Basic Financial Arithmetic
Simple and Compound Interest
- Simple Interest : TotalProceed=Principal×(1+interestrate∗daysyear)
- Compound Interest : TotalProceed=Principal×(1+interestrate∗daysyear)N
- Interest Rate:
- The period for which the investment/loan will last
- The absolute period to which the quoted interest rate applies
- The frequency with which interest is paid
Nominal and Effective Rates
1+effectrate=(1+nominalraten)n
-
effectiverate=(1+nominalraten)n−1
-
nominalrate=[(1+effectrate)1n−1]×n
Daily Compounding
-
Dailyequivalent=[(1+effectrate)1365−1]×365
Continuous Compounding
-
1+effectiverate=limx→∞(1+rcn)n=erc
⇒
Continuously compounded rate :
r=ln(1+i)
⇒
Nominal rate for a year :
i=er−1
Time Value of Money
| Items | Short-Term Investment | Long-Term Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Future Value |
FV=PV×(1+i×daysyear)
|
FV=PV×(1+i×daysyear)N
|
| Present Value |
PV=FV1+i×daysyear
|
PV=FV(1+i×daysyear)N
|
| yield |
yield=(FVPV−1)×yeardays
|
yield=(FVPV)1N−1
|
| effective yield |
effectiveyield=(1+yield×daysyear)yeardays−1
effectiveyield=(FVPV)365days−1
|
for simple invest :
yield=i
for compound invest :
yield=i×daysyear
-
PV=FV×DiscoutFactor
| Simple | Compound | Continuous Compounding |
|---|---|---|
|
FV=PV×(1+i×daysyear)
|
FV=PV×(1+i×daysyear)N
|
FV=PV×(ei×daysyear)
|
|
DF=11+i×daysyear
|
DF=(11+i×daysyear)N
|
DF=e−i×daysyear
|
- IRR
⇒
Internal Rate of Return
IRR : The one single interest rate used when discounting a series of future value to achieve a given net present value.
Example:
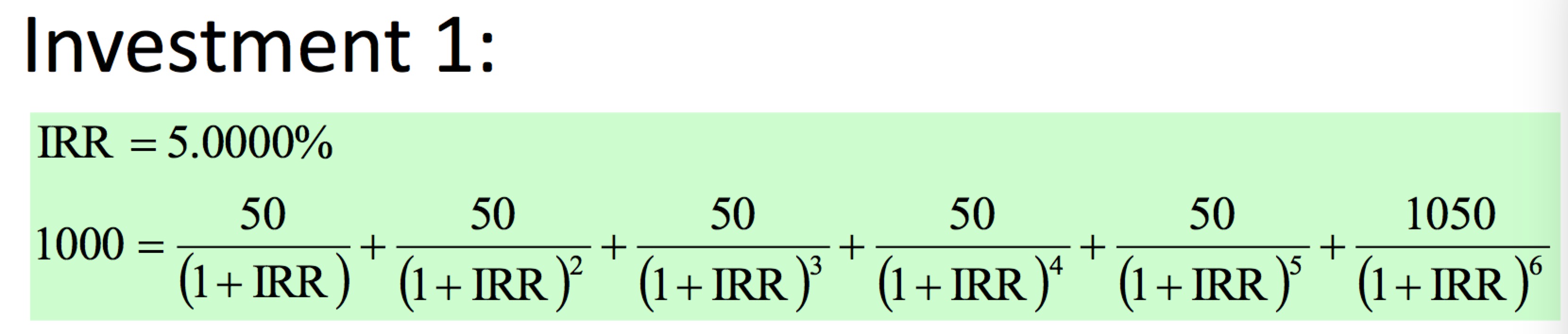
Basic Financial Modeling
Money Market
| Terminology | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Eurodoller | U.S. dollar-denominated deposits at banks outside of the U.S. |
| Coupon | Interest rate stated on an instrument when it is issued |
| Discount Instrument | An instrument which does not carry a coupon is a “discount” instrument. Discount equals the difference between the price paid for a security and security’s par value. |
| Bearer / registered | A “bearer” security is one where the issuer pays the principal (and coupon if there is one) to whoever is holding the security at maturity. |
| Fixed Income Security | Money market instrument whose future cash flows have been contractually defined and can be determined in advance. |
| Yield to Maturity | YTM is the rate of return that you would achieve on a fixed income security, if you bought it at a given price and held it to maturity |
| LIBOR, HIBOR | Interbank offered rate – interest rate at which one bank offers money to another bank. |
| Eurodeposit | Round-the-clock business spanning Singapore and Hong Kong, Bahrain, Frankfurt, Paris, London and New York |
Eurodeposit
- LIBOR
The rate dealers charge for lending money (they offer funds) - LIBID
The rate dealers pay for taking a deposit (they bid for funds) - In London, quote (offered rate – bid rate), Other places, quote (bid rate – offered rate)
- Rule: pay the higher rate for a loan, receive the lower for a deposit
- LIBOR
DAY/YEAR Conventions
- Interestpaid=interestratequoted×daysinperioddaysinyear
