R语言提升专题
专题1:玩转字符串
stringr包
将一个字符串拆分至以字符为最小单位进行操作
str_length()检测字符串长度
library(stringr)
x <- "The birch canoe slid on the smooth planks."
x
## [1] "The birch canoe slid on the smooth planks."
str_length(x)
## [1] 42
length(x)
## [1] 1
str_split()分割字符串
str_split(x," ")
## [[1]]
## [1] "The" "birch" "canoe" "slid" "on" "the"
## [7] "smooth" "planks."
- 输出格式是列表
class(str_split(x," "))
## [1] "list"
- 将列表取子集,即是拆分结果组成的向量
x2 = str_split(x," ")[[1]];x2
## [1] "The" "birch" "canoe" "slid" "on" "the"
## [7] "smooth" "planks."
- 将多个字符串拆分,每个字符串拆分结果为一个列表元素
y = c("jimmy 150","nicker 140","tony 152")
str_split(y," ")
## [[1]]
## [1] "jimmy" "150"
##
## [[2]]
## [1] "nicker" "140"
##
## [[3]]
## [1] "tony" "152"
- 加入
simplify = T参数,输出结果简化为矩阵
str_split(y," ",simplify = T)
## [,1] [,2]
## [1,] "jimmy" "150"
## [2,] "nicker" "140"
## [3,] "tony" "152"
str_sub()按位置提取字符串
空格也算
str_sub(x,5,9)
## [1] "birch"
str_detect()检测字符串
生成与元素数量一致的逻辑值,可用于取子集
#检测向量中有‘h’的元素
str_detect(x2,"h")
## [1] TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE FALSE
#检测向量中以‘T’开头的元素
str_starts(x2,"T")
## [1] TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#检测向量中以‘e’结尾的元素
str_ends(x2,"e")
## [1] TRUE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE
str_replace()字符串替换
x2
## [1] "The" "birch" "canoe" "slid" "on" "the"
## [7] "smooth" "planks."
str_replace(x2,"o","A")
## [1] "The" "birch" "canAe" "slid" "An" "the"
## [7] "smAoth" "planks."
str_replace_all(x2,"o","A")
## [1] "The" "birch" "canAe" "slid" "An" "the"
## [7] "smAAth" "planks."
str_replace(x2,"o|e","A")
