最短路径Djikstra算法:
主要思想:先找确定的(即当前最短的),不确定的则动态更新。
从(V-S)集合中找v0到其中最短的路径的顶点,加入到S中并更新(V-S)集合中其他顶点的路径值。
―――――――
参考模板:
Dp初值为v0到某个顶点v的权值weight[ v0][ v],S初值全为false,pre初值全为-1.(Dp,S,pre下标都从1开始)
Dp[ v0]=0;//此行也可以不要,因为下面用Dp[]时总会判断!S[],而S[v0]=TRUE,故Dp[ v0]永远不会被用到
S[ v0]=TRUE;//v0顶点属于S集合
for( int i= 1; i< n; ++i) //注意,下面的循环只需n-1次,将除v0之外的其他所有顶点逐个加入S集合(实际循环时,循环次数可能小于n-1,因为如果在(V-S)集合中找不到从v0可达的点,则会直接跳出:if ( minIndex == -1 ) break)。
{ min= INFINITY;
minIndex= -1;
for( int k= 1; k<= n; ++k) //求(V-S)集合内与v0距离最近的顶点(Dp[]最小)
{ if( !S[k] &&min>Dp[k])
{ minIndex= k;
min= Dp[ k];
}
}
if ( minIndex == -1 ){ break;}//此时 (V-S)集合中所有的Dp[]都是无穷大,则表明v0到这些顶点都不可达,故后面的不用再判断了,直接跳出循环
else//选中一个最短且可达点(即Dp[]最小,且不是无穷大)
{ S[ minIndex]= TRUE;//离v0最近的顶点minIndex加入到S集合
for(int k= 1; k<= n; ++k) //更新当前最短路径及距离
{ if( !S[ k] && weight[ minIndex][ k]< INFINITY && Dp[ k]> min+ weight[ minIndex][ k]) //一定要判断weight[ minIndex][ k]< INFINITY,
//否则后面的min+ weight[ minIndex][ k]可能会超出整数的范围而越界,其实应该用减法,因为用加法可能超出整数的范围,if里面只需2个条件即可:if ( !S[ k] && Dp[ k]- min> weight[ minIndex][ k] ) 但这样会不好理解,所以还是可以用上面的3个条件的。
{ Dp[ k]= min+ weight[ minIndex][ k]; //修改v0到(V-S)集合中其他顶点的路径长度
pre[ k]= minIndex;//minIndex作为桥梁(或中间人),vo与k变得更短,pre记录前一个,以便输出最短路径经过的顶点路径信息(如“1->3->4->2”)
}
}
}
}
―――――
伪代码参考:
Dp[]权值,S[]全false,pre全-1,下标都从1开始
Dp[ v0]=0;S[ v0]=T;
for( i= 1; i< n; ++i)
{ min= 无穷大; minIndex= -1;
for( k= 1; k<= n; ++k) //找最短
{ if( !S[k] && min>Dp[k])
{ minIndex= k;
min= Dp[ k];
}
}
if ( minIndex == -1 ) break;
else
{ S[ minIndex]= T;
for( k= 1; k<= n; ++k) //更新
{ if( !S[ k] && weight[ minIndex][ k]< INFINITY &&
Dp[ k]> min+ weight[ minIndex][ k])
{ Dp[ k]= min+ weight[ minIndex][ k];
pre[ k]= minIndex;
}
}
}
}
--------------------
加入最短的顶点(dp[]最小)后,更新其他顶点的dp[],如下图:
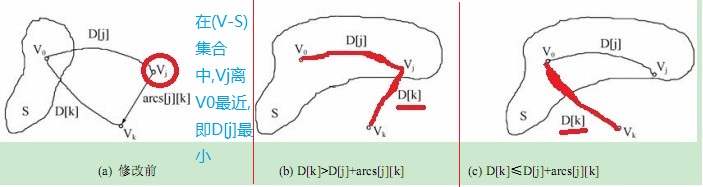

