论文全名:Multiview hyperedge-aware hypergraph embedding learning for multisite, multiatlas fMRI based functional connectivity network analysis
英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用
目录
2.3.1. Hypergraph and HGCN with FCN
2.3.2. The proposed CcSi-MHAHGEL
2.4.1. Dataset and data preprocessing
2.4.4. Classification performance
2.4.7. Most discriminative ROIs discovered by CcSi-MHAHGEL
2.5.1. Visualization of FCN embeddings
2.5.2. Influence of key hyperparameters
2.5.3. Generalization ability of the class-consistency and site-independence modules
2.5.4. Results of CcSi-MHAHGEL with three-atlas-based FCNs
2.5.5. Results of CcSi-MHAHGEL on the whole ABIDE
2.5.6. Influence of hyperedge construction schemes
2.5.7. Limitations and future work
1. 省流版
1.1. 心得
(1)既然作者想做的事情是跨站点那么只跨4/21个ABIDE站点是不是没有那么有说服力啊(消融实验测了很多的,19个站点,精度差不多)
(2)超图没什么选择,其实也就是多聚合了一下
(3)做了好多实验
(4)名字取得好长捏,有点让人记不住。最近KAN爆火,感觉凡事还是得从简
1.2. 论文总结图

2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
①They proposed Class-consistency and Site-independence Multiview Hyperedge-Aware HyperGraph Embedding Learning (CcSi-MHAHGEL) framework
②Existing problems: insufficient researches in multi-site and multi-atlas
③Graph construction: one hypergraph per subject
2.2. Introduction
①Shortcomings of GCNs: simple structure, inadequate connections between subjects, different brain graph distributions between different sites
②Atlas: AAL and HO
③Samples: 355 with 167 ASD and 188 HC from the bigest 4 sites from ABIDE
④怎么又是Grad-CAM
⑤Their contributions: proposed hypergraph based on multi-atlases, class-consistency and site-independence modules
⑥ denotes the cardinality of a set(就是一个集合里面有几个数)
atrophy n.萎缩 vi.萎缩;衰退 cardinality n.基数;集的势(mathematics) the number of elements in a set or group (considered as a property of that grouping)
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Hypergraph and HGCN with FCN
①Representation of hypergraph:
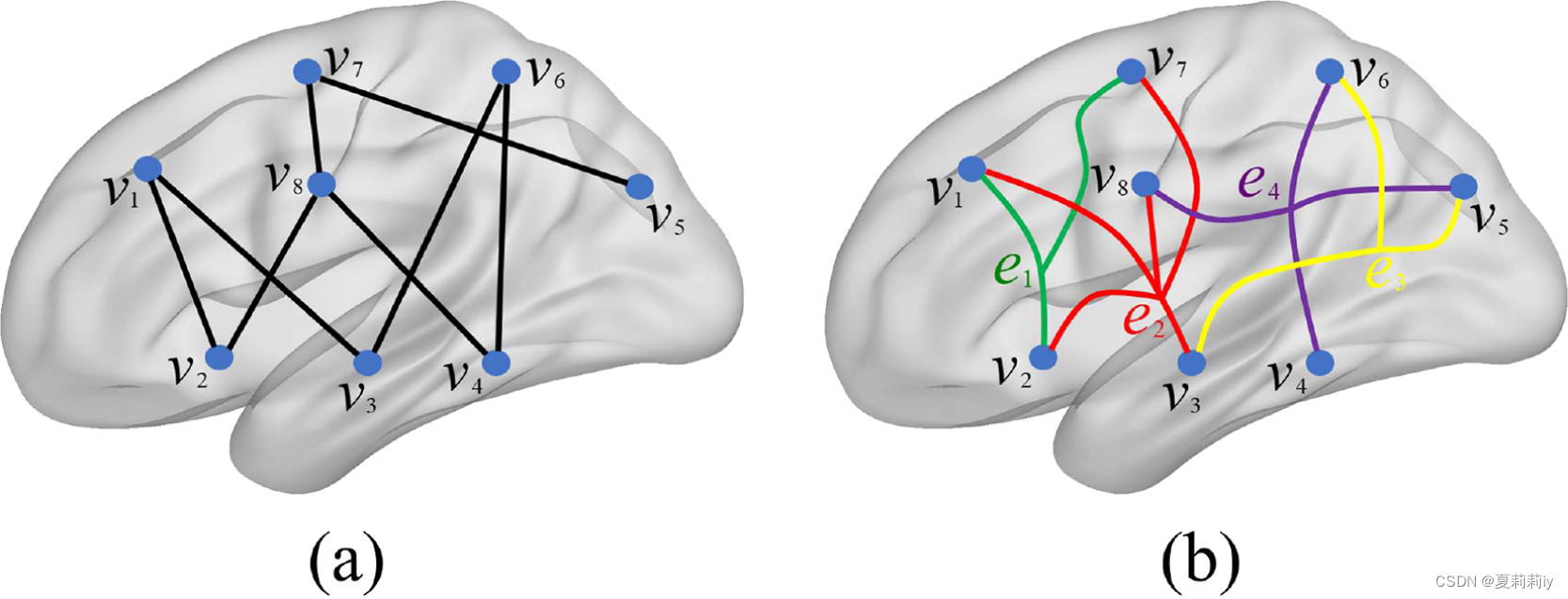
②Hypergtaph can be represented as , where
denotes vertex set (ROI),
denotes hyperedge set. Each hyperedge
has its own weight
, and
denotes diagonal matrix of the hyperedge weights.
③All the hyperedges satisfy
④Incidence matrix of is
with 0 or 1
⑤Degree of can be calculated by
(有边就将边权重*1加起来), and its diagonal degree matrices
⑥Degree of can be
and its diagonal degree matrices
⑦Hypergraph Laplacian matrix can be expressed as , where
.
⑧Funcional connectivity network (FCN) matrix each subject:
where the subscript denotes the order number of each ROI. They set for the feature of
⑨Similarity between vertexes:
is set to the mean of the Euclidean distances of all vertex pairs empirically
⑩Followed by ④, they further update incidence matrix to:
⑪To avoid differences weighted incidence matrix between subjects, they calculated it by average FCN
⑫Convolution operation on -th layer:
where denotes the learnable weight matrix,
represents nonlinear activation function
⑬总的就是说v是ROI,edge感觉是ROI相似度,然后节点特征是FCN的行捏
2.3.2. The proposed CcSi-MHAHGEL
The overall framework:

