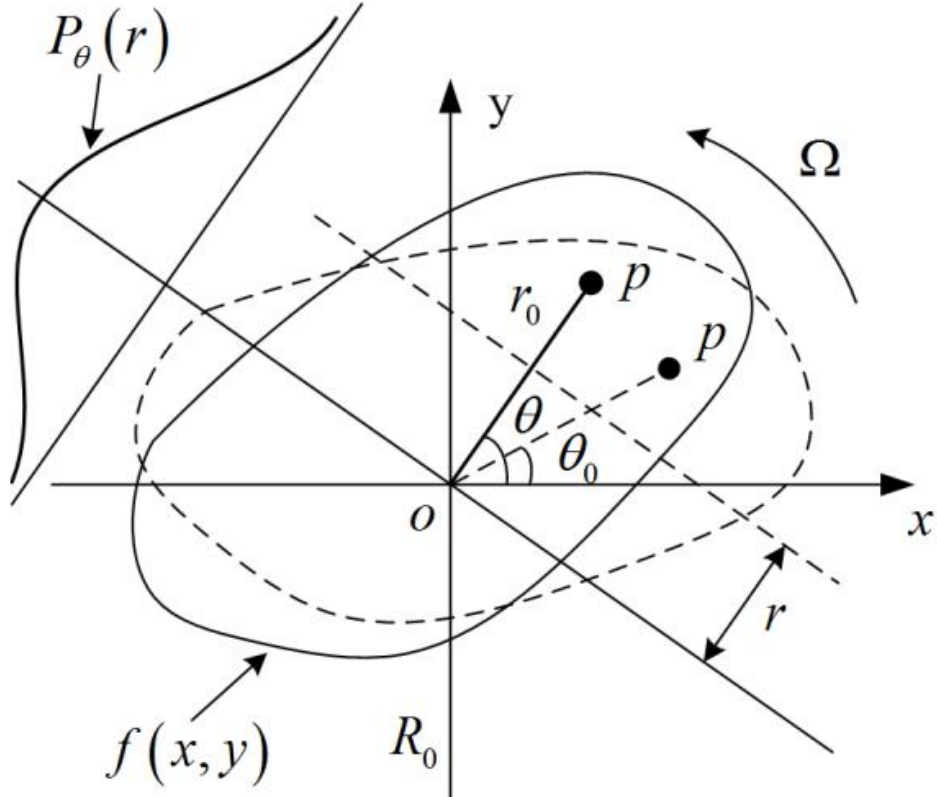
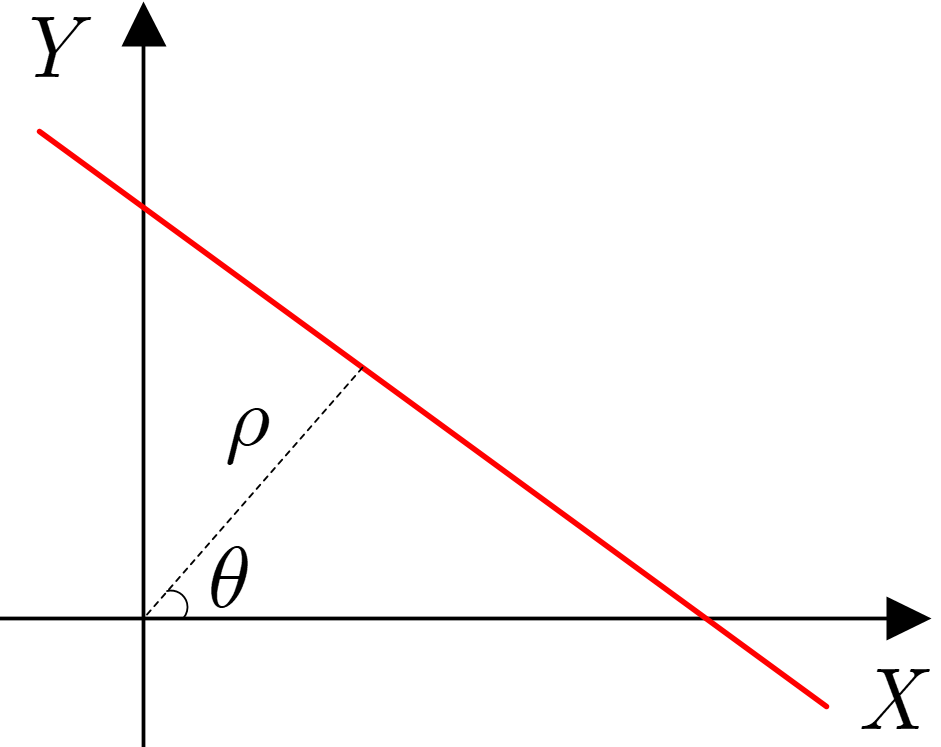
如图所示为Radon变换示意图,其中 f ( x , y ) f(x,y) f(x,y)为平面目标的轮廓,假设在远处有一个无限聚焦的光束沿某一个方向射向这个目标,假设这条光线所在的直线为 L L L,它的基本情况如下图所示,从下图可以计算得到,该直线的法向量为 n ⃗ = ( c o s θ , s i n θ ) \vec{n}=({\rm cos}\theta,{\rm sin}\theta) n=(cosθ,sinθ),且点 ( ρ c o s θ , ρ s i n θ ) (\rho {\rm cos}\theta,\rho {\rm sin}\theta) (ρcosθ,ρsinθ)在该直线上,所以根据直线的点法式方程( A ( x − x 0 ) + B ( y − y 0 ) = 0 A(x-x_0)+B(y-y_0)=0 A(x−x0)+B(y−y0)=0)可以求得该直线的方程为 x c o s θ + y s i n θ − ρ = 0 x{\rm cos}\theta+y{\rm sin}\theta-\rho=0 xcosθ+ysinθ−ρ=0。设想在这条光线穿过目标之后会在目标背后的光感应板上留下一个光点,这个光点的强度可以用线积分的形式表示: r = ∫ L f ( x , y ) d L r=\int_L{f(x,y)dL} r=∫Lf(x,y)dL,且这个光点的强度能够反映目标 f ( x , y ) f(x,y) f(x,y)内部的光反射情况,设想有一束包含 M M M条与 L L L平行的光线的光束同时射向目标,则后面的感光板上留下 M M M个强度不一的光点,调整入射光束的角度(或转动目标),设共调整了 N N N个角度,则将形成 N N N条上述包含 M M M个光点的光线,最终形成由 M × N M \times N M×N个强度不一的光电组成的光图像,记为 R ( ρ , θ ) R(\rho,\theta) R(ρ,θ),这个 R ( ρ , θ ) R(\rho,\theta) R(ρ,θ)能够反映目标内部或其轮廓的信息,这也就是医学上常用的层析成像的基本原理,上述从 f ( x , y ) → R ( ρ , θ ) f(x,y) \rightarrow R(\rho,\theta) f(x,y)→R(ρ,θ)的变化过程即为Radon变换。
引入冲激函数
δ
(
x
)
\delta(x)
δ(x)来表示Radon变换,则有
R
(
ρ
,
θ
)
=
∫
x
c
o
s
θ
+
y
s
i
n
θ
−
ρ
=
0
f
(
x
,
y
)
d
L
=
∬
f
(
x
,
y
)
δ
(
x
c
o
s
θ
+
y
s
i
n
θ
−
ρ
)
d
x
d
y
(1)
