ArchiMate教程 / ArchiMate Tutorial
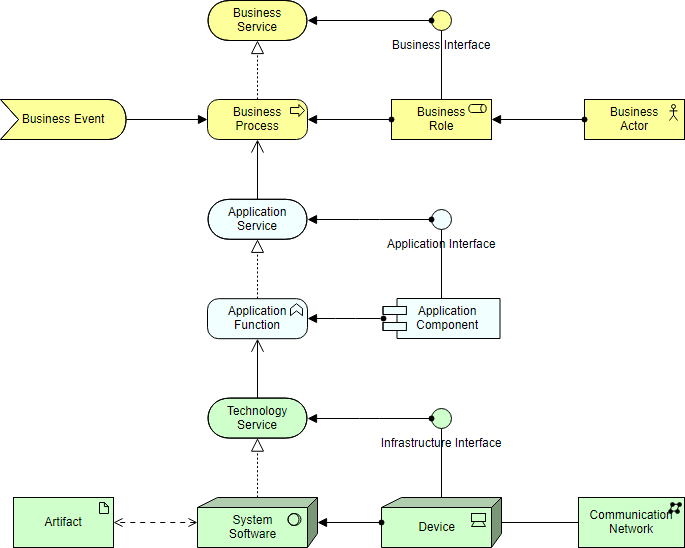
The OpenGroup ArchiMate language provides a graphical language for representing enterprise architectures over time, including strategy, transformation and migration planning, as well as the motivation and rationale for the architecture. The standard has been designed to be as compact as possible, yet still usable for most enterprise architecture modeling needs. The figure below shows the elements of the ArchiMate Core framework.
OpenGroup ArchiMate语言随着时间的推移提供了一种用于表示企业架构的图形化语言,包括策略,转换和迁移规划,以及架构的动机和基本原理。该标准的设计尽可能紧凑,但仍可用于大多数企业体系结构建模需求。下图显示了ArchiMate Core框架的元素。
What is ArchiMate?
The ArchiMate Specification is a modeling language that enables Enterprise Architects to describe, analyze and visualize relationships among architecture domains using easy to understand visuals representations. It also helps enterprise architects to:
- It provides a common language for describing how various parts of the enterprise are constructed and how they operate, including business processes, organizational structures, information flows, IT systems, and technical and physical infrastructures.
- In a time when many enterprises are undergoing rapid change, ArchiMate models help stakeholders design, assess and communicate those changes within and between architecture domains, as well as examine the potential consequences and impact of decisions throughout an organization.
什么是ArchiMate?
ArchiMate规范是一种建模语言,它使企业架构师能够使用易于理解的视觉表示来描述,分析和可视化架构域之间的关系。它还可以帮助企业架构师:
- 它提供了一种通用语言来描述企业的各个部分如何构建以及如何运作,包括业务流程,组织结构,信息流,IT系统以及技术和物理基础架构。
- 在许多企业正在经历快速变化的时期,ArchiMate模型帮助利益相关者设计,评估和沟通体系结构域内和之间的这些变化,并检查整个组织内决策的潜在影响。
TOGAF ADM and ArchiMate
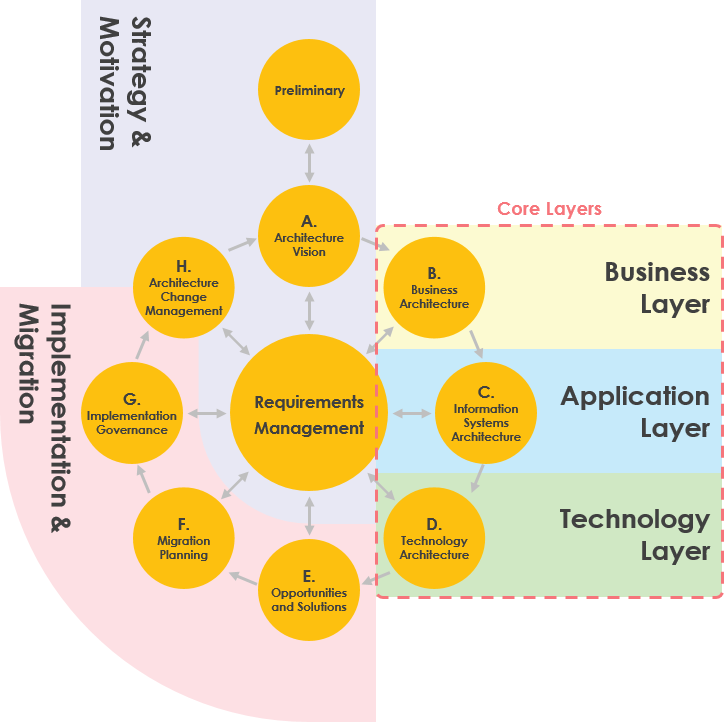
The ArchiMate language consists of the ArchiMate core language, which includes the Business, Application, and TechnologyLayers, along with elements to model the strategy and motivation underlying an architecture, as well as its implementation and migration. The Figure below shows a simplified mapping of how the ArchiMate language can be used in relation to the phases of the TOGAF Architecture Development Method (ADM).
