People in the Tomskaya region like magic formulas very much. You can see some of them below.
Imagine you are given a sequence of positive integer numbers p1, p2, ..., pn. Lets write down some magic formulas:
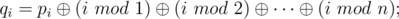
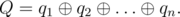
Here, "mod" means the operation of taking the residue after dividing.
The expression  means applying the bitwise xor (excluding "OR") operation to integers x and y. The given operation exists in all modern programming languages. For example, in languages C++ and Java it is represented by "^", in Pascal — by "xor".
means applying the bitwise xor (excluding "OR") operation to integers x and y. The given operation exists in all modern programming languages. For example, in languages C++ and Java it is represented by "^", in Pascal — by "xor".
People in the Tomskaya region like magic formulas very much, but they don't like to calculate them! Therefore you are given the sequence p, calculate the value of Q.
The first line of the input contains the only integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 106). The next line contains n integers: p1, p2, ..., pn (0 ≤ pi ≤ 2·109).
The only line of output should contain a single integer — the value of Q.
3 1 2 3
3
题意:
给出 N(1 ~ 10 ^ 6)代表有 N 个数,后给出 p1 …… pn(0 ~ 2 x 10 ^ 9)。求给出两条式子的和。
思路:
数学。0 与 任意数 异或 都不变 ( 0 ^ x == x ) ,任意数 与 本身 异或 一次 为 0 ( x ^ x == 0 ),异或 两次 数本身.( x ^ x ^ x == x ) 。于是列表格观察规律:
| 行 % 列 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 7 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 8 |
| 9 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 9 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
可以发现,对角线上值为 0,上三角元素为行列号。以行看看不出什么,但是以列来看的话,可以发现每个模数都对应有周期。而这个周期为 (n / i),若这个周期为偶数,则变为 0,可以忽略,若为奇数,则异或的结果为 0 ^ 1 ^ …… ^ i - 1。除此之外,若 (n % i)不等于 0 ,说明还需要 异或 1 ^ …… ^ ( n % i ) ^ (0)(后异或 0 可有可无,因为异或 0 不改变其值,故后面的预处理多异或了 0 也不会有影响),所以要预处理好连续 0 异或 到 n 的对应的每个值。
处理好后,根据 周期 和 余数 异或 便可得出答案了。
AC:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 1000001;
int num[MAX];
void solve () {
num[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < MAX; ++i)
num[i] = num[i - 1] ^ i;
}
int main() {
int n, ans = 0;
solve();
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
ans ^= a;
if ((n / i) % 2) ans ^= num[i - 1];
if (n % i) ans ^= num[n % i];
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
























 3329
3329

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








