C++ STL容器篇(四)折叠参数 day15
STL(tuple)
- tuple叫做元组,元组可以描述任何自定义数据类型,就是一个可变参数模版
- tuple官方手册
#include <iostream>
#include <tuple>
#include <vector>
class student
{
public:
student(std::string name = "", int age = 0, int phone = 0) :name(name), age(age), phone(phone) {}
protected:
std::string name;
int age;
int phone;
};
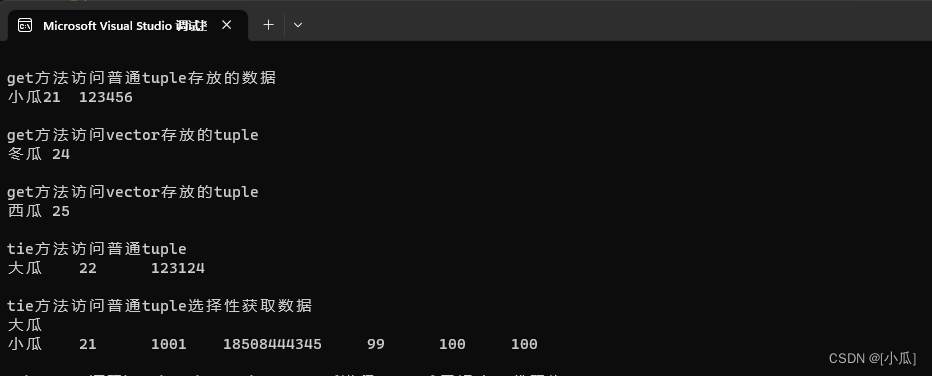
void tsetTuple()
{
std::tuple<std::string, int, int> tu = { "小瓜",21,123456 };
std::tuple<std::string, int, int> tu2 = std::make_tuple("大瓜", 22, 123124);
std::tuple<std::string, int, int> tu3 = std::forward_as_tuple("傻瓜", 23, 12312312);
std::vector<std::tuple<std::string, int>> tu4;
tu4.push_back(std::make_tuple("冬瓜", 24));
tu4.push_back(std::make_tuple("西瓜", 25));
std::cout << std::endl << "get方法访问普通tuple存放的数据" << std::endl;
std::cout << std::get<0>(tu) << std::get<1>(tu) << "\t" << std::get<2>(tu) << std::endl;
std::string getName = std::get<0>(tu4[0]);
int getAge = std::get<1>(tu4[0]);
std::cout << std::endl << "get方法访问vector存放的tuple" << std::endl
<< getName << " " << getAge << std::endl;
std::string getName2 = std::get<0>(tu4[1]);
int getAge2 = std::get<1>(tu4[1]);
std::cout << std::endl << "get方法访问vector存放的tuple" << std::endl
<< getName2 << " " << getAge2 << std::endl;
std::string name;
int age;
int phone;
std::tie(name, age, phone) = tu2;
std::cout << std::endl << "tie方法访问普通tuple" << std::endl
<< name << "\t" << age << "\t" << phone << std::endl;
std::tie(name, std::ignore, std::ignore);
std::cout << std::endl << "tie方法访问普通tuple选择性获取数据" << std::endl
<< name << std::endl;
}
void operationTuple()
{
std::tuple<std::string, int, int, std::string> mm = { "小瓜",21,1001,"18508444345" };
std::tuple<double, double, double> score = { 99,100,100 };
std::tuple<std::string, int, int, std::string, double, double, double>
info = std::tuple_cat(mm, score);
auto result = std::tuple_cat(mm, score);
std::string name;
int age;
int num;
std::string tel;
double math;
double english;
double c;
std::tie(name, age, num, tel, math, english, c) = result;
std::cout << name << "\t" << age << "\t" << num << "\t" << tel << "\t"
<< math << "\t" << english << "\t" << c << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
tsetTuple();
operationTuple();
return 0;
}
- 运行结果
折叠参数
- 写法:
- 定义折叠参数类型:tpename …Args 折叠参数叫做Args
- 定义折叠变量(参数列表) Args …args(折叠参数的变量名)
- 运算符
- sizeof …(args) 统计折叠参数中有多少个参数
#include <iostream>
template <typename ...Args>
void printArgs(Args ...args)
{
std::cout << "参数个数有:" << sizeof...(args) << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
printArgs<float>(1.11);
printArgs<float>(1.11,2.22);
printArgs<int, int, int >(1, 2, 3);
printArgs<std::string, int, double>("小瓜", 21, 99.9);
return 0;
}
- 运行结果

