小菊的语义分割3🌼——数据预处理及像素级分类实现原理
1. 数据预处理
思路: 读取train.txt文件,获取训练图像及对应标签的文件路径,读取图像,将图像转化为tensor之后,resize调整图像尺寸大小并进行归一化处理,之后也可通过旋转,色偏,增加噪声等方式进行数据增强。注意要保证图像和标签的处理一致。
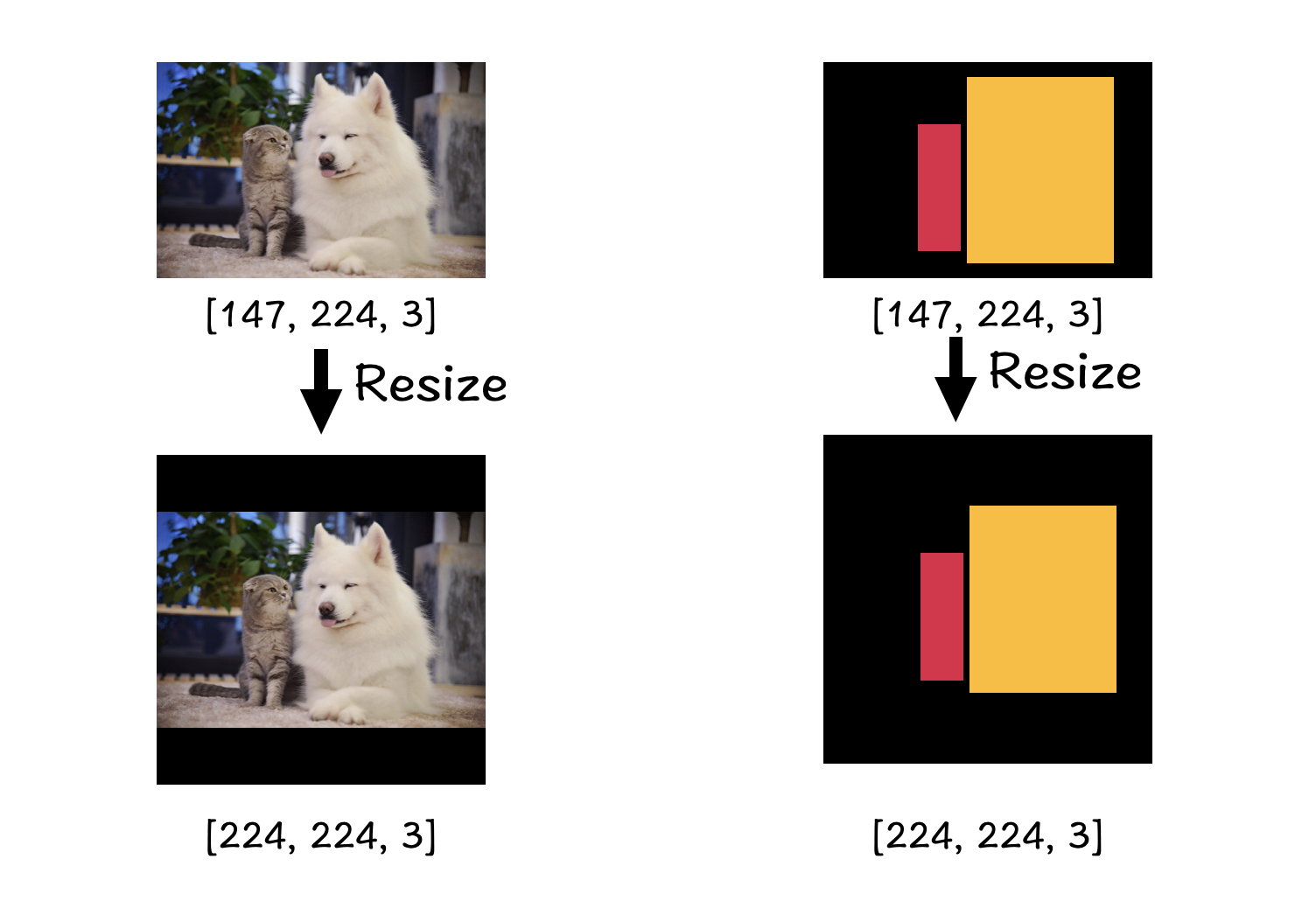
padding可以使图像在resize时不失真
2. label map 标签映射