- Most money markets use ACT/360
Interest rate on 360-day basis = Interest rate on 360-day basis ×360365 - Exceptions using ACT/365:
Interest rate on 365-day basis = Interest rate on 365-day basis ×365360
- International and domestic:
Sterling, Hong Kong dollar, Singapore dollar, Malaysian ringgit, Taiwan dollar, Thai baht, South African rand. - Domestic (but not international):
Japanese yen, Canadian dollar, Australian dollar, New Zealand dollar
- International and domestic:
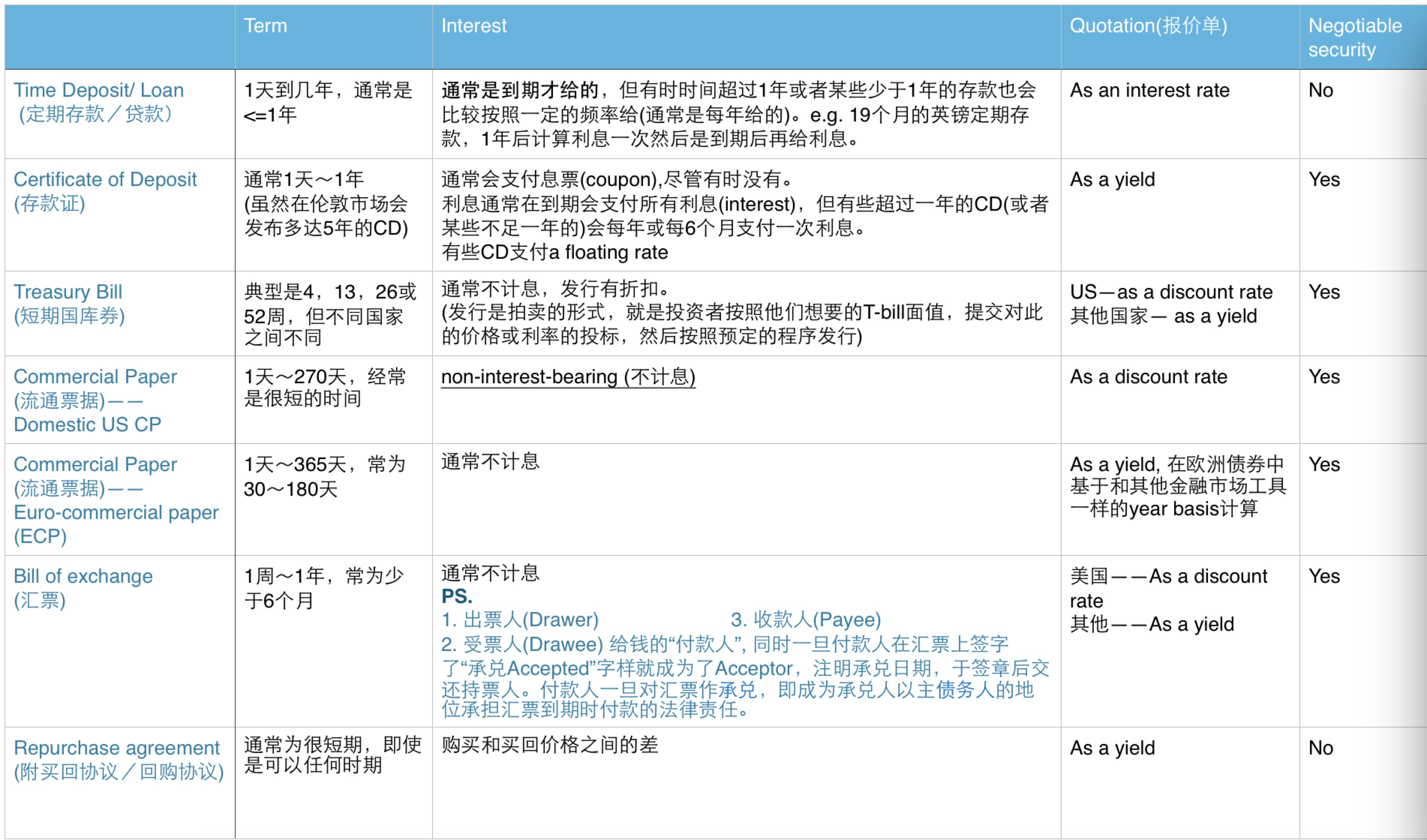
Money Market Instruments
| Instrument | Term | Interest | Quotation | Currency | Settlement | Registration | negotiable | Issuers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time deposit / loan | 1 day to several years, but usually less than 1 year | usually all paid on maturity | as an interest rate | any domestic or international currency | generally same day for domestic, 2 working days for international | no | no | |
| Certificate of deposit (CD) | generally up to one year | usually pay a coupon | as a yield | any domestic or international currency | generally same day for domestic, 2 working days for international | usually in bearer form | yes | Bank |
| Treasury Bill (T-bill) | generally 13, 26 or 52 weeks | mostly non-coupon bearing, issued at a discount | US and UK a “discount rate” basis; most places on a true yield basis | usually the currency of the country | bearer security | yes | Government | |
| Commercial Paper (CP) | for US, from 1 to 270 days; usually very short-term for ECP, from 2 to 365 days; usually 30 to 180 days | non-interest bearing; issued at a discount | for US, on a “discount rate” basis for ECP, as a yield | for US, domestic US dollar;for ECP, any Eurocurrency but largely US dollar | for US, same day;for ECP, 2 working days | in bearer form | yes | Corporation |
| Bill of exchange / Banker’s acceptance | From 1 week to 1 year but usually < 6 months | non-interest bearing; issued at a discount | for US and UK, quoted on a “discount rate” basis elsewhere on a yield basis | mostly domestic | available for discount immediately on being drawn | none | yes | |
| Repurchase agreement (repo) | usually for very short-term | difference between purchase and repurchase prices | as a yield | any currency | Generally cash against delivery of the security | n/a | no | Government / Bank |
- CD - Pricing
Price=presentvalue
maturityproceeds=facevalue×(1+couponrate×couponperiod(days)year
Price=facevalue×(1+couponrate×couponperiod(days)year)1+interestrate×dayspurchasetomaturityyear - CD - Return
yield=(FVPV−1)×yeardays
yield=(salepricepurchaseprice−1)×yeardaysheld
yield=((1+interestratepurchase×dayspurchasetomaturityyear)(1+interestratesale×dayssaletomaturityyear)−1)×yeardaysheld - Discount rate quote
Price=FaceValue×(1−DiscountRate×daystomaturityyear)
Price=FaceValue1+yield×daystomaturitysyear
yield=discountrate1−discoutrate×daystomaturityyear
discountrate=yield1+yield×daystomaturitysyear
Forward Rate Agreements (FRAs)
Forward-forward
- A cash borrowing or deposit which starts on one forward date and ends on another forward.
