概述
HarmonyOS编译子系统是以GN和Ninja构建为基座,对构建和配置粒度进行部件化抽象、对内建模块进行功能增强、对业务模块进行功能扩展的系统,该系统提供以下基本功能:
- 以部件为最小粒度拼装产品和独立编译。
- 支持轻量、小型、标准三种系统的解决方案级版本构建,以及用于支撑应用开发者使用IDE开发的SDK开发套件的构建。
- 支持芯片解决方案厂商的灵活定制和独立编译。
Ninja:是一个专注于快速编译的小型构建系统。
GN:Generate Ninja的缩写,用于产生Ninja文件。
编译环境配置
- Linux编译环境搭建(如果已有对应版本的Linux开发环境,可跳过Linux环境搭建过程):详细指导见以下链接。
编译环境目前主要支持Ubuntu18.04和Ubuntu20.04(Ubuntu22.04暂不支持)。
- HarmonyOS SDK镜像下载:
从DevEco Studio的SDK Manager中获取SDK。
- 安装构建工具depot_tools并添加到环境变量。
任意位置创建工作目录depot_tools,cd到自己创建的目录,拉取工具(需要网络环境):
mkdir depot_tools cd depot_tools git clone https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromium/tools/depot_tools.git将depot_tools的路径加到环境变量中:
编译.bashrc文件将depot_tools路径信息加到最后一行。
vi ~/.bashrc # 在.bashrc文件的最后添加下面一行代码export PATH="$PATH:/xxx/depot_tools"此处需配置绝对路径信息,例如这里创建的本地路径是/mnt/d/my_code/depot_tools,故此处配置入上图。
刷新环境变量使其生效:
source ~/.bashrc
使用GN需要Python环境,安装Python环境。
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python直接输入指令sudo apt install python可能会安装失败,需要先输入sudo apt update更新一下可用包的最新列表。

判断python是否安装成功:
输入python显示python版本即可。

GN构建工程适配流程

首先,需要添加HarmonyOS平台的宏定义;然后配置好HarmonyOS平台的工具链信息(包括clang工具链,sysroot以及clang版本);接着需要在toolchain路径下配置各个架构的ohos_clang_toolchain;然后扩充gcc_toolchain模版功能,配置HarmonyOS用于启动引导程序的.o文件信息。剩下的就是需要设置一些HarmonyOS的编译参数(主要是基础的编译选项、宏定义等);然后在BUILD.gn中不同架构平台的分支处,添加对应的HarmonyOS平台的分支,其中未适配HarmonyOS的三方库可以先走Linux分支的编译配置。更加详细的信息可参考下节的适配案例。
webRTC适配案例
本文中将通过webRTC的GN构建工程案例来对上一章节的流程进行实操讲解。WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communications) 是一项实时通讯技术,它允许网络应用或者站点,在不借助中间媒介的情况下,建立浏览器之间点对点(Peer-to-Peer)的连接,实现视频流和(或)音频流或者其他任意数据的传输。下面我们来了解下如何能通过GN构建工程将webRTC适配到HarmonyOS系统上。
适配流程
示例代码中D:\my_code\compare_src_ohos\src_ohos\中为源代码,D:\my_code\src_ohos\路径下为修改之后的代码。
- 添加HarmonyOS平台宏定义
主要是增加了适配HarmonyOS的default_compiler_configs以及_default_toolchain。在GN工程里面,BUILDCONFIG.gn是第一位被解析的,里面定义的变量相当于全局变量,可以被后续所有的.gn文件使用。我们编译过程中可能会配置一些编译选项以及一些头文件搜索路径。default_compiler_configs指向的文件里面会包括一些默认的编译选项以及头文件搜索路径等等。_default_toolchain指向了一个工具链相关的函数。具体修改点如下:

- 设置HarmonyOS平台clang工具链相关路径
不同平台的工具链会有一些差别,所以需要使用HarmonyOS的工具链。主要是修改config/clang/clang.gni文件,.gni文件类似于GN的头文件,会被import到各个.gn文件中使用其定义的一些变量。该文件中的核心修改点在于配置指向HarmonyOS SDK的工具链路径。另外还需修改clang_use_chrome_plugins的值为false,HarmonyOS中默认clang_use_chrome_plugins值为false,不设置可能会报错find-bad-constructs文件找不到。
此处ohos_sdk_native_root 的值需要对应修改为自己本地HarmonyOS SDK中的native的路径。具体修改点如下:

- 设置HarmonyOS平台sysroot路径
sysroot里面包含了许多头文件搜索路径,配置了sysroot之后,编译过程中会去该目录下搜索需要的头文件。SDK里面会提供大量的头文件,这些头文件都会放在sysroot目录下,所以我们需要引入HarmonyOS对应的sysroot。具体修改点如下:

- 修改HarmonyOS平台clang版本
这里主要是配置HarmonyOS对应的clang版本号。具体修改点如下:

- 设置各个架构的ohos_clang_toolchain
这里主要是在\src_ohos\build\toolchain路径下新建一个ohos/BUILD.gn文件,用于配置ohos_clang_toolchain,里面主要配置了HarmonyOS用于启动引导程序的.o文件。同时设置HarmonyOS不同架构(主要包括ohos_clang_arm、ohos_clang_arm64、ohos_clang_x86_64)的ohos_clang_toolchain配置信息。具体添加内容如下:
import("//build/config/sysroot.gni")
import("//build/toolchain/gcc_toolchain.gni")
declare_args() {
# Whether unstripped binaries, i.e. compiled with debug symbols, should be
# considered runtime_deps rather than stripped ones.
ohos_unstripped_runtime_outputs = true
ohos_extra_cflags = ""
ohos_extra_cppflags = ""
ohos_extra_cxxflags = ""
ohos_extra_asmflags = ""
ohos_extra_ldflags = ""
}
# The ohos clang toolchains share most of the same parameters, so we have this
# wrapper around gcc_toolchain to avoid duplication of logic.
#
# Parameters:
# - toolchain_root
# Path to cpu-specific toolchain within the ndk.
# - sysroot
# Sysroot for this architecture.
# - lib_dir
# Subdirectory inside of sysroot where libs go.
# - binary_prefix
# Prefix of compiler executables.
template("ohos_clang_toolchain") {
gcc_toolchain(target_name) {
assert(defined(invoker.toolchain_args),
"toolchain_args must be defined for ohos_clang_toolchain()")
toolchain_args = invoker.toolchain_args
toolchain_args.current_os = "ohos"
# Output linker map files for binary size analysis.
enable_linker_map = true
ohos_libc_dir =
rebase_path(invoker.sysroot + "/" + invoker.lib_dir, root_build_dir)
libs_section_prefix = "${ohos_libc_dir}/Scrt1.o"
libs_section_prefix += " ${ohos_libc_dir}/crti.o"
libs_section_postfix = "${ohos_libc_dir}/crtn.o"
if (invoker.target_name == "ohos_clang_arm") {
abi_target = "arm-linux-ohos"
} else if (invoker.target_name == "ohos_clang_arm64") {
abi_target = "aarch64-linux-ohos"