如图就是我们的语义分割标签图像,相同颜色(像素值)的像素点代表的是同一类物体。假设像我们这个标签图像所展示的那样,我们需要分割出来图片中的猫和狗,那对我们的语义分割任务来说就是总共要分3类:0 背景;1 猫;2 狗;因此,我们需要创建一个[Height, Width, N_classes]数组来表示每一个像素点的类别;如下图所示:

label[0, 0] = [1, 0, 0] 说明[0, 0]位置是背景,label[1, 1] = [0, 1, 0]说明[1, 1]这个像素点属于猫。我们Reshape之后好像更方便大家理解:
seg_labels = np.reshape(seg_labels, (-1,NCLASSES))
[[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1],
...
]
这就是我们最后用来和预测结果计算损失的数据啦🌼相信大家对为什么这样做还有点云里雾里的感觉,那么接下来就让我们揭开语义分割的神秘面纱吧🌼
3. 像素级分类原理
了解完lable的具体格式之后,我们来看一下网络的最后几层设计:
x = Conv2D(n_classes,(1,1), padding='vaild' )(x)
x = Reshape((-1,n_classes))(x)
output = Softmax()(x)
这个和我们label的处理是一致的,输出的是每一个像素点属于哪一类的概率,如下图:

tensor表示:
[[0.4, 0.3, 0.3],
[0.7, 0.2, 0.1],
[0.8, 0.2, 0.0],
[0.8, 0.1, 0.1],
...
]
将我们处理之后的label和预测得到的结果传给我们的损失函数就能计算出loss了,这样我们就实现了像素级的分类————也就是语义分割了🌼
下面是包含了数据预处理,损失定义等整个模型训练过程的train.py文件,大家稍作修改就可以训练自己的语义分割模型了🌼
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import keras
from keras import backend as K
from keras.optimizers import Adam
from keras.layers import Lambda
from keras.callbacks import TensorBoard, ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau, EarlyStopping
# 标签像素值对应的物体类别, 0为背景
CLASSES = {
'[0 0 0]' : 0, # 背景
'[7 7 7]' : 1,
'[26 26 26]' : 2,
}
NCLASSES = 2
HEIGHT = 576
WIDTH = 576
BATCH_SIZE = 2
# train.txt和val.txt的文件路径
path_train_txt = ''
path_val_txt = ''
# train的图像和标签路径
path_Xtrain = ''
path_Xlabel = ''
# val的图像和标签路径
path_Yval = ''
path_Ylabel = ''
# labels映射
def label_map(labels):
labelmap = np.zeros((int(HEIGHT),int(WIDTH),NCLASSES))
for h in range(int(HEIGHT)):
for w in range(int(WIDTH)):
if str(labels[h, w]) in CLASSES.keys():
c = CLASSES[str(labels[h, w])]
else:
c = 0
labelmap[h, w, c] = 1
return labelmap
def data_generator(mode):
assert mode in ['train', 'val'], \
'mode must be ethier \'train\' or \'val\''
if mode == 'train':
with open(path_train_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
np.random.shuffle(lines)
n = len(lines)
path0 = path_Xtrain
path1 = path_Xlabel
else:
with open(path_val_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
np.random.shuffle(lines)
n = len(lines)
path0 = path_Yval
path1 = path_Ylabel
i = 0
while 1:
images = []
labels = []
for _ in range(BATCH_SIZE):
if i==0:
np.random.shuffle(lines)
name = lines[i].split(';')[0]
img = Image.open(path0 + '/' + name)
img = img.resize((HEIGHT,WIDTH))
img = np.array(img)
img = img/255
images.append(img)
name = (lines[i].split(';')[1]).replace("\n", "")
img = Image.open(path1 + '/' + name)
img = img.resize((int(HEIGHT),int(WIDTH)))
img = np.array(img)
seg_labels = label_map(img)
seg_labels = np.reshape(seg_labels, (-1,NCLASSES))
labels.append(seg_labels)
i = (i+1) % n
yield (np.array(images),np.array(labels))
# 定义损失函数
def loss(y_true, y_pred):
crossloss = K.binary_crossentropy(y_true,y_pred)
loss = K.sum(crossloss)/HEIGHT/WIDTH
return loss
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 用于最后保存模型的路径
log_dir = ''
# 创建模型
model = Net()
# 获取训练样本和验证样本的数目
with open(path_train_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
num_train = len(lines)
with open(path_val_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
num_val = len(lines)
# 设置学习率下降方法,val_loss验证损失连续5个epoch不下降就让学习率减半
reduce_lr = ReduceLROnPlateau(
monitor='val_loss',
factor=0.5,
patience=5,
verbose=1
)
# 是否需要早停,当val_loss一直不下降的时候意味着模型基本训练完毕,可以停止
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_loss',
min_delta=0,
patience=10,
verbose=1
)
# 设置损失,优化器
model.compile(loss = loss,
optimizer = Adam(lr=1e-3),
metrics = ['accuracy'])
print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, BATCH_SIZE))
# 开始训练
model.fit_generator(data_generator('train'),
steps_per_epoch=max(1, num_train//BATCH_SIZE),
validation_data=data_generator('val'),
validation_steps=max(1, num_val//BATCH_SIZE),
epochs=50,
initial_epoch=0,
callbacks=[reduce_lr, early_stopping])
model.save_weights(log_dir+'Dali.h5')
上面的标签处理方便理解,但是时间复杂度高,在cup上处理慢,下面为改进版本:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
# import keras
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Lambda