##[1] "ThA" "birch" "canAe" "slid" "An" "thA"
##[7] "smAoth" "planks."
str_remove()字符删除
x
## [1] "The birch canoe slid on the smooth planks."
str_remove(x," ")
## [1] "Thebirch canoe slid on the smooth planks."
str_remove_all(x," ")
## [1] "Thebirchcanoeslidonthesmoothplanks."
专题2:玩转数据框
arrange()排序
library(dplyr)
arrange(test, Sepal.Length) #从小到大
## Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species
## 1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa
## 2 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa
## 3 5.8 2.7 5.1 1.9 virginica
## 4 6.3 3.3 6.0 2.5 virginica
## 5 6.4 3.2 4.5 1.5 versicolor
## 6 7.0 3.2 4.7 1.4 versicolor
arrange(test, desc(Sepal.Length)) #从大到小
## Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species
## 1 7.0 3.2 4.7 1.4 versicolor
## 2 6.4 3.2 4.5 1.5 versicolor
## 3 6.3 3.3 6.0 2.5 virginica
## 4 5.8 2.7 5.1 1.9 virginica
## 5 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa
## 6 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa
distinct()去重复
.keep_all =T这一参数保证表格完整性
distinct(test,Species,.keep_all = T)
## Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species
## 1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa
## 2 7.0 3.2 4.7 1.4 versicolor
## 3 6.3 3.3 6.0 2.5 virginica
*select()、filter()挑选列、行
mutate()数据框新增列
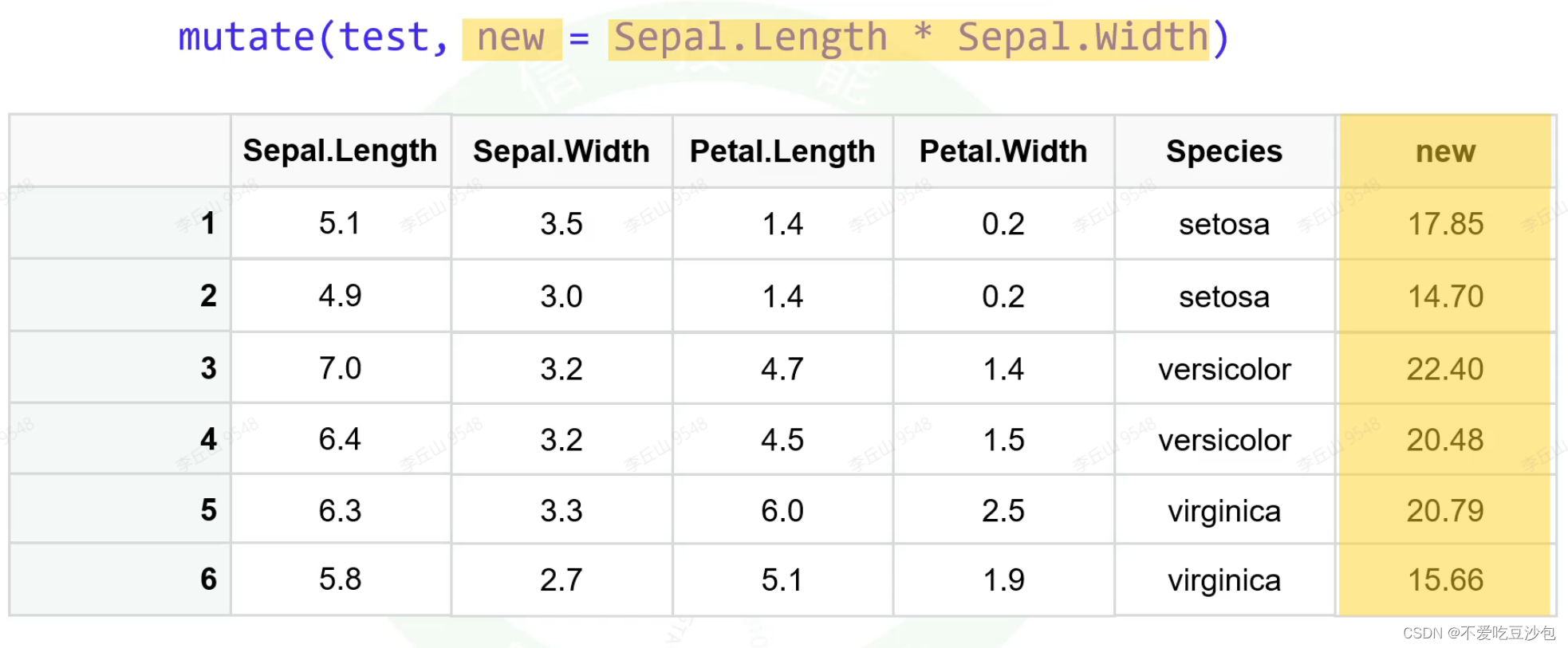
%>%管道符号
用于连续步骤时使用,避免产生很多中间变量,又避免了嵌套代码不易读的问题
快捷键Ctrl+Shift+m
#中间变量
x1 = select(iris,-5)
x2 = as.matrix(x1)
x3 = head(x2,50)
pheatmap::pheatmap(x3)
