原文链接:Cylinder model segmentation — Point Cloud Library 0.0 documentation
目录
本教程演示了如何运行圆柱形模型的Sample Consensus分割。为了使示例更实用一些,将以下操作应用于输入数据集(按顺序):
- 距离1.5米以上的数据点被过滤
- 每一点的表面法线被估计
- 一个平面模型被分割,显示,并保存到本地
- 一个圆柱形模型(在本数据集中是一个杯子)被分割,显示,并保存到本地
本次使用的数据集:table_scene_mug_stereo_textured.pcd
- 一个杯子
- 一个平面
- 离得很远的背景杂点
由于数据中存在噪声,圆柱模型并不完美。


处理流程
- 滤波去噪:pass_through_filter();
- 法线估计 normals_estimate();
- 把平面分割出来 plane_seg();
- 利用分割结果(获取到的下标):使用平面点云的下标将平面抽取出来,并保存:get_plane();
- 移除平面及其法线,将结果保存在cloud_filtered2,cloud_normals2:remove_plane();
- 将圆柱分割出来,得到系数因子和下标 cylinder_seg();
- 将圆柱抽取并保存 get_cylinder();
圆柱分割
平面分割可以参考博文:PCL教程-点云分割之平面模型分割
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_NORMAL_PLANE);
seg.setNormalDistanceWeight(0.1);
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setMaxIterations(100);
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.03);
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
seg.setInputNormals(cloud_normals);
- Using a model of type: SACMODEL_NORMAL_PLANE
- Setting normal distance weight to 0.100000
- Using a method of type: SAC_RANSAC with a model threshold of 0.030000
- Setting the maximum number of iterations to 100
下面重点介绍圆柱分割:
// Create the segmentation object for cylinder segmentation and set all the parameters
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients (true);
seg.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_CYLINDER);
seg.setMethodType (pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setNormalDistanceWeight (0.1);
seg.setMaxIterations (10000);
seg.setDistanceThreshold (0.05);
seg.setRadiusLimits (0, 0.1);
- 这里同样使用了RANSAC鲁棒估计来获取圆柱的系数因子。
- 还设置了距离阈值为0.05m(5cm):小于这个阈值的点将标记为圆柱内部点。
- 此外还设置了表面法线的距离权重为0.1
- 限制了圆柱模型的半径为0~0.1m(10cm)
- 最大的迭代次数为10000
程序代码
#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/extract_indices.h>
#include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h>
#include<pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include<string>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
// All the objects needed
pcl::PCDReader reader;
pcl::PassThrough<PointT> pass;
pcl::NormalEstimation<PointT, pcl::Normal> ne;
pcl::SACSegmentationFromNormals<PointT, pcl::Normal> seg;
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
pcl::ExtractIndices<PointT> extract;
pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::Normal> extract_normals;
pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>());
// Datasets
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr cloud_normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_filtered2(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr cloud_normals2(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients_plane(new pcl::ModelCoefficients), coefficients_cylinder(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers_plane(new pcl::PointIndices), inliers_cylinder(new pcl::PointIndices);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_plane(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>());
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_cylinder(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>());
//PCLVisualizer
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("Cylinder Segmentation");
int step_count;
void pass_through_filter()
{
// Build a passthrough filter to remove spurious NaNs
pass.setInputCloud(cloud);
pass.setFilterFieldName("z");
pass.setFilterLimits(0, 1.5);
pass.filter(*cloud_filtered);
std::cerr << "PointCloud after filtering has: " << cloud_filtered->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl;
}
void normals_estimate()
{
// Estimate point normals
ne.setSearchMethod(tree);
ne.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
ne.setKSearch(50);
ne.compute(*cloud_normals);
}
void plane_seg()
{
// Create the segmentation object for the planar model and set all the parameters
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_NORMAL_PLANE);
seg.setNormalDistanceWeight(0.1);
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setMaxIterations(100);
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.03);
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
seg.setInputNormals(cloud_normals);
// Obtain the plane inliers and coefficients
seg.segment(*inliers_plane, *coefficients_plane);
std::cerr << "Plane coefficients: " << *coefficients_plane << std::endl;
}
void get_plane()
{
