目录
1、钢条切割问题
假定我们知道sering公司出售一段长度为I英寸的钢条的价格为pi(i=1,2,3….)钢条长度为整英寸如图给出价格表的描述(任意长度的钢条价格都有)

先给我们一段长度为n的钢条,问怎么切割,获得的收益最大 rn?
考虑n=4的时候
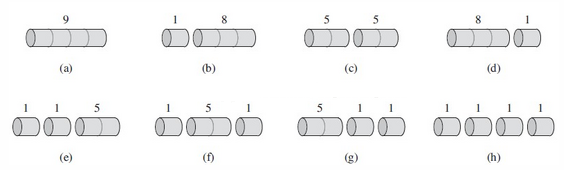
假如一个最优解把n段七个成了k段(1<=k<=n),那么最优切割方案:
![]()
最大收益:
![]()

第一种求最优解方案:
对于 r n (n>=1),最优切割收益:
![]()
将切割方案分成下面几种
1,不切割 收益为pn
2,将它切割成两半,切割成两半的情况有,对每种情况求最优解
(1,n-1) (2,n-2) (3,n-3) (4,n-4) ..... (n-1,1)
对这两半分别求最优解,最优解的和就是当前情况的最优解
第二种求最优解方案:
我们从钢条的左边切下长度为i的一段,只对右边剩下长度为n-i的一段继续进行切割,对左边的不再切割。这样,不做任何切割的方案就是:当第一段长度为n的时候,收益为pn,剩余长度为0,对应的收益为0。如果第一段长度为i,收益为pi:
![]()
代码实现 - 自顶向下递归实现
/****************************************************
* 功能:钢条切割问题—递归实现
*****************************************************/
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Test : MonoBehaviour
{
private int n = 5;//我们要切割售卖的钢条的长度
private int[] p = {0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20, 24, 30};//索引代表钢条的长度 值代表价格
void Start()
{
Debug.Log(UpDown(7, p));
}
/// <summary>
/// 自顶向下的递归方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n"></param>
/// <param name="p"></param>
/// UpDown(1,p):n=1 i=1 maxPrice=p[1]+UpDown(0,p)=1 maxPrice=1
/// UpDown(2,p):n=2 i=1 maxPrice=p[1]+UpDown(1,p)=1+1=2 i=2 maxPrice=p[2]+UpDown(0,p)=5 maxPrice=5
/// UpDown(3,p):n=3 i=1 maxPrice=p[1]+UpDown(2,p)=1+5=6 i=2 maxPrice=p[2]+UpDown(1,p)=5+1=6 i=3 maxPrice=p[3]+UpDown(0,p)=8 maxPrice=8
/// UpDown(4,p):n=4 i=1 maxPrice=p[1]+UpDown(3,p)=1+8=9 i=2 maxPrice=p[2]+UpDown(2,p)=5+5=10 i=3 maxPrice=p[3]+UpDown(1,p)=8+1=9 i=4 maxPrice=p[4]+UpDown(0,p)=9 maxPrice=10
/// <returns></returns>
public static int UpDown(int n,int[]p)//求长度为n的最大收益
{
if (n == 0) return 0;//终止条件
int tempMaxPrice = 0;//临时最大收益
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++)//i的最大值为n
{
int maxPrice = p[i] + UpDown(n - i, p);//p[i]+(n-i)的最大收益
if (maxPrice > tempMaxPrice)
{
tempMaxPrice = maxPrice;//跟新
}
}
return tempMaxPrice;
}
}
分析效率,关于上述方法的运行性能时间问题。
动态规划的方法进行求解
上面的方法之所以效率很低,是因为它反复求解相同的子问题。因此,动态规划算法安排求解的顺序,对每个子问题只求解一次,并将结果保存下来。如果随后再次需要此子问题的解,只需查找保存的结果,不必重新计算。因此动态规划的方法是付出额外的内存空间来节省计算时间。
动态规划有两种等价的实现方法(我们使用上面的钢条切割问题为例,实现这两种方法)
第一种方法是 带备忘的自顶向下法
此方法依然是按照自然的递归形式编写过程,但过程中会保存每个子问题的解(通常保存在一个数组中)。当需要计算一个子问题的解时,过程首先检查是否已经保存过此解。如果是,则直接返回保存的值,从而节省了计算时间;如果没有保存过此解,按照正常方式计算这个子问题。我们称这个递归过程是带备忘的。
/****************************************************
* 功能:钢条切割问题—带备忘的自顶向下法
*****************************************************/
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Test : MonoBehaviour
{
ArrayList al = new ArrayList(); //用于保存长度为n的最大收益
private int[] p = { 0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20, 24, 30 };//索引代表钢条的长度 值代表价格