TOGAF ADM和ArchiMate
ArchiMate语言由ArchiMate核心语言组成,其中包括业务,应用程序和技术层,以及用于模拟体系结构的战略和动机以及其实施和迁移的元素。下图显示了如何使用ArchiMate语言与TOGAF架构开发方法(ADM)阶段相关的简化映射。
Core Layers
The Business, Application, and Technology Layers support the description of the Business, Information Systems, and Technology Architecture domains defined by the TOGAF framework, as well as their interrelationships.
Strategy and Motivation Layers
The strategy and motivation elements in the ArchiMate language can be used to support the Requirements Management, Preliminary, and Architecture Vision phases of the TOGAF ADM, which establish the high level business goals, architecture principles, and initial business requirements. They are also relevant to the Architecture Change Management phase of the TOGAF ADM, since the phase deals with changing requirements.
Implementation and Migration Layers
The implementation and migration elements of the ArchiMate language support the implementation and migration of architectures through the Opportunities and Solutions, Migration Planning, and Implementation Governance phases of the TOGAF ADM.
核心层
该业务,应用和技术层支持业务,信息系统和技术架构领域由TOGAF框架中定义的描述,以及它们的相互关系。
战略和动机层
ArchiMate语言中的策略和动机元素可用于支持TOGAF ADM的需求管理,初步和架构愿景阶段,这些阶段建立了高层次的业务目标,架构原则和初始业务需求。它们也与TOGAF ADM的架构变更管理阶段相关,因为该阶段处理不断变化的需求。
实施和迁移层
ArchiMate语言的实现和迁移元素通过TOGAF ADM的机会和解决方案,迁移规划和实施治理阶段支持架构的实施和迁移。
TOGAF ADM and ArchiMate Mapping
ArchiMate Core Layers in ArchiMate 1
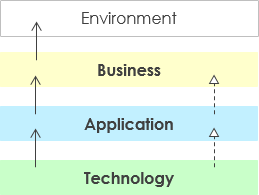
The core layers have been there since the beginning of ArchiMate. It is what ArchiMate makes an Enterprise Architecture language in the first place, because you can model all these different aspects in a single coherent model. A layered view provides a natural way to look at service-oriented models. The higher layers use services that are provided by the lower layers. ArchiMate distinguishes three main layers:
- The Business layer offers products and services to external customers, which are realized in the organization by business processes performed by business actors and roles.
- The Application layer supports the business layer with application services which are realized by (software) application components.
- The Technology layer offers infrastructural services (e.g., processing, storage and communication services) needed to run applications, realized by computer and communication hardware and system software.
