从编程实现角度学习Faster R-CNN(附极简实现)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/32404424
代码:
https://github.com/chenyuntc/simple-faster-rcnn-pytorch
先把程序跑起来,Ubuntu-pytorch1.1.0
https://github.com/chenyuntc/simple-faster-rcnn-pytorch/issues/157
python train.py train --env='fasterrcnn-caffe' --plot-every=100
首先配置文件:
simple-faster-rcnn-pytorch/utils/config.py
然后是数据流入:

def train(**kwargs):
opt._parse(kwargs)
dataset = Dataset(opt)
print('load data')
dataloader = data_.DataLoader(dataset, \
batch_size=1, \
shuffle=True, \
# pin_memory=True,
num_workers=opt.num_workers)
testset = TestDataset(opt)
test_dataloader = data_.DataLoader(testset,
batch_size=1,
num_workers=opt.test_num_workers,
shuffle=False, \
pin_memory=False
)class Dataset:
def __init__(self, opt):
self.opt = opt
self.db = VOCBboxDataset(opt.voc_data_dir)
self.tsf = Transform(opt.min_size, opt.max_size)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
ori_img, bbox, label, difficult = self.db.get_example(idx)
img, bbox, label, scale = self.tsf((ori_img, bbox, label))
# TODO: check whose stride is negative to fix this instead copy all
# some of the strides of a given numpy array are negative.
return img.copy(), bbox.copy(), label.copy(), scale
def __len__(self):
return len(self.db)class VOCBboxDataset:
def __init__(self, data_dir, split='trainval',
use_difficult=False, return_difficult=False,
):
# if split not in ['train', 'trainval', 'val']:
# if not (split == 'test' and year == '2007'):
# warnings.warn(
# 'please pick split from \'train\', \'trainval\', \'val\''
# 'for 2012 dataset. For 2007 dataset, you can pick \'test\''
# ' in addition to the above mentioned splits.'
# )
id_list_file = os.path.join(
data_dir, 'ImageSets/Main/{0}.txt'.format(split))
self.ids = [id_.strip() for id_ in open(id_list_file)]
self.data_dir = data_dir
self.use_difficult = use_difficult
self.return_difficult = return_difficult
self.label_names = VOC_BBOX_LABEL_NAMES
def get_example(self, i):
"""Returns the i-th example.
Returns a color image and bounding boxes. The image is in CHW format.
The returned image is RGB.
Args:
i (int): The index of the example.
Returns:
tuple of an image and bounding boxes
"""
id_ = self.ids[i]
anno = ET.parse(
os.path.join(self.data_dir, 'Annotations', id_ + '.xml'))
bbox = list()
label = list()
difficult = list()
for obj in anno.findall('object'):
# when in not using difficult split, and the object is
# difficult, skipt it.
if not self.use_difficult and int(obj.find('difficult').text) == 1:
continue
difficult.append(int(obj.find('difficult').text))
bndbox_anno = obj.find('bndbox')
# subtract 1 to make pixel indexes 0-based
bbox.append([
int(bndbox_anno.find(tag).text) - 1
for tag in ('ymin', 'xmin', 'ymax', 'xmax')])
name = obj.find('name').text.lower().strip()
label.append(VOC_BBOX_LABEL_NAMES.index(name))
bbox = np.stack(bbox).astype(np.float32)
label = np.stack(label).astype(np.int32)
# When `use_difficult==False`, all elements in `difficult` are False.
difficult = np.array(difficult, dtype=np.bool).astype(np.uint8) # PyTorch don't support np.bool
# Load a image
img_file = os.path.join(self.data_dir, 'JPEGImages', id_ + '.jpg')
img = read_image(img_file, color=True)
# if self.return_difficult:
# return img, bbox, label, difficult
return img, bbox, label, difficult
__getitem__ = get_example在VOC数据集中,是以XML形式存储的,
https://blog.csdn.net/zhangjunbob/article/details/52769381
<difficult>0</difficult>//目标是否难以识别(0表示容易识别)通过枚举VOC_BBOX_LABEL_NAMES,获取label数字,保存list
上述中,
difficult是存放是否为难例样本的list
bbox是存放样本的list
若use_difficult不开启,则不保存难例样本
读取图像:
def read_image(path, dtype=np.float32, color=True):
"""Read an image from a file.
This function reads an image from given file. The image is CHW format and
the range of its value is :math:`[0, 255]`. If :obj:`color = True`, the
order of the channels is RGB.
Args:
path (str): A path of image file.
dtype: The type of array. The default value is :obj:`~numpy.float32`.
color (bool): This option determines the number of channels.
If :obj:`True`, the number of channels is three. In this case,
the order of the channels is RGB. This is the default behaviour.
If :obj:`False`, this function returns a grayscale image.
