之前也有一篇笔记,都比较简单,做个记录,方便速查。
目录
1、向量的模
int main()
{
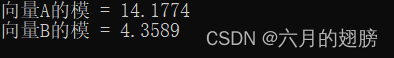
Vec3f A = Vec3f(10, 10, 1);
cout << "向量A的模 = " << norm(A) << endl;
Vec3f B = Vec3f(3, 3, 1);
cout << "向量B的模 = " << norm(B) << endl;
return 0;
} 
2、两点间距离(两点间的向量模)
int main()
{
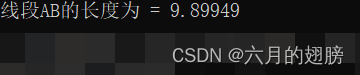
Vec3f A = Vec3f(10, 10, 1);
Vec3f B = Vec3f(3, 3, 1);
cout << "线段AB的长度为 = " << norm(A - B) << endl;
//结果为6*根2
return 0;
}
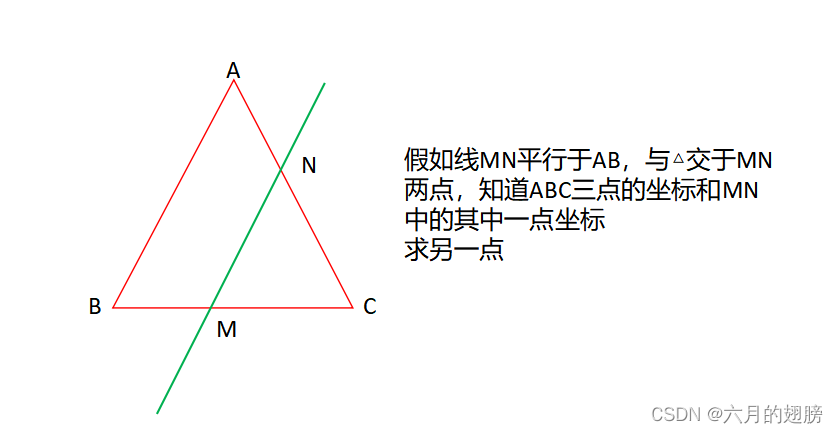
3、求线段中某点坐标
int main()
{
Vec3f A = Vec3f(0, 10, 0);
Vec3f B = Vec3f(0, 0, 0);
Vec3f C = Vec3f(10, 0, 0);
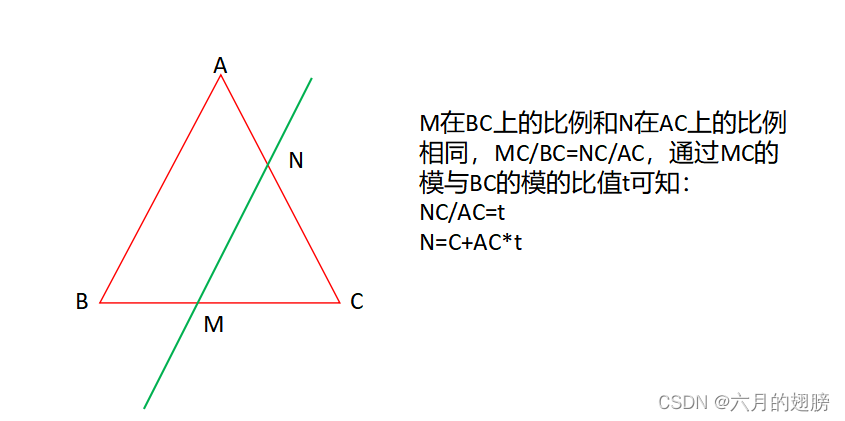
Vec3f M = Vec3f(3, 0, 0);
float t = norm(M - C) / norm(B - C);
Vec3f N = C + (A - C) * t;
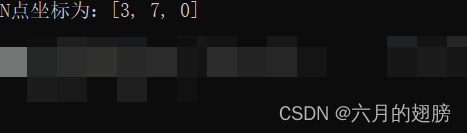
cout << "N点坐标为:" << N << endl;
return 0;
} 
4、叉乘,平面法向量
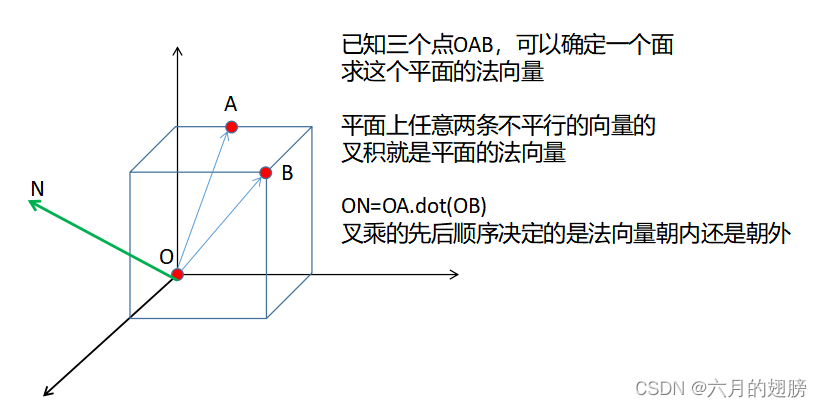
上面图中写错了,ON = OB.cross(OA)。右手定则
不仅点和叉写错了 方向还错了 /dog
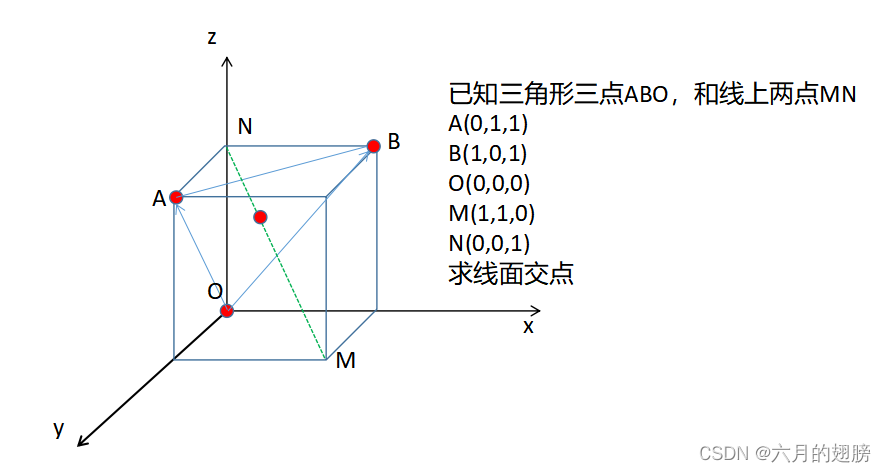
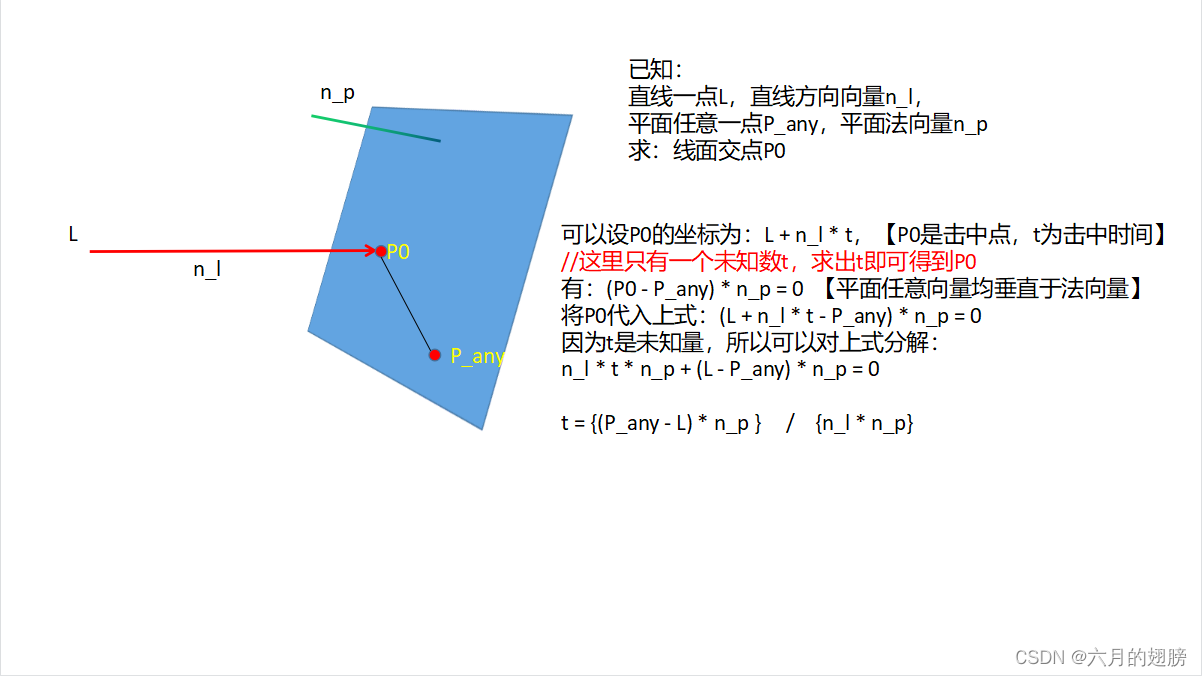
5、线面交点
int main()
{
//需要知道直线上一点和其方向向量,平面一点及其法向量
Vec3f A=Vec3f(0, 1, 1);
Vec3f B=Vec3f(1, 0, 1);
Vec3f O=Vec3f(0, 0, 0);
Vec3f M=Vec3f(1, 1, 0);
Vec3f N=Vec3f(0, 0, 1);
