转载自医学图像处理案例(十)——SIFT3D(3D尺度不变特征变换)算法 - 腾讯云开发者社区-腾讯云
一、SIFT3D算子
上述SIFT算子用于二维图像关键点检测,医学影像一般都是三维图像,所以要用SIFT3D算子来进行关键点检测。论文中《Volumetric Image Registration From Invariant Keypoints》设计了SIFT3D算子,主要步骤与上述步骤是一样的。
关键点在数据匹配、三维重建和物体识别方面发挥了巨大的作用。和narf关键点相比较,sift点用的更多。
SIFT3D的理论基础完全是从图像特征SIFT2D中迁移类比过来的,类似的还有Harris3D和Harris6D的理论也是来源于Harris2D的,这些点云特征在PCL库中都有具体的实现。Harris3D和Harris6D目前已经有很好的博客和视频讲解了但是SIFT3D却没有一个比较好的介绍。于是本人最近详细看了PCL库中SIFT3D关键点的提取流程,并类比SIFT2D在这里进行完整的介绍。
1.尺度空间极值检测
在高斯金字塔上来计算DoG,在尺度和空间上搜索图像的局部极值。例如在图像一个像素点的四邻域内进行比较,判断是否是局部极值,如果是局部极值,则可能是关键点。

2.关键点定位
当找到候选关键点位置后,就必须对其进行优化获取更准确的结果。计算出所有候选关键点的高斯差分数值,并去除小于一定比例的最大高斯差分数值的关键点。
采用梯度分量的相关性即结构张量来追踪关键点大致方向。由于结构张量是实对称矩阵,所以可以对其进行正交特征分解,因此可使用特征向量来标识关键点的局部方向。

由于特征向量只是关键点的大致方向,不具有鲁棒性,所以需要采用一些规则去除不可靠的关键点。
规则(1)、结构张量的特征值按升序排列,如果满足下式的话,就去除该关键点;

规则(2)、计算图像梯度与特征向量的角度。如果满足下式的话,就去除该关键点;

通过上面两个规则会消除大量不可靠的关键点,剩下的就强关键点。
3.关键点方向分配
对于检测出来的关键点,获取其二十面体区域,在该二十面体区域中计算梯度大小值和方向。通过二十面体的十二个顶点来表示柱,实现:对二十面体中相交三角形的三个顶点的梯度向量进行加权累加生成一个柱,这样一共就生成十二个柱。

4.关键点描述符
通过上述步骤,对于每一个关键点已经有了三个信息:位置、尺度以及方向。接下来就是为每个关键点建立一个描述符,用一组向量将这个关键点描述出来。对以关键点为中心的半径为4的球形区域划分为4x4x4大小的立方体子块,对于每个子块,创建12个柱向量,共有生成4x4x4x12=768个值向量形式来描述关键点。

