
7.3.2 编写编码器(encoder)和解码器(decoder)模型
实现一个基于注意力的“编码器-解码器”模型,关于这种模型的基本知识,可以阅读 TensorFlow 的神经机器翻译 (序列到序列) 教程。本实例采用一组更新的API来实现,实现了上述序列到序列教程中的注意力方程式。下图7-1显示了注意力机制为每个输入单词分配一个权重,然后解码器将这个权重用于预测句子中的下一个单词。下图中的和公式是 Luong 的论文中注意力机制的一个例子。

图7-1 注意力机制
输入经过编码器模型,编码器模型为我们提供形状为 (批大小,最大长度,隐藏层大小) 的编码器输出和形状为 (批大小,隐藏层大小) 的编码器隐藏层状态。下面是所实现的方程式:
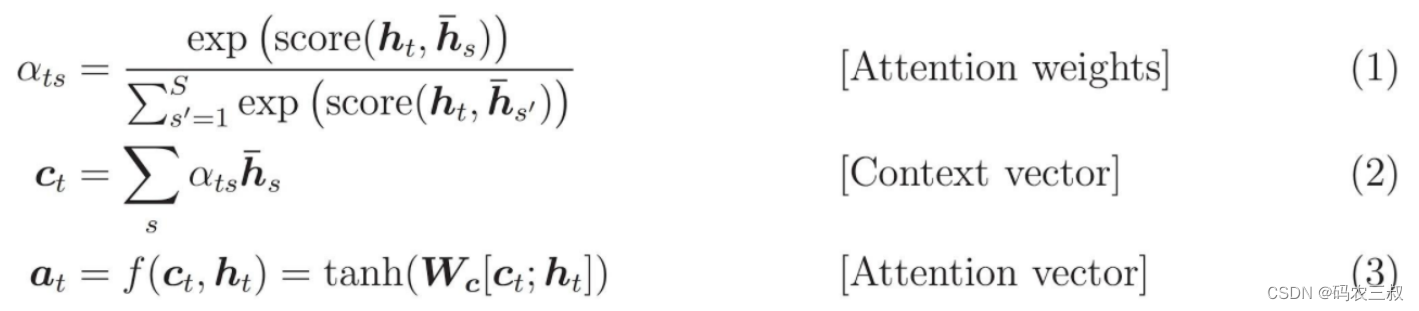
本实例的编码器采用 Bahdanau 注意力方式实现,在使用简化形式编写代码之前需要先决定符号:
- FC = 完全连接(密集)层
- EO = 编码器输出
- H = 隐藏层状态
- X = 解码器输入
以及如下所示的伪代码:
- score = FC(tanh(FC(EO) + FC(H)))
- attention weights = softmax(score, axis = 1)。 Softmax 默认被应用于最后一个轴,但是这里我们想将它应用于 第一个轴, 因为分数 (score) 的形状是 (批大小,最大长度,隐藏层大小)。最大长度 (max_length) 是我们的输入的长度。因为我们想为每个输入分配一个权重,所以 softmax 应该用在这个轴上。
- context vector = sum(attention weights * EO, axis = 1)。选择第一个轴的原因同上。
- embedding output = 解码器输入 X 通过一个嵌入层。
- merged vector = concat(embedding output, context vector)
- 此合并后的向量随后被传送到 GRU
上述每个步骤中所有向量的形状已在如下实现代码中进行了注释:
class Encoder(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, enc_units, batch_sz):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.batch_sz = batch_sz
self.enc_units = enc_units
self.embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.gru = tf.keras.layers.GRU(self.enc_units,
return_sequences=True,
return_state=True,
recurrent_initializer='glorot_uniform')
def call(self, x, hidden):
x = self.embedding(x)
output, state = self.gru(x, initial_state = hidden)
return output, state
def initialize_hidden_state(self):
return tf.zeros((self.batch_sz, self.enc_units))
encoder = Encoder(vocab_inp_size, embedding_dim, units, BATCH_SIZE)
# 样本输入
sample_hidden = encoder.initialize_hidden_state()
sample_output, sample_hidden = encoder(example_input_batch, sample_hidden)
print ('Encoder output shape: (batch size, sequence length, units) {}'.format(sample_output.shape))
print ('Encoder Hidden state shape: (batch size, units) {}'.format(sample_hidden.shape))
class BahdanauAttention(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, units):
super(BahdanauAttention, self).__init__()
self.W1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units)
self.W2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units)
self.V = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
def call(self, query, values):
# 隐藏层的形状 == (批大小,隐藏层大小)
# hidden_with_time_axis 的形状 == (批大小,1,隐藏层大小)
# 这样做是为了执行加法以计算分数
hidden_with_time_axis = tf.expand_dims(query, 1)
# 分数的形状 == (批大小,最大长度,1)
# 我们在最后一个轴上得到 1, 因为我们把分数应用于 self.V
# 在应用 self.V 之前,张量的形状是(批大小,最大长度,单位)
score = self.V(tf.nn.tanh(
self.W1(values) + self.W2(hidden_with_time_axis)))
# 注意力权重 (attention_weights) 的形状 == (批大小,最大长度,1)
attention_weights = tf.nn.softmax(score, axis=1)
# 上下文向量 (context_vector) 求和之后的形状 == (批大小,隐藏层大小)
context_vector = attention_weights * values