可变参函数模版
- 可变参函数模板的展开一般有三种方式
- 递归的方式进行剥离参数展开
- 列表的方式展开
- 完美转发的方式进行展开(统一接口)
#include <iostream>
#include <initializer_list>
#include <functional>
template <typename _Ty>
void print(_Ty data)
{
std::cout << data << std::endl;
}
template <typename _Ty,typename ...Args>
void print(_Ty data, Args ...args)
{
std::cout << data << " ";
print(args...);
}
template <typename _Ty>
void printData(_Ty data)
{
std::cout << data << " ";
}
template <typename ...Args>
void printArgs(Args ...args)
{
std::initializer_list<int>{ (printData(args), 0)...};
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void sum(int a, int b)
{
std::cout << a + b << std::endl;
}
void testSum()
{
std::function<void(int, int)> pSum(sum);
sum(1, 2);
pSum(1, 2);
auto result = std::bind(sum, 1, 2);
result();
auto result2 = std::bind(sum, 1, std::placeholders::_1);
result2(2);
}
class student
{
public:
void testFunc()
{
if (func)
{
func();
}
}
template<typename Func,typename ...Args>
void connect(Func&& f,Args&& ...args)
{
func = std::bind(std::forward<Func>(f), std::forward<Args>(args)...);
}
protected:
std::function<void()> func;
};
void printFunc()
{
std::cout << "无参函数" << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
print(1, "name", 1.111, "xiaogua");
printArgs(1, "name", 1.111, "dagua");
testSum();
student stu;
stu.connect(sum, 1, 2);
stu.testFunc();
stu.connect(printFunc);
stu.testFunc();
stu.connect([](int a, int b, int c) {std::cout << a + b + c << std::endl; }, 1, 2, 3);
stu.testFunc();
return 0;
}
- 运行结果

可变参类模板
- 可变参类模板的展开方式两种:
- 继承加上模版特化的方式实现展开
- 递归加上模版特化实现展开
#include <iostream>
#include <initializer_list>
#include <functional>
template <typename ...Args>
class Test;
template <>
class Test<>
{
};
template <typename _Ty,typename ...Args>
class Test<_Ty, Args...> :public Test<Args...>
{
public:
Test() {}
Test(_Ty data, Args ...args) :data(data), Test<Args...>(args...) {}
_Ty& getData()
{
return data;
}
Test<Args...>& object()
{
return *this;
}
protected:
_Ty data;
};
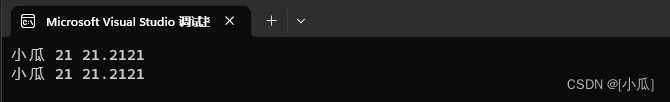
void testTest()
{
Test<std::string, int, double> test("小瓜", 21, 21.212121);
std::cout << test.getData() << " " << test.object().getData() <<
" " << test.object().object().getData() << std::endl;
}
template <class ...Args>
class my_tuple;
template <>
class my_tuple<> {};
template <typename _Ty,typename ...Args>
class my_tuple<_Ty, Args...>
{
public:
my_tuple() {}
my_tuple(_Ty data, Args ...args) :data(data), args(args...) {}
_Ty& getData()
{
return data;
}
my_tuple<Args...>& object()
{
return args;
}
protected:
_Ty data;
my_tuple<Args...> args;
};
void testTest2()
{
my_tuple<std::string, int, double> test("小瓜", 21, 21.212121);
std::cout << test.getData() << " " << test.object().getData() <<
" " << test.object().object().getData() << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
testTest();
testTest2();
return 0;
}
- 运行结果

























 626
626

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