Returns:
~numpy.ndarray: An image.
"""
f = Image.open(path)
try:
if color:
img = f.convert('RGB')
else:
img = f.convert('P')
img = np.asarray(img, dtype=dtype)
finally:
if hasattr(f, 'close'):
f.close()
if img.ndim == 2:
# reshape (H, W) -> (1, H, W)
return img[np.newaxis]
else:
# transpose (H, W, C) -> (C, H, W)
return img.transpose((2, 0, 1))这里会返回:return img, bbox, label, difficult
img为array形式的图像,bbox,label,是否为难例样本
比如'bird',索引为2
VOC_BBOX_LABEL_NAMES = (
'aeroplane',
'bicycle',
'bird',
'boat',
'bottle',
'bus',
'car',
'cat',
'chair',
'cow',
'diningtable',
'dog',
'horse',
'motorbike',
'person',
'pottedplant',
'sheep',
'sofa',
'train',
'tvmonitor')
然后经过:
img, bbox, label, scale = self.tsf((ori_img, bbox, label))
class Transform(object):
def __init__(self, min_size=600, max_size=1000):
self.min_size = min_size
self.max_size = max_size
def __call__(self, in_data):
img, bbox, label = in_data
_, H, W = img.shape
img = preprocess(img, self.min_size, self.max_size)
_, o_H, o_W = img.shape
scale = o_H / H
bbox = util.resize_bbox(bbox, (H, W), (o_H, o_W))
# horizontally flip
img, params = util.random_flip(
img, x_random=True, return_param=True)
bbox = util.flip_bbox(
bbox, (o_H, o_W), x_flip=params['x_flip'])
return img, bbox, label, scale处理图像和对应的box,并且随机翻转(将box也要对应处理)
def preprocess(img, min_size=600, max_size=1000):
"""Preprocess an image for feature extraction.
The length of the shorter edge is scaled to :obj:`self.min_size`.
After the scaling, if the length of the longer edge is longer than
:param min_size:
:obj:`self.max_size`, the image is scaled to fit the longer edge
to :obj:`self.max_size`.
After resizing the image, the image is subtracted by a mean image value
:obj:`self.mean`.
Args:
img (~numpy.ndarray): An image. This is in CHW and RGB format.
The range of its value is :math:`[0, 255]`.
Returns:
~numpy.ndarray: A preprocessed image.
"""
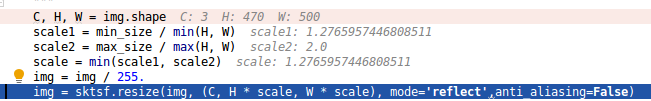
C, H, W = img.shape
scale1 = min_size / min(H, W)
scale2 = max_size / max(H, W)
scale = min(scale1, scale2)
img = img / 255.
img = sktsf.resize(img, (C, H * scale, W * scale), mode='reflect',anti_aliasing=False)
# both the longer and shorter should be less than
# max_size and min_size
if opt.caffe_pretrain:
normalize = caffe_normalize
else:
normalize = pytorch_normalze
return normalize(img)原本是H470,W500,改变后变成了H600,W639
from skimage import transform as sktsf

有两种归一化,一种是caffe,还有一种是pytorch
def caffe_normalize(img):
"""
return appr -125-125 BGR
"""
img = img[[2, 1, 0], :, :] # RGB-BGR
img = img * 255
mean = np.array([122.7717, 115.9465, 102.9801]).reshape(3, 1, 1)
img = (img - mean).astype(np.float32, copy=True)
return img
def pytorch_normalze(img):
"""
https://github.com/pytorch/vision/issues/223
return appr -1~1 RGB
"""
_normalize = Normalize_2_0(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
img = _normalize(t.from_numpy(img))
return img.numpy()
class Normalize_2_0(object):
"""Normalize an tensor image with mean and standard deviation.
Given mean: ``(M1,...,Mn)`` and std: ``(S1,..,Sn)`` for ``n`` channels, this transform
will normalize each channel of the input ``torch.*Tensor`` i.e.
``input[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]``
Args:
mean (sequence): Sequence of means for each channel.
std (sequence): Sequence of standard deviations for each channel.
"""
def __init__(self, mean, std):
self.mean = mean
self.std = std
def __call__(self, tensor):
"""
Args:
tensor (Tensor): Tensor image of size (C, H, W) to be normalized.
Returns:
Tensor: Normalized Tensor image.
"""
return normalize(tensor, self.mean, self.std)不要偷懒,尽可能的“Match Everything”。由于torchvision中有预训练好的VGG16,而caffe预训练VGG要求输入图片像素在0-255之间(torchvision是0-1),BGR格式的,标准化只减均值,不除以标准差,看起来有点别扭(总之就是要多写几十行代码+专门下载模型)。然后我就用torchvision的预训练模型初始化,最后用了一大堆的trick,各种手动调参,才把mAP调到0.7(正常跑,不调参的话大概在0.692附近)。某天晚上抱着试试的心态,睡前把VGG的模型改成caffe的,第二天早上起来一看轻轻松松0.705 ...