void Start()
{
Debug.Log(al.Count);
Debug.Log(UpDown(7, p, al));
Debug.Log(al.Count);
Debug.Log(UpDown(8, p, al));
Debug.Log(al.Count);
}
/// <summary>
/// 带备忘的自顶向下的递归方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n"></param>
/// <param name="p"></param>
/// UpDown(1,p):n=1 i=1 maxPrice=p[1]+UpDown(0,p)=1 maxPrice=1
/// UpDown(2,p):n=2 i=1 maxPrice=p[1]+UpDown(1,p)=1+1=2 i=2 maxPrice=p[2]+UpDown(0,p)=5 maxPrice=5
/// UpDown(3,p):n=3 i=1 maxPrice=p[1]+UpDown(2,p)=1+5=6 i=2 maxPrice=p[2]+UpDown(1,p)=5+1=6 i=3 maxPrice=p[3]+UpDown(0,p)=8 maxPrice=8
/// UpDown(4,p):n=4 i=1 maxPrice=p[1]+UpDown(3,p)=1+8=9 i=2 maxPrice=p[2]+UpDown(2,p)=5+5=10 i=3 maxPrice=p[3]+UpDown(1,p)=8+1=9 i=4 maxPrice=p[4]+UpDown(0,p)=9 maxPrice=10
/// <returns></returns>
public static int UpDown(int n, int[] p, ArrayList al)//求长度为n的最大收益
{
if (n == 0) return 0;//终止条件
int tempMaxPrice = 0;//临时最大收益
if (al.IndexOf(n).Equals(0))//结果已经被计算保存
{
return al.IndexOf(n);//返回结果不做保存
}
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++)//i的最大值为n
{
int maxPrice = p[i] + UpDown(n - i, p, al);//p[i]+(n-i)的最大收益
if (maxPrice > tempMaxPrice)
{
tempMaxPrice = maxPrice;//跟新
}
}
int temp = tempMaxPrice;
al.Clear();
al.Add(temp);
return temp;
}
}
第二种方法是 自底向上法
首先恰当的定义子问题的规模,使得任何问题的求解都只依赖于更小的子问题的解。因而我们将子问题按照规模排序,按从小到大的顺序求解。当求解某个问题的时候,它所依赖的更小的子问题都已经求解完毕,结果已经保存。
/****************************************************
* 功能:钢条切割问题—自底向上法 n既为长度 也为list所在列表的索引值
*****************************************************/
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Test : MonoBehaviour
{
List<int> list = new List<int>(); //用于保存长度为n的最大收益
private int[] p = {0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20, 24, 30};//索引代表钢条的长度 值代表价格
void Start()
{
Debug.Log(BottomUp(10,p,list));
}
/// <summary>
/// 自底向上法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n"></param>
/// <param name="p"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static int BottomUp(int n,int[]p, List<int> list)//求长度为n的最大收益
{
list.Add(0);
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++)//i的最大值为n
{
//下面取得钢条长度为i的时候的最大收益
int tempMaxPrice = 0;//临时最大收益
for (int j = 1; j <=i ; j++)//求i的最优解 遍历从1-i
{
//int maxPrice = p[j] + al.IndexOf(i-j);//p[i]+(n-i)的最大收益
int maxPrice = p[j] + (int)list[i - j];
if (maxPrice > tempMaxPrice)
{
tempMaxPrice = maxPrice;//跟新
}
} list.Add(tempMaxPrice);
}
int temp = list[n];
list.Clear();
return temp;
}
}
2、01背包问题
问题描述:
假设现有容量m kg的背包,另外有i个物品,重量分别为w[1] w[2] ... w[i] (kg),价值分别为p[1] p[2] ... p[i] (元),将哪些物品放入背包可以使得背包的总价值最大?最大价值是多少?
