1. 模型结构
本文只涉及利用Tensorflow实现CNN的手写数字识别,关于CNN的内容请参考:卷积神经网络(CNN)
MNIST数据集的格式与数据预处理代码input_data.py的讲解请参考 :Tutorial (2)
该CNN模型包含3个卷积层,2个全连接层,具体结构如下:
- 输入层 : CNN的输入是一张图片,用28x28的矩阵表示
- C1层 :该层为卷积层,卷积核大小是3x3,激活函数为RELU.输入一个28x28的矩阵,输出32个28x28 维的feature map
- S1层 :该层为max pooling层,窗口大小是2x2,输入32个28x28的矩阵,输出32个14x14 维的feature map
- C2层 :该层为卷积层,卷积核大小是3x3,激活函数为RELU.输入32个14x14的feature map,输出64个14x14 的feature map
- S2层 :该层为max pooling层,窗口大小是2x2,输入64个14x14 的feature map,输出64个7x7 的feature map
- C3层 :该层为卷积层,卷积核大小是3x3,激活函数为RELU.输入64个7x7 的feature map,输出128个7x7 的feature map
- S3层 :该层为max pooling层,窗口大小是2x2,输入128个7x7 的feature map,输出128个4x4 的feature map,并将这128个feature map合并为一个128x4x4=2048维的向量
- F4层 :该层为全连接层,神经元个数为625
- F5层 :该层为全连接层,输出一个10维向量,表示label的概率分布
2. 实验代码
实验代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import input_data
batch_size = 128
test_size = 256
#初始化参数
def init_weights(shape):
return tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape, stddev=0.01))
'''
tensorflow中conv2d的"padding"参数可以设为两个值SAME,VALID
它们对边界是这样处理的,对输入的矩阵,包裹n层0,然后再按照上面所说的卷积方法进行卷积,n的求法:
SAME: edge_row = (kernel_row - 1) / 2; edge_cols = (kernel_cols - 1) / 2;
VALID:edge_row = edge_cols = 0;
edge_row就是包裹0的行数,edge_cols就是包裹0的列数, kernel_row就是卷积核的行数
'''
def model(X, w, w2, w3, w4, w_o, p_keep_conv, p_keep_hidden):
#第一个卷积层:padding=SAME,保证输出的feature map与输入矩阵的大小相同
l1a = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(X, w, # l1a shape=(?, 28, 28, 32)
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'))
#max_pooling,窗口大小为2x2
l1 = tf.nn.max_pool(l1a, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], # l1 shape=(?, 14, 14, 32)
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
#dropout:每个神经元有p_keep_conv的概率以1/p_keep_conv的比例进行归一化,有(1-p_keep_conv)的概率置为0
l1 = tf.nn.dropout(l1, p_keep_conv)
#第二个卷积层
l2a = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(l1, w2, # l2a shape=(?, 14, 14, 64)
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'))
l2 = tf.nn.max_pool(l2a, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], # l2 shape=(?, 7, 7, 64)
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
l2 = tf.nn.dropout(l2, p_keep_conv)
#第三个卷积层
l3a = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(l2, w3, # l3a shape=(?, 7, 7, 128)
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'))
l3 = tf.nn.max_pool(l3a, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], # l3 shape=(?, 4, 4, 128)
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
#将所有的feature map合并成一个2048维向量
l3 = tf.reshape(l3, [-1, w4.get_shape().as_list()[0]]) # reshape to (?, 2048)
l3 = tf.nn.dropout(l3, p_keep_conv)
#后面两层为全连接层
l4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(l3, w4))
l4 = tf.nn.dropout(l4, p_keep_hidden)
pyx = tf.matmul(l4, w_o)
return pyx
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)#读取数据
#mnist.train.images是一个55000 * 784维的矩阵, mnist.train.labels是一个55000 * 10维的矩阵
trX, trY, teX, teY = mnist.train.images, mnist.train.labels, mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels
trX = trX.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1) # 将每张图片用一个28x28的矩阵表示,(55000,28,28,1)
teX = teX.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1) # 将每张图片用一个28x28的矩阵表示,(1000,28,28,1)
X = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 28, 28, 1])
Y = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 10])
w = init_weights([3, 3, 1, 32]) # 第一层卷积核大小为3x3,输入一张图,输出32个feature map
w2 = init_weights([3, 3, 32, 64]) # 第二层卷积核大小为3x3,输入32个feature map,输出64个feature map
w3 = init_weights([3, 3, 64, 128]) # 第三层卷积核大小为3x3,输入64个feature map,输出128个feature map
w4 = init_weights([128 * 4 * 4, 625]) # FC 128 * 4 * 4 inputs, 625 outputs
w_o = init_weights([625, 10]) # FC 625 inputs, 10 outputs (labels)
p_keep_conv = tf.placeholder("float") # 卷积层的dropout概率
p_keep_hidden = tf.placeholder("float")# 全连接层的dropout概率
py_x = model(X, w, w2, w3, w4, w_o, p_keep_conv, p_keep_hidden)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(py_x, Y))# 交叉熵目标函数
train_op = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(0.001, 0.9).minimize(cost)#RMSPro算法最小化目标函数
predict_op = tf.argmax(py_x, 1)#返回每个样本的预测结果
# Launch the graph in a session
with tf.Session() as sess:
# you need to initialize all variables
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
for i in range(100):
training_batch = zip(range(0, len(trX), batch_size),
range(batch_size, len(trX)+1, batch_size))
for start, end in training_batch:
sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={X: trX[start:end], Y: trY[start:end],
p_keep_conv: 0.8, p_keep_hidden: 0.5})
#test
test_indices = np.arange(len(teX))
np.random.shuffle(test_indices)
test_indices = test_indices[0:test_size]#选取一批测试数据
print(i, np.mean(np.argmax(teY[test_indices], axis=1) ==
sess.run(predict_op, feed_dict={X: teX[test_indices],
Y: teY[test_indices],
p_keep_conv: 1.0,
p_keep_hidden: 1.0})))3. 结果
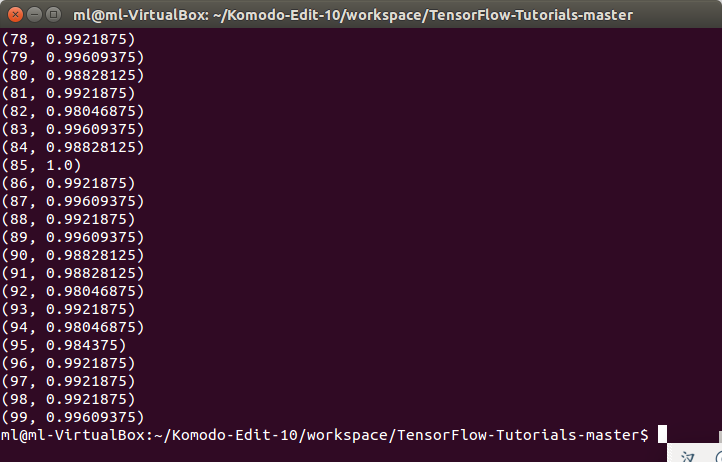
基于CNN的手写数字识别准确率可达到99.6%,与softmax模型(91%)和普通的NN(95%)模型相比,性能有了较大提升.






















 446
446

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