Vec3f line = M-N;//线方向向量,这里谁减谁都行
Vec3f plane = (A - O).cross(B - O);//平面两个向量叉乘就是法向量
float den = plane.dot(line);//面法向量乘线方向向量
float t = plane.dot(A - N) / den;//A是面上一点,用B也可以
Vec3f p0 = N + line * t;//这里线上的点用的N,也可以用M,只要上面求t的时候也是用的M就可以
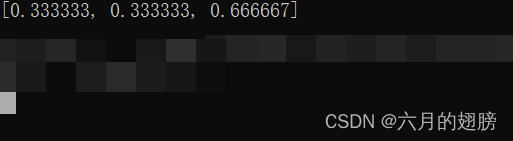
cout << p0 << endl;
return 0;
} 
//2023年1月10日 update
//2023年10月27日

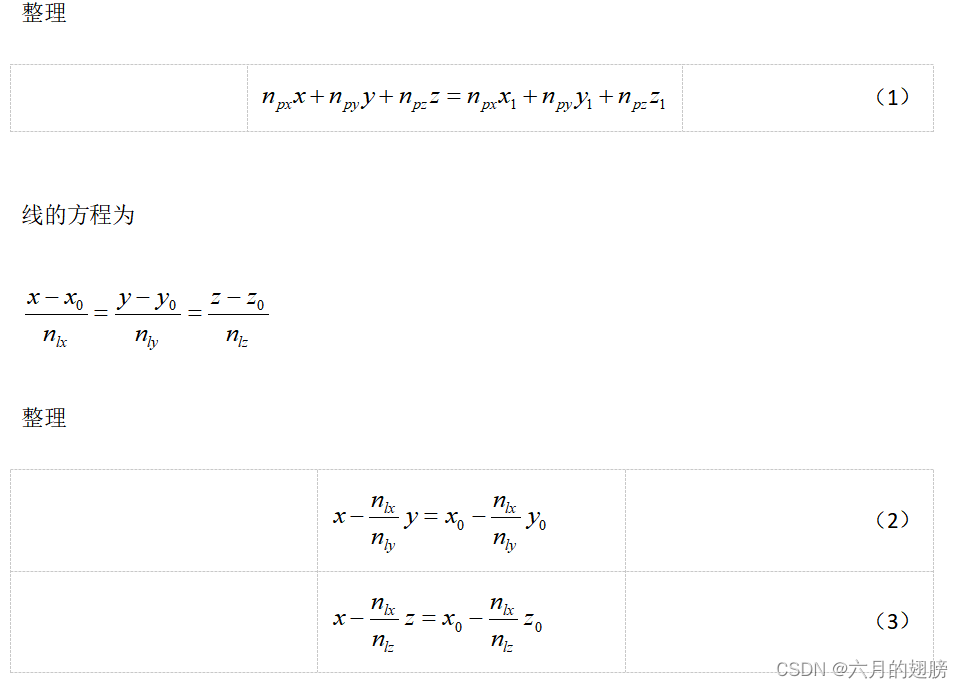
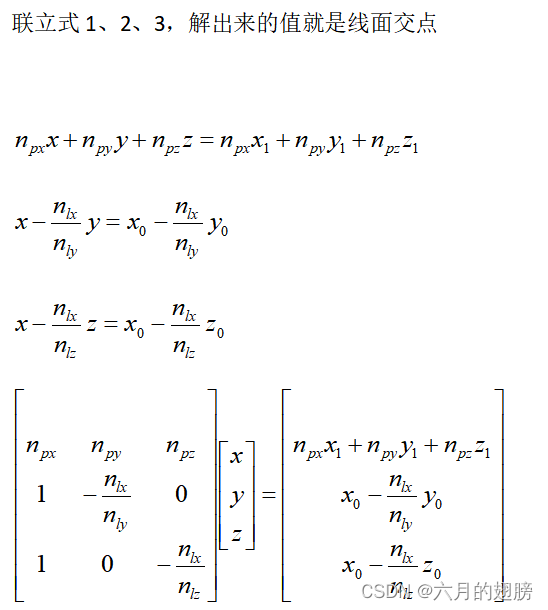
cv::Point3d pointOfLinePlaneSolve(Point3d L_p, Point3d L_dir, Point3d P_p, Point3d P_norm)
{
//这种方法要求线的方向向量的yz值不能为0,因为涉及到除法
Mat x = (cv::Mat_<double>(3, 3) << P_norm.x, P_norm.y, P_norm.z,
1, -L_dir.x / L_dir.y, 0,
1, 0, -L_dir.x / L_dir.z);
Mat y = (cv::Mat_<double>(3, 1) << P_norm.dot(P_p),
L_p.x - L_dir.x / L_dir.y * L_p.y,
L_p.x - L_dir.x / L_dir.z * L_p.z
);
// 使用solve函数求解方程
Mat coef;
solve(x, y, coef, DECOMP_QR);
return Point3d(coef);
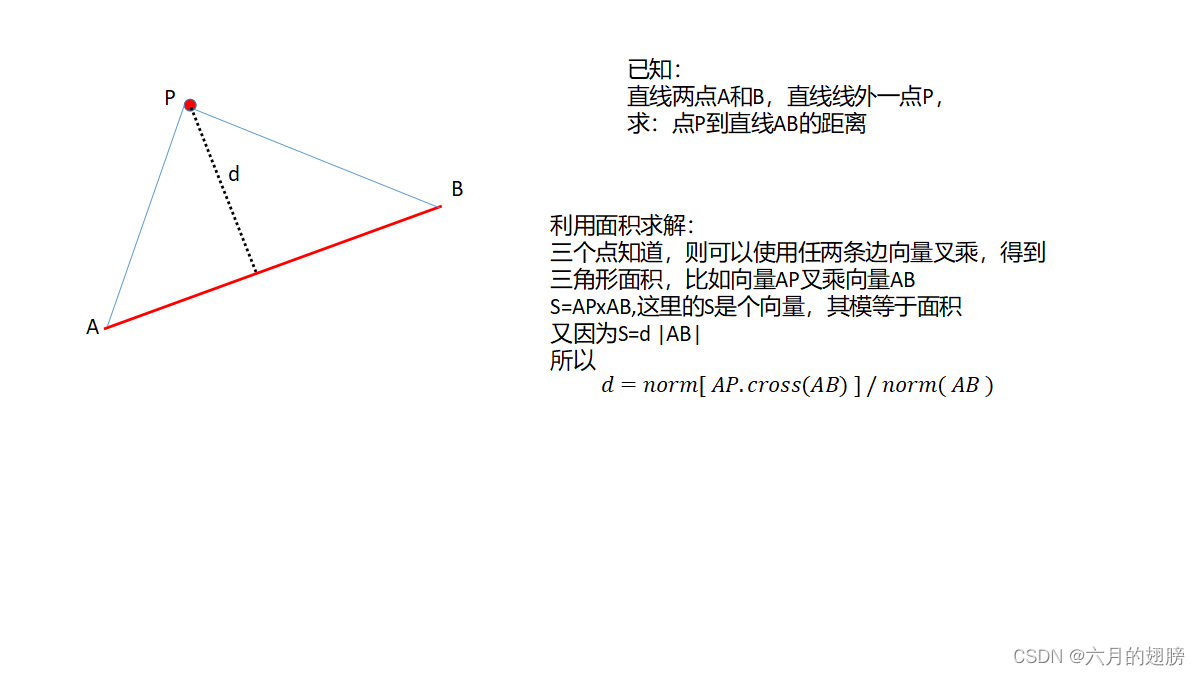
}6、空间点到直线的距离
/// <summary>
///
/// </summary>
/// <param name="P">线外一点</param>
/// <param name="A">线上点</param>
/// <param name="B">线上点</param>
/// <returns></returns>
float getDist_P2L(Vec3f P, Vec3f A, Vec3f B)
{
Vec3f PA = P - A;//线外点到线上一点的向量