TOGAF ADM和ArchiMate映射
ArchiMate中的ArchiMate核心层1
自ArchiMate开始以来,核心层就一直存在。这正是ArchiMate首先制定企业架构语言的原因,因为您可以将所有这些不同方面建模为一个一致的模型。分层视图提供了一种自然的方式来查看面向服务的模型。较高层使用由较低层提供的服务。ArchiMate区分了三个主要层次:
- 该业务层提供的产品和服务外部客户,这是在由业务人员和角色进行业务流程的组织来实现。
- 在应用层支持与由(软件)应用组件实现应用服务的业务层。
- 该技术层提供了运行应用程序所需的基础架构服务(例如,处理,存储和通信服务),通过计算机和通信硬件和系统软件来实现。
Full TOGAF ADM in ArchiMate 3
在ArchiMate 3中完整的TOGAF ADM
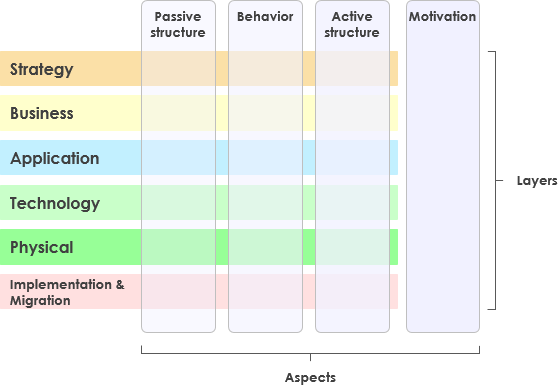
Layers
The first dimension core entities are assigned to are the different layers of an enterprise architecture model. In the new ArchiMate, the enterprise architecture model is split into six layers:
With regards to the graphical representation of single entities, the layer an entity belongs to is indicated using different colors.
Higher layers use services provided by lower layers. The Business layer offers products and services to external customers which are realized by business processes performed by business actors. Application layer supports the business layer with application services which are realized by (software) applications. Technology layer offers infrastructural services (e.g., processing, storage and communication services) needed to run applications, realized by computer and communication hardware and system software.
图层
第一维核心实体被分配到一个企业架构模型的不同层次。在新的ArchiMate中,企业架构模型分为六层:
- 战略
- 商业
- 应用
- 技术
- 物理
- 实施和迁移。
关于单个实体的图形表示,实体所属的层用不同的颜色表示。
较高层使用较低层提供的服务。业务层向外部客户提供产品和服务,这些产品和服务由业务主体执行的业务流程实现。应用层使用由(软件)应用程序实现的应用程序服务来支持业务层。技术层提供运行应用程序所需的基础设施服务(例如处理,存储和通信服务),由计算机和通信硬件和系统软件实现。
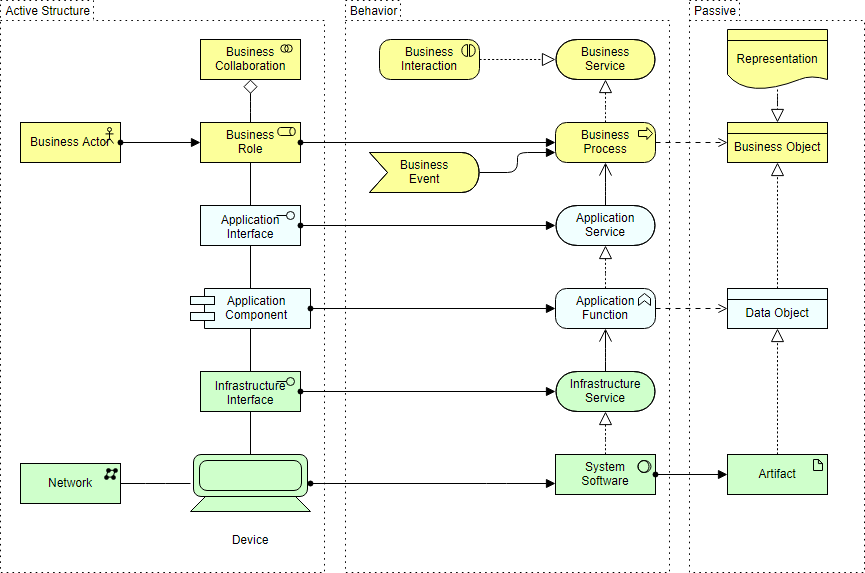
Aspects
The second dimension is made up of three aspects, which the core entities are allocated to. In the graphical representation of elements, the assignment of an element to an aspect is visualized using different shapes.
