Unity提供两种处理Input的方式,Input Manager (Old) and Input System (New), 而InputAction则属于Input System。
需求点介绍
当用户长按0.5s 键盘X或者VR left controller primaryButton (即X键)时,显示下一个图片。
步骤总览
- 创建InputAction资产
- 将该InputAction资产绑定到某个GameObject上
- 在对应的script中,接收InputAction触发的事件,完成“显示下一个图片”的逻辑
细节
-
创建InputAction资产

-
将该InputAction资产绑定到某个GameObject上。
如果Behaviour是send messages或者broadcast messages,那这个GameObject或者其子GameObject包含Component,这个Component有需要检测InputAction输入的function。
如果Behaviour是Invoke Unity Event,那好像绑定在哪个GameObject都没有关系,只要Player Input这个component能在function之前被初始化就行。
至于Behavior如何设置,见官网, 不过官网说得也不明不白的。

在我的例子中,我需要设置成Invoke Unity Events,然后像对待UI控件一样,显性绑定才能触发function的运行。Send/Broadcast Messages都不行。
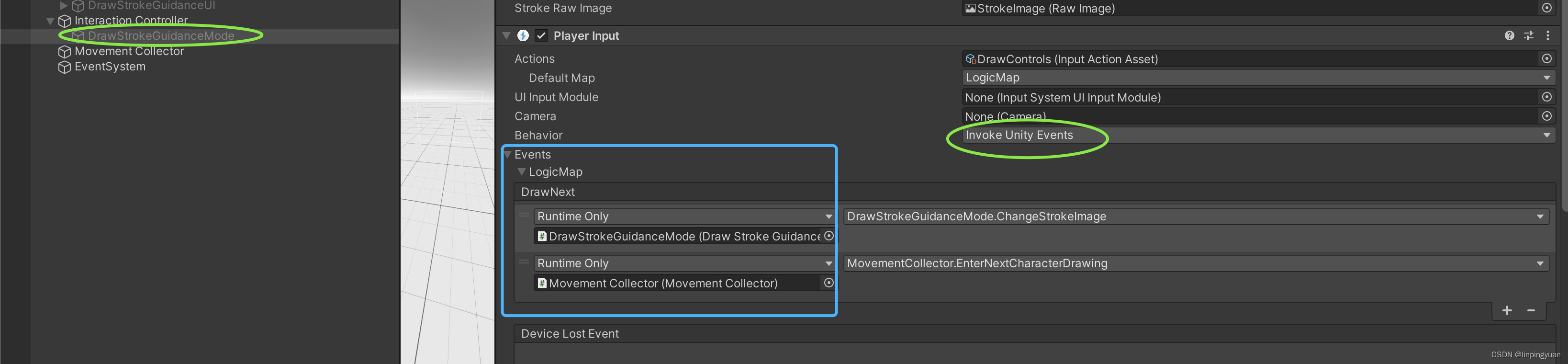
当有多个action时,在绑定事件时,需要添加到对应的Action下面,否则无法invoke unity event

- 在对应的script中,接收InputAction触发的事件,完成“显示下一个图片”的逻辑
public void ChangeStrokeImage(InputAction.CallbackContext context)
{ if (context.action.name == "DrawNext") {
if (context.performed) // Otherwise this will be triggered three times.
{
if (textures != null && textures.Length > 0)
{
currentIndex = currentIndex % textures.Length;
strokeRawImage.texture = textures[currentIndex];
currentIndex = currentIndex + 1;
}
}
}
}
附录 1: Controller提供的按键说明
官网:https://docs.unity3d.com/Manual/xr_input.html

附录2:使用InputAction的好处
如果不使用InputAction的话,而使用Input Manager的话代码可能会是下面这样:
- 需要在Update() 自己进行按键的检测。
- 需要对不同的设备进行定制,代码重复
- 当操作比较复杂的时候,例如hold,还需要自己写代码来判断;加上对不同设备的定制,代码会很长
- 如果同一个类有很多个事件需要处理,代码很长不易读

Input Manager (Old):
- Polling-based Input: You check the state of inputs (keys, buttons, axes) during each frame in your script’s
Updatemethod. - Limited to Predefined Axes: You need to predefine all the axes and buttons within the Input Manager settings. This can be inflexible for dynamic control setups.
- Single Binding per Action: Each action, like “Jump” or “Fire”, typically has one button or key bound to it. It’s difficult to handle multiple bindings.
- No Native Support for Advanced Features: Features like haptic feedback, gyroscopic controls, or touch screens must be manually implemented or require additional packages.
- Less Intuitive for Complex Setups: It can become cumbersome and less maintainable for complex input setups, such as those needed in games with multiple control schemes or local multiplayer with several players.
Input System (New):
- Event-based Input: Responds to input through events, reducing the need to constantly check the state of inputs each frame.
- Multiple Bindings per Action: You can bind multiple keys or buttons to the same action, making it easier to create complex control schemes.
- Control Schemes: Supports different control schemes out of the box, such as keyboard and mouse, gamepad, touch, which you can switch between easily.
- Action Assets: Allows you to define Actions in an asset file, making it reusable across different game objects and scenes.
- Supports Advanced Input Features: Easily integrates with modern controller features like haptic feedback, gyros, and more.
- Player Input Component: Provides a component that can be added to game objects for easy setup and management of input for different players.
- Device Management: Automatically recognizes and manages different input devices connected to the system.
- Customizable and Extensible: You can create custom input devices, composite bindings (like WASD as a single directional input), and processors for input values.
- Two Control Streams: Offers both value and action-based input handling, giving developers more flexibility in how they respond to user input.
























 3045
3045

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