Vec3f Ldir = B - A;//直线的方向向量
Vec3f Pnorm = PA.cross(Ldir);
float S1 = norm(Ldir);
float S2 = norm(Pnorm);
return S2 / S1;
}
int main()
{
Vec3f A = Vec3f(1.0, 0, 0);
Vec3f B = Vec3f(0.0, 1.0, 0);
Vec3f P = Vec3f(0.5, 0.5, 3);
float dis = getDist_P2L(P, A, B);
cout << dis << endl;
}//2023年1月12日 update
7、平面方程


vector<Vec3f> input;
vector<float> coeffi;
void GetPanelEquation(vector<Vec3f>& point3fArray)
{
if (point3fArray.size() < 3)
{
cerr << "GetPanelEquation(...)函数中输入点的数量小于3." << endl;
}
float a,b,c,d;
a = (point3fArray[1][1] - point3fArray[0][1])*(point3fArray[2][2] - point3fArray[0][2]) -
(point3fArray[1][2] - point3fArray[0][2])*(point3fArray[2][1] - point3fArray[0][1]);
b = (point3fArray[1][2] - point3fArray[0][2])*(point3fArray[2][0] - point3fArray[0][0]) -
(point3fArray[1][0] - point3fArray[0][0])*(point3fArray[2][2] - point3fArray[0][2]);
c = (point3fArray[1][0] - point3fArray[0][0])*(point3fArray[2][1] - point3fArray[0][1]) -
(point3fArray[1][1] - point3fArray[0][1])*(point3fArray[2][0] - point3fArray[0][0]);
d = 0 - (a * point3fArray[0][0] + b*point3fArray[0][1] + c*point3fArray[0][2]);
coeffi.push_back(a);