R(\rho,\theta)=\int_{x{\rm cos}\theta+y{\rm sin}\theta-\rho=0}{f(x,y)dL}=\iint{f(x,y)\delta(x{\rm cos}\theta+y{\rm sin}\theta-\rho)dxdy} \tag{1}
R(ρ,θ)=∫xcosθ+ysinθ−ρ=0f(x,y)dL=∬f(x,y)δ(xcosθ+ysinθ−ρ)dxdy(1)
(1)成立的逻辑是函数
δ
(
x
c
o
s
θ
+
y
s
i
n
θ
−
ρ
)
=
1
\delta(x{\rm cos}\theta+y{\rm sin}\theta-\rho)=1
δ(xcosθ+ysinθ−ρ)=1当且仅当
x
c
o
s
θ
+
y
s
i
n
θ
−
ρ
=
0
x{\rm cos}\theta+y{\rm sin}\theta-\rho=0
xcosθ+ysinθ−ρ=0时,即
(
x
,
y
)
(x,y)
(x,y)在直线
L
L
L上时成立。
在实际工程应用中,其实(1)式的用处并不是很大,因为通常情况下
R
(
ρ
,
θ
)
R(\rho,\theta)
R(ρ,θ)是能够利用物理装置直接得到的,而我们更想实现的是,能够根据得到的光图像
R
(
ρ
,
θ
)
R(\rho,\theta)
R(ρ,θ)来反推得到目标内部或轮廓的情况,即由
R
(
ρ
,
θ
)
→
f
(
x
,
y
)
R(\rho,\theta) \rightarrow f(x,y)
R(ρ,θ)→f(x,y)的转化,这个过程称为逆Radon变换。以下探讨如何实现逆Radon变换。
从(1)式可以看出要想从
R
(
ρ
,
θ
)
R(\rho,\theta)
R(ρ,θ)中解出
f
(
x
,
y
)
f(x,y)
f(x,y),需要去掉积分运算,联想到傅里叶变换能够起到去积分符号的效果,所以尝试对(1)两端进行傅里叶变换,具体地:
F
[
R
(
ρ
,
θ
)
]
=
∫
−
∞
∞
R
(
ρ
,
θ
)
e
−
i
ω
ρ
d
ρ
=
∫
−
∞
∞
[
∬
f
(
x
,
y
)
δ
(
x
c
o
s
θ
+
y
s
i
n
θ
−
ρ
)
d
x
d
y
]
e
−
i
ω
ρ
d
ρ
=
∬
f
(
x
,
y
)
[
∫
−
∞
∞
δ
(
x
c
o
s
θ
+
y
s
i
n
θ
−
ρ
)
e
−
i
ω
ρ
d
ρ
]
d
x
d
y
=
∬
f
(
x
,
y
)
e
−
i
ω
(
x
c
o
s
θ
+
y
s
i
n
θ
)
d
x
d
y
=
F
(
ω
c
o
s
θ
,
ω
s
i
n
θ
)
(2)
\boldsymbol{F} [R(\rho,\theta)]=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}{R(\rho,\theta)e^{-i\omega\rho}d\rho}=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}{[\iint f(x,y)\delta(x{\rm