#嵌套
pheatmap::pheatmap(head(as.matrix(select(iris,-5)),50))
#管道符号:把前一行的结果变量传至下一个函数的第一个参数
iris %>%
select(-5) %>%
as.matrix() %>%
head(50) %>%
pheatmap::pheatmap()
专题3:条件和循环
if条件语句
-
只有if,没有else
if(T/F){ <CODE> } #eg: if(!require(tidyr)) install.packages('tidyr')
()中代表一个逻辑值,如为T则运行{}中代码,如为F,则不运行。
- 长脚本管理方式
- 打包封装:
if(F){...}则跳过,if(T){...}则运行,带有{}的代码可以被折叠。 - 分成多个脚本,每个脚本保存RData,下个脚本开头清空再加载数据。
- 打包封装:
-
if…else…
if(T/F){ <CODE1> }else{ <CODE2> }如果
()中为T,执行CODE1,如果()中为F,执行CODE2。 -
ifelse()只有三个参数:
x逻辑值/逻辑值向量;yes逻辑值为T时的返回值;no逻辑值为F时的返回值。支持单个逻辑值,也支持逻辑值向量。
x ##[1] 0.6582069 -0.3887199 0.1477327 ifelse(x>0,"+","-") ##[1] "+" "-" "+"
-
和
str_detect()组合samples = c("tumor1","tumor2","tumor3","normal1","normal2","normal3") k1 = str_detect(samples,"tumor");k1 ##[1] TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE ifelse(k1,"tumor","normal") ##[1] "tumor" "tumor" "tumor" "normal" "normal" "normal"
-
多个条件嵌套
i=0 if (i>0){ print('+') } else if (i==0) { print('0') } else if (i< 0){ print('-') } ##[1] "0" ifelse(i>0,"+",ifelse(i<0,"-","0")) ##[1] "0" library(dplyr) case_when(i>0 ~ '+', i<0 ~ '-', TRUE ~ '0' )
For 循环
对x中的变量i进行循环
for (i in x){
<CODE>
}
for( i in 1:4){
print(i)
}
##[1] 1
##[1] 2
##[1] 3
##[1] 4
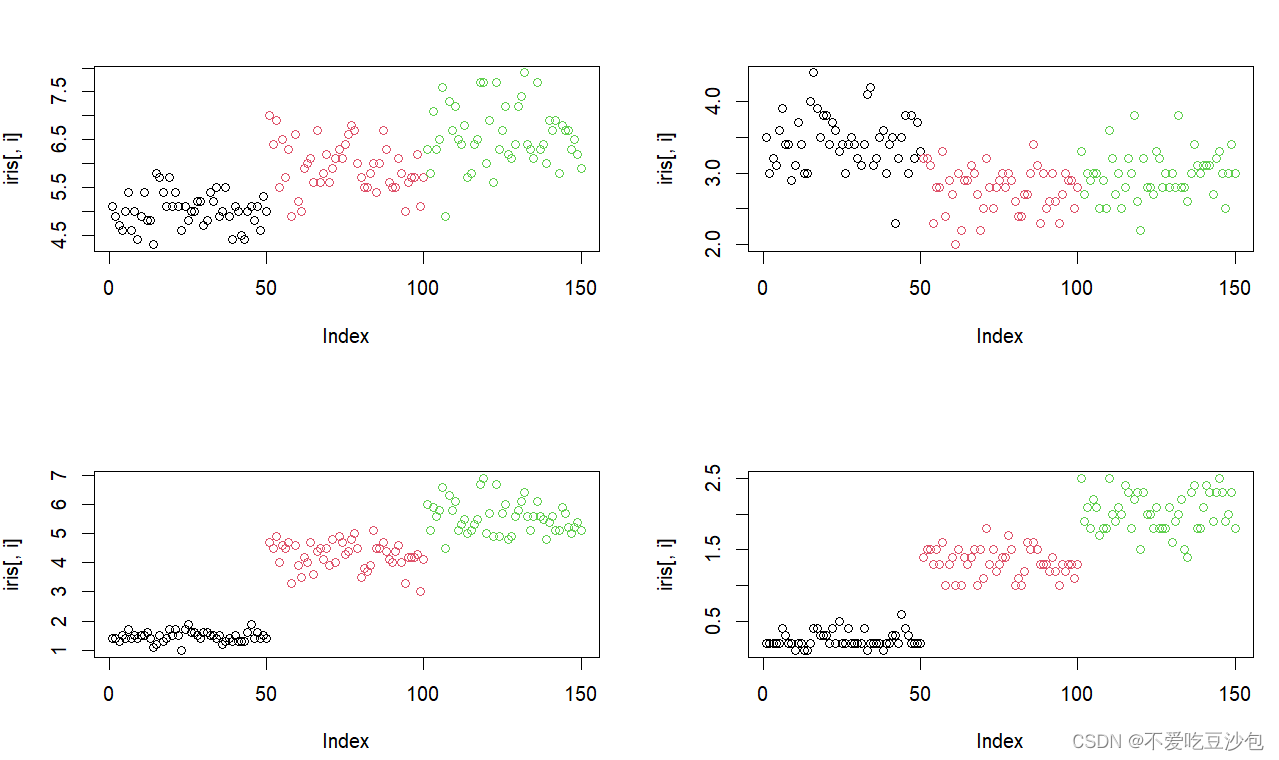
- 批量画图
par(mfrow = c(2,2)) ##用于基础包的拼图函数
for(i in 1:4){
plot(iris[,i],col = iris[,5])
}
- 批量装包
pks = c("tidyr","dplyr","stringr")
for(g in pks){
if(!require(g,character.only = T))
install.packages(g,ask = F,update = F)
}
专题4:隐式循环
apply矩阵/数据框的隐式循环
apply(X,MARGIN,FUN,...)
