1.nnMamba原理
论文题目:nnMamba: 3D Biomedical Image Segmentation, Classification and Landmark Detection with State Space Model
论文:https://arxiv.org/html/2402.03526v2
网上已经有全文翻译的,不再赘述,这里概述一下主要贡献
1.构建了 MICCSS (Mamba-In-Convolution with Channel-Spatial Siamese input) 模块作为 nnMamba 中的基本模块,它实现了通道和空间级别的远程关系建模能力。
2.对于密集的预测任务,使用 MICCSS 模块构建编码器,并使用 skip scaling 来稳定训练。对于分类任务,在 stem 层添加了 MICCSS 模块,并在 Mamba 的基础上定制设计了一种分层顺序学习方法。
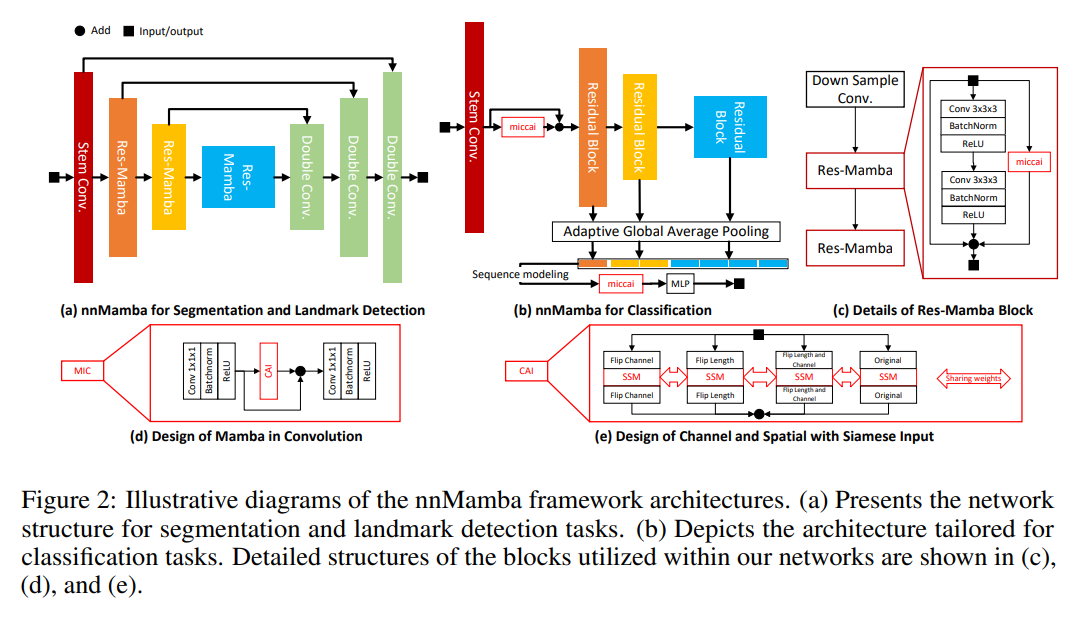
2.源码下载
nnMamba的源码在:https://github.com/lhaof/nnMamba
其中nnnunet对应的论文中的分割
nnMamba.py是基础模块和分割任务,完整的代码应该在nnnunet目录下
nnMamba4cls.py是基础模块和分类任务
3.nnMamba.py
先是3x3和1x1卷积的函数封装:
def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, groups=1, dilation=1):
"""3x3 convolution with padding."""
return nn.Conv3d(
in_planes,
out_planes,
kernel_size=3,
stride=stride,
padding=dilation,
groups=groups,
bias=False,
dilation=dilation,
)
def conv1x1(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""1x1 convolution."""