- Active Structure
Active structures captures subjects that display actual behavior (who?). These active structures are represented using boxes with square corners and an icon in the upper-right corner. - Behavior Structure
Behavior aspects represents behaviors of active structures (how?) and are visualized using boxes with round corners and an icon in the upper-right corner. - Passive Structure
Passive structures are the objects behavior is performed on (what?). There is no global way to visualize them with regards to the shape.
方面
第二个维度由核心实体分配的三个方面组成。在元素的图形表示中,元素对某个方面的分配使用不同的形状进行可视化。
- 主动结构
主动结构捕捉显示实际行为的主体(谁?)。这些活动结构使用方形角的方框和右上角的图标表示。 - 行为结构
行为方面表示活动结构的行为(如何?),并使用带有圆角的框和右上角的图标进行可视化。 - 被动结构
被动结构是对象行为在(什么?)上执行的。没有全局的方式来形象化他们的形状。
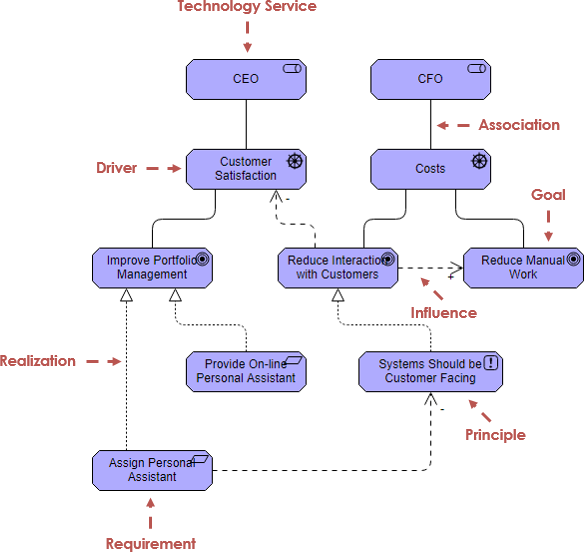
Motivation Extension
The Motivation Extension (Drivers, Goals, Requirements, Principles, etc.) has been introduced in ArchiMate 2. The Motivational concepts are used to model the motivations, or reasons, that underlie the design or change of some enterprise architecture. The motivation extension adds motivational concepts such as goal, principle, and requirement. It corresponds to the “Why” column of the Zachman framework
Motivation elements assigned to this aspect are depicted using boxes with diagonal corners but are also color coded, indicating that it also constitutes a layer.
激励延伸
动机扩展(驱动程序,目标,需求,原则等)已在ArchiMate 2中引入。动机概念用于模拟某些企业体系结构设计或更改背后的动机或原因。激励延伸增加了激励概念,如目标,原则和要求。它对应于Zachman框架的“为什么”列
分配给这个方面的动机元素用对角线的方框表示,但也用颜色编码,表明它也构成一个层。
为什么选择ArchiMate?
如上图所示,企业架构师采用ArchiMate的主要原因如下:
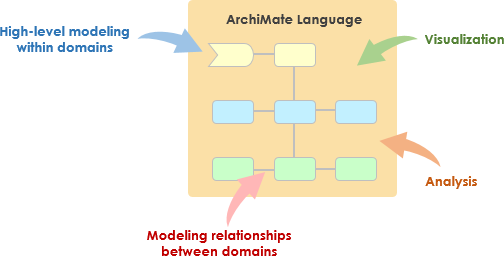
- Capture stakeholder concerns
- Address concerns by identifying and refining requirements
- Create EA models
- Create views of the model for stakeholders
- show how concerns and requirements will be addressed
- show trade-offs arising from conflicting concerns
- 捕捉利益相关者的担忧
- 通过确定和改进需求来解决问题
- 创建EA模型
- 为利益相关者创建模型的视图
- 展示如何解决关注和要求
- 显示由矛盾关注引起的折衷
Guideline for using ArchiMate Diagram with TOGAF ADM
- Follow the steps in TOGAF ADM for each development phase, starting from Preliminary Phase
- Follow the input, techniques and outputs to be performed for enterprise architecture development for each of the phases in ADM.
