要求
(1)掌握类的继承和派生概念;
(2)掌握派生类的定义与使用;
(3)掌握派生类的构造函数与析构函数的应用及调用顺序;
(4)理解赋值兼容原则的应用。
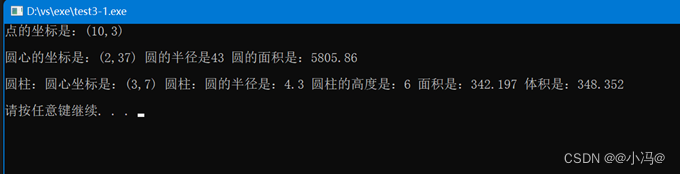
- 利用继承和派生建立3个类,分别为点类、圆类、圆柱类,点类派生得到圆类,圆类派生得到圆柱类。功能分别要求点类能输出点的坐标;圆类能输出圆的半径和面积;圆柱类能输出其高度、表面积和体积,请编写程序实现。(功能扩充,请对运算符“ 《”进行重载,实现一个点、圆、圆柱体对象的输出)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
protected:
int x;
int y;
public:
Point(int a,int b)//构造函数
{
x=a;
y=b;
}
void Show_p(Point p)
{
cout<<"点的坐标是:"<<p<<endl;
}
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream&,Point &);
};
ostream &operator<<(ostream&output,Point &p)
{
output<<"("<<p.x<<","<<p.y<<")"<<endl;
return output;
}
class Circle:public Point
{
protected:
double area;
double radius;
public:
Circle(int a,int b,double r=0.0):Point(a,b)
{
radius=r;
area=3.14*radius*radius;
}
void Show_C(Circle c)
{
cout<<c<<endl;
}
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream&,Circle &);
};
ostream &operator<<(ostream&output,Circle &c)
{
output<<"圆心的坐标是:("<<c.x<<","<<c.y<<")"<<" "<<"圆的半径是"<<c.radius<<" 圆的面积是:"<<c.area<<endl;
}
class Cylinder:public Circle
{
protected:
double height;//高度
public:
Cylinder(int a,int b,double r,double h=0.0):Circle (a,b,r)
{
height=h;
}
void Show_y(Cylinder y)//返回高度,面积,体积
{
cout<<y<<endl;
}
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream&,Cylinder &);
};
ostream &operator<<(ostream&output,Cylinder &y)
{
cout<<"圆柱:圆心坐标是:"<<"("<<y.x<<","<<y.y<<")"<<" ";
cout<<"圆柱:圆的半径是:"<<y.radius<<" ";
cout<<"圆柱的高度是:"<<y.height<<" 面积是:"<<2*y.area+2*3.14*y.height*y.height<<" 体积是:"<<y.area*y.height<<endl;
}
int main()
{
Point p1(10,3);
p1.Show_p(p1);
Circle c1(2,37,43);
c1.Show_C(c1);
Cylinder y1(3,7,4.3,6);
y1.Show_y(y1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
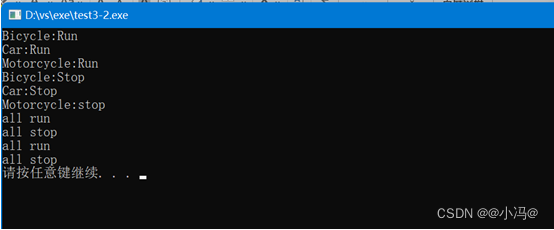
- 声明一个车(Vehicle)基类,有Run、Stop等成员函数,由此派生出自行车(Bicycle)类、汽车(car)类,从自行车和汽车类派生出摩托车(Motorcycle)类,它们都有Run()、Stop()等成员函数。利用继承和派生解决问题。
#include<bits\stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Vehicle
{
public:
void Run(){cout<<"all run"<<endl;}
void Stop(){cout<<"all stop"<<endl;}
};
class Bicycle:virtual public Vehicle
{
public:
Bicycle(){}
void Run();
void Stop();
};
class Car:virtual public Vehicle
{
public:
Car(){}
void Run();
void Stop();
};
class Motorcycle:public Bicycle,public Car
{
public:
Motorcycle(){}
void Run();
void Stop();
};
void Bicycle::Run()