(示例一:m=10 i=3 重量和价值分别为 3kg-4元 4kg-5元 5kg-6元 )
1,穷举法(把所有情况列出来,比较得到 总价值最大的情况)
如果容量增大,物品增多,这个方法的运行时间将成指数增长
/****************************************************
* 功能:01背包问题—穷举法
*****************************************************/
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Test : MonoBehaviour
{
private int m;//背包的容量
private int[] w = {0, 3, 4, 5};//物品的重量 w[0]代表第0个物品
private int[] p = {0, 4, 5, 6};//物品的价格 w[0]代表第0个物品
void Start()
{
Debug.Log(Exhaustivity(10,w,p));//取得容量为10的背包的最大总价值
}
/// <summary>
/// 穷举法获取最大总价值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="m"></param>
/// <param name="w"></param>
/// <param name="p"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static int Exhaustivity(int m,int[]w,int[]p)
{
int i = w.Length-1;//取得物品的个数
int maxPrice = 0;//最大总价值
for (int j = 0; j < Mathf.Pow(2,m) ;j++)//遍历i从0开始,到2的m次方 物品数量为i 有2的i次方中取法
{
//把j转换成i位的二进制 取得j上某一位的二进制值
int weightTotal = 0;//重量的和
int priceTotal = 0;//价格的和
for (int k = 1; k <= i; k++)//递归取得这个数字上某一位的值
{
int result=Get2(j, k);//取得j上第k位的数字
if (result==1)
{
weightTotal += w[k];
priceTotal += p[k];
}
}
if (weightTotal<=m&&priceTotal>maxPrice)//找到价值更大的方案
{
maxPrice = priceTotal;//记录最大价格
}
}
return maxPrice;//返回最大价值
}
/// <summary>
/// 取得j上number位的二进制值 是1还是0
/// </summary>
/// <param name="j"></param>
/// <param name="number"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static int Get2(int j,int number)
{
int A = j;
int B = (int)Mathf.Pow(2, number - 1);//第number位相当于2的number-1次方
int result = A & B;
return result==0?0:1;//结果=0返回0 否则返回1
}
}2,动态规划算法
我们要求得i个物体放入容量为m(kg)的背包的最大价值(记为 c[i,m])。在选择物品的时候,对于每种物品i只有两种选择,即装入背包或不装入背包。某种物品不能装入多次(可以认为每种物品只有一个),因此该问题被称为0-1背包问题
对于c[i,m]有下面几种情况:
a、c[i,0]=c[0,m]=0
b、c[i,m]=c[i-1,m] w[i]>m(最后一个物品的重量大于容量,直接舍弃不用)
w[i]<=m的时候有两种情况,一种是放入i,一种是不放入i
不放入i c[i,m]=c[i-1,m]
放入i c[i,m]=c[i-1,m-w[i]]+p[i]
c[i,m]=max(不放入i,放入i)
递归实现(不带备忘的自顶向下法)
/****************************************************
* 功能:01背包问题—递归实现(不带备忘的自顶向下法)
*****************************************************/
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Test : MonoBehaviour
{
private int m;//背包的容量
private int[] w = {0, 3, 4, 5};//物品的重量 w[0]代表第0个物品
private int[] p = {0, 4, 5, 6};//物品的价格 w[0]代表第0个物品
void Start()
{
Debug.Log(UpDown(10,3,w,p));//取得容量为10的背包的3个物品的最大总价值
}
/// <summary>
/// 动态规划算法获取最大总价值
/// </summary>
public static int UpDown(int m, int i,int[] w, int[] p) //背包容量 个数 重量 价值 返回值为m可以存储的最大价值
{
if (i == 0 || m == 0) return 0;//容量或个数为0
if (w[i]>m)//最后一个物品的重量大于容量,直接舍弃不用
{
return UpDown(m,i-1, w, p);//最多放到底i-1个
}
else
{
