首先世界上存在这么一个东西

先写出它的NFA

然后就可以开始转换了

那么具体是怎么转换的呢?
NFA首先看S
S可以通过0转换成P
所以在对应的DFA里写P

然后S可以通过1转化成S或R,所以在对应的地方写SR

那么多年后的我可能会问道:他们的角标是怎么来的?
据我观察,每一个中括号里面不同的字母们会对应不同的角标,就像S-A P-B SR-C R-D
这样也可以解释每一行的前面都会有一个字母。
这个字母也是DFA的新状态。
第一行写完之后,第二行就是下一个字符串对应的转化了
所以第二行是P的转化,第三行是SR的转化,这样竖排就对应ABCD
这样依次写下去,没有对应的就直接空格,像SR转换成0P。有重复的只写一个。
这样整个表就写完了。
那么就可以画出DFA

但是世界上还存在这个东西![]()
那么对于这种NFA,应该怎么转化呢
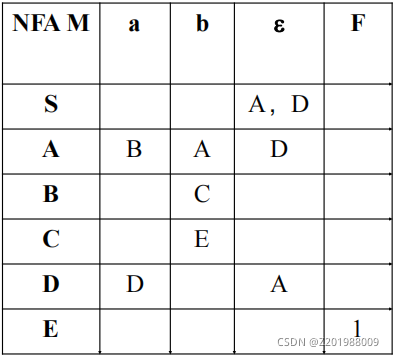
这个就直接把S加AD,A加D,D加A

只要转化之后就要加上其![]() 对应的状态。
对应的状态。
对于F这一列,只要DFA M这列的中括号里面有E,F就是1








 本文详细介绍了非确定有限自动机(NFA)如何转换为确定有限自动机(DFA),通过实例解析了转换过程,包括状态转移的规则和角标的确定。同时,文章探讨了具有ε转移的NFA的转换方法,强调了在转换过程中F状态的处理。内容适合计算机科学与信息技术领域的学生和从业者学习理解。
本文详细介绍了非确定有限自动机(NFA)如何转换为确定有限自动机(DFA),通过实例解析了转换过程,包括状态转移的规则和角标的确定。同时,文章探讨了具有ε转移的NFA的转换方法,强调了在转换过程中F状态的处理。内容适合计算机科学与信息技术领域的学生和从业者学习理解。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








