1、指针与链表
一、指针
指针是一种数据类型,具有指针类型的变量称为指针变量。但事实上,可以将指针直接看成一种特殊的变量。首先,它与一般变量一样具有变量的三个基本要素:名字、类型和值,不同点主要在于类型和值上,指针命名与一般变量命名一样,都用标识符。
指针所存放的是某个变量的地址值,或者说它所表示的数据值是某个变量在内存中的地址值。通常所说的指针存放哪个变量的地址值,它就指向那个变量。
指针的类型是它所指向变量的类型,而不是指针本身数据值的类型,因为任何指针它本身数据值的类型都是unsigned long int型。
空指针 NULL
当前不指向具体的对象,不同的系统会使编译取不同的NULL值。在PC中的BC或VC,都取值0。如果考虑到移植,不要养成把NULL当成为0的习惯。
二、链式结构
每一个结点的地址存放在它前面的结点的指针域中。
结点的定义
struct Node {
// data members
Node_entry entry;
Node *next;
// constructors
Node( );
Node(Node_entry item, Node *add_on = NULL);
};结点的构造函数(Constructors)
Node ∷Node( )
{
next = NULL;
}
Node ∷Node( Node_entry item, Node *add_on)
{
entry = item;
next = add_on;
}在使用中,第二个构造函数的第二个参数可以按缺省处理,即可作为NULL。也就是说第二个构造函数有2种方法引用,2个参数或1个参数。第二种情况下,第二个参数取缺省值NULL。
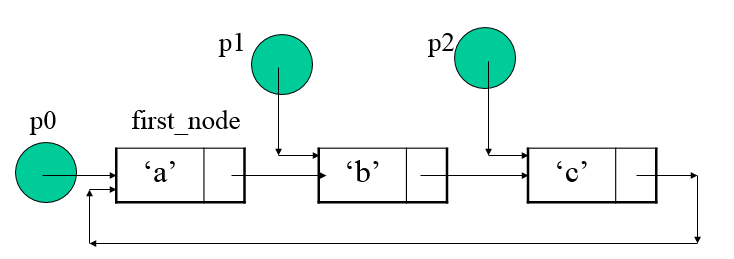
例
Node first_node(‘a’);
Node *p0 = &first_node;
Node *p1 = new Node(‘b’);
p0->next = p1;
Node *p2 = new Node(‘c’, p0);
p1->next = p2;2、链式栈
如何实现链式栈
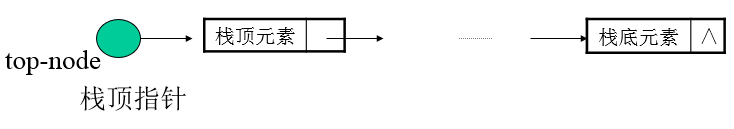
链式栈的组织形式
与顺序存储的栈区别
链式栈类说明
class Stack{
public:
Stack( );
bool empty( ) const;
Error_code push(const Stack_entry &item);
Error_code pop( );
Error_code top(Stack_entry &item) const;
protected:
Node *top_node;
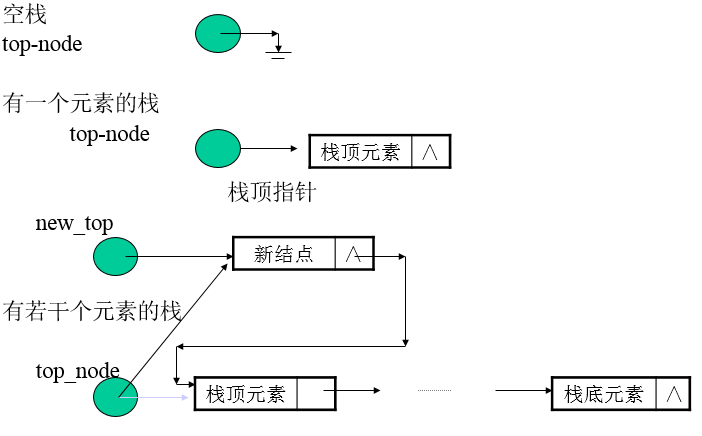
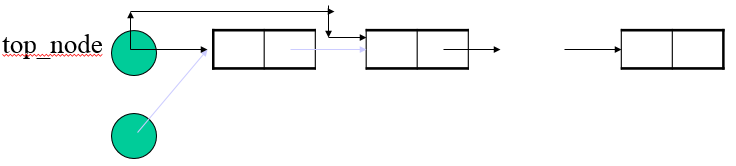
};链式栈的图示
链式栈的入栈运算
Error_code Stack ∷push(const Stack_entry &item)
/* Post: Stack_entry item is added to the top of the Stack; returns success or returns a code of overflow if dynamic menory is exhausted */
{
Node *new_top = new Node(item, top_node);
if(new_top = = NULL) return overflow;
top_node = new_top;
return success;
}链式栈的出栈运算
Error_code Stack ∷pop( )
/* Post: The top of the Stack is removed. If the Stack is empty the method returns underflow; otherwise it returns success */
{
Node *old_top = top_node;
if(top_node = = NULL) return underflow;
top_node = old_top - >next;
delete old_top;
return success;
}关于链式栈运算的副作用问题
例 一、 for(int i= 1; i<1000000; i + +)
{
Stack small;
small.push(some.data);
}每次迭代产生一个stack对象,数据加入到相应的存储空间。因为动态生成,前次存储的数据会成为碎片,积累到一定程度引起系统崩溃。引入析构函数(destructor)。
Stack ∷~Stack( )
/* Post: The Stack is cleared. */
{
