长度,p 和 q 是 其他两个链接的长度,如果两个构件之间存在连续的相对旋转,则有如下公式:
s + l ≤ p + q ( 1 ) s + l \le p + q \quad\quad\quad\quad(1) s+l≤p+q(1)
Note: if s + l > p + q, then no continuous relative motion is possible; i.e., if the above inequality is NOT satisfied, no link will make a complete revolution relative to another.
需要注意的是,如果s + l > p + q,则不可能有连续的相对运动。

4.The Degree of Freedom – Definition and Calculation Method
自由度定义和计算方法(刚体、二维)
Definition : The number of independent motions that are allowed to the body or, in case of a mechanism made of several bodies, number of possible independent relative motions between the pieces of the mechanism
定义:物体允许的独立运动的数量,或者在由多个物体组成的机构的情况下,机构部件之间可能的独立相对运动的数量
For a simple mechanism, the degree of freedom (F) is given by the Grubler’s criterion: F = 3 (n - 1) - 2j - h, where j = number of revolute joints, n = number of links, h = number of higher pairs
对于简单机构,自由度 (F) 由 Grubler 准则给出:F = 3 (n - 1) - 2j - h 其中,j = 旋转关节的数量,n = 链接的数量,h = 高副的数量
在平面四杆连杆机构中,n = 4, j = 4, h = 0 ,代入公式后,得 F = 1,即自由度为1。
5.扩展连接























 7771
7771

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