- The term, amount and interest rate are all fixed in advance.
forward−forwardrate=[(1+iL×dLyear)(1+iS×dSyear)−1]×yeardL−dS
L and S stand for longer and shorter period respectively
Forward Rate Agreements
- off-balance sheet instrument
- fix a future interest rate
- on the agreed date (fixing date), receives or pays the difference between the reference rate and the FRA rate on the agreed notional principal amount
- Principal is not exchanged
- Settles at the beginning of the period
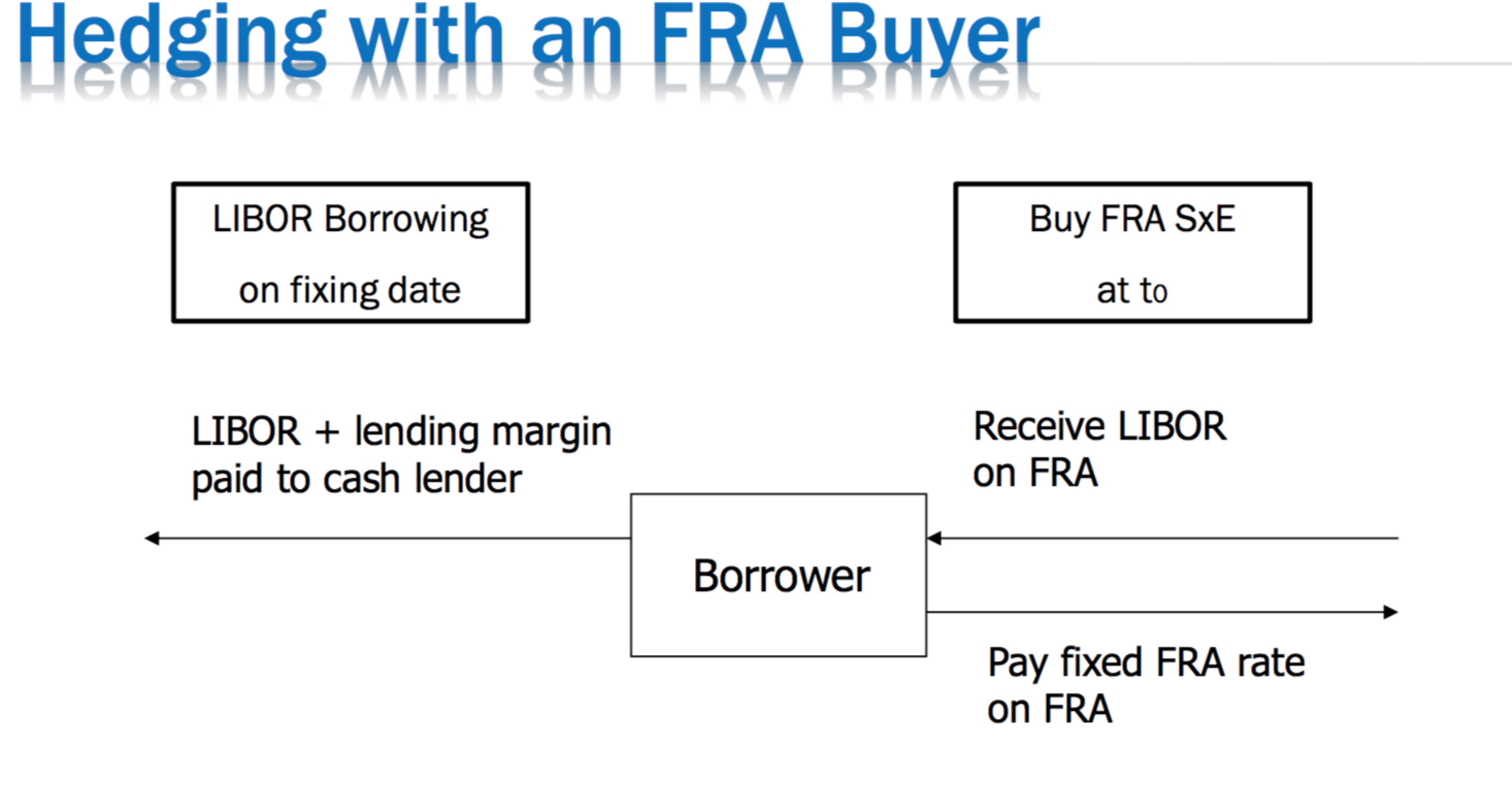
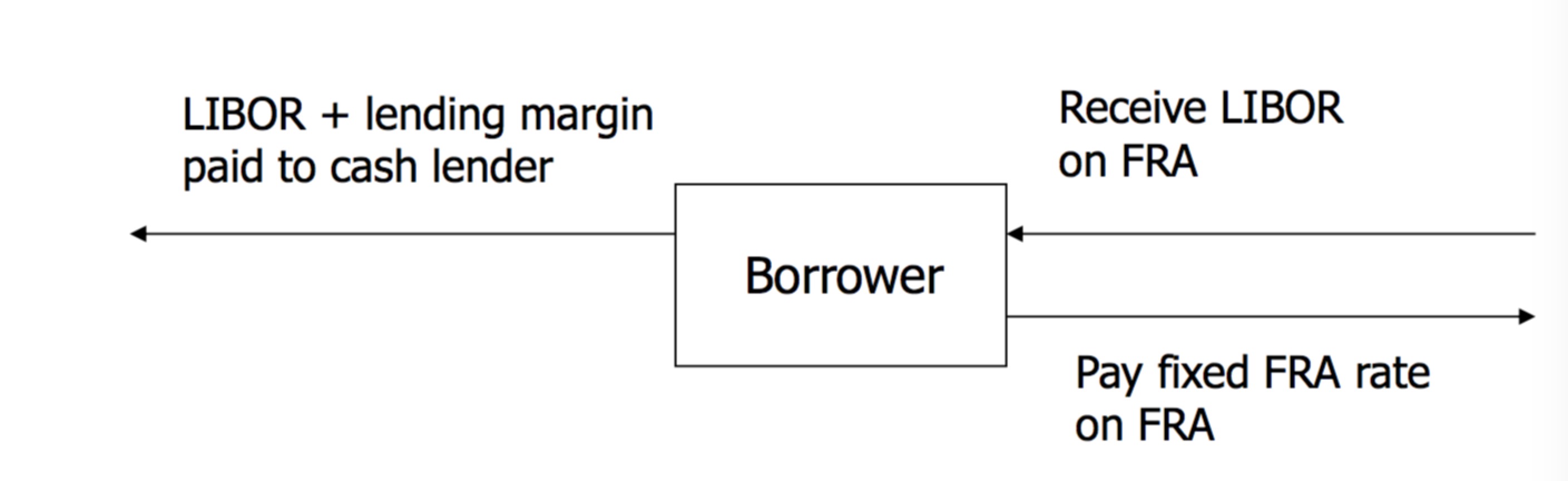
His flow will therefore be : - LIBOR
+ LIBOR
- FRA rate
————–
net cost : - FRA rate
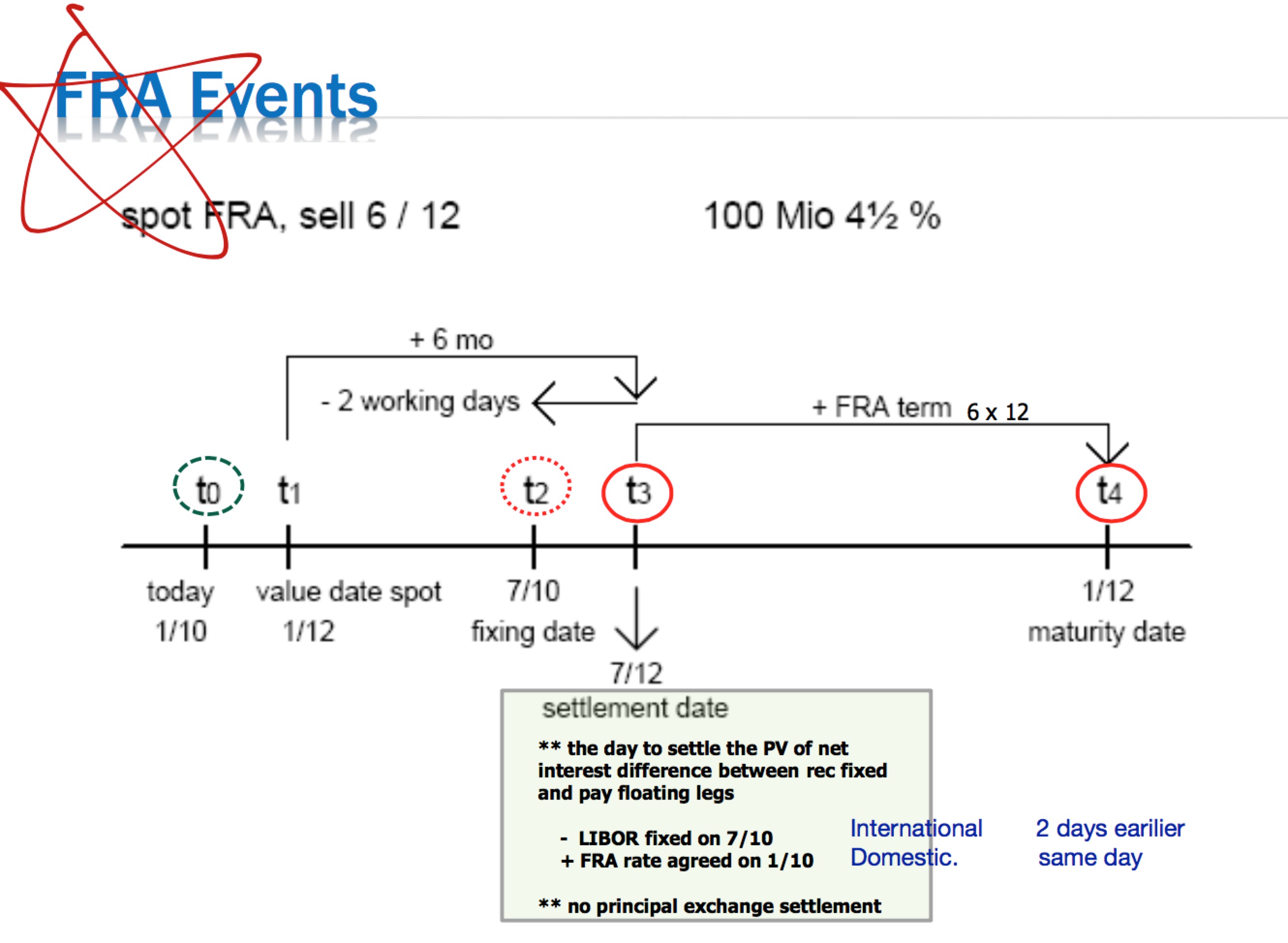
Usually two days before the settlement date, the FRA rate is compared to the agreed reference rate (LIBOR).