int maxValue1 = UpDown(m - w[i], i - 1, w, p)+p[i];
int maxValue2 = UpDown(m, i - 1, w, p);
return maxValue1 > maxValue2 ? maxValue1 : maxValue2;
}
}
}递归实现(带备忘的自顶向下法)
/****************************************************
* 功能:01背包问题—递归实现(带备忘的自顶向下法)
*****************************************************/
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Test : MonoBehaviour
{
private int m;//背包的容量
public static int[,] result = new int[11, 4];//创建保存结果的二维数组 测试的最大值为11,3
private int[] w = {0, 3, 4, 5};//物品的重量 w[0]代表第0个物品
private int[] p = {0, 4, 5, 6};//物品的价格 w[0]代表第0个物品
void Start()
{
Debug.Log(UpDown(10,3,w,p));//取得容量为10的背包的3个物品的最大总价值
}
/// <summary>
/// 动态规划算法获取最大总价值
/// </summary>
public static int UpDown(int m, int i,int[] w, int[] p) //背包容量 个数 重量 价值 返回值为m可以存储的最大价值
{
if (i == 0 || m == 0) return 0;//容量或个数为0
if (result[m,i]!=0)//结果被记录
{
return result[m, i]; //直接返回结果
}
if (w[i]>m)//最后一个物品的重量大于容量,直接舍弃不用
{
result[m,i]=UpDown(m,i-1, w, p);//最多放到底i-1个
return result[m, i];
}
else
{
int maxValue1 = UpDown(m - w[i], i - 1, w, p)+p[i];
int maxValue2 = UpDown(m, i - 1, w, p);
result[m,i]= maxValue1 > maxValue2 ? maxValue1 : maxValue2;
return result[m, i];
}
}
}动态规划—自底向上法
/****************************************************
* 功能:01背包问题—动态规划(自底向上法)
*****************************************************/
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Test : MonoBehaviour
{
private int m;//背包的容量
public static int[,] result = new int[11, 4];//创建保存结果的二维数组
private int[] w = {0, 3, 4, 5};//物品的重量 w[0]代表第0个物品
private int[] p = {0, 4, 5, 6};//物品的价格 w[0]代表第0个物品
void Start()
{
Debug.Log(BottomUp(10,3,w,p));//取得容量为10的背包的3个物品的最大总价值
}
/// <summary>
/// 动态规划(自底向上法)获取最大总价值
/// </summary>
public static int BottomUp(int m, int i,int[] w, int[] p) //背包容量 个数 重量 价值 返回值为m可以存储的最大价值
{
if (result[m,i]!=0) return result[m, i];
for (int tempM = 1; tempM < m+1; tempM++)//从1遍历到m 嵌套循环遍历 从小问题遍历到我们要解决的问题
{
for (int tempI = 1; tempI < i+1; tempI++)//内层循环
{
if (result[tempM, tempI] !=0)continue;
if (w[tempI] > tempM)//j中放不下w[k]
{
result[tempM, tempI] =result[tempM, tempI - 1];
}
else
{
int maxValue1 = result[tempM - w[tempI], tempI - 1] + p[tempI];
int maxValue2 = result[tempM, tempI - 1];
result[tempM, tempI] = maxValue1 > maxValue2 ? maxValue1 : maxValue2;
}
}
}
return result[m, i];
}
}







 本文深入探讨了如何使用动态规划解决钢条切割和01背包问题,旨在最大化收益和背包价值。介绍了自顶向下和自底向上的递归方法,以及备忘录技巧,以避免重复计算,提高算法效率。
本文深入探讨了如何使用动态规划解决钢条切割和01背包问题,旨在最大化收益和背包价值。介绍了自顶向下和自底向上的递归方法,以及备忘录技巧,以避免重复计算,提高算法效率。

















 1556
1556

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








