倾斜补偿的电子罗盘(1):地磁场,磁传感器,倾斜补偿
地磁场和磁传感器
地磁场可以用于获取方位信息。以北半球为例,地磁场方向不是与地面水平,而是与水平方向有一定的倾角(指向地面),称为磁倾角(Inclination)。同时,地磁场的方向也与地理的北方不同,两者的夹角称为磁偏角(Declination)。地磁场的磁感应强度大约在30~70uT,与所在地有关。
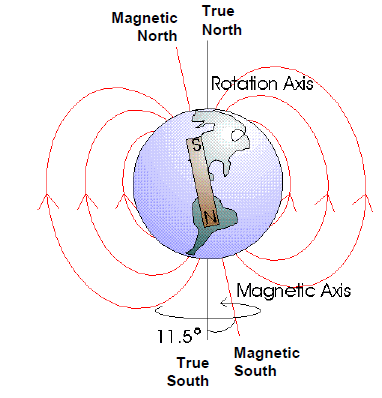
例如,根据下面这个网站,上海的磁偏角约为-6°,磁倾角约为47°,磁感应强度49.1uT(水平方向33uT,垂直方向36uT)。
World Magnetic Model Calculator (bgs.ac.uk)

(在后面的介绍中忽略磁倾角,假设磁北就是地理北。一般可以通过当地经纬度查询到磁偏角并加以换算)
地磁传感器,一般有XY两轴或者XYZ三轴,大部分基于霍尔效应或是磁阻效应,用于手机、无人机等,实现电子罗盘功能。例如,两轴磁传感器可以通过测量XY两个方向上的磁感应强度,通过简单的计算获得设备的朝向。假设磁传感器的XY平面保持水平,X轴读数hx,Y轴读数hy,则设备的X轴方向与磁北的夹角为 θ = a t a n 2 ( h y h x ) \theta=atan2(\frac{h_y}{h_x}) θ=atan2(hxhy),θ范围是(-180°,180°]。

| hx | hy | θ |
|---|---|---|
| + | 0 | 0 |
| + | + | (0,90°) |
| 0 | + | 90° |
| - | + | (90°,180°) |
| - | 0 | 180° |
| - | - | (-180°,-90°) |
| 0 | - | -90° |
| + | - | (-90°,0) |
2D和3D的旋转
某个位置地磁场的方向是相对恒定的,而磁传感器的姿态却是变化的,因此磁传感器每个方向的读数与姿态有关。如下图,对于MPU-6500,磁传感器的姿态可以使用绕着XYZ三个轴的旋转来表示,以逆时针旋转(从x轴的箭头看箭尾)为正。
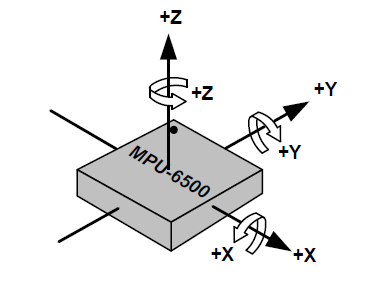
例如,绕着Z轴旋转,Z轴读数不变,仅改变X轴和Y轴的读数。

原读数:
v
0
=
[
h
x
,
h
y
]
T
=
[
H
c
o
s
θ
,
H
s
i
n
θ
]
T
v0=[h_x,h_y]^T=[Hcos\theta, Hsin\theta]^T
v0=[hx,hy]T=[Hcosθ,Hsinθ]T
根据示意图,XY逆时针旋转
δ
\delta
δ后的读数:
v
′
=
[
h
x
′
,
h
y
′
]
T
=
[
H
c
o
s
(
θ
−
δ
)
,
H
s
i
n
(
θ
−
δ
)
]
T
=
[
H
c
o
s
θ
c
o
s
δ
+
H
s
i
n
θ
s
i
n
δ
,
H
s
i
n
θ
c
o
s
δ
−
H
c
o
s
θ
s
i
n
δ
]
v'=[h_x',h_y']^T=[Hcos(\theta - \delta),Hsin(\theta - \delta)]^T=[Hcos\theta cos\delta+Hsin\theta sin\delta, Hsin\theta cos\delta - Hcos\theta sin\delta]
v′=[hx′,hy′]T=[Hcos(θ−δ),Hsin(θ−δ)]T=[Hcosθcosδ+Hsinθsinδ,Hsinθcosδ−Hcosθsinδ]
这种旋转可以用矩阵表示:
v
′
=
[
c
o
s
δ
s
i
n
δ
−
s
i
n
δ
c
o
s
δ
]
[
H
c
o
s
θ
H
s
i
n
θ
]
=
R
z
2
d
(
δ
)
v
0
v' = \left[ \begin{matrix} cos\delta & sin\delta \\ -sin\delta & cos\delta \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} Hcos\theta \\ Hsin\theta \end{matrix} \right] = R_{z2d}(\delta)v_0
v′=[cosδ−sinδsinδcosδ][HcosθHsinθ]=Rz2d(δ)v0