二、SIFT3D算子实现
c++ 代码
// STL
#include <iostream>
// PCL
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/common/io.h>
#include <pcl/keypoints/sift_keypoint.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/console/time.h>
/* This examples shows how to estimate the SIFT points based on the
* z gradient of the 3D points than using the Intensity gradient as
* usually used for SIFT keypoint estimation.
*/
namespace pcl
{
template<>
struct SIFTKeypointFieldSelector<PointXYZ>
{
inline float
operator () (const PointXYZ &p) const
{
return p.z;
}
};
}
int
main(int, char** argv)
{
std::string filename = argv[1];
std::cout << "Reading " << filename << std::endl;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_xyz(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>(filename, *cloud_xyz) == -1) // load the file
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file");
return -1;
}
std::cout << "points: " << cloud_xyz->points.size() << std::endl;
// Parameters for sift computation
const float min_scale = 0.005f; //the standard deviation of the smallest scale in the scale space
const int n_octaves = 6;//the number of octaves (i.e. doublings of scale) to compute
const int n_scales_per_octave = 4;//the number of scales to compute within each octave
const float min_contrast = 0.001f;//the minimum contrast required for detection
pcl::console::TicToc time;
time.tic();
// Estimate the sift interest points using z values from xyz as the Intensity variants
pcl::SIFTKeypoint<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointWithScale> sift;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointWithScale> result;
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());
sift.setSearchMethod(tree);
sift.setScales(min_scale, n_octaves, n_scales_per_octave);
sift.setMinimumContrast(min_contrast);
sift.setInputCloud(cloud_xyz);
sift.compute(result);
std::cout << "Computing the SIFT points takes " << time.toc() / 1000 << "seconds" << std::endl;
std::cout << "No of SIFT points in the result are " << result.points.size() << std::endl;
// Copying the pointwithscale to pointxyz so as visualize the cloud
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_temp(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
copyPointCloud(result, *cloud_temp);
std::cout << "SIFT points in the result are " << cloud_temp->points.size() << std::endl;
// Visualization of keypoints along with the original cloud
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("PCL Viewer");
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> keypoints_color_handler(cloud_temp, 0, 255, 0);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud_color_handler(cloud_xyz, 255, 0, 0);
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_xyz, cloud_color_handler, "cloud");//add point cloud
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_temp, keypoints_color_handler, "keypoints");//add the keypoints
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 7, "keypoints");
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
viewer.spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}论文作者也公开了SIFT3D算子的实现代码,详细见原文链接。使用的时候也是比较简单的,SIFT3D_detect_keypoints()函数用来找图像中的关键点,SIFT3D_extract_descriptors()函数是计算关键点的描述符即特征向量,代码如下。
// Detect keypoints
if (SIFT3D_detect_keypoints(&sift3d, &im, &kp))
goto demo_quit;
printf(" Detect keypoints ok \n");
// Write the keypoints to a file
if (write_Keypoint_store(keys_path, &kp))
goto demo_quit;
printf("Keypoints written to %s. \n", keys_path);
// Extract descriptors
if (SIFT3D_extract_descriptors(&sift3d, &kp, &desc))
goto demo_quit;
printf(" Extract descriptors ok \n");
// Write the descriptors to a file
if (write_SIFT3D_Descriptor_store(desc_path, &desc))
goto demo_quit;
printf("Descriptors written to %s. \n", desc_path);
// Convert the keypoints to a matrix
if (Keypoint_store_to_Mat_rm(&kp, &keys))
goto demo_quit;
// Draw the keypoints
if (draw_points(&keys, SIFT3D_IM_GET_DIMS(&im), 1, &draw))
goto demo_quit;
// Write the drawn keypoints to a file
if (im_write(draw_path, &draw))
goto demo_quit;
printf("Keypoints drawn in %s. \n", draw_path);最后将检测到关键点绘制在图像上。
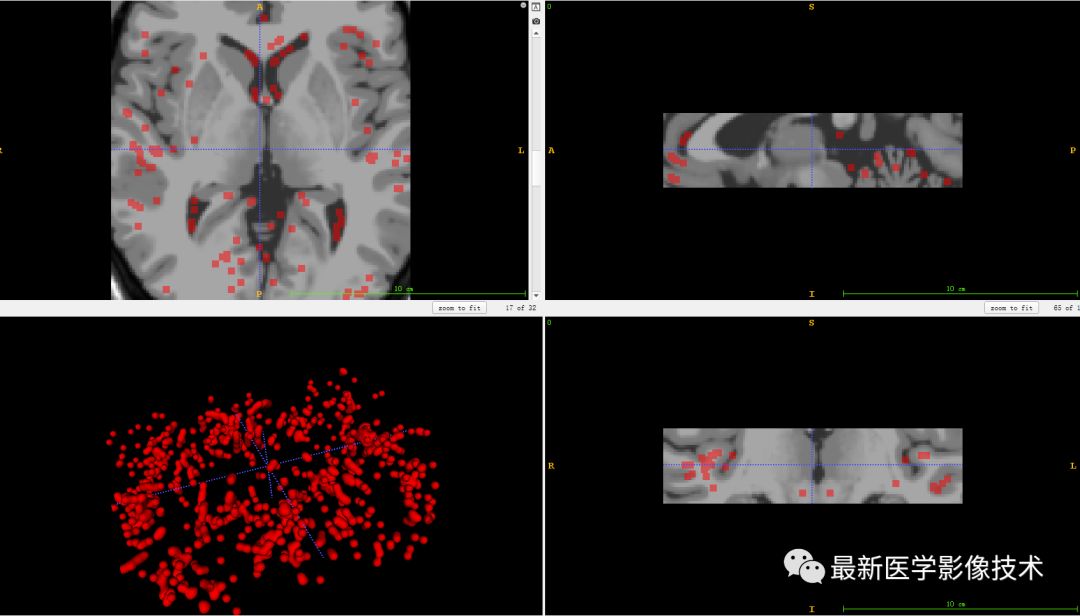







 本文详细介绍了SIFT3D算法在医学图像处理中的关键点检测过程,包括尺度空间极值检测、关键点定位、方向分配和描述符构建。并提供了PCL库中的C++代码示例,展示了如何提取3D点云的关键点。此外,还提及了SIFT3D算子相较于其他关键点检测方法如Harris3D和Harris6D的优势。
本文详细介绍了SIFT3D算法在医学图像处理中的关键点检测过程,包括尺度空间极值检测、关键点定位、方向分配和描述符构建。并提供了PCL库中的C++代码示例,展示了如何提取3D点云的关键点。此外,还提及了SIFT3D算子相较于其他关键点检测方法如Harris3D和Harris6D的优势。
















 2750
2750

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