while (!empty( )) pop( );
}产生垃圾(garbage)
例二、Stack outer_stack;
for (int i = 0; i<1000000; i + +) {
Stack inner_stack;
inner_stack.push(some_data);
inner_stack = outer_stack;
}
例三、
void destroy_the_stack (Stack copy)
{
}
int main( )
{
Stack vital_data;
destroy_the_stack(vital_data);
}链式栈改进方法
赋值重载
void Stack:: operator = (const Stack &original) // Overload assignment
/* Post: The Stack is reset as a copy of Stack original. */
{
Node *new_top, *new_copy, *original_node = original.top_node;
if (original_node = = NULL) new_top = NULL;
else { // Duplicate the linked nodes
new_copy = new_top = new Node(original_node − >entry);
while (original_node −>next != NULL) {
original_node = originaLnode − >next;
new_copy − >next = new Node(original_node − >entry);
new_copy = new_copy − >next;
}
}
while (! empty( )) // Clean out old Stack entries
pop( );
top_node = new_top; // and replace them with new entries.
}拷贝方法的改进
Stack:: Stack(const Stack &original) // copy constructor
/* Post: The Stack is initialized as a copy of Stack original. */
{
Node *new_copy, *original_node = original.top_node;
if (original_node = = NULL) top_node = NULL;
else { // 复制链式栈的结点
top_node = new_copy = new Node(original_node − >entry);
while (original_node − >next ! = NULL) {
original_node = original_node − >next;
new_copy − >next = new Node(original_node − >entry);
new_copy = new_copy − >next;
}
}
}修改后的链式栈说明
class Stack {
public:
// 标准的栈方法
Stack( );
bool empty( ) const;
Error_code push(const Stack_entry &item);
Error_code pop( );
Error_code top(Stack_entry &item) const;
// 关于链式栈的安全的特殊方法
~ Stack( );
Stack(const Stack &original);
void operator = (const Stack &original);
protected:
Node *top_node;
};3、链式队列
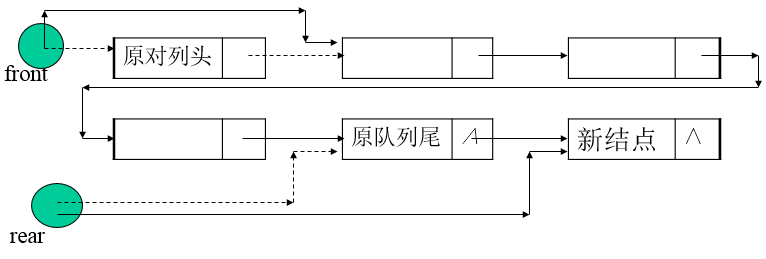
链式队列的操作示意
链式队列的说明
class Queue {
public:
// standard Queue methods
Queue( );
bool empty( ) const:
Error_code append (const Queue_entry &item);
Error_code serve( );
Error_code retrieve (Queue_entry &item) const;
// safety features for linked structures
~ Queue( ):
Queue (const Queue &original);
void operator = (const Queue &Original);
protected:
Node *front, *rear;