return nn.Conv3d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
-
Res-Mamba块
对应的是论文中的下图,但不知道是不是我下载的论文版本不对,感觉这个图有问题
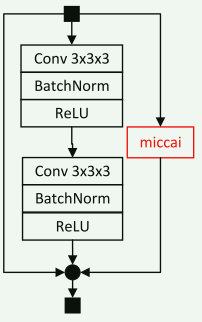
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, mamba_layer=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
# Both self.conv1 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm3d(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm3d(planes)
self.mamba_layer = mamba_layer
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.mamba_layer is not None:
global_att = self.mamba_layer(x)
out += global_att
if self.downsample is not None:
# if self.mamba_layer is not None:
# global_att = self.mamba_layer(x)
# identity = self.downsample(x+global_att)
# else:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
def make_res_layer(inplanes, planes, blocks, stride=1, mamba_layer=None):
downsample = nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(inplanes, planes, stride),
nn.BatchNorm3d(planes),
)
layers = []
layers.append(BasicBlock(inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
for _ in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(BasicBlock(planes, planes, mamba_layer=mamba_layer))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
其实仔细看和原文中的插图是不太一样的,最后一个relu的位置是三条路径求和和经过relu,不过影响不大,根据代码应该是如下:
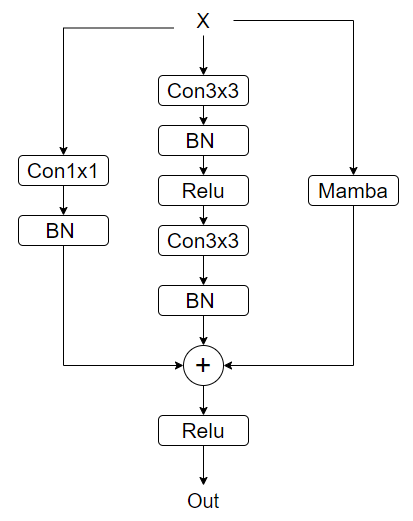
-
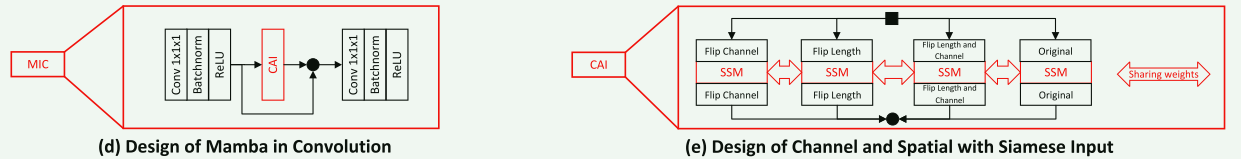
Mamba in Conv和Channel and Spatial with Siamese Input
对应论文中的图,看论文中的伪代码不是太清楚,看源码就知道了
class MambaLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, d_state=16, d_conv=4, expand=2):
super().__init__()
# 初始化输入参数,dim 为输入维度,d_state 表示 SSM 状态维度,d_conv 是卷积宽度,expand 为块扩展因子。
self.dim = dim
# 1x1 卷积层,用于改变维度,这里保持输入和输出维度相同
self.nin = conv1x1(dim, dim)
# 另一个 1x1 卷积层,稍后用于输出
self.nin2 = conv1x1(dim, dim)
# 3D 批归一化,用于标准化卷积层的输出
self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm3d(dim) # 层归一化
# ReLU 激活函数,inplace=True 表示在原地执行,提高内存效率
self.relu2 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.relu3 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
# 另一个 3D 批归一化层,用于标准化输入
self.norm = nn.BatchNorm3d(dim) # 层归一化
# ReLU 激活函数,用于激活
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
# Mamba 模块,进行更复杂的处理
self.mamba = Mamba(
d_model=dim, # 模型的维度
d_state=d_state, # SSM 状态扩展因子
d_conv=d_conv, # 卷积宽度
expand=expand # 块扩展因子
)
def forward(self, x):
# 获取输入张量的批量大小和通道数
B, C = x.shape[:2]
# 通过第一个 1x1 卷积处理输入
x = self.nin(x)
# 进行标准化
x = self.norm(x)
# 应用 ReLU 激活函数
x = self.relu(x)
# 保存激活后的张量,用于后续的残差连接
act_x = x
# 确保输入的通道数与层的维度匹配
assert C == self.dim
# 计算输入特征图中的 token 数量 height x width
n_tokens = x.shape[2:].numel()
# 获取输入的图像维度
img_dims = x.shape[2:]
# ->[B,C,hw]->[B,hw,C] 将通道维度放在最后,这是Mamba的输入要求
x_flat = x.reshape(B, C, n_tokens).transpose(-1, -2)