然后把Z轴补上,变成一个3x3的矩阵(因为Z轴读数不变,所以只有3,3的元素是1,其他都是0):
R
z
(
ψ
)
=
[
c
o
s
ψ
s
i
n
ψ
0
−
s
i
n
ψ
c
o
s
ψ
0
0
0
1
]
R_z(\psi)= \left[ \begin{matrix} cos\psi & sin\psi & 0\\ -sin\psi & cos\psi & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{matrix} \right]
Rz(ψ)=⎣⎡cosψ−sinψ0sinψcosψ0001⎦⎤
同理,围绕X轴和Y轴旋转,对应的矩阵为:
R
x
(
ϕ
)
=
[
1
0
0
0
c
o
s
ϕ
s
i
n
ϕ
0
−
s
i
n
ϕ
c
o
s
ϕ
]
,
R
y
(
θ
)
=
[
c
o
s
θ
0
−
s
i
n
θ
0
1
0
s
i
n
θ
0
c
o
s
θ
]
R_x(\phi)= \left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & cos\phi & sin\phi\\ 0 & -sin\phi & cos\phi \end{matrix} \right], \; R_y(\theta)= \left[ \begin{matrix} cos\theta & 0 & -sin\theta \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\ sin\theta & 0 & cos\theta \end{matrix} \right]
Rx(ϕ)=⎣⎡1000cosϕ−sinϕ0sinϕcosϕ⎦⎤,Ry(θ)=⎣⎡cosθ0sinθ010−sinθ0cosθ⎦⎤
注意 R y ( θ ) R_y(\theta) Ry(θ)的 s i n θ sin\theta sinθ符号与其他两个矩阵不同,这与坐标轴设置有关,这里对应于上图MPU6500。
对于三轴磁传感器,定义一个初始位置:XY平面平行于水平面,同时X轴与地磁场方向重合。此时读数为:
h
0
=
[
H
c
o
s
I
,
0
,
H
s
i
n
I
]
T
h_0=[HcosI,0,HsinI]^T
h0=[HcosI,0,HsinI]T。I是磁倾角。
-
如果只有Z轴的旋转,则读数变为:
h r z = R z ( ψ ) h 0 = h r z = R z ( ψ ) h 0 = [ c o s ψ s i n ψ 0 − s i n ψ c o s ψ 0 0 0 1 ] [ H c o s I 0 H s i n I ] = [ H c o s I c o s ψ − H c o s I s i n ψ H s i n I ] h_{rz}=R_z(\psi)h_0= h_{rz}=R_z(\psi)h_0= \left[ \begin{matrix} cos\psi & sin\psi & 0\\ -sin\psi & cos\psi & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} HcosI\\ 0 \\ HsinI \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} HcosIcos\psi \\ -HcosIsin\psi \\ HsinI \end{matrix} \right] hrz=Rz(ψ)h0=hrz=Rz(ψ)h0=⎣⎡cosψ−sinψ0sinψcosψ0001⎦⎤⎣⎡HcosI0HsinI⎦⎤=⎣⎡HcosIcosψ−HcosIsinψHsinI⎦⎤
此时可以直接用 ψ = a t a n ( − h y h x ) \psi = atan(\frac{-h_y}{h_x}) ψ=atan(hx−hy)获得方位角。 -
如果XYZ轴都有旋转,则读数变为:
h r x y z = R x ( ϕ ) R y ( θ ) R z ( ψ ) h 0 = R x ( ϕ ) R y ( θ ) h r z h_{rxyz}=R_x(\phi)R_y(\theta)R_z(\psi)h_0=R_x(\phi)R_y(\theta)h_{rz} hrxyz=Rx(ϕ)Ry(θ)Rz(ψ)h0=Rx(ϕ)Ry(θ)hrz
