目录
pytorch可视化
网络结构可视化
深度学习库Keras中可以调用一个叫做model.summary(),pytorch使用torchinfo:
可视化网络结构需要进行一次前向传播以获得特定层的信息
import torchvision.models as models
model = models.resnet18()
print(model)ResNet(
(conv1): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), padding=(3, 3), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(relu): ReLU(inplace=True)
(maxpool): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(layer1): Sequential(
(0): BasicBlock(
(conv1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(relu): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(1): BasicBlock(
(conv1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(relu): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
)
(layer2): Sequential(
(0): BasicBlock(
(conv1): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(relu): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(downsample): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
)
(1): BasicBlock(
(conv1): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(relu): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
)
(layer3): Sequential(
(0): BasicBlock(
(conv1): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(relu): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(downsample): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
)
(1): BasicBlock(
(conv1): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(relu): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
)
(layer4): Sequential(
(0): BasicBlock(
(conv1): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(relu): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(downsample): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
)
(1): BasicBlock(
(conv1): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(relu): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
)
(avgpool): AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=(1, 1))
(fc): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=1000, bias=True)
)可视化网络结构的重点在于看“output shape”和“param”
from torchinfo import summary
#1:batch_size 3:图片通道数 224:图片高度
summary(model,(1,3,224,224))==========================================================================================
Layer (type:depth-idx) Output Shape Param #
==========================================================================================
ResNet [1, 1000] --
├─Conv2d: 1-1 [1, 64, 112, 112] 9,408
├─BatchNorm2d: 1-2 [1, 64, 112, 112] 128
├─ReLU: 1-3 [1, 64, 112, 112] --
├─MaxPool2d: 1-4 [1, 64, 56, 56] --
├─Sequential: 1-5 [1, 64, 56, 56] --
│ └─BasicBlock: 2-1 [1, 64, 56, 56] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-1 [1, 64, 56, 56] 36,864
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-2 [1, 64, 56, 56] 128
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-3 [1, 64, 56, 56] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-4 [1, 64, 56, 56] 36,864
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-5 [1, 64, 56, 56] 128
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-6 [1, 64, 56, 56] --
│ └─BasicBlock: 2-2 [1, 64, 56, 56] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-7 [1, 64, 56, 56] 36,864
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-8 [1, 64, 56, 56] 128
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-9 [1, 64, 56, 56] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-10 [1, 64, 56, 56] 36,864
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-11 [1, 64, 56, 56] 128