}:链式队列的构造函数与入队列操作
构造函数
Queue:: Queue( )
/* Post: The Queue is initialized to be empty */
{
front = rear = NULL;
}入队列操作
Error_code Queue:: append (const Queue_entry &item)
/* Post: Add item to the rear of the Queue and return a code of success or return a code of overflow if dynamic memory is exhausted. */
{
Node *new_rear = new Node(item);
if (new_rear = = NULL) return overflow;
if (rear = = NULL) front = rear = new_rear;
else {.
rear - >next = new_rear;
rear = new_rear;
}
return success;
}链式队列的出队列操作
Error_code Queue:: serve( )
/* Post: The front of the Queue is removed. If the Queue is empty return an Error_code overflow. */
{
if (front = = NULL) return underflow;
Node *old_front = front;
front = old_front - >next;
if (front = = NULL) rear = NULL;
delete old_front;
return success:
}派生链式队列与其长度函数
class Extended_queue: public Queue {
public:
bool full( ) const;
int size( ) const;
void clear( );
Error_code serve_and_retrieve(Queue_entry &item);
};
int Extended_queue:: size( ) const
/* post: return the number of entries in the Extended_queue. */
{
Node *window = front;
int count = 0;
while(window ! = NULL) {
window = window - >next;
count + +;
}
return count;
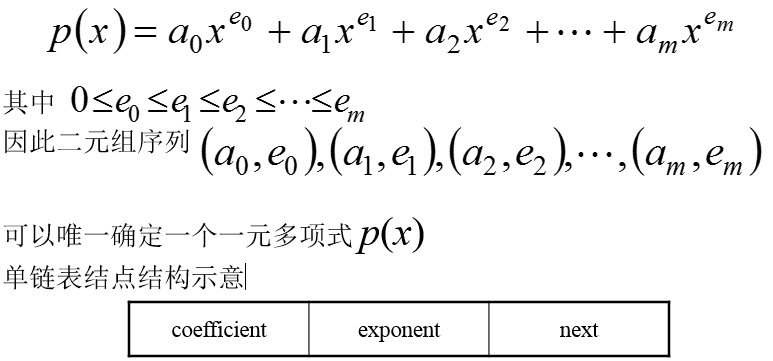
}4、多项式及其计算
需要解决的问题:多项式的表示及计算算法。
struct Term {
int degree;
double coefficient;
Term (int exponent = 0, double scalar = 0):
};
Term:: Term(int exponent, double scalar)
/* Post: The Term is initialized with the given coefficient and exponent, or with default parameter values of 0. */
{
degree = exponent;
coefficient = scalar;
}链表的应用
- 多项式
多项式相加
相加算法思想
多项式存储结构
链式栈、队列、通常的单链表,也可以是连续存储结构。视具体应用需要而定。
多项式的运算
基本程序
int mainO
/* Post: The program has executed simple polynomialarithmetic comi
tered by the user.
Uses: The classes Stack and Polynomial and the functions introductio
tions, do_command, and get_command. */
{
Stack stored_polynomials;
introductionO;
instructionsO;
while (do_command(get_command(), stored_polynomials));
}多项式运算(do command命令)
bool do_command(char command. Stack &stored_polynomials)
/* Pre: The first parameter specifies a valid calculator command.
