memory hierarchy

cache 基本概念
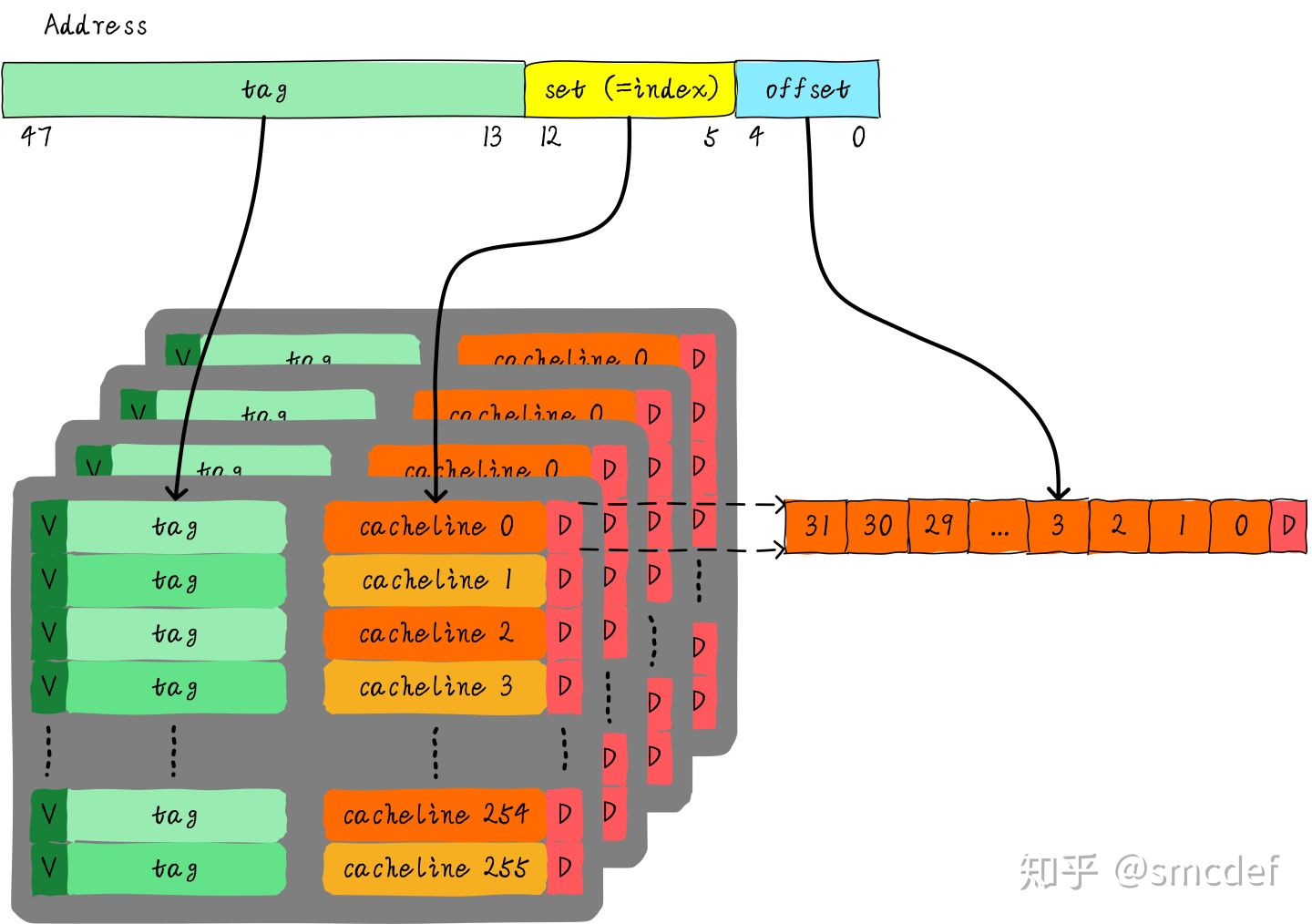
cache line: 一条cache的大小
cache size: 整个cache的大小
offset: 对应cache line中的那个byte, eg:8byte cache line size, 需要3bit的offset
index: 对应哪条cache line, eg: 64byte cache 大小,每条cache line是8byte,所以一共有8条cache line, 需要3bit
tag: 对应地址位宽,比如48bit位宽, cache size是64byte, 需要48-6=42bit
performance 计算公式
AMAT = HitTime + MissRate * MissPenalty
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dkCM0Hc_v3Y&list=PLeWkeA7esB-PN8dBeEjWveHwnpQk7od0m&index=5
Reduce hit time
- way prediction
- column associative
- victim cache
Reduce Miss Penalty
- early restart
- merging write buffer
Reduce miss rate
compiler optimizations
-
instruction reordering: reorder procedures in memory; 2. profiling to look at conflicts 3
- data reordering: 1.merging arrays; 2. loop interchange; 3.loop fusion; 4.blocking
increasing cache bandwidth
- pileline cache access: pro: bandwidth; con: higher branch penalty
- multibanked cache: core i7 L1$ 4banks, L2$ 8banks
- nonblocking cache: hit under miss; hit under multiple miss/miss under miss; need Miss Status Holding Registers(MSHRs)
reducing miss penalty or miss rate via prefetching
- sequential prefetching
- strided prefetching


直接映射缓存
两路组相连缓存
全相连缓存
一个四路组相连缓存实例问题
一条cache 实际需要的位宽: valid width + dirty width + tag width + data width
write through
没有dirty位
read:
hit: return data from cache
miss:read data from memory to cache, then return data from cache
write:
hit: write data to cache, then write data to lower memory
miss: write data to lower memory
write back
有dirty位
read:
hit: return data
miss: if dirty, write dirty data to lower memory first, and then read data from memory to cache, market not diryt, at last return data from cache
write:
hit: write data to cache, mark dirty data
miss: if dirty: write dirty data to lower memory first, and then read data from memory to cache(write allocate), then write data to cache, mark dirty data
各种buffer
victim cache


cache coherency
two types of protocol
snooping (or broadcast) based
- valid tag
- extra tag for sharing status
- monitor all bus transactiion
directory based
snooping protocol MESI/MOESI
Modified: 1. only valid copy in any cache; 2.different with main memory
Exclusive: 1. valid data, 2, only exist on this cache, 3. data same with main memory. 当别的缓存读取它时,状态变为共享;当前写数据时,变为已修改状态。
Shared: 1. valid copy, other cache may exist; 2. same with main memory
Invalid: the copy is out of date and can't be used; 2. need to fetch data from memory or other cache
Owned:
MSI flow
there are three L$ , and there are below operation: R1, R2, W3, R2, W1, W2, R3, R2

R1: 1. read data from main memory, and L1: value|S
R2: 1. read data from main memory, and :L1: value|S
W3: 1.read data from main memory 2. write data to cache, cache: value|M, and p0,p1 cache: value|I

R2: 因为cache tag是invalid, cache3 flush data to main memory and cache2, cache2,3 tag 变成S
W1: 因为1 tag是invalid, bus read, 然后write data, cache: value|M, cache2,3: value: I

W2:tag is invalid, p1 flush data to main memory and cache2; 2. p2 write,

R3:tag is invalid, p2 flush, and p2,p3 cache: value|S
R2:tag is shared, the data is up-to-date copy
MSI protocol:

MESI protocol:

E: exclusive: other don't have copy

MOESI protocol:

当支持cache to cache transfer, 如果cache2中的数据被write 重写后,不会去更新main memory, 如果process 1再读A, 数据可以直接从cache2中来,
不cache miss, 就不会write back 刷新main memory?
























 2635
2635











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