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-12 [1, 64, 56, 56] --
├─Sequential: 1-6 [1, 128, 28, 28] --
│ └─BasicBlock: 2-3 [1, 128, 28, 28] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-13 [1, 128, 28, 28] 73,728
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-14 [1, 128, 28, 28] 256
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-15 [1, 128, 28, 28] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-16 [1, 128, 28, 28] 147,456
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-17 [1, 128, 28, 28] 256
│ │ └─Sequential: 3-18 [1, 128, 28, 28] 8,448
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-19 [1, 128, 28, 28] --
│ └─BasicBlock: 2-4 [1, 128, 28, 28] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-20 [1, 128, 28, 28] 147,456
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-21 [1, 128, 28, 28] 256
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-22 [1, 128, 28, 28] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-23 [1, 128, 28, 28] 147,456
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-24 [1, 128, 28, 28] 256
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-25 [1, 128, 28, 28] --
├─Sequential: 1-7 [1, 256, 14, 14] --
│ └─BasicBlock: 2-5 [1, 256, 14, 14] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-26 [1, 256, 14, 14] 294,912
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-27 [1, 256, 14, 14] 512
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-28 [1, 256, 14, 14] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-29 [1, 256, 14, 14] 589,824
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-30 [1, 256, 14, 14] 512
│ │ └─Sequential: 3-31 [1, 256, 14, 14] 33,280
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-32 [1, 256, 14, 14] --
│ └─BasicBlock: 2-6 [1, 256, 14, 14] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-33 [1, 256, 14, 14] 589,824
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-34 [1, 256, 14, 14] 512
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-35 [1, 256, 14, 14] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-36 [1, 256, 14, 14] 589,824
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-37 [1, 256, 14, 14] 512
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-38 [1, 256, 14, 14] --
├─Sequential: 1-8 [1, 512, 7, 7] --
│ └─BasicBlock: 2-7 [1, 512, 7, 7] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-39 [1, 512, 7, 7] 1,179,648
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-40 [1, 512, 7, 7] 1,024
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-41 [1, 512, 7, 7] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-42 [1, 512, 7, 7] 2,359,296
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-43 [1, 512, 7, 7] 1,024
│ │ └─Sequential: 3-44 [1, 512, 7, 7] 132,096
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-45 [1, 512, 7, 7] --
│ └─BasicBlock: 2-8 [1, 512, 7, 7] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-46 [1, 512, 7, 7] 2,359,296
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-47 [1, 512, 7, 7] 1,024
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-48 [1, 512, 7, 7] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-49 [1, 512, 7, 7] 2,359,296
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-50 [1, 512, 7, 7] 1,024
│ │ └─ReLU: 3-51 [1, 512, 7, 7] --
├─AdaptiveAvgPool2d: 1-9 [1, 512, 1, 1] --
├─Linear: 1-10 [1, 1000] 513,000
==========================================================================================
