From: http://www.ulpi.org
1. UTMI USB 2.0 Transceiver Macrocell Interace
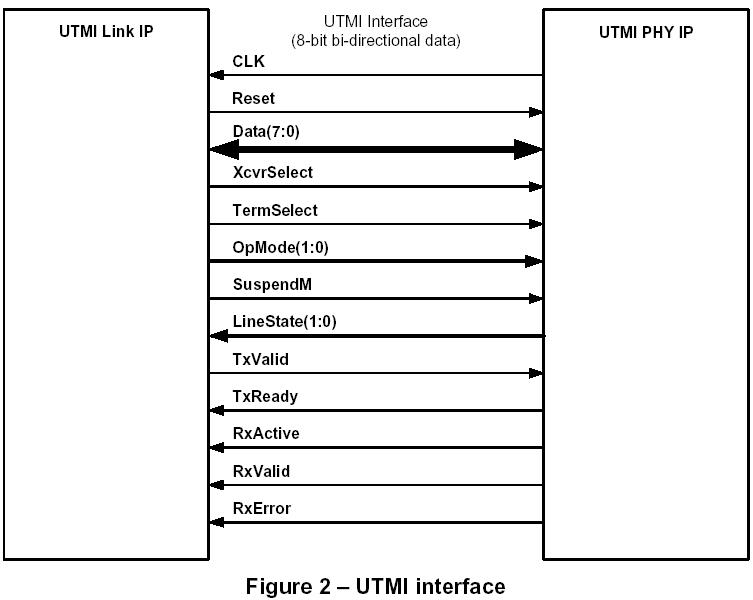
defines an interface between two IP blocks: the USB Transceiver Macrocell (IP) and the USB Link layer (SIE). The UTMI interface provides functionality for USB peripherals only, not for USB hosts or On-The-Go.
2. UTMI+
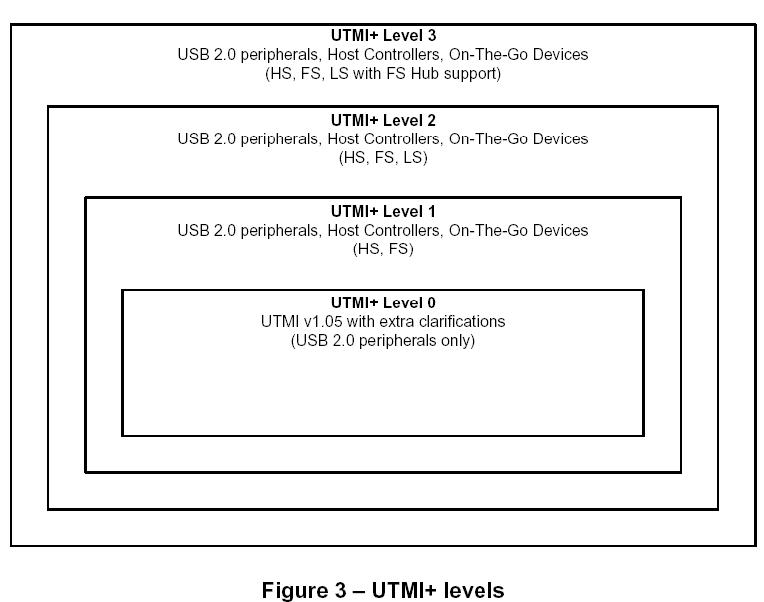
adds host and On-The-Go capabilities to the USB system.
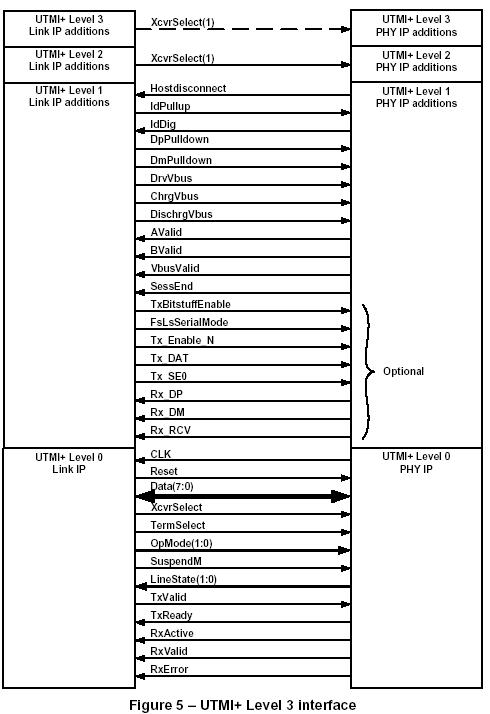
UTMI+ incrementally adds new functionality and interface signals to the Link and PHY.