// Extract the planar inliers from the input cloud
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
extract.setIndices(inliers_plane);
extract.setNegative(false);
// Write the planar inliers to disk
extract.filter(*cloud_plane);
std::cerr << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl;
writer.write("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured_plane.pcd", *cloud_plane, false);
}
void remove_plane()
{
// Remove the planar inliers, extract the rest
extract.setNegative(true);
extract.filter(*cloud_filtered2);
extract_normals.setNegative(true);
extract_normals.setInputCloud(cloud_normals);
extract_normals.setIndices(inliers_plane);
extract_normals.filter(*cloud_normals2);
}
void cylinder_seg()
{
// Create the segmentation object for cylinder segmentation and set all the parameters
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_CYLINDER);
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setNormalDistanceWeight(0.1);
seg.setMaxIterations(10000);
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.05);
seg.setRadiusLimits(0, 0.1);
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered2);
seg.setInputNormals(cloud_normals2);
// Obtain the cylinder inliers and coefficients
seg.segment(*inliers_cylinder, *coefficients_cylinder);
std::cerr << "Cylinder coefficients: " << *coefficients_cylinder << std::endl;
}
void get_cylinder()
{
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered2);
extract.setIndices(inliers_cylinder);
extract.setNegative(false);
extract.filter(*cloud_cylinder);
if (cloud_cylinder->points.empty())
std::cerr << "Can't find the cylindrical component." << std::endl;
else
{
std::cerr << "PointCloud representing the cylindrical component: " << cloud_cylinder->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl;
writer.write("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured_cylinder.pcd", *cloud_cylinder, false);
}
}
void keyboard_event_occurred(const pcl::visualization::KeyboardEvent& event,
void * nothing)
{
if (event.getKeySym() == "space" && event.keyDown())
{
++step_count;
}
}
int
main(int argc, char** argv)
{
step_count = 1;
std::string str = "STEP";
//初始化PCLVisualizer
//viewer.addCoordinateSystem(1);
//viewer.setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 255);
viewer.addText(str+ std::to_string(step_count), 10, 10,16, 200,200,100,"text");
viewer.registerKeyboardCallback(&keyboard_event_occurred, (void*)NULL);
// Read in the cloud data
reader.read("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured.pcd", *cloud);
std::cerr << "PointCloud has: " << cloud->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl;
// 显示原始点云
//pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> color_cloud(cloud, 255, 0, 0);
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud,"cloud");
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1,"cloud");
//滤波去噪
pass_through_filter();
// 法线估计
normals_estimate();
// 把平面分割出来
plane_seg();
// 利用平面点云的下标将平面抽取出来,并保存
get_plane();
// 移除平面及其法线,将结果保存在cloud_filtered2,cloud_normals2
remove_plane();
// 将圆柱分割出来,得到系数因子和下标
cylinder_seg();
// 将圆柱抽取并保存
get_cylinder();
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
viewer.spinOnce();
if (step_count < 8)
{
viewer.updateText(str + std::to_string(step_count), 10, 10, 16, 50, 100, 200, "text");
switch (step_count)
{
case 2:
//滤波去噪
viewer.updatePointCloud(cloud_filtered, "cloud"); break;
case 3:
//法线估计
plane_seg();break;
case 4:
//利用平面点云的下标将平面抽取出来,并保存
viewer.updatePointCloud(cloud_plane, "cloud"); break;
case 5:
//移除平面及其法线,将结果保存在cloud_filtered2,cloud_normals2
viewer.updatePointCloud(cloud_filtered2, "cloud"); break;
case 6:
// 将圆柱分割出来,得到系数因子和下标
cylinder_seg();
break;
case 7:
将圆柱抽取并保存
viewer.updatePointCloud(cloud_cylinder, "cloud"); break;
default:
break;
}
}
else {
break;
}
}
return (0);
}
实验结果
打印结果
PointCloud has: 307200 data points.
PointCloud after filtering has: 139897 data points.
Plane coefficients: header:
seq: 0 stamp: 0 frame_id:
values[]
values[0]: 0.0161902
values[1]: -0.837667
values[2]: -0.545941
values[3]: 0.528862PointCloud representing the planar component: 116300 data points.
Cylinder coefficients: header:
seq: 0 stamp: 0 frame_id:
values[]
values[0]: 0.0543319
values[1]: 0.100139
values[2]: 0.787577
values[3]: -0.0135876
values[4]: 0.834831
values[5]: 0.550338
values[6]: 0.0387446PointCloud representing the cylindrical component: 11462 data points.
原始点云