Total params: 11,689,512
Trainable params: 11,689,512
Non-trainable params: 0
Total mult-adds (G): 1.81
==========================================================================================
Input size (MB): 0.60
Forward/backward pass size (MB): 39.75
Params size (MB): 46.76
Estimated Total Size (MB): 87.11
==========================================================================================CNN可视化
卷积神经网络(CNN):
深度学习中非常重要的模型结构,广泛用于图像处理,
极大地提升了模型表现,推动了计算机视觉的发展和进步。
“黑盒模型”
理解CNN工作的方式,解释所获得的结果,提升模型的鲁棒性,有针对性地改进CNN的结构以获得进一步的效果提升。
卷积核
卷积核在CNN中负责提取特征,可视化卷积核能够帮助人们理解CNN各个层在提取什么样的特征,进而理解模型的工作原理。
只有卷积层才有卷积核
#dict类似字典
# print(dict(model.named_children()))
conv1=dict(model.named_children())["conv1"]
print(conv1)#二维卷积层,输入3信道,输出64信道,用7*7大小的卷积核进行特征提取
Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), padding=(3, 3), bias=False)可视化:
conv1=dict(model.named_children())["conv1"]
#weight提取权重,detach得到数值
kernel_set=conv1.weight.cpu().detach()
num=len(conv1.weight.cpu().detach())
print(num,kernel_set.shape)#将3个channel上数值映射到64个channel上,卷积核大小为7*7
64 torch.Size([64, 3, 7, 7])展示图像:
for i in range(0,num):
i_kernel=kernel_set[i]
plt.figure(figsize=(20,17))
if (len(i_kernel))>1:
for idx,filer in enumerate(i_kernel):
plt.subplot(9,9,idx+1)
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(filer[:,:].detach(),cmap='bwr')查看计算矩阵:
#-1代表最后一个
i_kernel_final=i_kernel[-1]
print(i_kernel_final)tensor([[ 5.2824e-03, 2.8821e-02, -9.7930e-03, -4.2806e-02, 2.9733e-02,
1.0845e-02, -4.4320e-03],
[-4.8608e-02, 3.1222e-03, -1.8700e-02, -2.3249e-02, 2.9002e-02,
2.3333e-04, 3.5090e-02],
[-5.5837e-03, -8.9409e-03, 4.5929e-02, -3.6766e-02, 1.3506e-02,
1.1846e-02, -2.6823e-02],
[-4.3843e-02, 1.1372e-02, -4.8122e-02, -9.6665e-03, 1.6674e-02,
1.3634e-03, 9.4643e-05],
[-6.2728e-03, 1.5998e-02, -3.9044e-02, -2.6574e-02, -2.5292e-02,
2.1845e-02, -2.3790e-03],
[-1.3369e-03, -2.2121e-02, -2.7334e-02, 3.3645e-02, 2.6368e-02,
8.5366e-04, -2.4240e-02],
[ 4.6692e-02, -1.0535e-02, -6.7471e-02, -4.4751e-02, -1.5243e-02,
3.2308e-02, 4.0211e-02]])特征图
我们需要在层上挂上钩子hook,当数据向水流一样向前传播后,这一层钩子上所留下的东西就是我们想要的特征图。
class Hook(object):
def __int__(self):
self.module_name=[]
self.features_in_hook=[]
self.features_out_hook=[]
#module获得层名,fea_in输入,fea_out输出
def __call__(self,module, fea_in, fea_out):
print("hooker working", self)
self.module_name.append(module.__class__)
self.features_in_hook.append(fea_in)
self.features_out_hook.append(fea_out)
return None
def plot_feature(model, idx, inputs):
#bich_size=1 3个channel
inputs=torch.rand(1,3,224,224)
#变量初始化
hh=Hook()
#在该层添加钩子
dict(model.named_children())["conv1"].register_forward_hook(hh)
model.eval()
_ = model(inputs)
print(hh.module_name)
print((hh.features_in_hook[0][0].shape))
print((hh.features_out_hook[0].shape))
out1=hh.features_out_hook[0]
total_ft=out1.shape[1]
first_item=out1[0].clone()
plt.figure(figsize=(20,17))
for ftidx in range(total_ft):
if ftidx > 99:
break
ft=first_item[ftidx]
plt.subplot(10,10,ftidx=1)
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(ft[:,:].detach())features_out_hook 是一个list,每次前向传播一次,都是调用一次,也就是features_out_hook 长度会增加1
可视化CNN显著class activation map
研究分类模型某一层对于输出某一类的激活效果
可借助grad-map包快速实现
import torch
from torchvision.models import vgg11,resnet18,resnet101,resnext101_32x8d
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
model = vgg11(pretrained=True)
img_path = './dog.jpg'
# resize操作是为了和传入神经网络训练图片大小一致
img = Image.open(img_path).resize((224,224))