论证:每次从(V-S)集合中找v0到其中最短的路径的顶点v(即Dp[v]最小),Dp[v]为从v0到v的最短路径长度。从v0到v,还有比Dp[v]更短的路径吗?没有了。因为如果还有更短的,则必是经过其他某点vt(属于(V-S)),使Dp[v]> Dp[vt]+ weight[ vt][v],而Djikstra算法要求权值为正,所以Dp[v]> Dp[vt],即Dp[v]不是从v0到(V-S)中路径最短的顶点,而路径最短的顶点应该是vt,这与假设(Dp[v]最小)矛盾。
ACM例题:
http://ac.jobdu.com/problem.php?id=1341
九度acm1341: 艾薇儿的演唱会(已AC)
#include <iostream>
#include <memory.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_NUM_VERTICES= 101;//最大的节点个数
//const int MAX_NUM_EDGES= 1001;//最大的边个数
const int MAX_INT= 1000000;//最大的整数
//查询最短路径并输出
void SearchPathAndPrint( int* pre, int v0, int v1)
{
vector< int> viShortestPath;//最短路径的向量
viShortestPath.push_back( v1);//加入终点
int iCurr= pre[ v1];
while( v0 != iCurr)
{
viShortestPath.push_back( iCurr);
iCurr= pre[ iCurr];
}
viShortestPath.push_back( v0);//加入起点
输出
//cout<< v0;
从某个终点v1开始,根据pre[]从后往前搜索,直到找到起始点v0
//for ( int i= ( int) viShortestPath.size()- 2; i>= 0 ; --i)
//{
// cout<< "->"<< viShortestPath[ i];
//}
//cout<< endl;
}
int main()
{
int n;//节点个数(节点下标从1开始)
cin>> n;
int iWeight[ MAX_NUM_VERTICES][ MAX_NUM_VERTICES];//一点到另一点的权值
//memset( iWeight, MAX_INT, MAX_NUM_VERTICES* MAX_NUM_VERTICES* sizeof( int));//初始值为无穷大
for ( int i= 1; i<= n; ++i)
{
for ( int j= 1; j<= n; ++j)
{
iWeight[ i][ j]= MAX_INT;
}
}
int iNumEdges;//边的个数
cin>> iNumEdges;
int v0, vEnd;
cin>> v0>> vEnd;
int iv1, iv2, iWght;
for ( int i= 0; i< iNumEdges; ++i)//输入每条边的信息(起点索引,终点索引,边的权值)
{
cin>> iv1>> iv2>> iWght;
if ( iWeight[ iv1][ iv2] > iWght)
{
iWeight[ iv1][ iv2]= iWeight[ iv2][ iv1]= iWght;
}
}
int iShortestLenFromStart[ MAX_NUM_VERTICES];//连通分量的数组
bool abSetOK[ MAX_NUM_VERTICES];//已经加入到最短路径组的集合
int pre[ MAX_NUM_VERTICES];
/*最短路径中上一个的索引(注:输出时要倒着来,我开始想到用next,但不行,
因为树的任一节点A只能有一个父节点,但A可同时有几个孩子)*/
memset( iShortestLenFromStart, 0, MAX_NUM_VERTICES* sizeof( int));//初始值为无穷大
for ( int i= 1; i<= n; ++i)//输入每条边的信息(起点索引,终点索引,边的权值)
{
iShortestLenFromStart[ i]= iWeight[ v0][ i];//初始值为权值
}
//iShortestLenFromStart[ v0]= 0;
memset( abSetOK, false, MAX_NUM_VERTICES* sizeof( bool));//初始值为无穷大
abSetOK[ v0]= true;
memset( pre, -1, MAX_NUM_VERTICES* sizeof( int));//初始值为无穷大
int iLastInserted= v0;
int iOutOfSetMin, iOutOfSetMinIndex;//在已加入到最短路径组外的最小值
for ( int i= 1; i< n; ++i)
{
iOutOfSetMin= MAX_INT;
iOutOfSetMinIndex= -1;
for ( int w= 1; w<= n; ++w)
{
if ( !abSetOK[ w] && iShortestLenFromStart[ w]< iOutOfSetMin)
{
iOutOfSetMin= iShortestLenFromStart[ w];
iOutOfSetMinIndex= w;
}//if ( !abSetOK[ w]
}//for ( int w
if ( iOutOfSetMinIndex == -1)//如==-1则表明剩下的是孤立的不可达点(即不连通),
//此时 (V-S)集合中所有的Dp[]都是无穷大,故后面的不用再判断了,直接跳出循环
{
break;
}
else
{
abSetOK[ iOutOfSetMinIndex]= true;
pre[ iOutOfSetMinIndex]= iLastInserted;
iLastInserted= iOutOfSetMinIndex;
for ( int w= 1; w<= n; ++w)
{
if ( !abSetOK[ w] && iWeight[ iOutOfSetMinIndex][ w]< MAX_INT
&& iWeight[ iOutOfSetMinIndex][ w]+ iOutOfSetMin < iShortestLenFromStart[ w])
{
iShortestLenFromStart[ w]= iWeight[ iOutOfSetMinIndex][ w]+ iOutOfSetMin;
pre[ w]= iOutOfSetMinIndex;
}//if ( !abSetOK[ w]
}//for ( int w
}//if ( iOutOfSetMinIndex
}//for ( int i
//cout<<"最短的路径为: ";
SearchPathAndPrint( pre, v0, vEnd);//查询最短路径并输出
cout<< iShortestLenFromStart[ vEnd]<< endl;
//system("pause");
return 0;
}






















 2976
2976

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








