最近在打造一款有温度、有情怀的陪伴式 AI 对话机器人。
既然有温度、有情怀,自然少不了记忆功能。
前面和大家分享过短期记忆的实现:
简单来说,短期记忆的实现:利用 SQLite 数据库缓存用户的聊天记录,将多轮对话的内容作为上下文,和当前对话内容一起交给 LLM 进行推理。
随着对话内容的增多,输入 LLM 的 Token 数量也会急剧增加!显然,这种方案无法适用于长期记忆。
问题来了:如何才能优雅地实现 LLM 的长期记忆?
个人理解:肯定少不了 RAG,但实操起来才发现麻烦重重!
直到发现阿里开源的 MemoryScope,问题似乎有解了。
今日分享,手把手带大家实操 MemoryScope 的具体实现,全程免费。
1. 长期记忆的实现思路
长期记忆通常涉及更复杂的数据结构和存储机制。常见的两种技术方案如下:
-
知识图谱(Knowledge Graphs):知识图谱是一种用于表示实体及其关系的结构化数据模型,适合存储和检索复杂的知识。
-
向量数据库(Vector Database):用于存储和检索高维向量数据,适合处理嵌入和相似性搜索。
本文关注的 MemoryScope 采用的就是第二种方案,向量数据库采用 ElasticSearch。
2. MemoryScope 简介
老规矩,先来简单介绍下~
MemoryScope 有哪些亮点?
- ⚡低延迟:多线程实现。
- 🌲分层记忆:首先从对话内容中抽取有价值的观察结果,结合多个观察结果,实现对用户行为和偏好的持续学习,从而更新对用户的认知。
- ⏰时间敏感记忆:除了事实和观点,也存储明确的时间信息。
怎么做到的?
下面是官方提供的架构图:
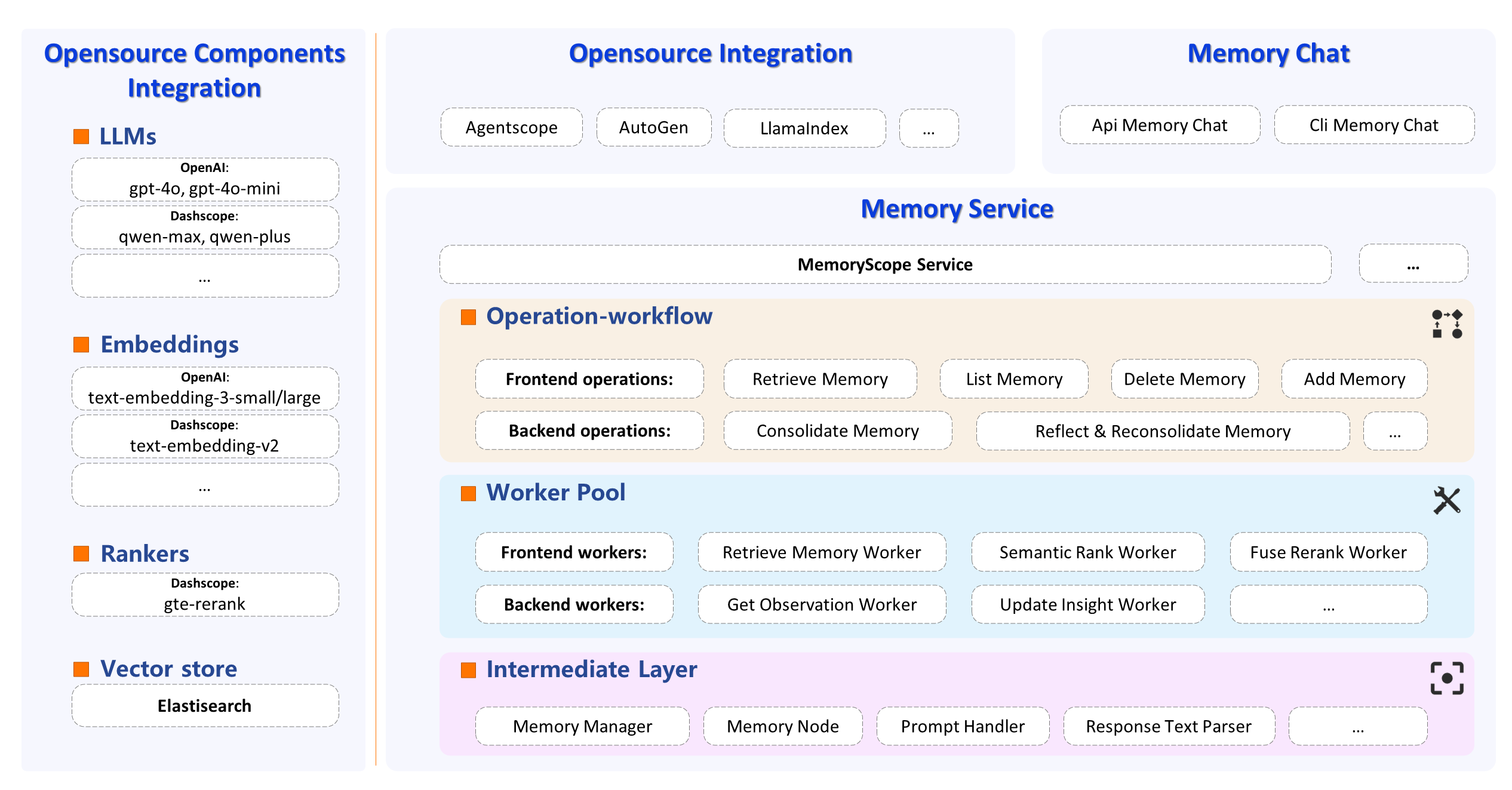
上图和项目源码是对应的,其底层依赖四大组件:
- 对话大模型:官方支持 OpenAI 和 阿里百炼的 API。
- Embedding模型;
- 重排序模型;
- 向量数据库。
注:通过简单的适配,我们也可接入其他大模型,见 3.3 部分。
基于上述四大组件,MemoryScope 的核心框架包含三个部分:
-
数据库中间件: 和 ElasticSearch 交互的函数实现,提示词模板等。
-
Worker库: 能力原子化,抽象成单独的worker,包括query信息过滤、observation抽取,insight更新等20+Worker。
-
记忆工作流: 每个工作流集成多个Worker,实现“记忆检索”,“记忆巩固”,“反思与再巩固”等核心能力。
所谓“记忆巩固”,就是每接收一批聊天记录,从对话中提取重要信息,以observation形式的记忆片段存储在数据库中。
“反思与再巩固”,则是对observations进行反思,以insight形式的记忆片段存储起来,确保记忆片段不矛盾和重复。
3. MemoryScope 实战
3.1 环境准备
首先准备 MemoryScope 环境,这里推荐大家本地安装,方便后续对代码修改:
git clone https://github.com/modelscope/memoryscope
cd memoryscope
conda create -n memoryscope python=3.10 -y
conda activate memoryscope
pip install -e . # 基于项目根目录的 `setup.py` 进行安装
3.2 ElasticSearch 部署
项目依赖 ElasticSearch 作为向量数据库,推荐大家采用 Docker 一键安装:
# -e用于设置环境变量,-d 用于放到后台运行
docker run -d -p 9200:9200 -e "discovery.type=single-node" -e "TZ=Asia/Shanghai" -e "xpack.security.enabled=false" -e "xpack.license.self_generated.type=trial" --name es docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:8.13.2