# 原代码中这里有对 mamba 的一次调用,已被注释
# x_mamba = self.mamba(x_flat)
# 沿着C维度翻转张量
x_flip_l = torch.flip(x_flat, dims=[2])
# 沿着HW维度翻转张量
x_flip_c = torch.flip(x_flat, dims=[1])
# 同时沿着C通道和HW翻转张量
x_flip_lc = torch.flip(x_flat, dims=[1,2])
# 对原始张量应用 mamba 模块
x_ori = self.mamba(x_flat)
# 对翻转后的张量应用 mamba 模块
x_mamba_l = self.mamba(x_flip_l)
# 对通道翻转的张量应用 mamba 模块
x_mamba_c = self.mamba(x_flip_c)
# 对通道和维度都翻转的张量应用 mamba 模块
x_mamba_lc = self.mamba(x_flip_lc)
# 将 mamba 处理后的张量沿着最后一个维度再翻转回去
x_ori_l = torch.flip(x_mamba_l, dims=[2])
# 将 mamba 处理后的张量沿着通道维度翻转回去
x_ori_c = torch.flip(x_mamba_c, dims=[1])
# 将 mamba 处理后的张量沿着通道和最后一个维度翻转回去
x_ori_lc = torch.flip(x_mamba_lc, dims=[1,2])
# 将四个方向的处理结果平均起来,得到最终的 mamba 输出
x_mamba = (x_ori+x_ori_l+x_ori_c+x_ori_lc)/4
# 将输出转置回原来的形状
out = x_mamba.transpose(-1, -2).reshape(B, C, *img_dims)
# 残差连接,原始激活的张量与输出相加
out += act_x
# 通过第二个 1x1 卷积进行进一步处理
out = self.nin2(out)
# 再次进行标准化
out = self.norm2(out)
# 最后应用 ReLU 激活函数
out = self.relu2(out)
# 返回最终输出
return out
这里使用了torch.flip,这个API是一个用于沿指定维度翻转张量(tensor)的函数。它会将张量在给定的维度上反转顺序,类似于镜像翻转。例如,如果有一个张量表示某些数据的顺序,使用 torch.flip 可以让顺序颠倒。
用法是:torch.flip(input, dims)
dims 参数指定了要沿哪个维度进行翻转。例如,如果是二维的图像张量,维度 [0, 1] 分别代表高度和宽度,指定哪个维度进行翻转会导致该维度的数值顺序反转。
例如,在 [1, 2, 3] 这样的向量上进行翻转,得到的结果会是 [3, 2, 1]。
这里使用torch.flip翻转输入相当于不改变原始的Mamba情况下,同时使用了三种不同的序列扫描方式,也比较巧妙。原文中的图是原始+三种翻转后的mamba处理结果求和,代码中看到是取了平均。
-
单层卷积和双层卷积
这个没有什么可说的
class DoubleConv(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch, stride=1, kernel_size=3): super(DoubleConv, self).__init__() self.conv = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv3d(in_ch, out_ch, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=int(kernel_size / 2)), nn.BatchNorm3d(out_ch), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Conv3d(out_ch, out_ch, 3, padding=1, dilation=1), nn.BatchNorm3d(out_ch), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), ) def forward(self, input): return self.conv(input) class SingleConv(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch): super(SingleConv, self).__init__() self.conv = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv3d(in_ch, out_ch, 3, padding=1), nn.BatchNorm3d(out_ch), nn.ReLU(inplace=True)) def forward(self, input): return self.conv(input) -
AttentionLayer
这个类似SENET中的SE分支计算加权系数,贴了一个SENet中的图,实现的就是下面红框部分
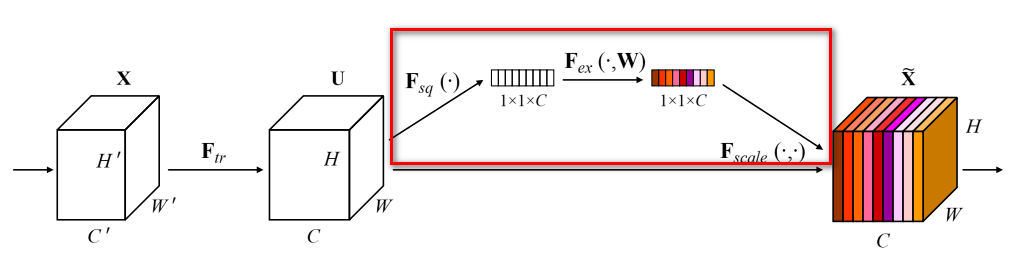
class Attentionlayer(nn.Module): def __init__(self,dim,r=16,act='relu'): super(Attentionlayer, self).__init__() self.layer1 = nn.Linear(dim, int(dim//r)) self.layer2 = nn.Linear(int(dim//r), dim) self.relu = nn.ReLU() self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid() def forward(self, inp): att = self.sigmoid(self.layer2(self.relu(self.layer1(inp)))) return att.unsqueeze(-1) -