{
cout<<"Bicycle:Run"<<endl;
}
void Car::Run()
{
cout<<"Car:Run"<<endl;
}
void Motorcycle::Run()
{
cout<<"Motorcycle:Run"<<endl;
}
void Bicycle::Stop()
{
cout<<"Bicycle:Stop"<<endl;
}
void Car::Stop()
{
cout<<"Car:Stop"<<endl;
}
void Motorcycle::Stop()
{
cout<<"Motorcycle:stop"<<endl;
}
int main()
{
Bicycle a;
Car b;
Motorcycle c;
a.Run();
b.Run();
c.Run();
a.Stop();
b.Stop();
c.Stop();
Vehicle *p;
p=&a;
p->Run();
p->Stop();
p=&b;
p->Run();
p->Stop();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
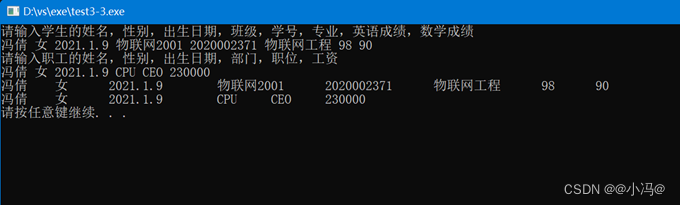
3.定义个人信息类Person,其数据成员有姓名、性别、出生年月。并以Person为基类定义一个学生的派生类Student,增加描述学生的信息:班级、学号、专业、英语成绩和数学成绩。再由基类Person定义一个职工的派生类Employee,增加描述职工的信息:部门、职务、工资。编写程序实现学生与职工信息的输入与输出。
#include<bits\stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
protected:
string name,sex,birth;
public:
Person(string n,string s,string b):name(n),sex(s),birth(b){};
};
class Student:public Person
{
protected:
string Class,id,major;
int eng,math;
public:
Student(string n,string s,string b,string C,string i,string m,int en,int ma):Person(n,s,b){
Class=C;
id=i;
major=m;
eng=en;
math=ma;
}
void pS()
{
cout<<name<<"\t"<<sex<<"\t"<<birth<<"\t"<<Class<<"\t"<<id<<"\t"<<major<<"\t"<<eng<<"\t"<<math<<endl;
}
};
class Employee:public Person
{
protected:
string BuMen,ZhiWu;
int salary;
public:
Employee(string n,string s,string b,string Bu,string Zh,int sa):Person(n,s,b)
{
BuMen=Bu;
ZhiWu=Zh;
salary=sa;
}
void pE()
{
cout<<name<<"\t"<<sex<<"\t"<<birth<<"\t"<<BuMen<<"\t"<<ZhiWu<<"\t"<<salary<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
//信息录入;
//学生
string n,s,b;
string C,i,m;
int en,ma;
cout<<"请输入学生的姓名,性别,出生日期,班级,学号,专业,英语成绩,数学成绩"<<endl;
cin>>n>>s>>b>>C>>i>>m>>en>>ma;
Student s1(n,s,b,C,i,m,en,ma);
//职工
string Bu,Zh;
int sa;
cout<<"请输入职工的姓名,性别,出生日期,部门,职位,工资"<<endl;
cin>>n>>s>>b>>Bu>>Zh>>sa;
Employee e1(n,s,b,Bu,Zh,sa);
//输出
s1.pS();
e1.pE();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
- 基类没有加virtual,那么通过派生类指针输出的都是基类的函数,无法实现多态性;
- 多态可以简单的概括为”一个接口,多种方法”(接口重用),程序在运行时才决定调用的函数。C++的多态性是通过虚函数来实现的,虚函数允许子类重新定义成员函数,而子类重新定义父类的做法称为重写,多态和非多态的实质区别在于函数地址的早还是晚绑定,如果编译期间就可以确定的,是早绑定也就是静态的。而如果函数调用的地址不能在编译器期间确定,需要在运行时才确定,这就属于晚绑定。
- 派生类定义构造函数,函数中可以使用基类构造函数定义一部分量























 3931
3931











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