由于官方仓库默认只支持 OpenAI 和 阿里百炼的 API,二者都需要付费使用。
对于只想上手体验一下的小伙伴来说,有没有免费的平替方案?
推荐大家使用硅基流动 ,它的免费模型覆盖了:LLM/Embedding/ReRank,还没注册的小伙伴先去申请一个 api_key,下文实操将采用这里的免费模型。
此外,还需在代码层面做简单的适配,接下来我们一起搞定它。
3.3 配置文件准备
MemoryScope 所有参数配置均基于 yaml 文件,为此,可以复制一份配置文件,后续只需替换其中的模型部分即可:
cd memoryscope/core/config/
cp demo_config_zh.yaml demo_config_local.yaml
3.4 LLM 模型配置
MemoryScope 依赖 LlamaIndex 实现 RAG 部分,而 LlamaIndex 是一个专门用于构建RAG系统的框架,后面有机会单独开一篇来聊 LlamaIndex。
LLM 模型定义在memoryscope/core/models/llama_index_generation_model.py。
因为硅基的 LLM 兼容 OpenAI 格式,所以需要安装 OpenAILike 依赖:
pip install llama-index-llms-openai-like
然后引入并完成模型注册:
from llama_index.llms.openai_like import OpenAILike
class LlamaIndexGenerationModel(BaseModel):
MODEL_REGISTRY.register("like_generation", OpenAILike)
最后,yaml 配置文件的generation_model部分修改如下,比如我这里采用Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct模型:
model:
generation_model:
class: core.models.llama_index_generation_model
module_name: like_generation
model_name: Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct
model: Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct
api_key: xxx
api_base: https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1
max_tokens: 2000
temperature: 0.01
3.5 Embedding 模型配置
Embedding 模型定义在memoryscope/core/models/llama_index_embedding_model.py。
为了能够使用硅基的 Embedding 模型,我们可以参考源码中的 DashScopeEmbedding,新建一个 Embedding 类:
class BgeEmbedding(BaseEmbedding):
base_url: str = Field(description="The base URL for the BGE API")
api_key: str = Field(description="The API key for the BGE API")
model_name: str = Field(description="The model name")
然后,修改Embedding获取的同步实现函数:
def get_general_text_embedding(self, texts: str) -> List[float]:
"""Get embedding."""