然后box进行resize:
def resize_bbox(bbox, in_size, out_size):
"""Resize bounding boxes according to image resize.
The bounding boxes are expected to be packed into a two dimensional
tensor of shape :math:`(R, 4)`, where :math:`R` is the number of
bounding boxes in the image. The second axis represents attributes of
the bounding box. They are :math:`(y_{min}, x_{min}, y_{max}, x_{max})`,
where the four attributes are coordinates of the top left and the
bottom right vertices.
Args:
bbox (~numpy.ndarray): An array whose shape is :math:`(R, 4)`.
:math:`R` is the number of bounding boxes.
in_size (tuple): A tuple of length 2. The height and the width
of the image before resized.
out_size (tuple): A tuple of length 2. The height and the width
of the image after resized.
Returns:
~numpy.ndarray:
Bounding boxes rescaled according to the given image shapes.
"""
bbox = bbox.copy()
y_scale = float(out_size[0]) / in_size[0]
x_scale = float(out_size[1]) / in_size[1]
bbox[:, 0] = y_scale * bbox[:, 0]
bbox[:, 2] = y_scale * bbox[:, 2]
bbox[:, 1] = x_scale * bbox[:, 1]
bbox[:, 3] = x_scale * bbox[:, 3]
return bbox进行随机翻转:
def random_flip(img, y_random=False, x_random=False,
return_param=False, copy=False):
"""Randomly flip an image in vertical or horizontal direction.
Args:
img (~numpy.ndarray): An array that gets flipped. This is in
CHW format.
y_random (bool): Randomly flip in vertical direction.
x_random (bool): Randomly flip in horizontal direction.
return_param (bool): Returns information of flip.
copy (bool): If False, a view of :obj:`img` will be returned.
Returns:
~numpy.ndarray or (~numpy.ndarray, dict):
If :obj:`return_param = False`,
returns an array :obj:`out_img` that is the result of flipping.
If :obj:`return_param = True`,
returns a tuple whose elements are :obj:`out_img, param`.
:obj:`param` is a dictionary of intermediate parameters whose
contents are listed below with key, value-type and the description
of the value.
* **y_flip** (*bool*): Whether the image was flipped in the\
vertical direction or not.
* **x_flip** (*bool*): Whether the image was flipped in the\
horizontal direction or not.
"""
y_flip, x_flip = False, False
if y_random:
y_flip = random.choice([True, False])
if x_random:
x_flip = random.choice([True, False])
if y_flip:
img = img[:, ::-1, :]
if x_flip:
img = img[:, :, ::-1]
if copy:
img = img.copy()
if return_param:
return img, {'y_flip': y_flip, 'x_flip': x_flip}
else:
return img
def flip_bbox(bbox, size, y_flip=False, x_flip=False):
"""Flip bounding boxes accordingly.
The bounding boxes are expected to be packed into a two dimensional
tensor of shape :math:`(R, 4)`, where :math:`R` is the number of
bounding boxes in the image. The second axis represents attributes of
the bounding box. They are :math:`(y_{min}, x_{min}, y_{max}, x_{max})`,
where the four attributes are coordinates of the top left and the
bottom right vertices.
Args:
bbox (~numpy.ndarray): An array whose shape is :math:`(R, 4)`.
:math:`R` is the number of bounding boxes.
size (tuple): A tuple of length 2. The height and the width
of the image before resized.
y_flip (bool): Flip bounding box according to a vertical flip of
an image.
x_flip (bool): Flip bounding box according to a horizontal flip of
an image.
Returns:
~numpy.ndarray:
Bounding boxes flipped according to the given flips.
"""
H, W = size
bbox = bbox.copy()
if y_flip:
y_max = H - bbox[:, 0]
y_min = H - bbox[:, 2]
bbox[:, 0] = y_min
bbox[:, 2] = y_max
if x_flip:
x_max = W - bbox[:, 1]
x_min = W - bbox[:, 3]
bbox[:, 1] = x_min
bbox[:, 3] = x_max
return bbox回到训练代码:
for epoch in range(opt.epoch):
trainer.reset_meters()
for ii, (img, bbox_, label_, scale) in tqdm(enumerate(dataloader)):
scale = at.scalar(scale)
img, bbox, label = img.cuda().float(), bbox_.cuda(), label_.cuda()
trainer.train_step(img, bbox, label, scale)






















 1615
1615











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