Post: The command specified by the first parameter has been applie
Stack of Polynomial objects given by the second parameter. A
true is returned unless command == 'q'. A"^-" ' S-y*
Uses: The c/asses Stack and Polynomial. */ D '‘
{
Polynomial p, q, r;
switch (command) {
case '?':
p.readO;
if (stored_polynomials.,push(p) == overflow)
cout « "Warning: Stack full, lost polynomial" « endl;
break;
case '=':
if (stored_polynomials.empty())
cout « "Stack empty" « endl;
else {
stored_polynomials.top(p);
p.printO;
}
break;
case'+':
if (storecLpolynomials.emptyO)
cout« "Stack empty" « endl;
else{
stored_polynomials.top(p); (?y{i-^a ^<%»/ |,
storecLpolynomials.popO; 3; ^'
if(stored_polynomials.empty()) {
cout « "Stack has just one polynomial" « endl;
stored_polynomials.push(p);
}
else{
» stored_polynomials.top(q);
stored_polynomials.pop();
r.equals_sum(q, p); f '^- ^+ P
if (stored_polynomials.push(r) == overflow)
cout « "Warning: Stack full, lost polynomial" « endl;
}
break;
// Add options for further user commands.
case 'q': ~^^-
cout « "Calculation finished." « endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}多项式类的说明
class Polynomial {
public:
void read();
void printO;
void equals_sum(Polynomial p. Polynomial q);
void equals_difference(Polynomial p. Polynomial q);
void equals_product(Polynomial p. Polynomial q);
Error_code equals_quotient(Polynomial p. Polynomial q);
private:
double value;
};
class Polynomial: private Extended_queue { // Use private inheritance.
public: .
void read( );
void print( ) const;
equals_sum(Polyoornial p. Polynomial q);
void equals_difference(Polynomial p. Polynomial q);
void equals_product(Polynomial p. Polynomial q);
Error_code equals_quotient(Polynom»al p. Polynomial q);
int degree() const;
private:
void mult_term(Polynomial p. Term t);
} 多项式的打印
void Polynomial:: print( ) const
/* Post: The Polynomial /s printed to cout */
Node *print_node = front;
bool first_term= true;
while (print.node != NULL) {
Term &print_term = print_node->entry;
if (first_term) { // In this case, suppress printing an initial'+'
first_term = false;
if (print_term.coefficient < 0) cout « " - ";
}
else if (print_term.coefficient < 0) cout « " - ";
else cout « " + ";
double r = (print_term.coefficient >= 0)
? print_term.coefficient: -(print_term.coefficient);
if(r != 1) cout « r;
if (print.term.degree > 1) cout « " X"" « print_term.degree;
if (print_term. degree == 1) cout « " X";
if (r == 1 && print_term.degree == 0) cout « " 1";
print.node = print_node->next;
}
if (first.term)
cout « “0"; // Print 0 for an empty Polynomial.