Settlement Paid
- Period < 1year
Buyerpaid=notional×(FRARate−LIBOR)×daysyear1+LIBOR×daysyear
- Period > 1year
FRAsettlement=Principal×[(f−L)×d1year1+×d1year+(f−L)×d2year(1+×d1year)×(1+×d2year)]
如果参照利率(e.g., LIBOR)比协议利率为高(>), 卖方需支付给买方合约差额;
反之,如果参照利率比协议利率为低(<), 买方需支付给卖方合约差额。
Constructing a strip
The interest rate for a longer period up to one year =
Futures Contract
Futures
- A contract in which the commodity being bought or sold is considered as being delivered (may not physically occur) at some future date
- Exchange traded (vs OTC in “forward”)
- Contract standardized by exchange
- Pricing depends on underlying commodity
Quotation
Futuresprice=100−(impliedforwardinterestrate×100)
Futures & FRAs are in opposite directions :
Dealing
- Open outcry
buyer and seller deal face to face in public in the exchange’s “trading pit” - Screen trading
designed to simulate the transparency of open outcry
Clearing
Following the confirmation of a transaction, the clearing house substitutes itself as a counterparty to each user and becomes
- the seller to every buyer and
- the buyer to every seller
Margin Requirements
- Initial Margin
- Collateral for each deal transacted
- Protect clearing house for the short period until position can be revalued
- Variation (Maintenance) Margin
- Marking to market
- Paid daily based on adverse price movements
Profit and Loss
Profit/los s on long position in a 3-month contract :
Profit/loss=numberofcontract×contractamount×pricemovement100×14
Hedging FRA with Futures
- Settlement for FRA = Profit or loss on sold futures
- Hedge required is the combination of the hedges for each leg
e.g.,
• Sell 3x6 FRA + Sell 6x9 FRA, hence hedged by
• Sell 10 June futures + Sell 10 Sept futuresImperfect FRA Hedging with Futures
- Future contracts are for standardized amount
- Futures P&L are based on 90-day period rather than 91 or 92 days as in FRA
- FRA settlements are discounted but futures settlements are not.
- Future price when the Sept contract is closed out in June may not exactly match the theoretical forward- forward rate at that time
- Slight discrepancy in dates.
Open Interest : number of purchases of contract not yet been reversed or “close out”
Volume : total number of contracts traded during the day
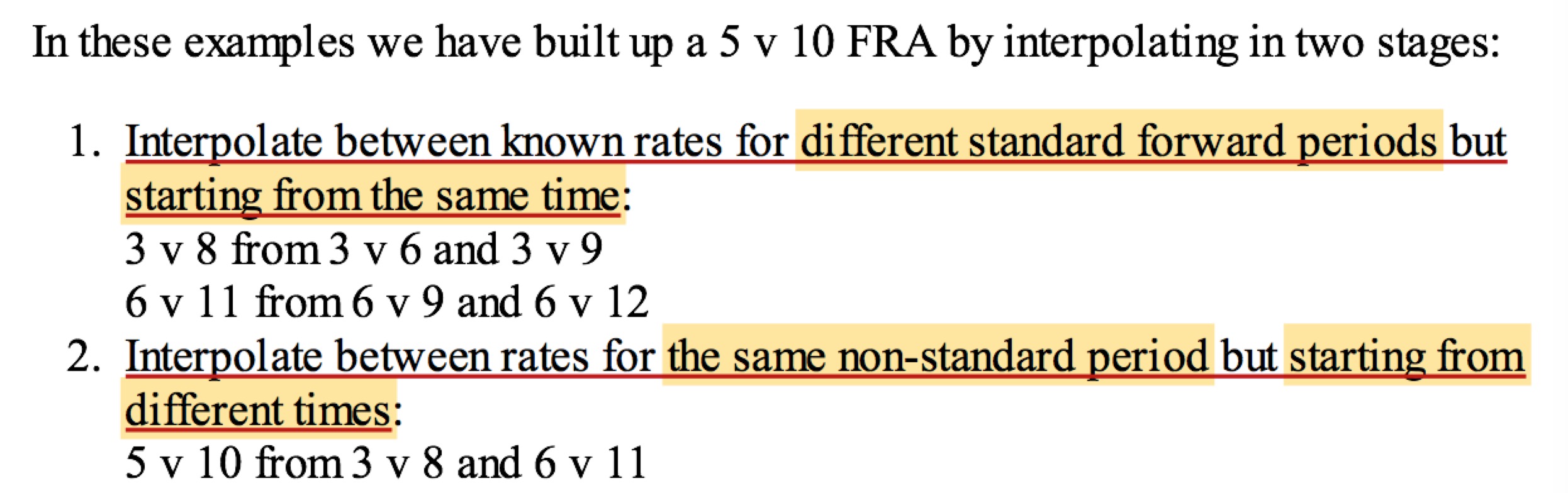
3v8 FRA:
3v6+(3v9−3v6)×daysin3v8−daysin3v6daysin3v9−daysin3v6
5v10 FRA:
3v8+(6v11−3v8)×daysinfixing5v10−daysinfixing3v8daysinfixing6v11−daysinfixing3v8
Arbitrage
Any must win strategy?
buy-buy / sell-sell
Interest Rate Swaps (IRS)
Definitions
- A swap is a derivative in which two counterparties agree to exchange one stream of cash flows against another stream.
- These streams are called the legs of the swap.
- An interest rate swap is a derivative in which one party exchanges a stream of interest payments for another party’s stream of cash flows.
