Power Network
| Time Limit: 2000MS | Memory Limit: 32768K | |
| Total Submissions: 23318 | Accepted: 12213 |
Description
A power network consists of nodes (power stations, consumers and dispatchers) connected by power transport lines. A node u may be supplied with an amount s(u) >= 0 of power, may produce an amount 0 <= p(u) <= p
max(u) of power, may consume an amount 0 <= c(u) <= min(s(u),c
max(u)) of power, and may deliver an amount d(u)=s(u)+p(u)-c(u) of power. The following restrictions apply: c(u)=0 for any power station, p(u)=0 for any consumer, and p(u)=c(u)=0 for any dispatcher. There is at most one power transport line (u,v) from a node u to a node v in the net; it transports an amount 0 <= l(u,v) <= l
max(u,v) of power delivered by u to v. Let Con=Σ
uc(u) be the power consumed in the net. The problem is to compute the maximum value of Con.
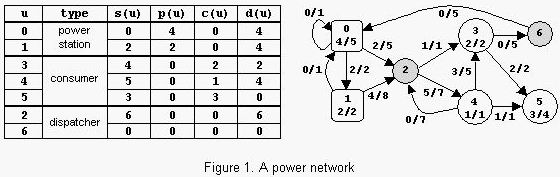
An example is in figure 1. The label x/y of power station u shows that p(u)=x and p max(u)=y. The label x/y of consumer u shows that c(u)=x and c max(u)=y. The label x/y of power transport line (u,v) shows that l(u,v)=x and l max(u,v)=y. The power consumed is Con=6. Notice that there are other possible states of the network but the value of Con cannot exceed 6.

An example is in figure 1. The label x/y of power station u shows that p(u)=x and p max(u)=y. The label x/y of consumer u shows that c(u)=x and c max(u)=y. The label x/y of power transport line (u,v) shows that l(u,v)=x and l max(u,v)=y. The power consumed is Con=6. Notice that there are other possible states of the network but the value of Con cannot exceed 6.
Input
There are several data sets in the input. Each data set encodes a power network. It starts with four integers: 0 <= n <= 100 (nodes), 0 <= np <= n (power stations), 0 <= nc <= n (consumers), and 0 <= m <= n^2 (power transport lines). Follow m data triplets (u,v)z, where u and v are node identifiers (starting from 0) and 0 <= z <= 1000 is the value of l
max(u,v). Follow np doublets (u)z, where u is the identifier of a power station and 0 <= z <= 10000 is the value of p
max(u). The data set ends with nc doublets (u)z, where u is the identifier of a consumer and 0 <= z <= 10000 is the value of c
max(u). All input numbers are integers. Except the (u,v)z triplets and the (u)z doublets, which do not contain white spaces, white spaces can occur freely in input. Input data terminate with an end of file and are correct.
Output
For each data set from the input, the program prints on the standard output the maximum amount of power that can be consumed in the corresponding network. Each result has an integral value and is printed from the beginning of a separate line.
Sample Input
2 1 1 2 (0,1)20 (1,0)10 (0)15 (1)20
7 2 3 13 (0,0)1 (0,1)2 (0,2)5 (1,0)1 (1,2)8 (2,3)1 (2,4)7
(3,5)2 (3,6)5 (4,2)7 (4,3)5 (4,5)1 (6,0)5
(0)5 (1)2 (3)2 (4)1 (5)4
Sample Output
15 6
Hint
The sample input contains two data sets. The first data set encodes a network with 2 nodes, power station 0 with pmax(0)=15 and consumer 1 with cmax(1)=20, and 2 power transport lines with lmax(0,1)=20 and lmax(1,0)=10. The maximum value of Con is 15. The second data set encodes the network from figure 1.
Source
最大流处女题~~
该题目虽然不是赤裸裸的最大流应用,但是转化非常简单。单独设立源点S和汇点T,由源点S发出单向边指向生产节点,边的容量 是作为边终点的生产者的生产能力P(x);所有的消费者都发出一条边指向汇点T,边的容量是消费者的消费能力C(x)。每个节点指向自身的边可以忽略,因为,自身流向自身没有意义。这样图里面的所有边都转化成中间传输节点,只有源点S和汇点T。问题就转化成了,由源点到汇点的最大流。该题目还有一个变化:由x指向y的边的最大流量和由y指向x的边不一样,也就是说,该图是有向图。那么构建残余图的时候,初始化逆流量不再是0,而是有设定数值,其他完全一样。
通过标准的最大流算法,BFS搜索增广路径,就是传说中的赤裸的SAP算法,一次AC。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int n,np,nc,m,sum;
int a[105][105],cai[105][105],use[105],pre[105],tmin;
char tem[10];
void init()
{
int i,j;
int x,y,value;
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
memset(cai,0,sizeof(cai));
memset(use,0,sizeof(use));
memset(pre,0,sizeof(pre));
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
{
scanf("%s",tem);
sscanf(tem,"(%d,%d)%d",&x,&y,&value);
if(x!=y)
cai[x+1][y+1]=a[x+1][y+1]=value;
}
for(i=0;i<np;i++)
{
scanf("%s",tem);
sscanf(tem,"(%d)%d",&x,&value);
cai[0][x+1]=a[0][x+1]=value;
}
for(i=0;i<nc;i++)
{
scanf("%s",tem);
sscanf(tem,"(%d)%d",&x,&value);
cai[x+1][n+1]=a[x+1][n+1]=value;
}
sum=0;
}
int bfs()
{
int i,j;
int que[1000],head,end;
int index;
head=end=0;
memset(use,0,sizeof(use));
memset(pre,0,sizeof(pre));
que[end++]=0;
use[0]=1;
while(head<end)
{
index=que[head++];
if(cai[index][n+1])
{
pre[n+1]=index;
return 1;
}
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!use[i]&&cai[index]
[i])
{
que[end++]=i;
use[i]=1;
pre[i]=index;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
void update()
{
int i,j;
int q,pq;
q=n+1;
tmin=10000;
while(q)
{
pq=pre[q];
if(cai[pq][q]<tmin)
tmin=cai[pq][q];
q=pq;
}
sum+=tmin;
q=n+1;
while(q)
{
pq=pre[q];
cai[pq][q]-=tmin;
cai[q][pq]+=tmin;
q=pq;
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j;
while(scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&np,&nc,&m)!=EOF)
{
init();
while(bfs())
{
update();
}
printf("%d\n",sum);
}
return 0;
}





















 542
542

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