cos}\theta+y{\rm sin}\theta-\rho)dxdy]e^{-i\omega\rho}d\rho}=\iint {f(x,y)[\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}{\delta(x{\rm cos}\theta+y{\rm sin}\theta-\rho)e^{-i\omega\rho}d\rho}]dxdy}=\iint{f(x,y)e^{-i\omega(x{\rm cos}\theta+y{\rm sin}\theta)}dxdy}=F(\omega{\rm cos}\theta,\omega{\rm sin}\theta) \tag{2}
F[R(ρ,θ)]=∫−∞∞R(ρ,θ)e−iωρdρ=∫−∞∞[∬f(x,y)δ(xcosθ+ysinθ−ρ)dxdy]e−iωρdρ=∬f(x,y)[∫−∞∞δ(xcosθ+ysinθ−ρ)e−iωρdρ]dxdy=∬f(x,y)e−iω(xcosθ+ysinθ)dxdy=F(ωcosθ,ωsinθ)(2)
(2)式说明一个投影的一维傅里叶变换,是二维投影的二维傅里叶变换的一个切片,上式中最后一个等式利用了二维傅里叶变换,二维傅里叶变换和逆变换的表达如下
F
(
μ
,
υ
)
=
∫
−
∞
∞
∫
−
∞
∞
f
(
x
,
y
)
e
−
i
(
μ
x
+
υ
y
)
d
x
d
y
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
∫
−
∞
∞
∫
−
∞
∞
F
(
μ
,
υ
)
e
i
(
μ
x
+
υ
y
)
d
μ
d
υ
(3)
F(\mu,\upsilon)=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}{\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}{f(x,y)e^{-i(\mu x+\upsilon y)}}dxdy}\\ f(x,y)=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}{\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}{F(\mu,\upsilon)e^{i(\mu x+\upsilon y)}}d\mu d\upsilon} \tag{3}
F(μ,υ)=∫−∞∞∫−∞∞f(x,y)e−i(μx+υy)dxdyf(x,y)=∫−∞∞∫−∞∞F(μ,υ)ei(μx+υy)dμdυ(3)
(3)中二维傅里叶逆变换省略了前面的归一化系数,关于Radon变换的其他信息可以参考该文章《平行线投影radon变换》






















 1205
1205

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