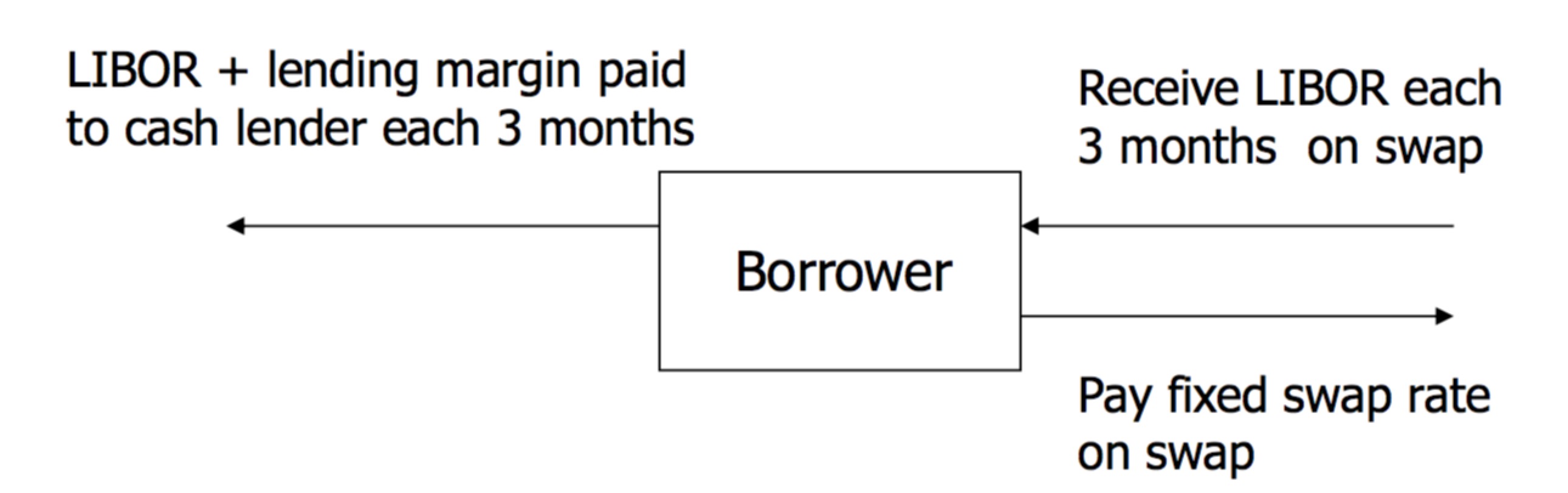
Hedging with FRA
Hedging with IRS
Characteristics of IRS
- Similar to FRA
- No exchange of principal
- Only interest flows are exchanged and netted
- Different from FRA
- Settlement amount paid at the end of relevant period
Motivation: win-win
Type of Swap
- Coupon Swap
Party A pay fixed interest rate and receive floating interest rate from party B - Basis Swap
Floating vs floating but on different rate basis
e.g.,
- Index Swap
The flow in one / other direction are based on index
e.g.,
Valuation of Swap
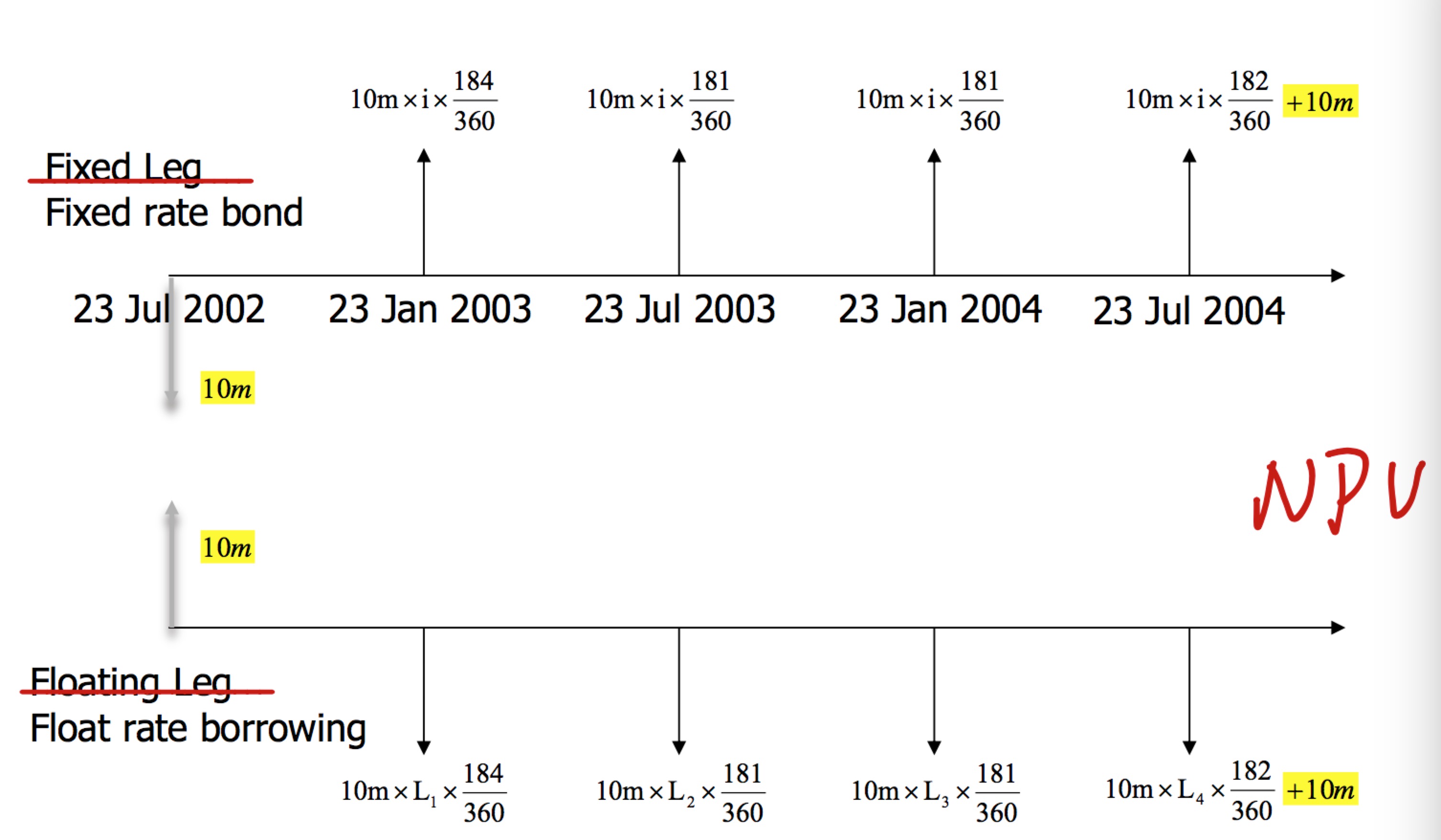
- Long Swap = + Long a Fixed rate bond - Floating rate borrowing
- Swap Value = + PV of Fixed leg cashflow - PV of floating leg cashflow
- Swap = NPV of Fixed leg cashflow
- At inception, NPV = 0
NPV=−P+∑ni=1CiDi+PDn
NPV=0
Dn=(1−r∑n−1i=1tiDi)1+rtn
;
r=1−Dn∑ni=1tiDi
where:
P = hypothetical principal notional