三个函数:
-
x:数据框/矩阵;
-
MARGIN:1为行,2为列;
-
FUN:对行/列所作的操作。
test<- iris[1:6,1:4]
apply(test, 2, mean)
## Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length
## 4.9500000 3.3833333 1.4500000
## Petal.Width
## 0.2333333
apply(test, 1, sum)
返回值是向量,列名/行名是向量元素的名字
lapply向量/列表的隐式循环
lapply(list,FUN,...)
对列表/向量中的每个元素实施相同的操作
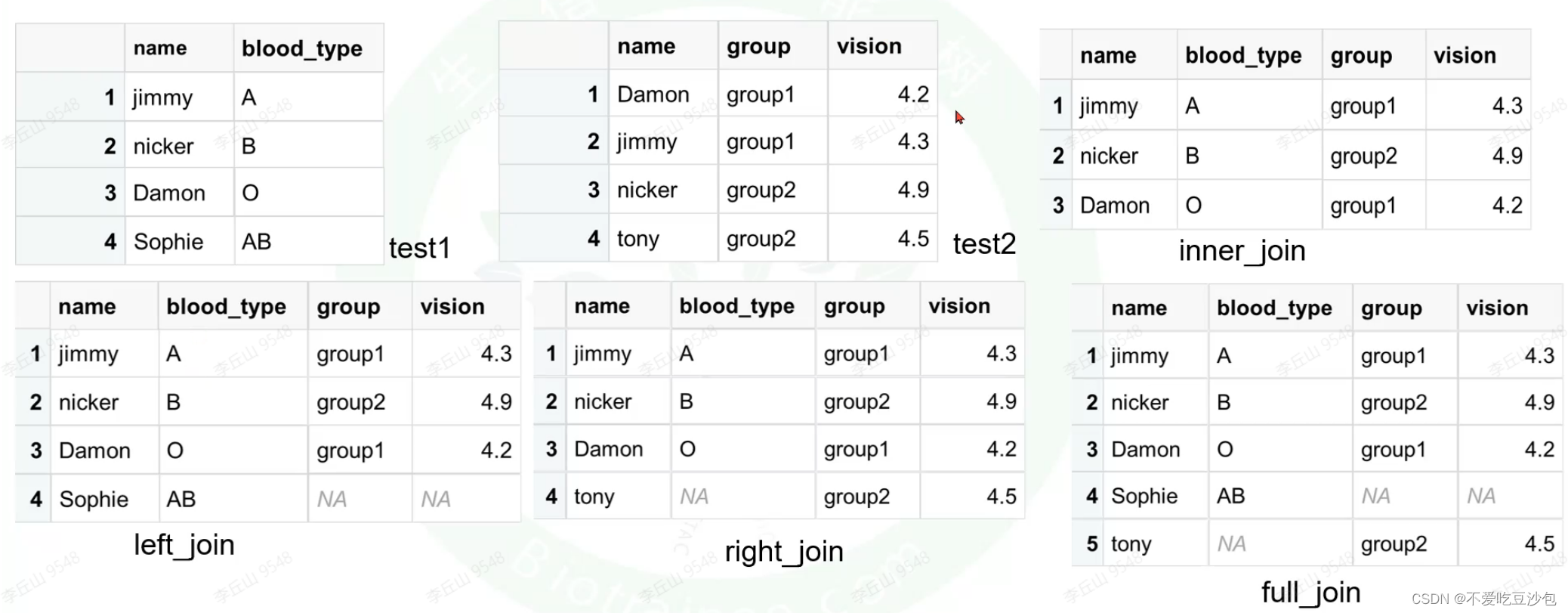
专题5:两个数据框的连接
-
inner_join取交集 -
full_join全连接 -
left_join左连接 -
right_join右连接
FUNCTION(x, y, by='')
专题6:表达矩阵画箱线图
表达矩阵的格式不是ggplot2能够直接使用的格式,因此需要更改数据组织方式
- 转置数据框
- 把行名变成其中一列,避免行名丢失
- 把数据的参数变为列:行名、基因、表达量、分组(宽边长)
exp
## test1 test2 test3 test4 test5 test6
##gene1 1.55 1.49 1.80 -0.37 -1.82 -1.62
##gene2 -1.74 0.37 2.08 2.11 -0.22 1.42
##gene3 1.57 1.25 1.32 2.49 0.58 -0.81
dat = t(exp) %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
rownames_to_column() %>%
mutate(group = rep(c("control","treat"),each = 3))
dat
## rowname gene1 gene2 gene3 group
## 1 test1 1.55 -1.74 1.57 control
## 2 test2 1.49 0.37 1.25 control
## 3 test3 1.80 2.08 1.32 control
## 4 test4 -0.37 2.11 2.49 treat
## 5 test5 -1.82 -0.22 0.58 treat
## 6 test6 -1.62 1.42 -0.81 treat
- 宽变长