context_vector = tf.reduce_sum(context_vector, axis=1)
return context_vector, attention_weights
attention_layer = BahdanauAttention(10)
attention_result, attention_weights = attention_layer(sample_hidden, sample_output)
print("Attention result shape: (batch size, units) {}".format(attention_result.shape))
print("Attention weights shape: (batch_size, sequence_length, 1) {}".format(attention_weights.shape))
class Decoder(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, dec_units, batch_sz):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.batch_sz = batch_sz
self.dec_units = dec_units
self.embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.gru = tf.keras.layers.GRU(self.dec_units,
return_sequences=True,
return_state=True,
recurrent_initializer='glorot_uniform')
self.fc = tf.keras.layers.Dense(vocab_size)
# 用于注意力
self.attention = BahdanauAttention(self.dec_units)
def call(self, x, hidden, enc_output):
# 编码器输出 (enc_output) 的形状 == (批大小,最大长度,隐藏层大小)
context_vector, attention_weights = self.attention(hidden, enc_output)
# x 在通过嵌入层后的形状 == (批大小,1,嵌入维度)
x = self.embedding(x)
# x 在拼接 (concatenation) 后的形状 == (批大小,1,嵌入维度 + 隐藏层大小)
x = tf.concat([tf.expand_dims(context_vector, 1), x], axis=-1)
# 将合并后的向量传送到 GRU
output, state = self.gru(x)
# 输出的形状 == (批大小 * 1,隐藏层大小)
output = tf.reshape(output, (-1, output.shape[2]))
# 输出的形状 == (批大小,vocab)
x = self.fc(output)
return x, state, attention_weights
decoder = Decoder(vocab_tar_size, embedding_dim, units, BATCH_SIZE)
sample_decoder_output, _, _ = decoder(tf.random.uniform((64, 1)),
sample_hidden, sample_output)
print ('Decoder output shape: (batch_size, vocab size) {}'.format(sample_decoder_output.shape))执行后会输出:
Encoder output shape: (batch size, sequence length, units) (64, 16, 1024)
Encoder Hidden state shape: (batch size, units) (64, 1024)
Attention result shape: (batch size, units) (64, 1024)
Attention weights shape: (batch_size, sequence_length, 1) (64, 16, 1)
Decoder output shape: (batch_size, vocab size) (64, 4935)然后通过如下代码定义优化器和损失函数:
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()
loss_object = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(
from_logits=True, reduction='none')
def loss_function(real, pred):
mask = tf.math.logical_not(tf.math.equal(real, 0))
loss_ = loss_object(real, pred)
mask = tf.cast(mask, dtype=loss_.dtype)
loss_ *= mask
return tf.reduce_mean(loss_)最后通过如下代码设置检查点(基于对象保存):
checkpoint_dir = 'training_checkpoints'
checkpoint_prefix = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, "ckpt")
checkpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint(optimizer=optimizer,
encoder=encoder,
decoder=decoder)
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