ti
= day count fraction of each interest payment period i
Ci
= cashflow at time period
i=P×r×ti
Di
= discount factor at time i
Dn
= discount factor at time n. (e.g., at maturity)
r = swap par rate (fixed leg)
Construction of Yield Curve
Definitions
- The relationship of interest rate for different maturity
- Market rate of interest for:
- theoretical zero coupon instrument
- matures at any future date
- Derived from
- prices of real financial instrument
- trade in a liquid market
Type
- Curve Shape
- positive
- negative
- flat
- Curve Categories
- Par Yied Curves
- Zero Coupon Yield Curve
- Forward Rate Yield Curve
Example
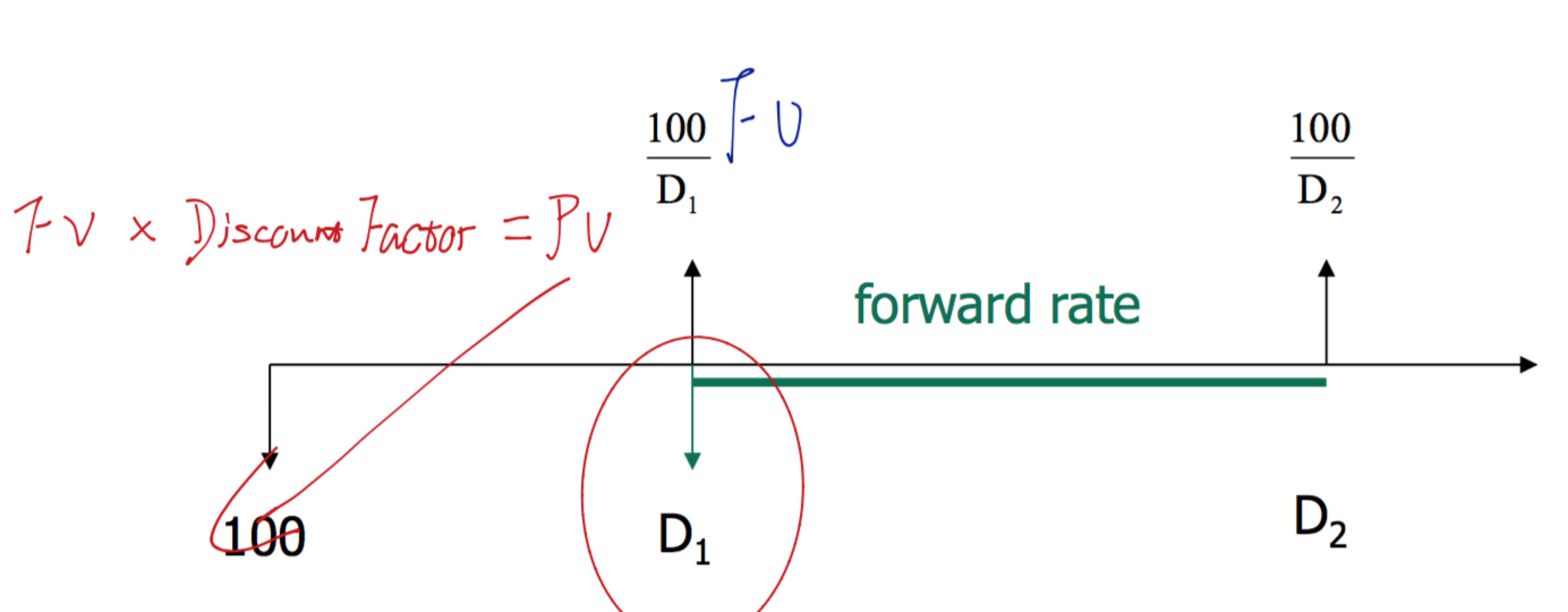
forward rate =
(100D2100D1−1)×yearperiod=(D1D2−1)×yearperiod
Therefore,
D2=D11+forwardrate×periodyear
Base on that and construct further, and this formula use again & again to construct the yield curve.