(1)Multiview hyperedge-aware HGCN for learning embeddings of multiatlas-based FCNs
①They introduced categories of atlas, then update
②The corresponding convolution:
and they separate and combine the of patients (PTs) and HCs by:
③They proposed an adaptive hyperedge weight learning. They first obtain the hyperedge features by:
(感觉是个[2e,v] matmul [v,v]的操作,得到个[2e,v]。相当于是一个超边的特征是它连接的所有节点特征的和。但是这样确实一个超边特征是个[1,v]的向量了(⭐但是为什么作者的H是[n,2n]我的是[2e,v]呢我只是想区别一下啦。作者构建了N个超边,所以和N个顶点等同了。每个超边连K个顶点,即从一个ROI开始算距离最近的K-1条边捏))
④To squeez the features, they further:
where denotes learnable vector of weight coefficients. (应该就是[2e,v]mutmal[v,1] )
⑤The hyperedge weight matrix . They mention that the traditional hyperedge weight is not adaptive
⑥The apply max and mean pooling in the last layer of HGCN. For finall output , they concatenate max vector and mean vector to
. And further concatenating
under different atlases:
where are the weight coefficients which:
(2)Class-consistency module for promoting discrimination across classes in the multiatlas-based FCN embeddings
①To penalize the intra-class dissimilarities and inter-class similarities, they designed:
where denotes training subjects(嘛他意思就是同类别的缩小差异,不同类别的扩大差异)
(3)Site-independence module for mitigating site influences in the multiatlas-based FCN embeddings
①The site information is calculated by:
where it is one-hot encoder~ and denotes the type of site
②They introduce the Hilbert–Schmidt independence criterion (HSIC) (the smaller the less dependence) to minimize FCN embeddings and the one-hot site vectors
:
where ,
and
. Both
are kernel functions, such as linear (the authors choosed), polynomial, and radial basis. Thus:
(4)Classification and loss function
①The loss function: , where
and
are tunable hyperparameters or regularization parameters(CE就不多说了吧?交叉熵啊)
2.4. Experimental results
2.4.1. Dataset and data preprocessing
①Dataset: ABIDE I/II(作者说的是”ABIDE“,但是根据有21个站点来推断,应该是把I和II加在一起选的,最大的四个)
②Samples: 167 ASD and 188 HC:

③Preprocessing pipeline: DPARSF
④Preprocessing processes: "head motion correction, co-registration, spatial normalization to the standard Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space, spatial smoothing with a 6-mm full width half maximum (FWHM) Gaussian kernel, and band-pass filtering at 0.01 to 0.1Hz."
⑤Atlases: AAL 116 ad HO 111, for AAL and
for HO
⑥FCN: "Fisher’s z-transformed Pearson’s correlation coefficient between BOLD time series of each pair of ROIs"
2.4.2. Experimental settings
①Cross validation: 10 fold
②Running times: 5
③Metrics: accuracy, sensitivity, precision, F1-score, and AUC
④Hyperparameters: , hidden dim = 256/64 in the first/second HGCN layer,
is ReLU, weight coefficients
, MLP: 128/32/2, regularization parameters
,
⑤Epoch: 30
⑥Batch size: 24
⑦Learning rate: 0.001
2.4.3. Methods for comparison
①Briefly listing and introducing the parameter settings of compared models. All the models adopt the same convolution layers, MLP layers, hidden dim numbers, pochs, batch size, activation function, and learning rate for fair
2.4.4. Classification performance
①Comparison table:

the multiview methods (i.e., MGEL, MHGEL, and CcSi-MHAHGEL) mostly perform better performance than all those single-view methods (i.e., SVM, DNN, BrainNetCNN, GEL, BrainGNN, GAT and HGEL) and the hypergraph-based deep learning methods (i.e., HGEL, MHGEL, and CcSi-MHAHGEL) also outperform simple-graph-based counterparts (namely GEL and MGEL)
2.4.5. Ablation study
①Ablation study:

where it concludes different signle atlas models, HGEL with HGCN (HAHGEL), MHGEL with HGCN (MHAHGEL), and CcSi-MHAHGEL w/o loss
2.4.6. Construction of the shared incidence matrix
①Ablation between different readout methods:

2.4.7. Most discriminative ROIs discovered by CcSi-MHAHGEL
①They got class activation values of ROIs in fully connection layer by Grad-Cam and visualized the top 10 by BrainNet Viewer:



②They start to analyse some medical findings
visuospatial adj. 视觉空间;视觉空间的
2.5. Discussions
2.5.1. Visualization of FCN embeddings
①2D t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE)

2.5.2. Influence of key hyperparameters
①Ablation of :

②Ablation of and
:

③Ablation of and
:

2.5.3. Generalization ability of the class-consistency and site-independence modules
①Adding two loss functions to other models:

2.5.4. Results of CcSi-MHAHGEL with three-atlas-based FCNs
①Three atlas based ablation:

2.5.5. Results of CcSi-MHAHGEL on the whole ABIDE
①They choosed 19 sites which more than 10 subjects with 372 ASD and 433 HC:

2.5.6. Influence of hyperedge construction schemes
①Introducing the impacts
2.5.7. Limitations and future work
①They did not consider sex, age and other influences
②There are substitution of HSIC
③They only consider static graph
2.6. Conclusion
ok
3. Reference List
Wang, W. et al. (2024) 'Multiview hyperedge-aware hypergraph embedding learning for multisite, multiatlas fMRI based functional connectivity network analysis', Medical Image Analysis, 94. doi: Redirecting






















 773
773











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