- TOGAF ADM is a iterative process rather than linear and sequential steps and phases
- The deliverables developed in the previous phase(s) will typically be used as the input documentation of the follow phases, they might be related in parts the data or the entire documentation
- Some information in a deliverable is interrelated with other deliverables in the subsequently development phases, such as, principals, mission and vision, request for architecture work and etc.
- TOGAF ADM might be tailored to fit your specific needs of your organization, modify it whichever it is necessary
- Most of the visual models can be model by ArchiMate in TOGAF ADM as kind of visual artifacts, but not all TOGAF ADM deliverables (such as textual documentation, logs, meeting minutes) can be represented by ArchiMate. In fact, TOGAF has much wider scope than ArchiMate.
TOGAF ADM使用ArchiMate Diagram的指南
- 从初步阶段开始,按照TOGAF ADM中的步骤进行每个开发阶段
- 遵循针对ADM中每个阶段的企业架构开发的输入,技术和输出。
- TOGAF ADM是一个迭代过程,而不是线性和连续的步骤和阶段
- 前一阶段开发的可交付成果通常将用作后续阶段的输入文档,它们可能与数据或整个文档相关
- 可交付成果中的某些信息与后续开发阶段的其他交付成果相关,例如校长,使命和愿景,对建筑工作的要求等。
- TOGAF ADM可能会根据您组织的特定需求量身定制,并根据需要对其进行修改
- 大多数视觉模型可以由ArchiMate在TOGAF ADM中作为一种视觉工件进行建模,但并非所有TOGAF ADM可交付成果(如文本文档,日志,会议纪要)均可由ArchiMate表示。事实上,TOGAF比ArchiMate的范围更广。
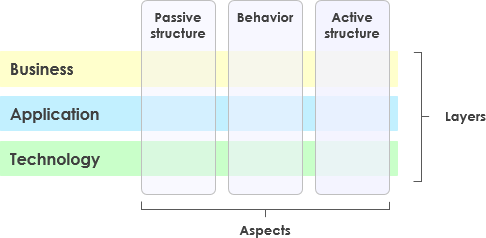
Core Layers (Business, Application, Technology)
A layered view provides a natural way to look at service-oriented models. The higher layers use services that are provided by the lower layers. ArchiMate distinguishes three main (Core) layers:
- The Business layer offers products and services to external customers, which are realized in the organization by business processes performed by business actors and roles.
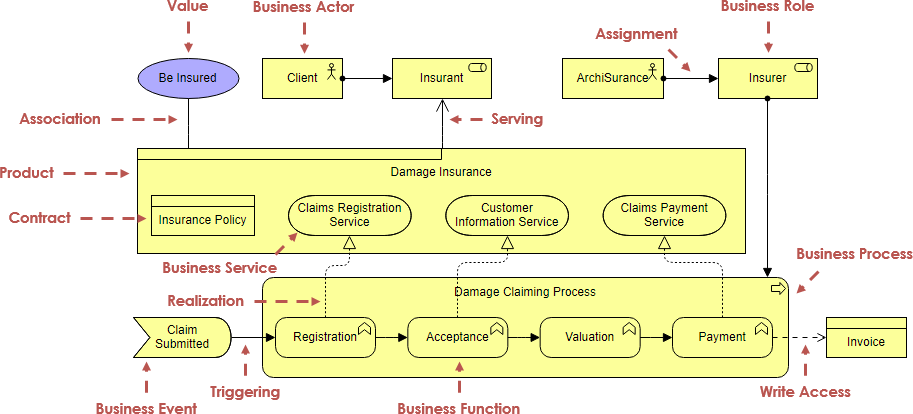
2. The Application layer supports the business layer with application services which are realized by (software) application components.
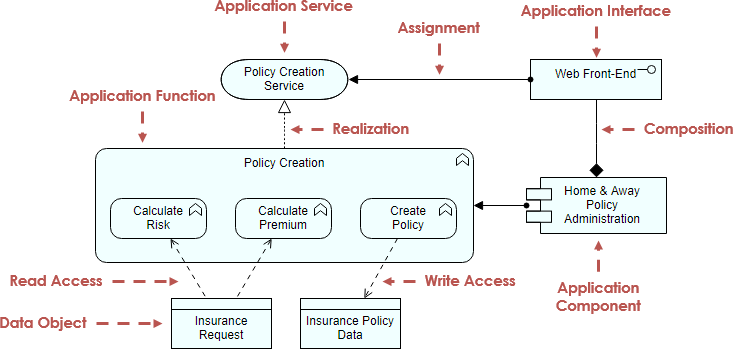
3. The Technology layer offers infrastructural services (e.g., processing, storage and communication services) needed to run applications, realized by computer and communication hardware and system software.