pdat = dat%>%
pivot_longer(cols = starts_with("gene"),
names_to = "gene",
values_to = "count")
pdat
### A tibble: 18 × 4
## rowname group gene count
## <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 test1 control gene1 1.55
## 2 test1 control gene2 -1.74
## 3 test1 control gene3 1.57
## 4 test2 control gene1 1.49
## 5 test2 control gene2 0.37
## 6 test2 control gene3 1.25
## 7 test3 control gene1 1.8
## 8 test3 control gene2 2.08
## 9 test3 control gene3 1.32
## 10 test4 treat gene1 -0.37
## 11 test4 treat gene2 2.11
## 12 test4 treat gene3 2.49
## 13 test5 treat gene1 -1.82
## 14 test5 treat gene2 -0.22
## 15 test5 treat gene3 0.58
## 16 test6 treat gene1 -1.62
## 17 test6 treat gene2 1.42
## 18 test6 treat gene3 -0.81
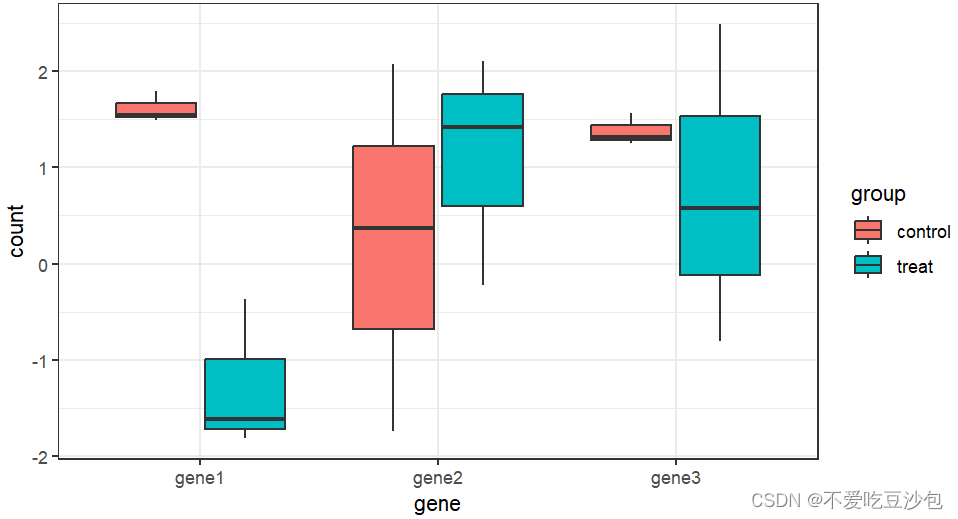
- 画图
library(ggplot2)
p = ggplot(pdat,aes(gene,count))+
geom_boxplot(aes(fill = group))+
theme_bw()
p
一些优秀函数!