过滤杂点

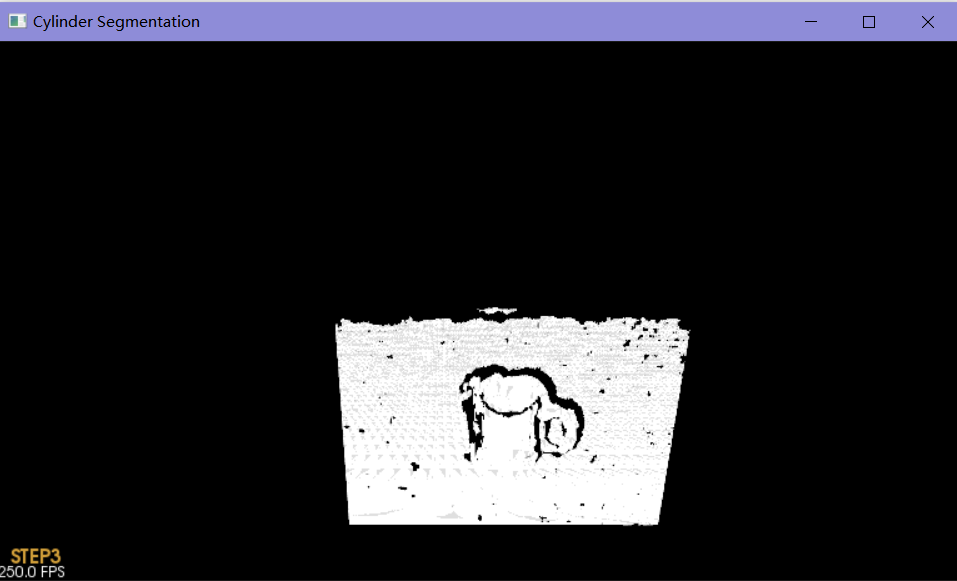
平面分割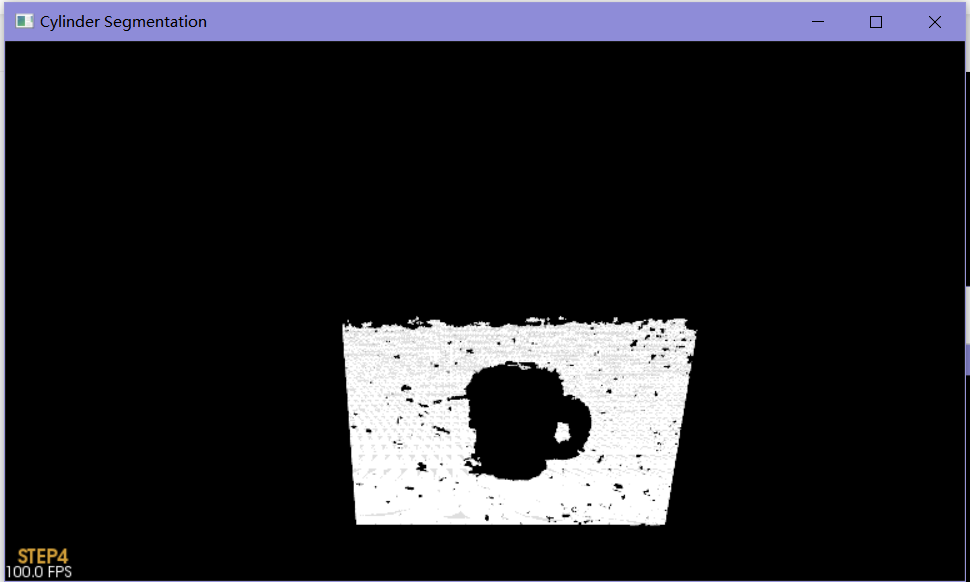
将平面去除

分割圆柱

CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8 FATAL_ERROR)
project(cylinder_segmentation)
find_package(PCL 1.2 REQUIRED)
include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS})
link_directories(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS})
add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS})
add_executable (cylinder_segmentation cylinder_segmentation.cpp)
target_link_libraries (cylinder_segmentation ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
























 932
932

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