3. 该技术层提供了运行应用程序所需的基础架构服务(例如,处理,存储和通信服务),通过计算机和通信硬件和系
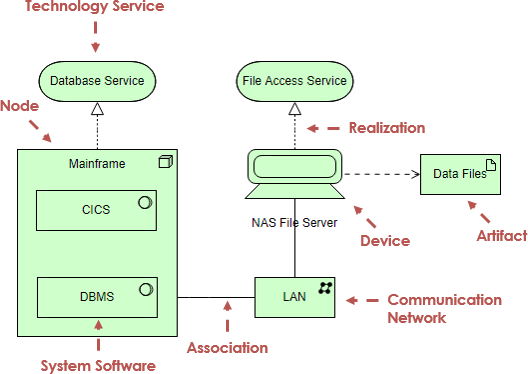
Motivation Extension
The ArchiMate Motivation elements enable the modeling of stakeholders, drivers for change, business goals, principles and requirements.
激励延伸
ArchiMate动机元素支持利益相关者建模,变革驱动因素,业务目标,原则和要求。
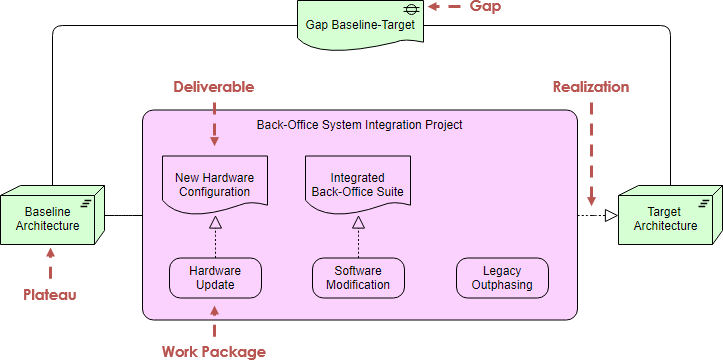
Implementation and Migration Extension
The ArchiMate Implementation and Migration elements enable the modeling of project portfolio management, gap analysis and transition and migration planning.
实施和迁移扩展
ArchiMate实施和迁移要素可以对项目组合管理,差距分析和过渡和迁移规划进行建模。
ArchiMate Examples
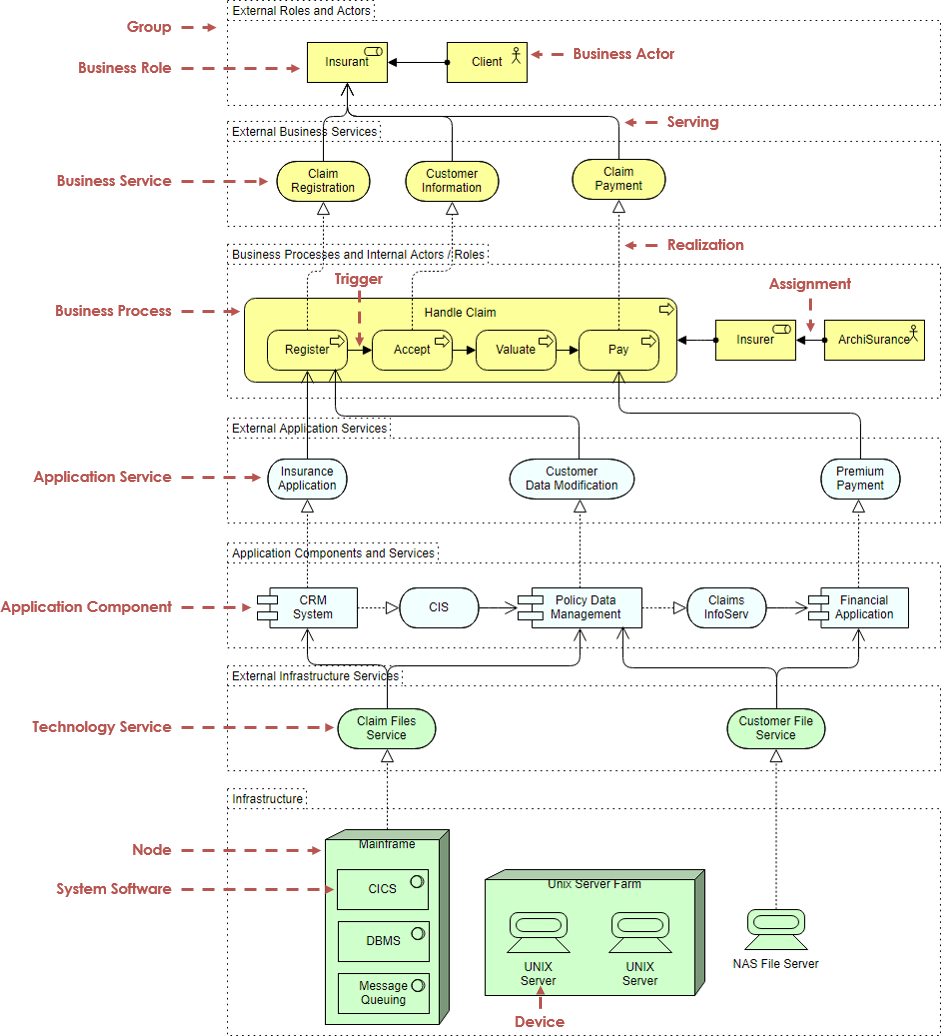
ArchiMate example – All layers
In the example ArchiMate model below, you can see the integration of the various ArchiMate layers.
ArchiMate示例
ArchiMate示例 - 所有图层
在下面的示例ArchiMate模型中,您可以看到各种ArchiMate图层的集成。
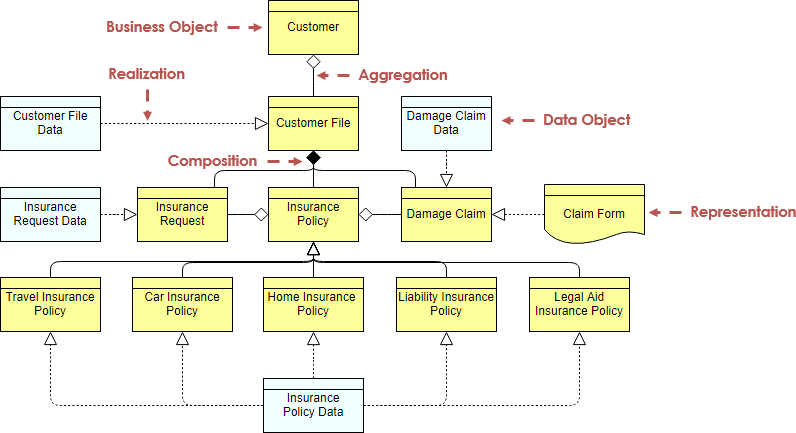
ArchiMate diagram example – Information Structure
This example is comparable to the traditional information models created in the development of almost any information system. It shows the structure of the information used in the enterprise or in a specific business process or application, in terms of data types or (object-oriented) class structures. Furthermore, it may show how the information at the business level is represented at the application level in the form of the data structures used there, and how these are then mapped onto the underlying infrastructure; e.g., by means of a database schema.
ArchiMate图示例 - 信息结构
这个例子与几乎任何信息系统开发过程中创建的传统信息模型相当。它以数据类型或(面向对象)类结构的形式显示了企业或特定业务流程或应用程序中使用的信息的结构。此外,它可能会显示业务级别的信息如何以应用级别的数据结构的形式表示,以及这些信息如何映射到底层基础架构; 例如通过数据库模式。
rchiMate Diagram example: Infrastructure
This example contains the software and hardware infrastructure elements supporting the application layer, such as physical devices, networks, or system software (e.g., operating systems, databases, and middleware).