# 需要将原始图片转为np.float32格式并且在0-1之间
rgb_img = np.float32(img)/255
plt.imshow(img)
from pytorch_grad_cam import GradCAM,ScoreCAM,GradCAMPlusPlus,AblationCAM,XGradCAM,EigenCAM,FullGrad
from pytorch_grad_cam.utils.model_targets import ClassifierOutputTarget
from pytorch_grad_cam.utils.image import show_cam_on_image
img_tensor=torch.tensor(rgb_img.transpose(2,0,1)).unsqueeze(0).cpu()
target_layers = [model.features[-1]]
# 选取合适的类激活图,但是ScoreCAM和AblationCAM需要batch_size
cam = GradCAM(model=model,target_layers=target_layers)
targets = [ClassifierOutputTarget(200)]
# 上方preds需要设定,比如ImageNet有1000类,这里可以设为200
grayscale_cam = cam(input_tensor=img_tensor, targets=targets)
grayscale_cam = grayscale_cam[0, :]
cam_img = show_cam_on_image(rgb_img, grayscale_cam, use_rgb=True)
print(type(cam_img))
plt.imshow(cam_img)
plt.show()
Image.fromarray(cam_img)
使用tensorBoard完成训练可视化
我们可以将TensorBoard看做一个记录员,它可以记录我们指定的数据,
模型每一层的feature map
权重,以及训练loss等等。
TensorBoard将记录下来的内容保存在一个用户指定的文件夹里,程序不断运行中TensorBoard会不断记录。记录下的内容可以通过网页的形式加以可视化。
from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter
writer = SummaryWriter('./runs')如果使用PyTorch自带的tensorboard,则采用如下方式import:
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter启动tensorboard也很简单,在命令行中输入
tensorboard --logdir=/path/to/logs/ --port=xxxx模型
import torch
from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter
import torchvision.models as models
resnet18 = models.resnet18()
#指定writer的输出目录
writer = SummaryWriter('./runs')
writer.add_graph(resnet18,input_to_model=torch.rand(1,3,224,224).cpu())
writer.close()
import torch.nn as nn
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3,out_channels=32,kernel_size = 3)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size = 2,stride = 2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32,out_channels=64,kernel_size = 5)
self.adaptive_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d((1,1))
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(64,32)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(32,1)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self,x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.pool(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.pool(x)
x = self.adaptive_pool(x)
x = self.flatten(x)
x = self.linear1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.linear2(x)
y = self.sigmoid(x)
return y
model = Net()
print(model)Net(
(conv1): Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
(pool): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv2): Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(adaptive_pool): AdaptiveMaxPool2d(output_size=(1, 1))
(flatten): Flatten(start_dim=1, end_dim=-1)
(linear1): Linear(in_features=64, out_features=32, bias=True)
(relu): ReLU()
(linear2): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=1, bias=True)
(sigmoid): Sigmoid()
)
在生成tensorboard可视图时出现各种问题:
比如:
-
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘tensorboard‘
-
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘tensorflow.compat‘
-
AttributeError: module 'tensorflow.compat.v2.summary' has no attribute 'scalar'
在网上找到各种办法:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘tensorboard‘_奶盐cookie的博客-CSDN博客
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘tensorboard‘_奶盐cookie的博客-CSDN博客
但是我安装的版本是匹配的,试了很多方法都没有解决问题
为了吃口饭,连碗都换了:

- 打开Anconda Prompt重新建立环境:
conda create -n my_env python==3.8有解决方案说是conda安装问题,所以选择pip进行安装
- 打开终端,激活环境:
activate my_env
