Abstract
这个算法是在写实验的时候要执行的,因为阅读的文档和最后的报告都是要用英文写,所以这里就用英文来写了,用的英文句子都比较简单,希望理解起来容易一些。所参照的论文,课件都在博文中说道。大家觉得算法介绍,执行不对的地方欢迎指出来共同探讨。
Iterated Tverberg point algorithm was used to compute an approximate of center point in computational geometry. Here, we use it to combine a set of models computed by machine learning algorithm to a much better model.
Definitions
- Closed Halfspace is a set { x∈Rd:a⋅x≤b,a∈Rd,b∈R} .
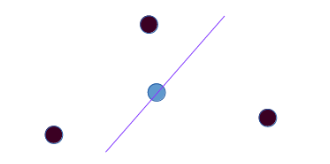
- The Tukey depth of a point x with respect to a set P is the minimum number of points of P in any halfspace containing x. In the following figure, the depth of the blue point w.r.t the black points set is 1.
- A point x is a centerpoint with respect to a set P⊂Rd if depth of x is at least nd+1 .
- Convex hull of a set A, denoted by conv(A), is the set of all convex combination of points in A. conv(A)={ x|∃a1,...,aN∈A,α1,...,αn≥0;∑Ni=1αi=1;x=∑Ni=1αiai.} .
主要参照 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/academic/class/15456-s10/ClassNotes/
Theorems
这个部分的理论证明是后面算法执行必须要用的所以很必要。
Radon Theorem
Let a1,a2,...,am∈Rd , m ≥d+2 , then there is a partition of {1,…,m} into I and J such that the convex hull of { ai,i∈I} and { aj,j∈J} is nonempty.Proof: Denote bi:=(ai,1) . There are m≥d+2 vectors in d+1 dimensional space,
thus they are linearly dependent. It means that there exists α1,...,αm not all zero
such that:
∑i=1mαibi=0.
Construct I={ i|αi≥0} and J={ j|αj<0} .
As the last coordinate of bi is 1, thus:
∑i∈Iαi








 本文介绍了迭代Tverberg点算法在计算几何中用于寻找近似中心点的应用,特别是在结合机器学习算法生成更优模型时的作用。文章涵盖了定义、定理和算法的详细步骤,包括Radon定理和Carathéodory定理的证明,以及算法如何确保找到具有至少n/2(d+1)^2 Tukey深度的点。
本文介绍了迭代Tverberg点算法在计算几何中用于寻找近似中心点的应用,特别是在结合机器学习算法生成更优模型时的作用。文章涵盖了定义、定理和算法的详细步骤,包括Radon定理和Carathéodory定理的证明,以及算法如何确保找到具有至少n/2(d+1)^2 Tukey深度的点。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 551
551

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