ArchiMate Diagram示例:基础结构
此示例包含支持应用层的软件和硬件基础架构元素,例如物理设备,网络或系统软件(例如操作系统,数据库和中间件)。

More ArchiMate Diagram examples:
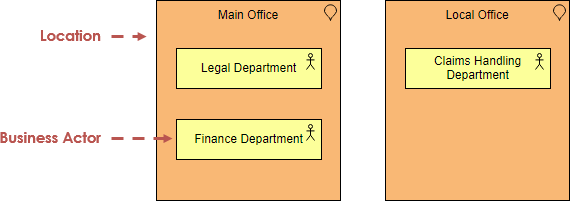
- Example 1 – Location
The model below shows that the departments of an insurance company are distributed over different locations. The Legal and Finance departments are centralized at the main office, and there are claims handling departments at various local offices throughout the country. - 示例1 - 地点
- 下面的模型显示,一家保险公司的部门分布在不同的地点。法律和财务部门集中在总部,全国各地办事处都设有索赔处理部门。
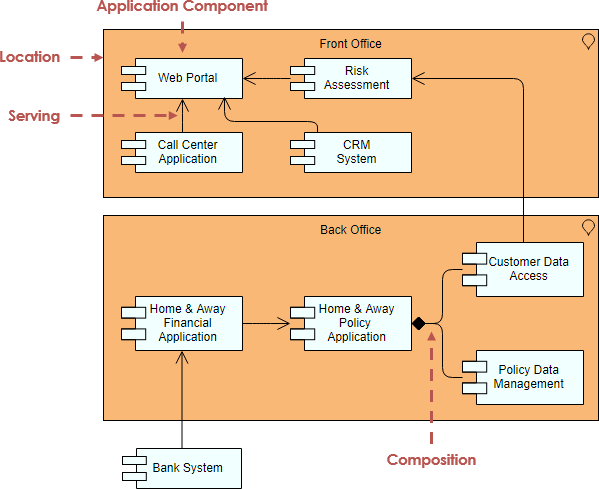
- Example 2 – Business Actor
The model below illustrates the use of business actors. The company ArchiSurance is modeled as a business actor that is composed of two departments. The Travel insurance seller role is assigned to the travel department. In this role, the travel department performs the Take out insurance process, which offers a service that is accessible via the business interface assigned to this role.
- 示例2 - 业务角色
下面的模型说明了业务角色的使用。公司ArchiSurance是一个由两个部门组成的商业演员。旅行保险卖家角色分配给旅行部门。在这个角色中,旅游部门执行取出保险流程,该流程提供可通过分配给该角色的业务接口访问的服务。

- Example 3 – Application Cooperation
- 示例3-应用程序合作
Other ArchiMate Articles:
- What is ArchiMate?
- Full ArchiMate Viewpoints Guide
- ArchiMate 3 Update
- What's New in ArchiMate 3?
- Using ArchiMate Tool with TOGAF ADM
Other TOGAF Articles:
- What is TOGAF?
- TOGAF ADM Tutorial
- TOGAF 9.1 Framework - A Comprehensive Guide
- TOGAF Software for Enterprise Architecture
- The Best TOGAF Software








 ArchiMate是一种企业架构建模语言,用于描述、分析和可视化不同架构领域之间的关系,包括业务、应用和技术层。它与TOGAF ADM紧密集成,支持在TOGAF架构开发方法的各个阶段中的建模。ArchiMate包含战略和动机元素,用于描述架构的动力和目的,以及实施和迁移元素,帮助规划架构的实施。该语言的核心层包括业务、应用和技术层,分别用于建模业务流程、应用服务和基础设施服务。
ArchiMate是一种企业架构建模语言,用于描述、分析和可视化不同架构领域之间的关系,包括业务、应用和技术层。它与TOGAF ADM紧密集成,支持在TOGAF架构开发方法的各个阶段中的建模。ArchiMate包含战略和动机元素,用于描述架构的动力和目的,以及实施和迁移元素,帮助规划架构的实施。该语言的核心层包括业务、应用和技术层,分别用于建模业务流程、应用服务和基础设施服务。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