对于分割
对应论文中的图,就是将上面的基本块组合在Unet中
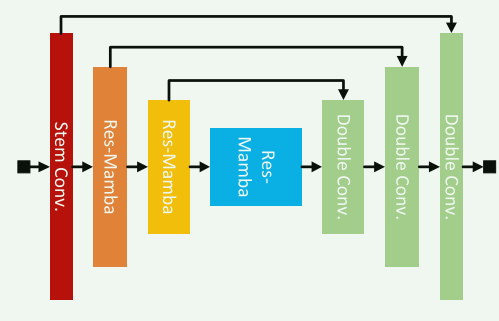
class nnMambaSeg(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_ch=1, channels=32, blocks=3, number_classes=6):
super(nnMambaSeg, self).__init__()
self.in_conv = DoubleConv(in_ch, channels, stride=2, kernel_size=3)
# self.mamba_layer_stem = MambaLayer(channels)
self.pooling = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool3d((1, 1, 1))
self.att1 = Attentionlayer(channels)
self.layer1 = make_res_layer(channels, channels * 2, blocks, stride=2, mamba_layer=MambaLayer(channels*2))
self.att2 = Attentionlayer(channels*2)
self.layer2 = make_res_layer(channels * 2, channels * 4, blocks, stride=2, mamba_layer=MambaLayer(channels*4))
# self.mamba_layer_2 = MambaLayer(channels*4)
self.att3 = Attentionlayer(channels*4)
self.layer3 = make_res_layer(channels * 4, channels * 8, blocks, stride=2, mamba_layer=MambaLayer(channels*8))
# self.mamba_layer_3 = MambaLayer(channels*8)
self.up5 = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='trilinear', align_corners=False)
self.conv5 = DoubleConv(channels * 12, channels * 4)
self.up6 = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='trilinear', align_corners=False)
self.conv6 = DoubleConv(channels * 6, channels * 2)
self.up7 = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='trilinear', align_corners=False)
self.conv7 = DoubleConv(channels * 3, channels)
self.up8 = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='trilinear', align_corners=False)
self.conv8 = DoubleConv(channels, number_classes)
def forward(self, x):
c1 = self.in_conv(x)
scale_f1 = self.att1(self.pooling(c1).reshape(c1.shape[0], c1.shape[1])).reshape(c1.shape[0], c1.shape[1], 1, 1, 1)
# c1_s = self.mamba_layer_stem(c1) + c1
c2 = self.layer1(c1)
# c2_s = self.mamba_layer_1(c2) + c2
scale_f2 = self.att2(self.pooling(c2).reshape(c2.shape[0], c2.shape[1])).reshape(c2.shape[0], c2.shape[1], 1, 1, 1)
c3 = self.layer2(c2)
# c3_s = self.mamba_layer_2(c3) + c3
scale_f3 = self.att3(self.pooling(c3).reshape(c3.shape[0], c3.shape[1])).reshape(c3.shape[0], c3.shape[1], 1, 1, 1)
c4 = self.layer3(c3)
# c4_s = self.mamba_layer_3(c4) + c4
up_5 = self.up5(c4)
merge5 = torch.cat([up_5, c3*scale_f3], dim=1)
c5 = self.conv5(merge5)
up_6 = self.up6(c5)
merge6 = torch.cat([up_6, c2*scale_f2], dim=1)
c6 = self.conv6(merge6)
up_7 = self.up7(c6)
merge7 = torch.cat([up_7, c1*scale_f1], dim=1)
c7 = self.conv7(merge7)
up_8 = self.up8(c7)
c8 = self.conv8(up_8)
return c8
4.nnMamba4cls.py
这个文件对应于分类任务,其他模块和nnMamba.py相同不在赘述,只说明不同的部分
-
MambaSeq
这个部分就是relu+mamba,对应论文中的图:
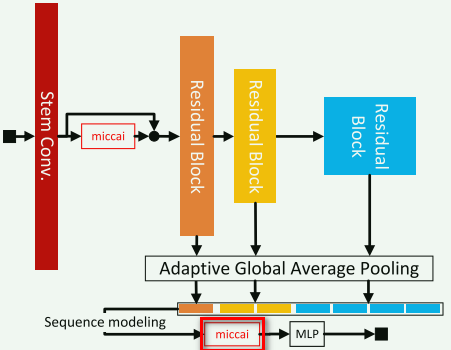