payload = {"model": self.model_name, "input": texts, "encoding_format": "float"}
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.api_key}","Content-Type": "application/json"}
response = requests.request("POST", self.base_url, json=payload, headers=headers)
return response.json()['data'][0]["embedding"]
修改Embedding获取的异步实现函数:
async def aget_general_text_embedding(self, prompt: str) -> List[float]:
payload = {"model": self.model_name, "input": prompt, "encoding_format": "float"}
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.api_key}","Content-Type": "application/json"}
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.post(self.base_url, json=payload, headers=headers) as response:
return await response.json()['data'][0]["embedding"]
最后,修改 yaml 配置文件的embedding_model部分:
embedding_model:
class: core.models.llama_index_embedding_model
module_name: bge_embedding
model_name: BAAI/bge-m3
base_url: https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1/embeddings
api_key: xxx
3.6 ReRank 模型配置
ReRank 模型定义在memoryscope/core/models/llama_index_rank_model.py。
为了能够使用硅基的 ReRank 模型,我们可以参考源码中的 DashScopeRerank,新建一个 Rank 类:
class BGERerank(BaseNodePostprocessor):
model: str = Field(description="Dashscope rerank model name.")
top_n: int = Field(description="Top N nodes to return.")
api_key: Optional[str] = Field(description="API key for accessing the DashScope rerank model.")
api_base: Optional[str] = Field(description="API base URL for accessing the DashScope rerank model.")
然后,修改 self._postprocess_nodes 函数部分:
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.api_key}","Content-Type": "application/json"}
response = requests.request("POST", self.api_base, json=payload, headers=headers)
new_nodes = []
for result in response.json()['results']:
new_node_with_score = NodeWithScore(
node=nodes[result['index']].node, score=result['relevance_score']
)
new_nodes.append(new_node_with_score)
最后,修改 yaml 配置文件的rank_model部分:
rank_model:
class: core.models.llama_index_rank_model
module_name: bge_rank
model_name: BAAI/bge-reranker-v2-m3
api_key: xxx
api_base: https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1/rerank
top_n: 500
4. 效果实测
如果要在服务端调用,需要修改 yaml 配置文件的memory_chat部分,采用 api_memory_chat 模式:
memory_chat:
api_memory_chat:
class: core.chat.api_memory_chat
memory_service: memoryscope_service
generation_model: generation_model
stream: false
然后,通过指定 cofig_path 实现服务配置:
config_path="memoryscope/core/config/demo_config_local.yaml"
ms = MemoryScope(config_path=config_path)
memory_chat = ms.default_memory_chat
最后,测试下记忆是否生效:
response = memory_chat.chat_with_memory(query="我的爱好是吉他。")
print("回答:\n", response.message.content)
print("记忆:\n", response.meta_data["memories"])
result = memory_chat.run_service_operation("consolidate_memory")
print(result)
response = memory_chat.chat_with_memory(query="你知道我的乐器爱好是什么?")
print("回答2:\n", response.message.content)
print("记忆2:\n", response.meta_data["memories"])
返回结果如下:
回答:
很高兴听到你的爱好是吉他!你可以尝试学习新的吉他曲目,或者加入吉他社群交流经验。
记忆:
None
[MEMORY ACTIONS]:
new observation: 用户爱好是吉他。 (valid)
回答2:
你的乐器爱好是吉他。
记忆2:
[2024-10-26 21:26:20 周六] 用户爱好是吉他。
Nice!
写在最后
本文带大家实操了 LLM 长期记忆框架 MemoryScope,为构建更加个性化的智能体,提供了一种可能。
记忆,连接着过去和当下,承载着经验和人格。
期待拥有长期记忆能力的智能体,能够成为你的第二大脑。
如果对你有帮助,欢迎点赞收藏备用。
为方便大家交流,新建了一个 AI 交流群,欢迎感兴趣的小伙伴加入。
最近打造的微信机器人小爱(AI)也在群里,公众号后台「联系我」,拉你进群。
























 94
94

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