coeffi.push_back(b);
coeffi.push_back(c);
coeffi.push_back(d);
}
int main()
{
input.push_back(Vec3f(100, 0, 0));
input.push_back(Vec3f(0, 100, 0));
input.push_back(Vec3f(0, 0, 3));
GetPanelEquation(input);
cout << "平面方程为:"<< endl << coeffi[0] << " X + " << coeffi[1] << " Y + " << coeffi[2] << " Z + " << coeffi[3] << " = 0" << endl;
if (abs(coeffi[3])>1e-6)
{
cout << "平面方程为:" << endl << -coeffi[0] / coeffi[3] << " X + " << -coeffi[1] / coeffi[3] << " Y + " << -coeffi[2] / coeffi[3] << " Z = 1" << endl;
}
return 1;
}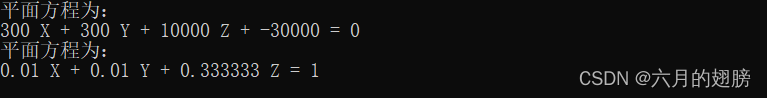
8、两直线的交点

double r_xy12 = PointOnLine[0].x * PointOnLine[1].y - PointOnLine[1].x * PointOnLine[0].y;
double r_x12 = PointOnLine[0].x - PointOnLine[1].x;
double r_xy34 = PointOnLine[2].x * PointOnLine[3].y - PointOnLine[3].x * PointOnLine[2].y;
double r_x34 = PointOnLine[2].x - PointOnLine[3].x;
double r_y12 = PointOnLine[0].y - PointOnLine[1].y;
double r_y34 = PointOnLine[2].y - PointOnLine[3].y;
double fenmu = r_x12 * r_y34 - r_y12 * r_x34;
GridPoint[i].x = (r_xy12 * r_x34 - r_x12 * r_xy34) / fenmu;
GridPoint[i].y = (r_xy12 * r_y34 - r_y12 * r_xy34) / fenmu;struct LinePara