class MambaSeq(nn.Module): def __init__(self, dim, d_state=16, d_conv=4, expand=2): super().__init__() self.dim = dim self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) self.mamba = Mamba( d_model=dim, # Model dimension d_model d_state=d_state, # SSM state expansion factor d_conv=d_conv, # Local convolution width expand=expand # Block expansion factor ) def forward(self, x): B, C = x.shape[:2] x = self.relu(x) assert C == self.dim n_tokens = x.shape[2:].numel() img_dims = x.shape[2:] x_flat = x.reshape(B, C, n_tokens).transpose(-1, -2) x_mamba = self.mamba(x_flat) out = x_mamba.transpose(-1, -2).reshape(B, C, *img_dims) return out -
nnMambaEncoder
这个实现的就是分类模型,我对原文中图像和源码进行了一定的标注,方便理解,论文中针对的3D图像,我这里按照2D的简单写,不影响理解。对照源码和图像可以发现,源码中是每组3个Res-Mamba块,每组的输出进行了分辨率维度的池化,然后拼接reshape后送入mamba,图中还有一个池化拼接后的特征和经过mamba的特征加和的操作图中没有体现。
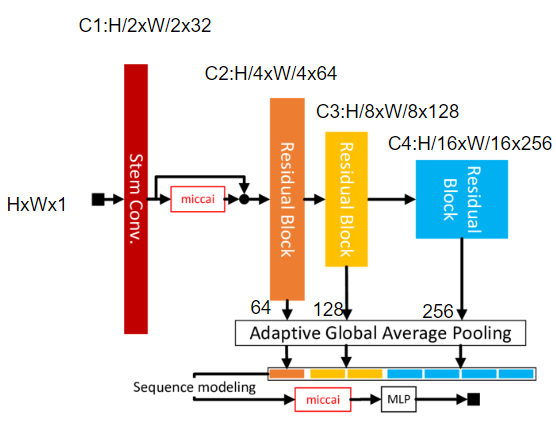
class nnMambaEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_ch=1, channels=32, blocks=3, number_classes=1):
super(nnMambaEncoder, self).__init__()
self.in_conv = DoubleConv(in_ch, channels, stride=2, kernel_size=3)
self.mamba_layer_stem = MambaLayer(
dim=channels, # Model dimension d_model
d_state=8, # SSM state expansion factor
d_conv=4, # Local convolution width
expand=2 # Block expansion factor
)
self.layer1 = make_res_layer(channels, channels * 2, blocks, stride=2)
self.layer2 = make_res_layer(channels * 2, channels * 4, blocks, stride=2)
self.layer3 = make_res_layer(channels * 4, channels * 8, blocks, stride=2)
self.pooling = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool3d((1, 1, 1))
self.mamba_seq = MambaSeq(
dim=channels*2, # Model dimension d_model
d_state=8, # SSM state expansion factor
d_conv=2, # Local convolution width
expand=2 # Block expansion factor
)
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(channels*14,
channels),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(channels, number_classes))
def forward(self, x):
c1 = self.in_conv(x)
c1_s = self.mamba_layer_stem(c1) + c1
c2 = self.layer1(c1_s)
c3 = self.layer2(c2)
c4 = self.layer3(c3)
pooled_c2_s = self.pooling(c2) # B 64 1 1 1
pooled_c3_s = self.pooling(c3) # B 128 1 1 1
pooled_c4_s = self.pooling(c4) # B 256 1 1 1
# B 64 1
# B 64 2
# B 64 4
h_feature = torch.cat((pooled_c2_s.reshape(c1.shape[0], c1.shape[1]*2, 1),
pooled_c3_s.reshape(c1.shape[0], c1.shape[1]*2, 2),
pooled_c4_s.reshape(c1.shape[0], c1.shape[1]*2, 4)),
dim=2) # -> B 64 7
h_feature_att = self.mamba_seq(h_feature) + h_feature # B 64 7
h_feature = h_feature_att.reshape(c1.shape[0], -1) # B 64 7 -> B 448
return self.mlp(h_feature)


























 2405
2405

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