3. ULPI: UTMI+ Low Pin Interface
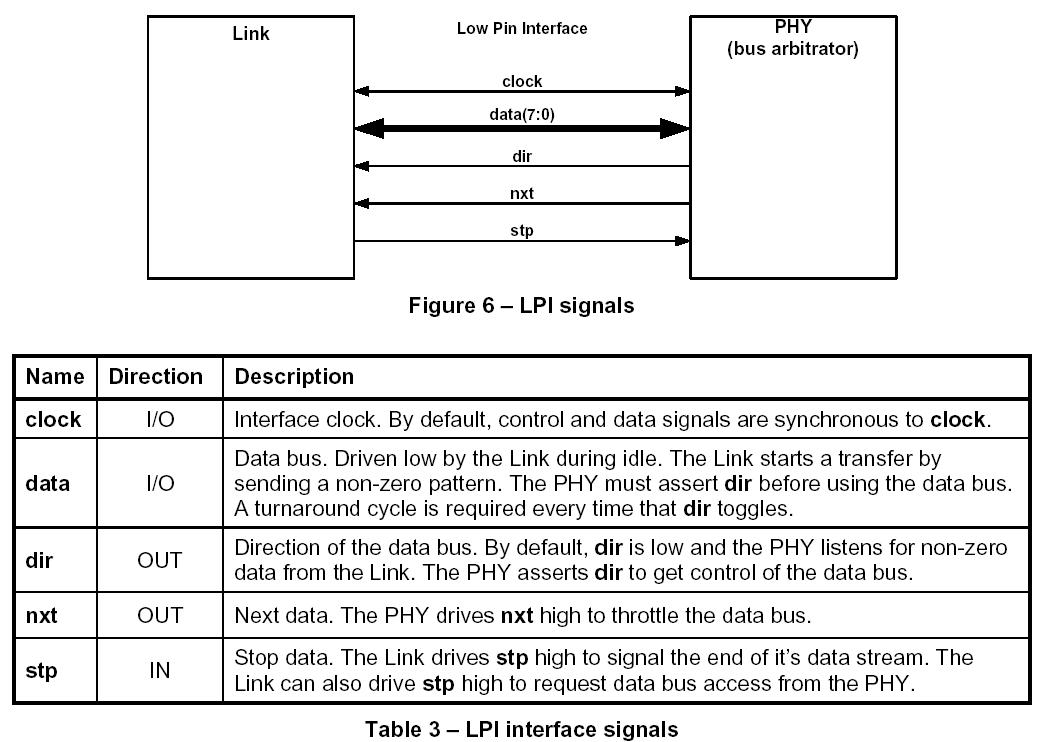
The ULPI specification reduces the Link to PHY interface to 12 or 8 signals, with support for all the features needed by USB peripherals, hosts, and OTG. The result is a package size as small as 32 pins or less, compared with 64 to 80 pins for UTMI+.
4. ULPI PHY Register Set
There are four main types of registers:
ID Registers These registers provide a unique identifier to the USB system. If necessary,system software can change behavior based on different PHY attachment. This is not generally needed because PHY capabilities are chosen at hardware design time.
Mode Registers These registers control how the PHY behaves. Many signals from UTMI+ are changed only when the USB is idle, so they are placed in registers that are accessed only when the ULPI bus is idle. Several new features have also been introduced, including Carkit Mode.
Interrupt Registers These registers inform the Link of status changes in the PHY. Many signals in UTMI+ convey information to the Link that is not timing critical. Those signals have been replaced with status bytes and interrupt signaling. Status information is sent only when the ULPI bus is idle.
Extra Registers Additional register space is provided for two reasons. Some addresses have been reserved for future use, while other registers are available for vendorspecific use.






















 156
156

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