此时需要进行倾斜补偿,即基于读数 h r x y z h_{rxyz} hrxyz,还原为仅有Z轴旋转的读数 h r z h_{rz} hrz,然后同样可以获得方位角。
倾斜补偿
原理
进行倾斜补偿,需要对X轴和Y轴反向转动,按之前的记号,X轴转动
(
−
ϕ
)
(-\phi)
(−ϕ),Y轴转动
(
−
θ
)
(-\theta)
(−θ):
h
r
z
=
[
h
x
0
,
h
y
0
,
h
z
0
]
=
[
h
x
,
h
y
,
h
z
]
=
R
y
(
−
θ
)
R
x
(
−
ϕ
)
h
r
x
y
z
=
[
c
o
s
θ
0
s
i
n
θ
0
1
0
−
s
i
n
θ
0
c
o
s
θ
]
[
1
0
0
0
c
o
s
ϕ
−
s
i
n
ϕ
0
s
i
n
ϕ
c
o
s
ϕ
]
h
r
x
y
z
=
[
c
o
s
θ
s
i
n
θ
s
i
n
ϕ
s
i
n
θ
c
o
s
ϕ
0
c
o
s
ϕ
−
s
i
n
ϕ
−
s
i
n
θ
c
o
s
θ
s
i
n
ϕ
c
o
s
θ
c
o
s
ϕ
]
[
h
x
h
y
h
z
]
h_{rz} =[h_{x0},h_{y0},h_{z0}]= [h_x,h_y,h_z]=R_y(-\theta)R_x(-\phi)h_{rxyz} \\ = \left[ \begin{matrix} cos\theta & 0 & sin\theta \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\ -sin\theta & 0 & cos\theta \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & cos\phi & -sin\phi\\ 0 & sin\phi & cos\phi \end{matrix} \right] h_{rxyz} \\ = \left[ \begin{matrix} cos\theta & sin\theta sin\phi & sin\theta cos\phi \\ 0 & cos\phi & -sin\phi\\ -sin\theta & cos\theta sin\phi & cos\theta cos\phi \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} h_x \\ h_y \\ h_z \end{matrix} \right]
hrz=[hx0,hy0,hz0]=[hx,hy,hz]=Ry(−θ)Rx(−ϕ)hrxyz=⎣⎡cosθ0−sinθ010sinθ0cosθ⎦⎤⎣⎡1000cosϕsinϕ0−sinϕcosϕ⎦⎤hrxyz=⎣⎡cosθ0−sinθsinθsinϕcosϕcosθsinϕsinθcosϕ−sinϕcosθcosϕ⎦⎤⎣⎡hxhyhz⎦⎤
其中,
[
h
x
,
h
y
,
h
z
]
T
[h_x,h_y,h_z]^T
[hx,hy,hz]T是实际读数。
因此,考虑倾斜补偿后,方位角变为:
ψ
=
a
t
a
n
(
−
h
y
0
h
x
0
)
=
a
t
a
n
(
h
y
s
i
n
ϕ
−
h
x
c
o
s
ϕ
h
x
c
o
s
θ
+
h
y
s
i
n
θ
s
i
n
ϕ
+
h
z
s
i
n
θ
c
o
s
ϕ
)
\psi = atan\left( \frac{-h_{y0}}{h_{x0}}\right)=atan \left( \frac{ h_y sin\phi- h_xcos\phi}{h_xcos\theta + h_ysin\theta sin\phi + h_z sin\theta cos\phi} \right)
ψ=atan(hx0−hy0)=atan(hxcosθ+hysinθsinϕ+hzsinθcosϕhysinϕ−hxcosϕ)
所以,基于当前
ϕ
\phi
ϕ和
θ
\theta
θ的信息,就可以进行倾斜补偿。
使用加速度传感器获得角度信息
根据三轴加速度传感器的读数可以获得所需的角度信息。注意在读数时,加速度传感器没有其他方向上的加速,只受到重力影响。