Quick Recap
Over night

DON=11+RON(1365)
DTN=DON1+DTN(1365)
Money Market

D=11+r×t
r=[1D−1]×1t
e.g., DF3M=11+r3M×t3M
FRA
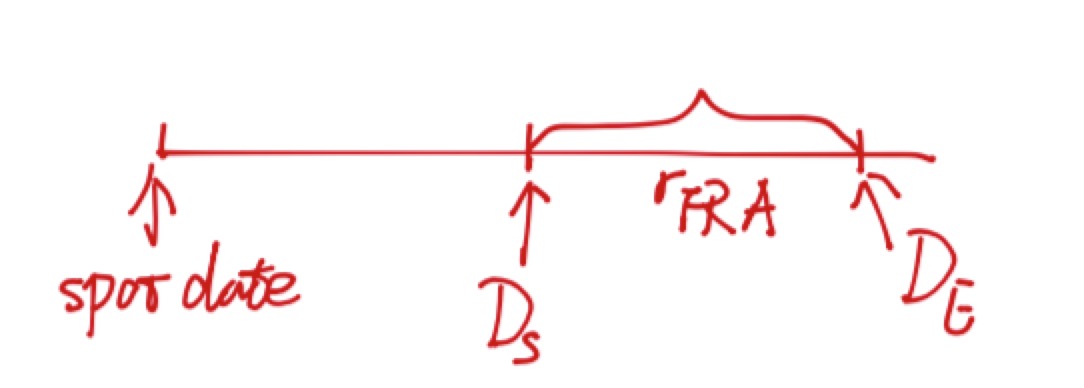
r=DS−DEDE×t
DE=DS1+rt
where,
DS
: Discount factor on forward start date
DE
: Discount factor on forward maturity date
t : period of FRA
r : FRA forward rate
SWAP Valuation
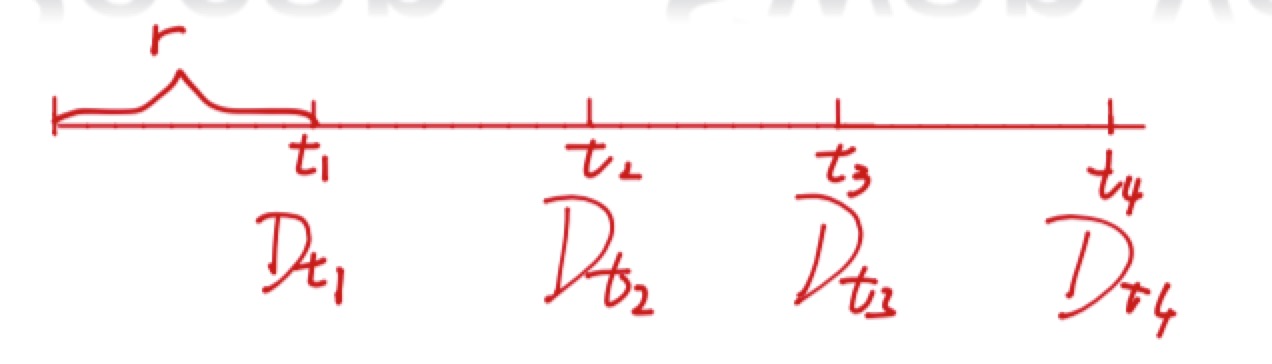
NPV=−P+∑ni=1CiDi+PDn
NPV=0
Dn=(1−r∑n−1i=1tiDi)1+rtn
;
r=1−Dn∑ni=1tiDi
(点与点之间可以通过一次函数求解)
Zero Coupon Rate
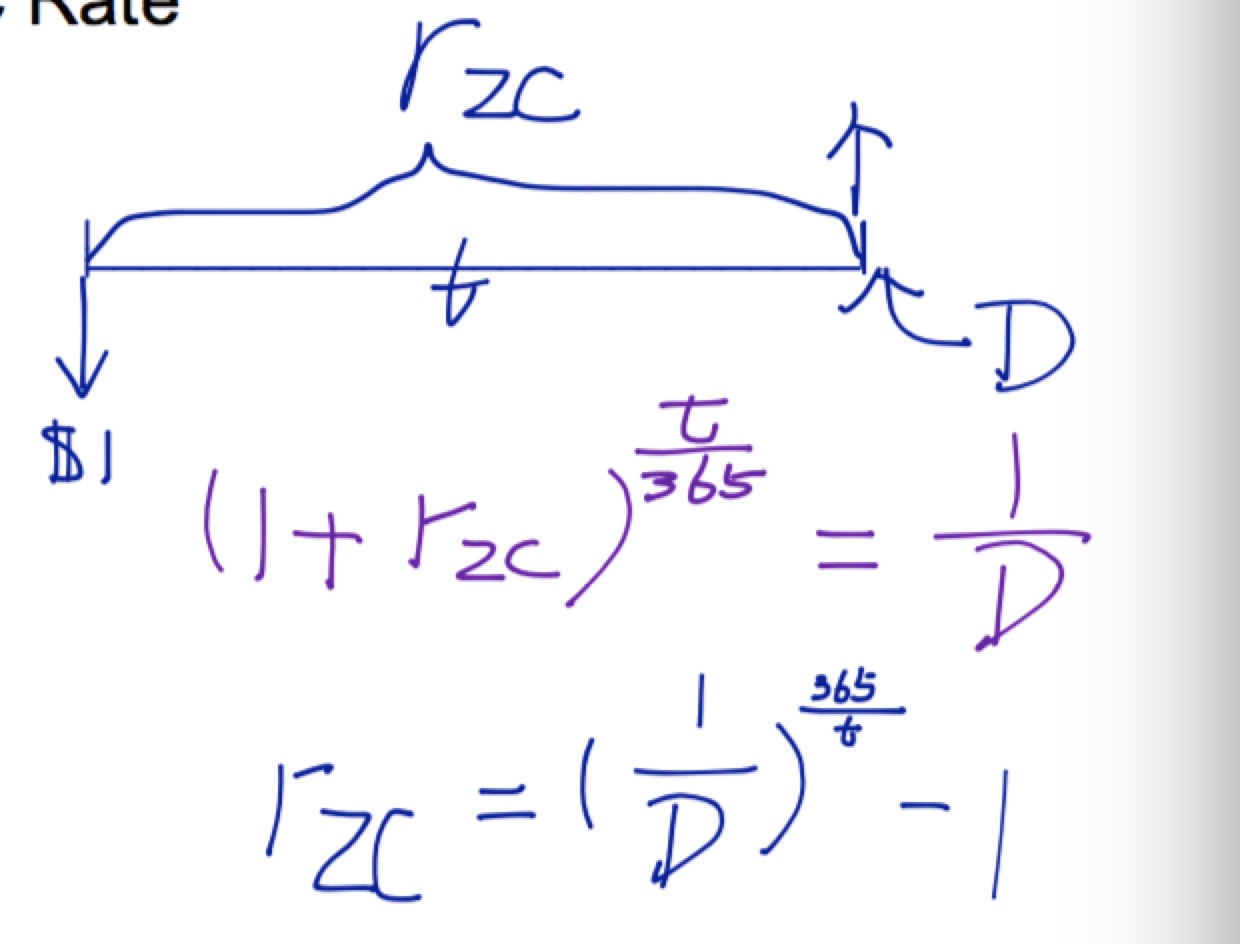
Dt=1(1+ZCt)days/year
ZCt=(1Dt)1days/year−1
























 9993
9993

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








