实验目的
- 掌握操作系统并发的概念
- 理解并发中的生产-消费者问题
- 熟悉Linux线程编程机制,掌握线程同步的实现方式
实验内容
- 1. 完成Linux线程程序,完成利用Linux线程信 号量及PV操作实现消费者的 同步关系的程序。
- 2. 利用Linux线程信号量及PV操作实现哲学家 就餐的同步关系的程序。
实验环境
Ubuntu 12.04 LTS
Device name: oslinux-virtual-machine
Memory: 1001.2MiB
Processor: AMD Ryzen 77730U with Radeon Graphics
Graphics: Unknown
OS type: 32-bit
Disk: 20.3GB
实验步骤
- 1. 在test3.c中编写生产者和消费者两个线程函数,编译运行程序,并测试运 行结果。
- 2. 新建工程philosophers,实现哲学家就餐问题。
实验结果
结果展示
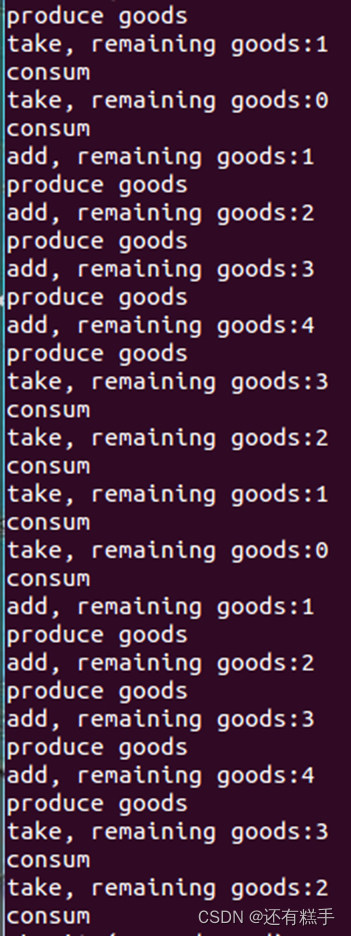
生产者消费者问题:
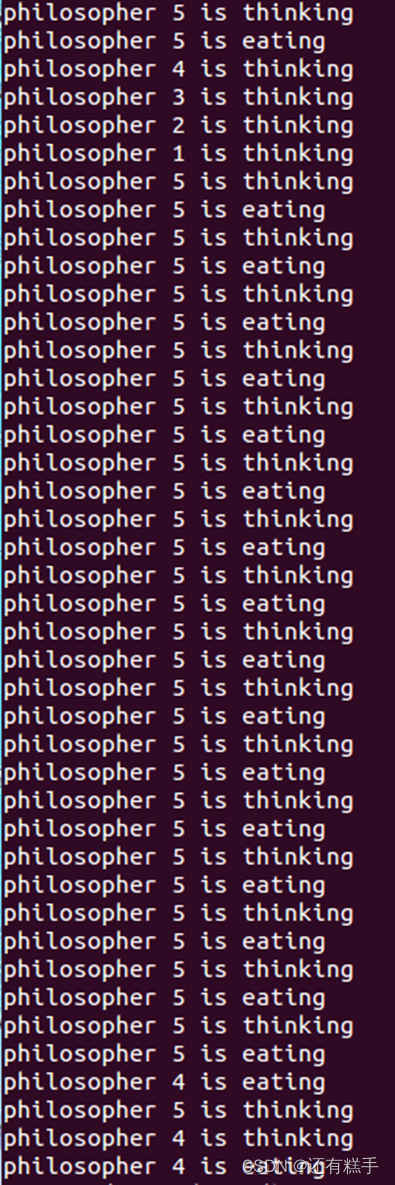
哲学家就餐问题:
核心代码
生产者消费者问题代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define msleep(x) usleep(x*1000) //微秒
#define PRODUCT_SPEED msleep(200) //生产速度
#define CONSUM_SPEED msleep(300) //消费速度
#define INIT_NUM 2 //仓库原有产品数
#define TOTAL_NUM 4 //仓库容量
sem_t p_sem,c_sem,sh_sem;
int num = INIT_NUM;
void product(void) {
sleep(CONSUM_SPEED);
}
int add_to_lib() {
num++;
msleep(500);
return num;
}
void consum() {
sleep(PRODUCT_SPEED);
}
int remove_from_lib() {
num--;
msleep(500);
return num;
}
void *productor(void *arg) {
while (1) {
printf("produce goods\n");
sem_wait(&p_sem);
sem_wait(&sh_sem);
product();
printf("add, remaining goods:%d\n", add_to_lib());
sem_post(&sh_sem);
sem_post(&c_sem);
}
}
void *consumer(void *arg) {
while (1) {
sem_wait(&c_sem);
sem_wait(&sh_sem);
consum();
printf("take, remaining goods:%d\n",remove_from_lib());
sem_post(&sh_sem);
sem_post(&p_sem);
printf("consum\n");
}
}
int main() {
pthread_t tid_1, tid_2;
sem_init(&p_sem, 0, TOTAL_NUM - INIT_NUM);
sem_init(&c_sem, 0, INIT_NUM);
sem_init(&sh_sem, 0, 1);
pthread_create(&tid_1, NULL, productor, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid_2, NULL, consumer, NULL);
pthread_join(tid_1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid_2, NULL);
sem_destroy(&p_sem);
sem_destroy(&c_sem);
sem_destroy(&sh_sem);
return 0;
}哲学家就餐问题代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define msleep(x) usleep(x * 1000)
sem_t forks[5];
sem_t room;
int number[5] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4};
void *philosopher(void *arg){
int i = *(int *)arg;
while(1){
printf("philosopher %d is thinking\n", i+1);
sem_wait(&room);
sem_wait(&forks[i]);
sem_wait(&forks[(i+1) % 5]);
printf("philosopher %d is eating\n", i+1);
msleep(500);
sem_post(&forks[(i+1) % 5]);
sem_post(&forks[i]);
sem_post(&room);
}
}
int main(void){
pthread_t phi[5];
int j;
for(j = 0;j < 5;++j){
sem_init(&forks[j], 0, 1);
}
sem_init(&room, 0, 4);
for(j = 0;j < 5;++j){
pthread_create(&phi[j], NULL, philosopher, &number[j]);
}
for(j = 0;j < 5;++j){
pthread_join(phi[j], NULL);
}
for(j = 0;j < 5;++j){
sem_destroy(&forks[j]);
}
sem_destroy(&room);
return 0;
}





















 612
612

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