} else if (invoker.target_name == "ohos_clang_x86_64") {
abi_target = "x86_64-linux-ohos"
}
clang_rt_dir =
rebase_path("${clang_lib_path}/${abi_target}/nanlegacy",
root_build_dir)
print("ohos_libc_dir :", ohos_libc_dir)
print("clang_rt_dir :", clang_rt_dir)
solink_libs_section_prefix = "${ohos_libc_dir}/crti.o"
solink_libs_section_prefix += " ${clang_rt_dir}/clang_rt.crtbegin.o"
solink_libs_section_postfix = "${ohos_libc_dir}/crtn.o"
solink_libs_section_postfix += " ${clang_rt_dir}/clang_rt.crtend.o"
_prefix = rebase_path("${clang_base_path}/bin", root_build_dir)
cc = "${_prefix}/clang"
cxx = "${_prefix}/clang++"
ar = "${_prefix}/llvm-ar"
ld = cxx
readelf = "${_prefix}/llvm-readobj"
nm = "${_prefix}/llvm-nm"
if (!is_debug) {
strip = rebase_path("${clang_base_path}/bin/llvm-strip", root_build_dir)
use_unstripped_as_runtime_outputs = ohos_unstripped_runtime_outputs
}
extra_cflags = ohos_extra_cflags
extra_cppflags = ohos_extra_cppflags
extra_cxxflags = ohos_extra_cxxflags
extra_asmflags = ohos_extra_asmflags
extra_ldflags = ohos_extra_ldflags
}
}
ohos_clang_toolchain("ohos_clang_arm") {
sysroot = "${sysroot}"
lib_dir = "usr/lib/arm-linux-ohos"
toolchain_args = {
current_cpu = "arm"
}
}
ohos_clang_toolchain("ohos_clang_arm64") {
sysroot = "${sysroot}"
lib_dir = "usr/lib/aarch64-linux-ohos"
toolchain_args = {
current_cpu = "arm64"
}
}
ohos_clang_toolchain("ohos_clang_x86_64") {
sysroot = "${sysroot}"
lib_dir = "usr/lib/x86_64-linux-ohos"
toolchain_args = {
current_cpu = "x86_64"
}
}- 扩充原本的gcc_toolchain模版功能
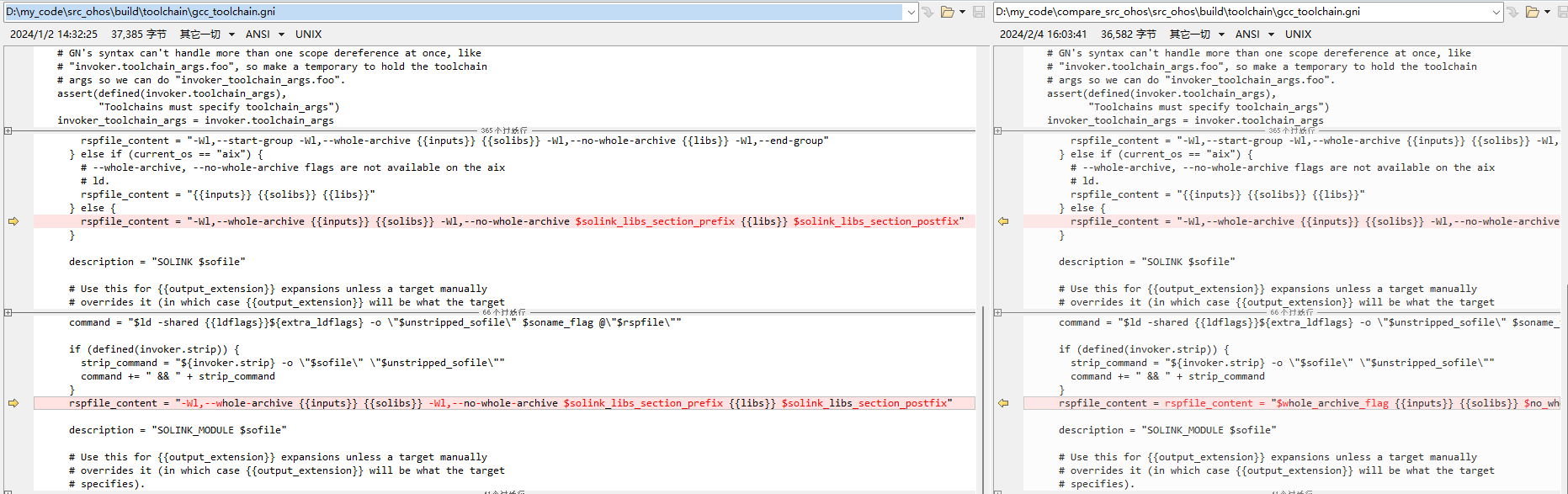
GN工程里面默认会配置gcc_toolchain,里面会包括一些tool,例如tool("cc")、tool("cxx")、tool("tolink")等等,编译不同的内容时调用其对应的配置项。这里主要是需要修改tool("solink")、tool("solink_module")中的rspfile_content配置以及tool("link")中的link_comand配置。我们需要在gcc_toolchain.gni中template("gcc_toolchain")下添加几个参数(libs_section_prefix、libs_section_postfix 、solink_libs_section_prefix、solink_libs_section_postfix )的识别。这几个参数是指向了上一步骤中配置的用于启动引导程序的.o文件。这些参数会在我们需要修改的rspfile_content、link_comand中用到。具体修改如下:

修改tool("solink")和tool("solink_module")中的rspfile_content为rspfile_content = "-Wl,--whole-archive {{inputs}} {{solibs}} -Wl,--no-whole-archive $solink_libs_section_prefix {{libs}} $solink_libs_section_postfix",这里需要用到刚刚定义的参数信息。具体修改如下:
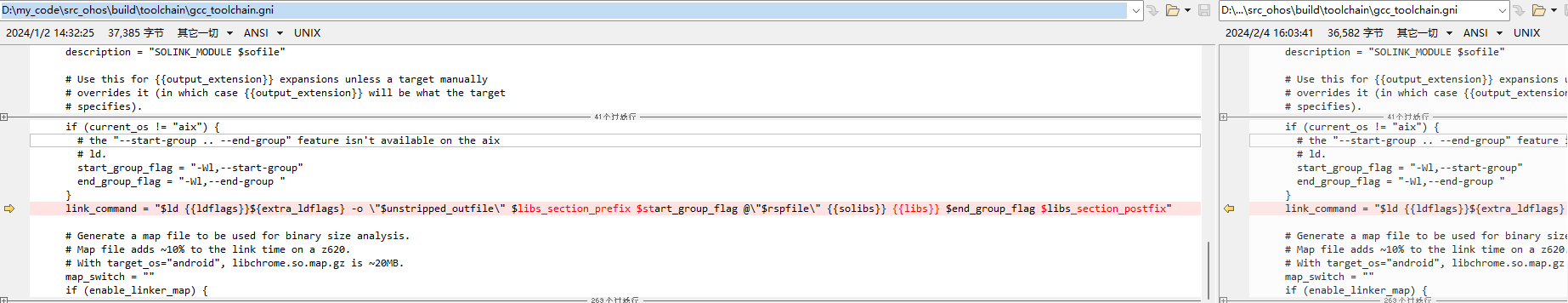
修改tool("link") 中link_command为link_command = "$ld {{ldflags}}${extra_ldflags} -o \"$unstripped_outfile\" $libs_section_prefix $start_group_flag @\"$rspfile\" {{solibs}} {{libs}} $end_group_flag $libs_section_postfix",这里需要用到刚刚定义的参数信息。
- 设置HarmonyOS的一些编译参数,将其加入到BUILDCONFIG.gn中
这里需要在config路径下新建一个ohos/BUILD.gn文件,该文件主要是定义了一个config("compiler"),该config会被注册到所有的编译目标,该config里面主要设置了基础的编译选项、宏定义等。
此处ohos_clang_base_path 的值需要对应修改为自己本地HarmonyOS SDK中的llvm的路径。具体添加内容如下:
import("//build/config/sysroot.gni")
assert(is_ohos)
ohos_clang_base_path = "/mnt/d/ohos/ohos-sdk/linux/native/llvm"
ohos_clang_version = "15.0.4"
if (is_ohos) {
if (current_cpu == "arm") {
abi_target = "arm-linux-ohos"
} else if (current_cpu == "x86") {
abi_target = ""
} else if (current_cpu == "arm64") {
abi_target = "aarch64-linux-ohos"
} else if (current_cpu == "x86_64") {
abi_target = "x86_64-linux-ohos"
} else {
assert(false, "Architecture not supported")
}
}
config("compiler") {
cflags = [
"-ffunction-sections",
"-fno-short-enums",
"-fno-addrsig",
]
cflags += [
"-Wno-unknown-warning-option",
"-Wno-int-conversion",
"-Wno-unused-variable",
"-Wno-misleading-indentation",
"-Wno-missing-field-initializers",
"-Wno-unused-parameter",
"-Wno-c++11-narrowing",
"-Wno-unneeded-internal-declaration",
"-Wno-undefined-var-template",
"-Wno-implicit-int-float-conversion",
]
defines = [
# The NDK has these things, but doesn't define the constants to say that it
# does. Define them here instead.
"HAVE_SYS_UIO_H",
]
defines += [
"OHOS",
"__MUSL__",
"_LIBCPP_HAS_MUSL_LIBC",
"__BUILD_LINUX_WITH_CLANG",
"__GNU_SOURCE",
"_GNU_SOURCE",
]
ldflags = [
"-Wl,--no-undefined",
"-Wl,--exclude-libs=libunwind_llvm.a",
"-Wl,--exclude-libs=libc++_static.a",
# Don't allow visible symbols from libraries that contain
# assembly code with symbols that aren't hidden properly.
# http://crbug.com/448386
"-Wl,--exclude-libs=libvpx_assembly_arm.a",
]
cflags += [ "--target=$abi_target" ]
include_dirs = [
"${sysroot}/usr/include/${abi_target}",
"${ohos_clang_base_path}/lib/clang/${ohos_clang_version}/include",
]
ldflags += [ "--target=$abi_target" ]
# Assign any flags set for the C compiler to asmflags so that they are sent
# to the assembler.
asmflags = cflags
}- build/config/compiler/BUILD.gn中增加对is_ohos的判断
保证可以正确走HarmonyOS支持的编译分支。这里主要是为了防止clang版本号校验失败导致异常。具体修改如下:

- 未适配HarmonyOS的三方库走linux编译配置
当前部分三方库还未适配HarmonyOS,涉及到时可以先走linux的编译配置,例如:需要获取config.h文件时。
修改video_capture的BUILD.gn。具体修改如下:

修改zlib的BUILD.gn。具体修改如下:

修改libevent中的BUILD.gn。HarmonyOS SDK中没有queue.h头文件,需要使用compat dir目录下的queue.h头文件。具体修改如下:

- 编译
先通过GN命令生成对应的ninja文件,然后使用ninja编译命令进行编译。
gn gen ../out/xxx --args='is_clang=true target_os="ohos" target_cpu="arm64" xxx' ninja -v -C ../out/xxx ${target_name} -j16可以根据需要在编译指令中添加对应参数信息。
查看具体编译命令:
可以在gn gen命令中添加--ninja-args="-v -dkeeprsp"用于查看具体编译命令,这个命令将会在编译过程中打印详细的编译命令,并且保留编译过程中生成的rsp文件。
查看一个目标被谁依赖:
例如gn refs out/intermediate/arm64_72 //pc:rtc_pc_base。这个命令将显示与目标//pc:rtc_pc_base相关的所有依赖项并列出所有引用了该目标的其他目标或文件。
- gn gen ../out/xxx --args='is_clang=true target_os="ohos" target_cpu="arm64" xxx'
- ninja -v -C ../out/xxx ${target_name} -j16
常见问题总结
在对webRTC的GN工程进行HarmonyOS工具链适配过程中,遇到了一些常见问题场景。下面针对这些问题做一个具体分析。
- Assertion failed. Unsupported ARM OS
问题详情:

问题原因/解决措施:
三方库内部没有做对is_ohos的判断,导致走到错误分支。当前很多业务模块还未适配HarmonyOS,暂时可以走linux分支以保证正常编译。
具体修改:

- python找不到pkg-config文件:No such file or directory: 'pkg-config'
问题详情:

问题原因/解决措施:
缺少pkg-config插件,安装该插件。
具体指令:
- sudo apt-get install pkg-config
- Unknown command line argument '-split-threshold-for-reg-with-hint=0'
问题详情:

问题原因/解决措施:
编译过程中会提示部分配置不识别,需要将这些配置项删除。
具体修改:

- WARN类型导致的ERROR
问题详情:

问题原因/解决措施:
编译器驱动程序有时(很少)会在调用之前发出警告。实际的链接器需要确保这些警告是否也被视为致命错误。为了避免编译中出现因警告而造成出错,可以添加编译参数treat_warnings_as_errors = false,或者去除config(treat_warnings_as_errors)中配置的“-Werror”,详情如下:

具体修改:
- 添加编译指令配置项treat_warnings_as_errors (建议使用)

- 修改源代码

- 添加编译指令配置项treat_warnings_as_errors (建议使用)
- error: reinterpret_cast from 'pthread_t' (aka 'unsigned long') to 'rtc::PlatformThreadId' (aka 'int') is not allowed
问题详情:

问题原因/解决措施:
rtc_base/platform_thread_types.cc未识别到is_ohos导致内部走错分支导致异常。目前HarmonyOS支持的接口是gettid(),rtc_base/platform_thread_types.cc需要识别到is_ohos然后调用gettid()。由于当前很多业务模块还未进行识别,暂时需要走linux分支,故需要保留liunx的定义。
具体修改:
- 首先需要在根目录的BUILD.gn中配置识别HarmonyOS系统的变量is_ohos:

- 修改rtc_base/platform_thread_types.cc业务代码:

- 首先需要在根目录的BUILD.gn中配置识别HarmonyOS系统的变量is_ohos:
- fatal error: 'config.h' file not found
fatal error: 'sys/queue.h' file not found
问题详情:
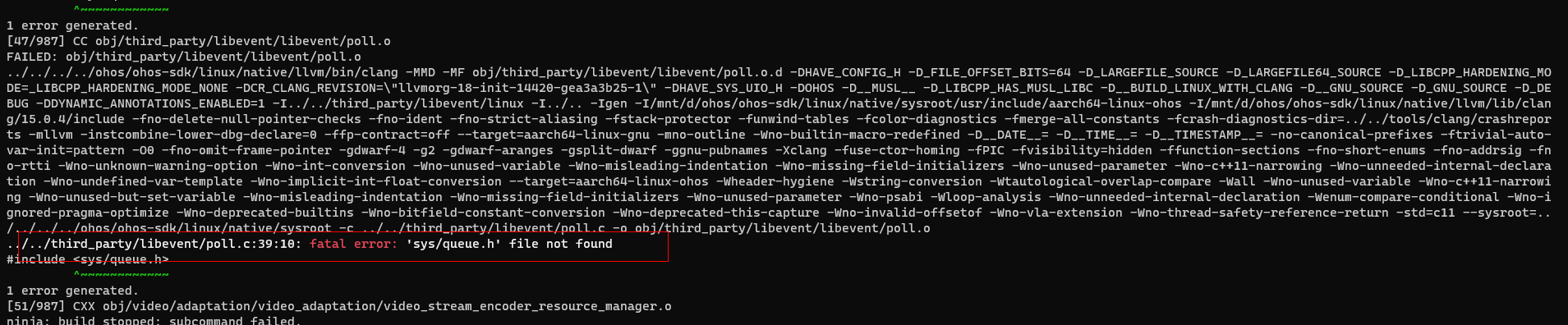

问题原因/解决措施:
找不到config.h头文件,libevent尚未适配HarmonyOS,需要添加is_ohos的判断并走linux的文件路径寻找config.h。
找不到'sys/queue.h'文件,HarmonyOS SDK中没有queue.h头文件,需要使用compat dir目录下的queue.h头文件。
具体修改:

最后
有很多小伙伴不知道学习哪些鸿蒙开发技术?不知道需要重点掌握哪些鸿蒙应用开发知识点?但是又不知道从哪里下手,而且学习时频繁踩坑,最终浪费大量时间。所以本人整理了一些比较合适的鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)学习路径和一些资料的整理供小伙伴学习
点击领取→纯血鸿蒙Next全套最新学习资料希望这一份鸿蒙学习资料能够给大家带来帮助,有需要的小伙伴自行领取~~
一、鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)最新学习路线

有了路线图,怎么能没有学习资料呢,小编也准备了一份联合鸿蒙官方发布笔记整理收纳的一套系统性的鸿蒙(OpenHarmony )学习手册(共计1236页)与鸿蒙(OpenHarmony )开发入门教学视频,内容包含:(ArkTS、ArkUI开发组件、Stage模型、多端部署、分布式应用开发、音频、视频、WebGL、OpenHarmony多媒体技术、Napi组件、OpenHarmony内核、Harmony南向开发、鸿蒙项目实战等等)鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)…等技术知识点。
获取以上完整版高清学习路线,请点击→纯血版全套鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料
二、HarmonyOS Next 最新全套视频教程

三、《鸿蒙 (OpenHarmony)开发基础到实战手册》
OpenHarmony北向、南向开发环境搭建

四、大厂面试必问面试题

五、鸿蒙南向开发技术

六、鸿蒙APP开发必备

完整鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料,请点击→纯血版全套鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料
总结
总的来说,华为鸿蒙不再兼容安卓,对中年程序员来说是一个挑战,也是一个机会。只有积极应对变化,不断学习和提升自己,他们才能在这个变革的时代中立于不败之地。




























 8829
8829

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