cout« end l;多项式的读取
void Polynomial:: read( )
/* Post: The Polynomial /s read from cin. */
{
clear( );
double coefficient;
int last_exponent, exponent;
bool first_term = true;
cout « "Enter the coefficients and exponents for the polynomial, "
« "one pair per line. Exponents must be in descending order." « endl
« "Enter a coefficient of 0 or an exponent of 0 to terminate." «endl;
多项式的读取
do {
cout « "coefficient? " « flush;
cin »coefficient;
if (coefficient != 0.0) {
cout « "exponent? " « flush;
cin » exponent;
if ((! first_term && exponent >= last_exponent) || exponent < 0) {
exponent =0;
cout « "Bad exponent: Polynomial terminates without its last term « endl;
}
else {
Term new_term(exponent, coefficient);
append(new_term);
first_term = false;
}
last_exponent = exponent;
}
} while (coefficient != 0.0 && exponent !=0);
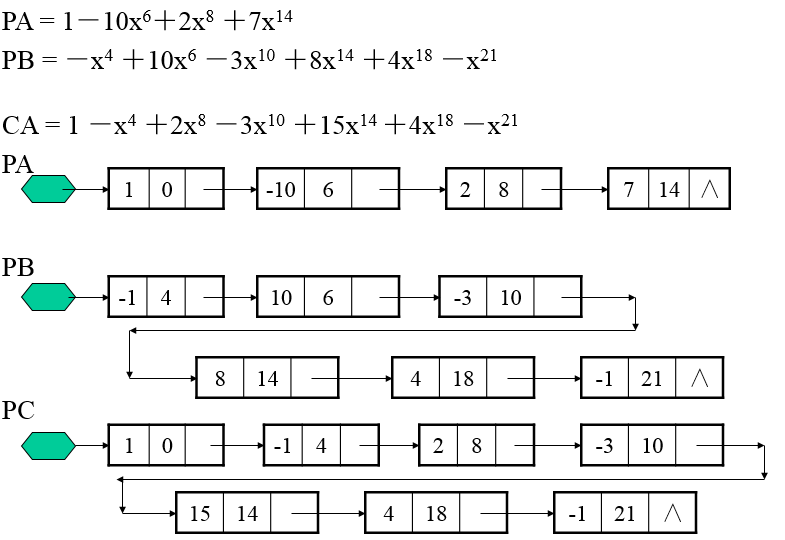
}多项式加法
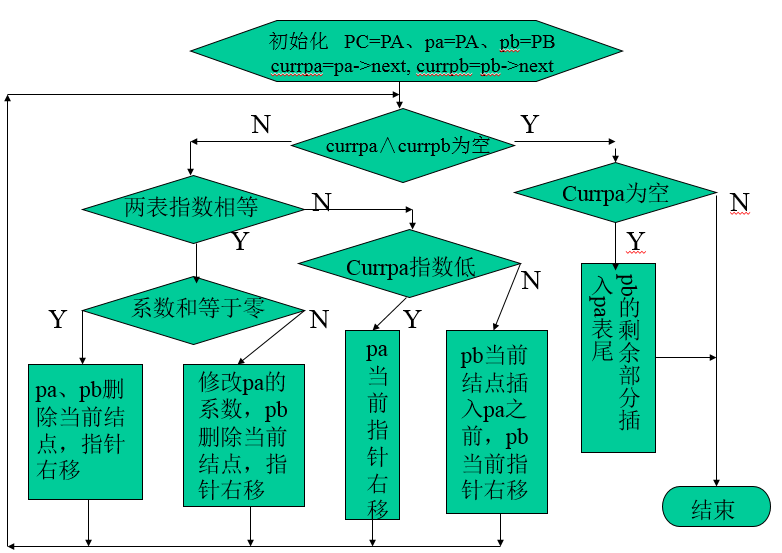
void Polynomial ::equals_sum(Polynomial p, Polynomial q)
/* Post: The Polynomial object is reset as the sum of the two parameters. */
{
dear( );
while (!p.empty( ) || !q.empty( )){
Term p_term, q_term;
if (p.degree( ) > q.degree( )) {
p.serve_and_retrieve(p_term);
append(p_term);
}
else if (q.degree( ) > p.degre( )) {
q.serve_and_retrieve(q_term);
append(q_term);
}
else{
p.serve_and_retrieve<p_term);
q.serve_and_retrieve(q_term);
if (p_term.coefficient + q_term.coefficient ! = 0) {
Term answer_term(p_term.degree, p_term.coefficient + q_term.coefficient);
append(answer_term);
}
}
}
}持续更新中。。。
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (一) 绪论
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (二) 栈
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (三) 队列
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (四) 链式栈和队列
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (五) 递归
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (六) 表与串
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (七) 查找
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (八) 排序
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (九) 表与信息检索
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (十) 二叉树
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (十一) 多路数
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (十二) 集合及其表示
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (十三) 图
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (十四) 波兰表达式

























 514
514

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