假设初始状态下,加速度传感器的XY轴平行于水平面,Z轴与重力方向相同,则初始状态的读数: a 0 = [ 0 , 0 , g ] T a_0=[0,0,g]^T a0=[0,0,g]T
可以看出,围绕Z轴旋转对读数没有影响,即: R z ( ψ ) a 0 = a 0 R_z(\psi)a_0=a_0 Rz(ψ)a0=a0
在分别围绕XY两轴旋转后,
a
r
x
y
z
=
R
x
(
ϕ
)
R
y
(
θ
)
R
z
(
ψ
)
a
0
=
R
x
(
ϕ
)
R
y
(
θ
)
a
0
a_{rxyz}=R_x(\phi)R_y(\theta)R_z(\psi)a_0=R_x(\phi)R_y(\theta)a_{0}
arxyz=Rx(ϕ)Ry(θ)Rz(ψ)a0=Rx(ϕ)Ry(θ)a0
同样,在XY两轴反向旋转后,理论上,读数应和初始位置的读数相同:
R
y
(
−
θ
)
R
x
(
−
ϕ
)
a
r
x
y
z
=
[
c
o
s
θ
s
i
n
θ
s
i
n
ϕ
s
i
n
θ
c
o
s
ϕ
0
c
o
s
ϕ
−
s
i
n
ϕ
−
s
i
n
θ
c
o
s
θ
s
i
n
ϕ
c
o
s
θ
c
o
s
ϕ
]
[
a
x
a
y
a
z
]
=
[
0
0
g
]
R_y(-\theta)R_x(-\phi)a_{rxyz} = \left[ \begin{matrix} cos\theta & sin\theta sin\phi & sin\theta cos\phi \\ 0 & cos\phi & -sin\phi\\ -sin\theta & cos\theta sin\phi & cos\theta cos\phi \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} a_x\\ a_y \\ a_z \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 0 \\ 0 \\ g \end{matrix} \right]
Ry(−θ)Rx(−ϕ)arxyz=⎣⎡cosθ0−sinθsinθsinϕcosϕcosθsinϕsinθcosϕ−sinϕcosθcosϕ⎦⎤⎣⎡axayaz⎦⎤=⎣⎡00g⎦⎤
因此有:
a
x
c
o
s
θ
+
a
y
s
i
n
θ
s
i
n
ϕ
+
a
z
s
i
n
θ
c
o
s
ϕ
=
0
a
y
c
o
s
ϕ
−
a
z
s
i
n
ϕ
=
0
a_xcos\theta + a_ysin\theta sin\phi +a_z sin\theta cos\phi =0 \\ a_ycos \phi - a_z sin\phi = 0
axcosθ+aysinθsinϕ+azsinθcosϕ=0aycosϕ−azsinϕ=0
从而计算两个角度:
ϕ
=
a
t
a
n
(
a
y
a
z
)
θ
=
a
t
a
n
(
−
a
x
a
y
s
i
n
ϕ
+
a
z
c
o
s
ϕ
)
\phi = atan\left( \frac{a_y}{a_z}\right) \\ \theta = atan \left( \frac{-a_x}{a_ysin\phi + a_zcos\phi}\right)
ϕ=atan(azay)θ=atan(aysinϕ+azcosϕ−ax)
总结
- 地磁场和磁传感器
- 电子罗盘基本原理
- 通过加速度传感器获得角度信息,进行倾斜补偿
目前是假设这些传感器的测量值是完全准确的。但实际上会有各种测量误差, 需要进行校准,后面继续补充。
参考资料
-
NXP的应用手册AN4246、AN4247、AN4248,解释得比较清楚 (https://www.nxp.com/docs/en/application-note/AN4248.pdf)
-
很多三轴(磁、加速度、陀螺仪)、六轴(一般是加速度+陀螺仪,少量加速度+磁)、九轴(磁+加速度+陀螺仪)的传感器,可以看下应用手册
例如,ISM303DAC集成了三轴加速度传感器和三轴磁传感器,便于实现电子罗盘。

























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