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import TensorBoard, ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau, EarlyStopping
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
from models.decoders.segnet import resnet50_segnet
import glob
# tf.device('/device:GPU:0')
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "0"
# ===================>
import logging
logging.basicConfig(filename='./work_dirs/segnet/segnet.log', filemode='a', level=logging.DEBUG, format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.handlers.clear()
logger.setLevel(level = logging.DEBUG)
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
console = logging.StreamHandler()
console.setLevel(logging.INFO)
console.setFormatter(formatter)
logger.addHandler(console)
# <==================
# 标签像素值对应的物体类别, 0为背景
CLASSES = {
# 默认背景为0
76 : 1, # 建筑物
150 : 2, # 植被
255 : 3, # 道路
}
NCLASSES = 4
HEIGHT = 512
WIDTH = 512
BATCH_SIZE = 8
# train.txt和val.txt的文件路径
path_train_txt = './dataset/train.txt'
path_val_txt = './dataset/val.txt'
# train的图像和标签路径
path_Xtrain = './dataset/jpg/'
path_Xlabel = './dataset/png/'
# val的图像和标签路径
path_Yval = './dataset/val_jpg/'
path_Ylabel = './dataset/val_png/'
# labels映射
def label_map(labels):
labelmap = np.zeros((int(HEIGHT),int(WIDTH),NCLASSES)).astype('float32')
for h in range(int(HEIGHT)):
for w in range(int(WIDTH)):
if str(labels[h, w]) in CLASSES.keys():
c = CLASSES[str(labels[h, w])]
else:
c = 0
labelmap[h, w, c] = 1
return labelmap
def data_generator(mode):
assert mode in ['train', 'val'], \
'mode must be ethier \'train\' or \'val\''
if mode == 'train':
with open(path_train_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
np.random.shuffle(lines)
n = len(lines)
path0 = path_Xtrain
path1 = path_Xlabel
else:
with open(path_val_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
np.random.shuffle(lines)
n = len(lines)
path0 = path_Yval
path1 = path_Ylabel
i = 0
while 1:
images = []
labels = []
for _ in range(BATCH_SIZE):
if i==0:
np.random.shuffle(lines)
name = lines[i].split(';')[0]
img = Image.open(path0 + name)
img = img.resize((HEIGHT,WIDTH))
img = np.array(img).astype('float32')
img = img/255
images.append(img)
name = (lines[i].split(';')[1]).replace("\n", "")
img = Image.open(path1 + name).convert('L')
img = img.resize((int(HEIGHT),int(WIDTH)))
img = np.array(img)
img = tf.convert_to_tensor(img)
seg_labels = np.zeros((HEIGHT, WIDTH))
for k in CLASSES:
seg_labels[(img == k)] = CLASSES[k]
seg_labels = np.reshape(seg_labels, (-1,1))
seg_labels = to_categorical(seg_labels, NCLASSES)
# print(seg_labels)
labels.append(seg_labels)
i = (i+1) % n
yield (np.array(images).astype('float32'),np.array(labels).astype('float32'))
# 定义损失函数
def loss(y_true, y_pred):
crossloss = K.binary_crossentropy(y_true, y_pred)
loss = K.sum(crossloss)/HEIGHT/WIDTH
return loss
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 用于最后保存模型的路径
log_dir = './work_dirs/segnet/'
# 创建模型
model = resnet50_segnet(n_classes=NCLASSES, input_height=HEIGHT, input_width=WIDTH)
# 获取训练样本和验证样本的数目
with open(path_train_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
num_train = len(lines)
with open(path_val_txt, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
num_val = len(lines)
# 设置学习率下降方法,val_loss验证损失连续5个epoch不下降就让学习率减半
reduce_lr = ReduceLROnPlateau(
monitor='val_loss',
factor=0.5,
patience=5,
verbose=1
)
# 是否需要早停,当val_loss一直不下降的时候意味着模型基本训练完毕,可以停止
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_loss',
min_delta=0,
patience=10,
verbose=1
)
# 设置损失,优化器
model.compile(loss = loss,
optimizer = Adam(lr=1e-3),
metrics = ['accuracy'])
logger.info('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, BATCH_SIZE))
# print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, BATCH_SIZE))
# 开始训练
history = model.fit(data_generator('train'),
steps_per_epoch=max(1, num_train//BATCH_SIZE),
validation_data=data_generator('val'),
validation_steps=max(1, num_val//BATCH_SIZE),
epochs=50,
initial_epoch=0,
callbacks=[reduce_lr, early_stopping])
logger.info(history)
model.save_weights(log_dir+'segnet.h5')






















 1639
1639











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