先mark一下!以后再整理吧~
match()dir()file.create()file.exists()file.remove()
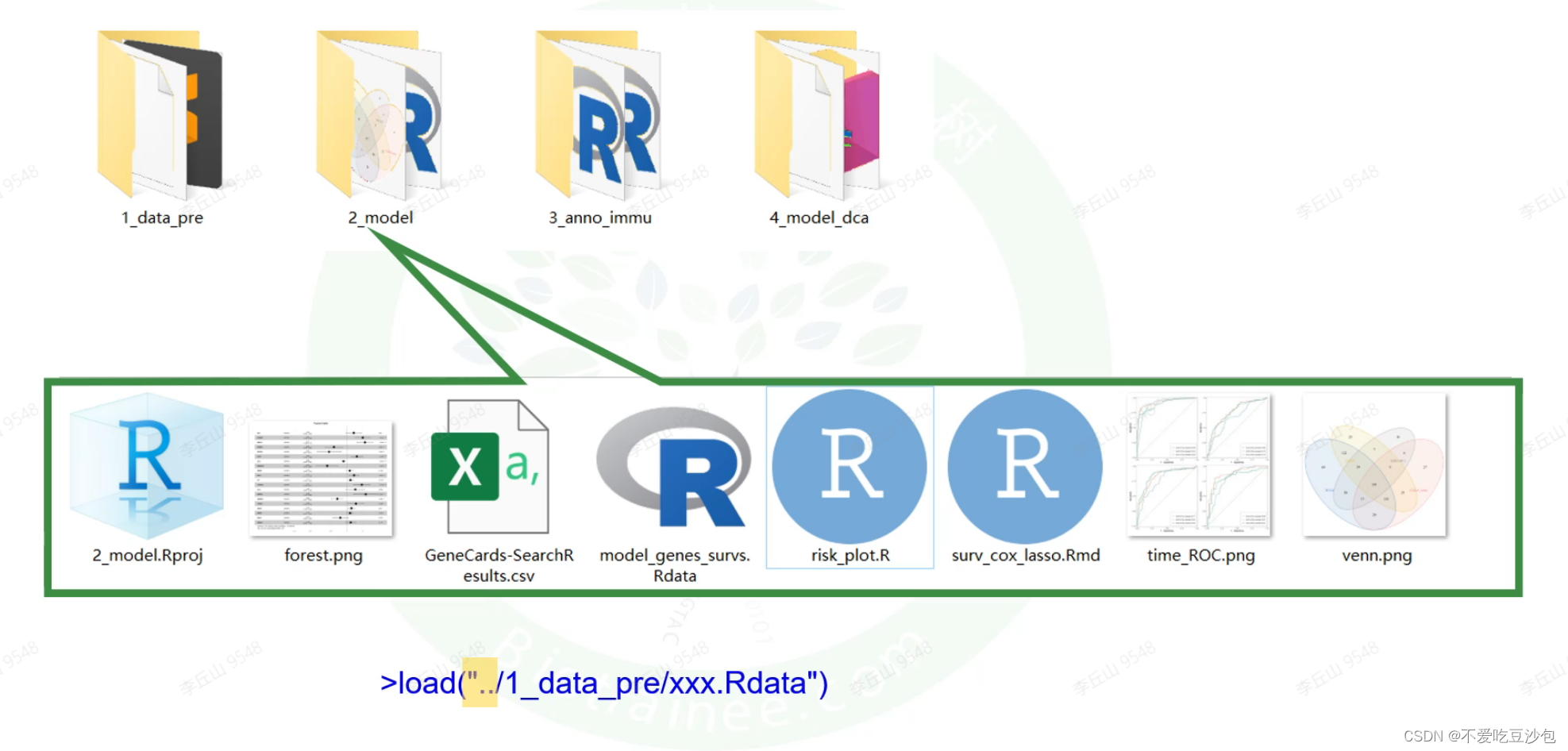
实战项目的组织方式
-
一个项目下建立输出文件、输入文件、图片、Rdata等文件夹分别管理

-
每个步骤使用一个文件夹进行管理,尽量不改变文件夹组织的位置






















 592
592











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