{
float k;
float b;
};
// 获取直线参数
void getLinePara(float& x1, float& y1, float& x2, float& y2, LinePara& LP)
{
double m = 0;
// 计算分子
m = x2 - x1;
if (0 == m)
{
LP.k = 10000.0;
LP.b = y1 - LP.k * x1;
}
else
{
LP.k = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1);
LP.b = y1 - LP.k * x1;
}
}
// 获取交点
bool getCross(Point2f& p1, Point2f& p2, Point2f& p3, Point2f& p4, Point2f& pt) {
LinePara para1, para2;
getLinePara(p1.x, p1.y, p2.x, p2.y, para1);
getLinePara(p3.x, p3.y, p4.x, p4.y, para2);
pt.x = (para2.b - para1.b) / (para1.k - para2.k);
pt.y = para1.k * pt.x + para1.b;
// 判断是否平行
if (abs(para1.k - para2.k) > 0.5)
{
pt.x = (para2.b - para1.b) / (para1.k - para2.k);
pt.y = para1.k * pt.x + para1.b;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}9、两向量的夹角
template <typename DataType>
double getAngle3d(DataType _in1, DataType _in2)
{
double theta2 = acos(_in1.dot(_in2) / (norm(_in1) * norm(_in2)));
if (abs(_in1.dot(_in2)-1)<10e-6)//这里做个判断,否则nan
{
theta2 = 0;
}
else
{
theta2 = theta2 * 180 / acos(-1);
}
return theta2;
}


























 384
384

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