- 安装pytorch
PyTorch官网

输入命令:
pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio之前有看到tensorboardX与torch.utils.tensorboard有冲突导致error,保险起见,使用torch.utils.tensorboard,不安装tensorboardX
- 运行代码:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
writer = SummaryWriter('./runs')
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3,out_channels=32,kernel_size = 3)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size = 2,stride = 2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32,out_channels=64,kernel_size = 5)
self.adaptive_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d((1,1))
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(64,32)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(32,1)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self,x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.pool(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.pool(x)
x = self.adaptive_pool(x)
x = self.flatten(x)
x = self.linear1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.linear2(x)
y = self.sigmoid(x)
return y
model = Net()
print(model)
writer.add_graph(model, input_to_model = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224))
writer.close()查看生成文件:
- 打开文件所在目录:

复制该路径,打开终端——记得先激活环境
输入:
tensorboard --logdir="E:\python code\2\runs"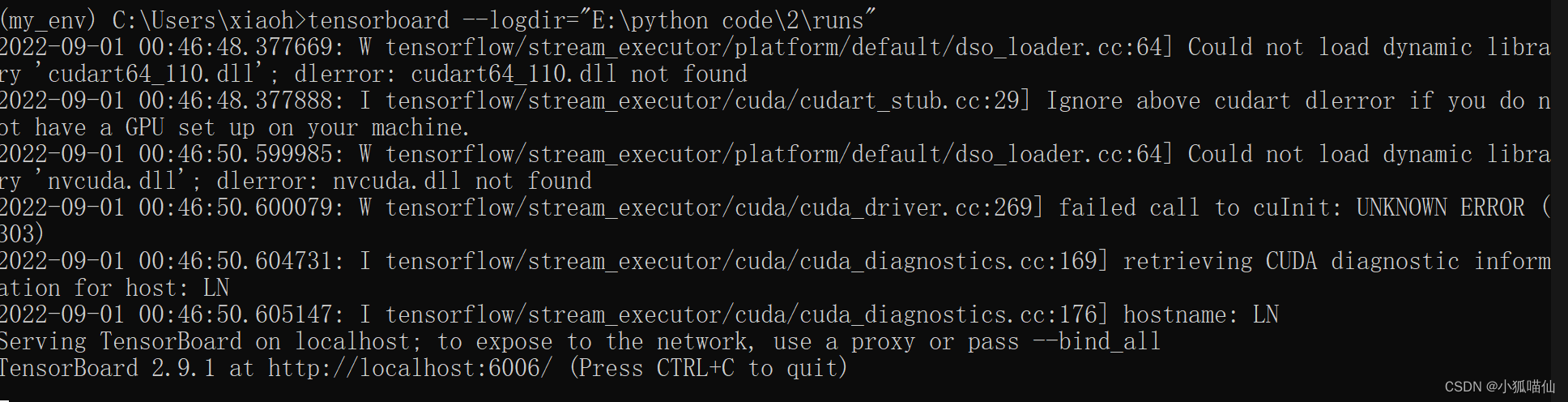
成功,复制下方网站:


tensorboard成功启动
图像
对于单张图片的显示使用add_image
对于多张图片的显示使用add_images
有时需要使用torchvision.utils.make_grid将多张图片拼成一张图片后,用writer.add_image显示
import torchvision
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
transform_train = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor()])
transform_test = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor()])
train_data = datasets.CIFAR10(".", train=True, download=True, transform=transform_train)
test_data = datasets.CIFAR10(".", train=False, download=True, transform=transform_test)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=64)
images, labels = next(iter(train_loader))
# 仅查看一张图片
writer = SummaryWriter('./pytorch_tb')
writer.add_image('images[0]', images[0])
writer.close()
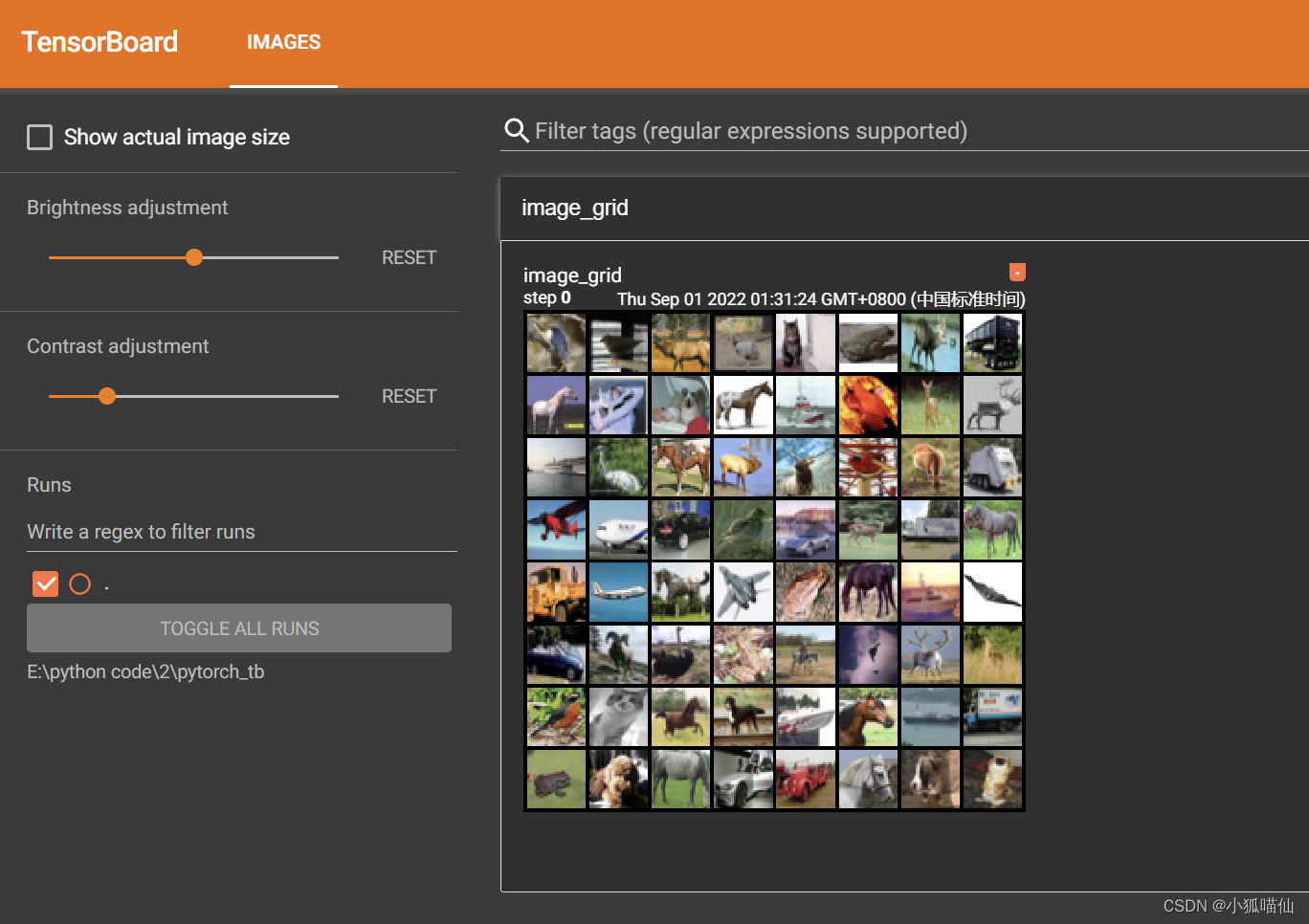
# 将多张图片拼接成一张图片,中间用黑色网格分割
# create grid of images
writer = SummaryWriter('./pytorch_tb')
img_grid = torchvision.utils.make_grid(images)
writer.add_image('image_grid', img_grid)
writer.close()
# 将多张图片直接写入
writer = SummaryWriter('./pytorch_tb')
writer.add_images("images",images,global_step = 0)
writer.close()依次运行上面三组可视化(注意不要同时在notebook的一个单元格内运行),得到的可视化结果如下(最后运行的结果在最上面):


参数
TensorBoard可以用来可视化连续变量(或时序变量)的变化过程,通过add_scalar实现:
writer = SummaryWriter('./pytorch_tb')
for i in range(500):
x = i
y = x**2
writer.add_scalar("x", x, i) #日志中记录x在第step i 的值
writer.add_scalar("y", y, i) #日志中记录y在第step i 的值
writer.close()
writer1 = SummaryWriter('./pytorch_tb/x')
writer2 = SummaryWriter('./pytorch_tb/y')
for i in range(500):
x = i
y = x*2
writer1.add_scalar("same", x, i) #日志中记录x在第step i 的值
writer2.add_scalar("same", y, i) #日志中记录y在第step i 的值
writer1.close()
writer2.close()
当我们需要对参数(或向量)的变化,或者对其分布进行研究时,可以方便地用TensorBoard来进行可视化,通过add_histogram实现。
import torch
import numpy as np
# 创建正态分布的张量模拟参数矩阵
def norm(mean, std):
t = std * torch.randn((100, 20)) + mean
return t
writer = SummaryWriter('./pytorch_tb/')
for step, mean in enumerate(range(-10, 10, 1)):
w = norm(mean, 1)
writer.add_histogram("w", w, step)
writer.flush()
writer.close(





















 778
778











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








